Preface
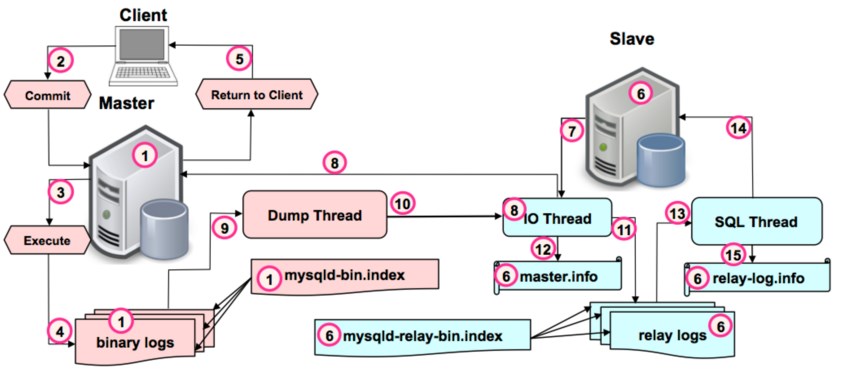
As we all know,there're three kinds of replication in MySQL nowadays.Such as,asynchronous replication,(full)synchronous replication,semi-synchronous replication.What's the difference between them?First of all,let's see the intact architecture picture of MySQL replication:
What will master do?
What will slave do?
- connects to master
- IO Thread asks for data(binary logs) and gets them
- generates relay logs
- SQL Thread applies data(relay logs)
Method of different MySQL Replication
Generally speaking,the data changed on master will be continuously sent to slave.So the data on slave seems to be equal with the master.This mechanism is usually used to backup on slave(reduce the pressure of master),construct HA architecture(failover or separate reading/writing operations),etc.
Nevertheless,on account of different reasons,slave frequently defers in almost all the scenarios what's often grumbled by MySQL dba.Below are different kinds of MySQL replication.Let's see the details.
Since MySQL 3.2.22,this kind of replication was supported with statement format of binary log.Then,untill MySQL 5.1.5,row format of binary log was supported either.The mechanism of it is that as soon as the master dump thread has sent the binary logs to the slave,the master server returns the result to client.There's nothing to guarantee the binary logs are normally received by the slave(maybe the network failure occurs simultaneously).So it's unsafe in consistency what means your transactions will lose in the replication.This is also the original replication of MySQL.Here's the picture about the procedure:
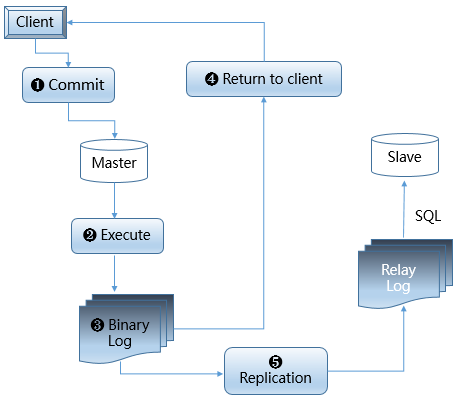

1. Client sends dml operations to the master while the transaction starts.
2. Master executes these dml operations from client in transaction.
3. Generates some binary logs which contains the transaction information.
4. Master will return results to the client immediately after dump thread has sent these binary logs to slave.
5. Slave receives the binary logs by IO_Thread and apply the relay logs by SQL_Thread.
In step 4,master won't judge whether slave has received the binary logs (which are sent by itself) or not.If the master crashs suddenly after it has sent the binary logs,but slave does not receive them at all on account of network delay.Only if the slave takes over the application at this time,the committed transactions will miss which means data loss.This is not commonly acceptable in most important product systems especially in the financial ones.
Synchronous replication requires master to return results to client only after the transactions have been committed by all the slaves(receive and apply).This method will severely lead to bad performance on master unless you can guarantee the slaves can commit immediate without any delay(infact it's tough).Now,the only solution of synchronous replication is still the MySQL NDB Cluster.Therefore,it's not recommended to use synchronous replication way.
- semi-synchronous replication
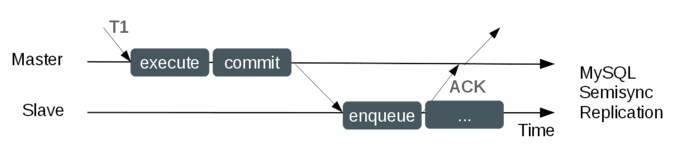
Semi-synchronous replication seems a workaround of above two method which can strongly increase the consistency between master and slave.It's supported since MySQL 5.5 and enhanced in MySQL 5.7.What's the mechanism of semi-sychronouos replication?Master is permitted to return the result to client merely after only one slave has received binary logs,write them to the relay logs and returns an ACK signal to master.There're two ways of it,that is,after_commit & after_sync.Let's see the difference of them:
after_commit(Since MySQL 5.5):
In this method,master performs a commit before it receives ACK signal from slave.Let's suppose a situation that once master crashs after it commits a transaction but it hasn't receive the ACK signal from slave.Meanwhile,failover makes slave become the new master.How does the slave deal with then?Will the transaction lose?It depends.There're two scenarios:
- Slave has received the binary log,and then turns it into relay log and applys it.There's no transaction loss.
- Slave hasn't received the binary log,the transaction committed by master just now will lose,but the client won't fail(only inconsistent in replication).
Therefore,after_commit cannot guarantee lossless replication.after_commit is the default mode(actually it's the only mode can be use) which is supported by MySQL 5.5 & 5.6.
after_sync(since MySQL 5.7):
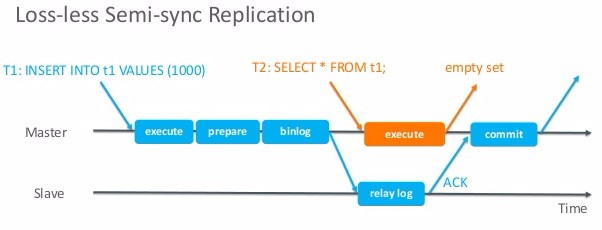
In the picture above,the t1 transaction shouldn't be lost because of the master merely commits to the storage engine after receive the ACK signal from slave.In spite of master may crash before receiving ACK signal,no transaction will lose as the master hasn't commit at all.Meanwhile,the t2 transaction also get consistent query here.
In order to improve the data consistency(since after_commit has avoidless deficiency),MySQL official enhances the semi-synchronous replication which can be called "loss-less semi-synchronous replication" in MySQL 5.7 by add after_sync mode in parameter "rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_point".
Caution,semi-synchronous replication may turn into asynchronous replication whenever the delay time of slave surpass the value which is specified in parameter "rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout"(default values is 10000 milliseconds).Why it is permitted?I'm afraid in order to consider the performance of master.Notwithstanding,you can also play a trick to prevent it from being converted over by set a infinite number in this parameter such as "10000000" or above.Especially in case that your product system is too important to not lose data.
Further more,to configure semi-sychronous replication,you should implement the optional plugin component "rpl_semi_sync_master",which can be check by using command "show plugins;"
Summary:
- Commonly,semi-sync replication is strongly recommended when implements MySQL replication nowadays(with gtid).
- I utterly recommend to upgrade product system to MySQL 5.7 in order to use "after_sync" mode which can avoid data loss.
- Be careful of specify an inappropriate value in parameter "rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout" which will cause converting semi-sync to async replication.
- MySQL 5.7 新特性之增强半同步复制
1. 背景介绍 半同步复制 普通的replication,即mysql的异步复制,依靠mysql二进制日志也即binary log进行数据复制.比如两台机器,一台主机(master),另外一台是从机( ...
- 深入MySQL复制(三):半同步复制
1.半同步复制 半同步复制官方手册:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/replication-semisync.html 默认情况下,MySQL的复制是异 ...
- mysql半同步复制跟无损半同步区别
mysql半同步复制跟无损半同步复制的区别: 无损复制其实就是对semi sync增加了rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_point参数,来控制半同步模式下主库在返回给会话事务成功之 ...
- MySQL主从复制技术与读写分离技术amoeba应用
MySQL主从复制技术与读写分离技术amoeba应用 前言:眼下在搭建一个人才站点,估计流量会非常大,须要用到分布式数据库技术,MySQL的主从复制+读写分离技术.读写分离技术有官方的MySQL-pr ...
- MySQL异步、同步、半同步复制
异步复制 MySQL复制默认是异步复制,Master将事件写入binlog,提交事务,自身并不知道slave是否接收是否处理: 缺点:不能保证所有事务都被所有slave接收. 同步复制 Master提 ...
- MySQL高可用方案 MHA之四 keepalived 半同步复制
主从架构(开启5.7的增强半同步模式)master: 10.150.20.90 ed3jrdba90slave: 10.150.20.97 ed3jrdba97 10.150.20.132 ...
- MySQL主从复制技术(纯干货)
1.复制配置 主机一定要开启二进制日志(这里建议配置RBR) 每个主机和每个从机一定要配置一个位移的id,即server-id 每个从机配置一定要包含主机名称,日志名称,和位置 ...
- MySQL主从同步和半同步配置
mysql主从配置: 1,安装maraidb,使用国内yum镜像站下载:[root@localhost mysql]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/MairaDB.repo # Mari ...
- MySQL主从复制技术的简单实现
配置环境: 主从服务器操作系统均为 ubuntu15.10 主从服务器MySQL版本均为 MySQL5.6.31 主服务器IP:192.168.0.178 从服务器IP:192.168.0.145 主 ...
随机推荐
- 06_javassist
[简述] Javassist是一个开源的java字节码操作工具,主要是对已经编译好class文件进行修改和处理,可以直接检查.修改.创建 java类. [javassist实例] package co ...
- Android SurfaceView播放视频时横竖屏的调整
对于横屏录制的视频就横屏播放,对于竖屏录制的视频就竖屏播放. 在mainifest文件里对负责播放的Activity添加以下属性“ android:configChanges="orient ...
- 购物车动画(Android)
购物车动画(Android) 前言:当我们写商城类的项目的时候,一般都会有加入购物车的功能,加入购物车的时候会有一些抛物线动画,最近做到这个功能,借助别人的demo写了一个. 效果: 开发环境:And ...
- GIT团队合作探讨之三--使用分支
这篇文章是一个作为对git branch的综合介绍.首先,我们会看看创建branch,这有点像是请求一个新的项目历史.然后,我们看看git checkout是如何能够被用来选择一个branch,最后看 ...
- LeetCode-Subsets ZZ
LeetCode:Subsets Given a set of distinct integers, S, return all possible subsets. Note: Elements in ...
- 事件循环进阶:macrotask与microtask
这段参考了参考来源中的第2篇文章(英文版的),(加了下自己的理解重新描述了下), 这里没法给大家演示代码,我就简单说下我的理解吧. promise和settimeout 在一起的时候执行顺序是个有意思 ...
- Oracle 12c logminer测试
首先开启归档:SQL> archive log list Database log mode Archive ModeAutomatic archival ...
- 最详细的Vue Hello World应用开发步骤
很多Vue的初学者想尝试这个框架时,都被webpack过于复杂的配置所吓倒,导致最后无法跑出一个期望的hello word效果.今天我就把我第一次使用webpack打包一个Vue Hello Worl ...
- NET对象的跨应用程序域
NET对象的跨应用程序域 转眼就到了元宵节,匆匆忙忙的脚步是我们在为生活奋斗的写照,新的一年,我们应该努力让自己有不一样的生活和追求.生命不息,奋斗不止.在上篇博文中主要介绍了.NET的AppDoma ...
- mysql执行sql文件
mysql -uspider_55haitao -pspider_55haitao -Dspider_55haitao</home/gphonebbs/Dump20161109.sql 方法一 ...