个人对spring的IOC+DI的封装
暂时支持8种基本数据类型,String类型,引用类型,List的注入。
核心代码
package day01;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomEditorConfigurer;
/**
* 模拟 IOC+DI
* @author fh
*@date 下午7:26:50
*/
public class springIOCTest {
//存入所有一级对象+类名
public static Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
//存入注入对象与其需要注入对象名称
public Map<Class<?>, String> map2 = new HashMap<Class<?>, String>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
springIOCTest st = new springIOCTest();
st.xmlParse();
for (Object string : st.map.values()) {
//System.out.println(string);
}
// for (Entry<Class<?>, String> enrty :st.map2.entrySet() ) {
// Class<?> class1 = enrty.getKey();
// class1.getDeclaredField(enrty.getValue());
// }
}
/**
* dom解析
* @throws DocumentException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
* @throws SecurityException
* @throws NoSuchFieldException
* @throws NoSuchMethodException
* @throws InvocationTargetException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* @throws Exception
*/
public void xmlParse() throws DocumentException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
SAXReader sr=new SAXReader();
Document document=sr.read("D:\\eclipseworkspace\\Briup-SpringStudy\\test.xml");
//根目录
Element root = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> elements = root.elements();
//所有一级节点
for (Element element : elements) {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String parkagename = element.attributeValue("class");
Class<?> class1 = Class.forName(parkagename);
Object Instance = class1.newInstance();
//保存到map集合
map.put(id, Instance);
List<Element> elements2 = element.elements();
if (elements2.size() > 0) {
//所有二级节点
for (Element element2 : elements2) {
String refname = element2.attributeValue("name");
String value = element2.attributeValue("value");
Field field1 = null;
String ref = element2.attributeValue("ref");
//缺陷:注入对象必须在被注入对象之前
if (value==null&&ref!=null) {
//引用对象类型
field1 = class1.getDeclaredField(refname);
basicType(true,Modifier.isPrivate(field1.getModifiers()), class1, Instance, field1, ref, refname);
}else if (ref==null&&value!=null) {
//String类型或者基本类型
field1 = class1.getDeclaredField(refname);
basicType(false,Modifier.isPrivate(field1.getModifiers()), class1, Instance, field1, value, refname);
}else {
//是否有三级节点
List<Element> elements3 = element2.elements();
if (elements3.size()>0) {
Element e = (Element) element2.elements().get(0);
String name = e.getName();
if ("list".equals(name)) {
ListType(class1,Instance,element2);
}else if ("array".equals(name)) {
}else if ("map".equals(name)) {
}else if ("set".equals(name)) {
}else {
throw new RuntimeException(name+" is not defined");
}
}
}
//方法二:先保存依赖关系,最后注入
//map2.put(class1, refname);
}
}
}
}
private <T> void ListType(Class<T> c,Object instance, Element elements2) throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
String Typename = elements2.attributeValue("name");
//Class<?> forName = Class.forName(Typename);
List<Element> elements = elements2.elements();
Element e = (Element) elements2.elements().get(0);
List<Element> elements3 = e.elements();
String fieldname = e.getName();
//System.out.println(fieldname);
Field field = c.getDeclaredField(Typename);
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
for (Element element :elements3) {
//System.out.println(element.getName());
String text = element.getText();
al.add(text);
}
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(instance, al);
}
/**
* 注入方式判断,注入类型判断
* @param isQuoteType
* @param b
* @param class1
* @param Instance
* @param field1
* @param value
* @param refname
* @throws NoSuchMethodException
* @throws SecurityException
* @throws NumberFormatException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* @throws InvocationTargetException
*/
public static <T> void basicType(boolean isQuoteType,boolean b,Class<T> class1,Object Instance,Field field1,String value,String refname) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, NumberFormatException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException{
Method method = null;
//是否为private ,若为private必须通过set,get方法访问
if(b){
//方法二:通过set方法注入
if (isQuoteType) {
//引用类型
method = class1.getMethod("set"+Character.toUpperCase(refname.charAt(0))+refname.substring(1, refname.length()), map.get(value).getClass());
}else{
//基本类型+String
method = class1.getMethod("set"+Character.toUpperCase(refname.charAt(0))+refname.substring(1, refname.length()), field1.getType());
}
MethodTypeHander(field1,method,Instance,value);
}else{
//方法一:属性直接注入
FieldTypeHander(field1,Instance,value);
}
}
/**
* 属性直接注入
* @param field
* @param Instance
* @param value
* @throws NumberFormatException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* @throws InvocationTargetException
*/
public static void FieldTypeHander(Field field,Object Instance,String value) throws NumberFormatException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// System.out.println("FieldTypeHander "+field.getType());
//设置能否访问,不然private,protected属性会被阻止,破坏封装
field.setAccessible(true);
if ("byte".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
field.setByte(Instance, Byte.parseByte(value));
}else if ("short".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
field.setShort(Instance, Short.parseShort(value));
}else if ("int".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
field.setInt(Instance, Integer.parseInt(value));
}else if ("long".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
field.setLong(Instance, Long.parseLong(value));
}else if ("double".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
field.setDouble(Instance, Double.parseDouble(value));
}else if ("float".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
field.setFloat(Instance, Float.parseFloat(value));
}else if ("class java.lang.String".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
field.set(Instance,value);
}else if ("boolean".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
field.setBoolean(Instance,Boolean.parseBoolean(value));
}else {
field.set(Instance, map.get(value));
}
}
/**
* 通过方法注入
* @param field
* @param method
* @param Instance
* @param value
* @throws NumberFormatException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* @throws InvocationTargetException
*/
public static void MethodTypeHander(Field field,Method method,Object Instance,String value) throws NumberFormatException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
//System.out.println("MethodTypeHander "+field.getType());
if ("byte".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
method.invoke(Instance, Byte.parseByte(value));
}else if ("short".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
method.invoke(Instance, Short.parseShort(value));
}else if ("int".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
method.invoke(Instance, Integer.parseInt(value));
}else if ("long".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
method.invoke(Instance, Long.parseLong(value));
}else if ("double".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
method.invoke(Instance, Double.parseDouble(value));
}else if ("float".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
method.invoke(Instance, Float.parseFloat(value));
}else if ("class java.lang.String".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
method.invoke(Instance,value);
}else if ("boolean".equals(field.getType().toString())) {
method.invoke(Instance,Boolean.parseBoolean(value));
}else {
method.invoke(Instance, map.get(value));
}
}
}
xml文件
test.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:u="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="Address" class="day01.bean.Address">
<property name="city" value="南昌"/>
<property name="street" value="双港东大街"/>
<property name="country" value="中国"/>
</bean>
<bean id="Person" class="day01.bean.Person">
<property name="sNo" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="fh"/>
<property name="gender" value="true"/>
<property name="age" value="21"/>
<property name="arraytest">
<list value-type="int">
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="address" ref="Address"/>
</bean>
<bean id="UserDAO" class="day01.dao.UserDAO"/>
<bean id="UserService" class="day01.service.UserService">
<property name="userDAO" ref="UserDAO"/>
</bean>
</beans>
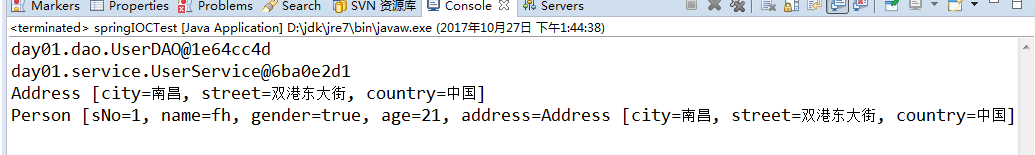
结果:
个人对spring的IOC+DI的封装的更多相关文章
- Spring框架-IOC/DI详细学习
一.IOC/DI概念 参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/xdp-gacl/p/4249939.html IOC(inversion of control, 控制反转)是一种设计 ...
- Spring的IOC/DI使用到的技术
一.了解Spring IOC/DI 1:Spring有两大核心技术,控制反转(Inversion of Control, IOC)/依赖注入(Dependency Injection,DI)和面向切面 ...
- spring的IOC/DI功能实践
一.写在前面: 做这个Demo主要是为了能够更好的理解Spring的原理,看再多的文章,听再多的讲解最终都最好自己去实现一遍,可以将Spring的功能分块实现,最终自然比较容易将各个功能组合起来. 这 ...
- Spring之IOC/DI(反转控制/依赖注入)_入门Demo
在平时的java应用开发中,我们要实现某一个功能或者说是完成某个业务逻辑时至少需要两个或以上的对象来协作完成,在没有使用Spring的时候,每个对象在需要使用他的合作对象时,自己均要使用像new ob ...
- Spring框架——IOC&DI
Spring Spring 目标 内容 Spring与web整合的原理 Spring 中包含的关键特性 Spring架构图 企业级框架 企业级系统 IOCDI IOC DI IOC和DI 为什么使用依 ...
- Spring基础[IOC/DI、AOP]
一.Spring作用:管理项目中各种业务Bean(service类.Dao类.Action类),实例化类,属性赋值 二.Spring IOC(Inversion of Control )控制反转,也被 ...
- Spring理解IOC,DI,AOP作用,概念,理解。
IOC控制反转:创建实例对象的控制权从代码转换到Spring容器.实际就是在xml中配置.配置对象 实例化对象时,进行强转为自定义类型.默认返回类型是Object强类型. ApplicationCon ...
- Spring注解IOC/DI(4)
2019-03-08/11:10:17 演示:使用注解的方式完成注入对象中的效果 注解参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/szlbm/p/5512931.html Spring中 ...
- 解释Spring中IOC, DI, AOP
oc就是控制翻转或是依赖注入.通俗的讲就是如果在什么地方需要一个对象,你自己不用去通过new 生成你需要的对象,而是通过spring的bean工厂为你长生这样一个对象.aop就是面向切面的编程.比如说 ...
随机推荐
- 洛谷P1044 栈(Catalan数)
P1044 栈 题目背景 栈是计算机中经典的数据结构,简单的说,栈就是限制在一端进行插入删除操作的线性表. 栈有两种最重要的操作,即pop(从栈顶弹出一个元素)和push(将一个元素进栈). 栈的重要 ...
- 「BZOJ2127」happiness(最小割)
题目描述 高一一班的座位表是个n*m的矩阵,经过一个学期的相处,每个同学和前后左右相邻的同学互相成为了好朋友.这学期要分文理科了,每个同学对于选择文科与理科有着自己的喜悦值,而一对好朋友如果能同时选文 ...
- I.Algorithm Choosing Mushrooms
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/908/I 题意: Baby bear and his good friends are very fond of mus ...
- Python基本的数据类型(补发)
python基本的数据类型 一.python的基本数据类型 int => 整数,主要用来进行数学运算 str ==> 字符串 可以用来保存少量数据并进行相应操作 bool ==> ...
- 线程池(1)ThreadPoolExecutor梳理
使用默认的 thread factory创建ThreadPoolExecutor实例 public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPo ...
- MapReduce编程入门实例之WordCount:分别在Eclipse和Hadoop集群上运行
上一篇博文如何在Eclipse下搭建Hadoop开发环境,今天给大家介绍一下如何分别分别在Eclipse和Hadoop集群上运行我们的MapReduce程序! 1. 在Eclipse环境下运行MapR ...
- nginx配置SSL证书实现https服务
在前面一篇文章中,使用openssl生成了免费证书 后,我们现在使用该证书来实现我们本地node服务的https服务需求.假如我现在node基本架构如下: |----项目 | |--- static ...
- jQuery:如何给动态生成的元素绑定事件?
jQuery的html()可以给现在元素附加新的元素,innerHTML也可以,那么,如何给这些新生成的元素绑定事件呢?直接在元素还未生成前就绑定肯定是无效的,因为所绑定的元素目前根本不存在. 然而, ...
- Linux mount实际使用
查看所有文件系统(设备):fdisk -l 1.当要重新挂载一个文件系统时(设备):可以直接 #mount -o remount,rw /dev/sdb9/(文件系统) /mnt/sdb9/(目录) ...
- fastjson格式化输出内容
引入fastjson <!--fastjson--><dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <ar ...
