Selenium2+python自动化56-unittest之断言(assert)【转载】
前言
在测试用例中,执行完测试用例后,最后一步是判断测试结果是pass还是fail,自动化测试脚本里面一般把这种生成测试结果的方法称为断言(assert)。
用unittest组件测试用例的时候,断言的方法还是很多的,下面介绍几种常用的断言方法:assertEqual、assertIn、assertTrue
一、简单案例
1.下面写了4个case,其中第四个是执行失败的
# coding:utf-8
import unittest
class Test(unittest.TestCase):
def test01(self):
'''判断 a == b '''
a = 1
b = 1
self.assertEqual(a, b)
def test02(self):
'''判断 a in b '''
a = "hello"
b = "hello world!"
self.assertIn(a, b)
def test03(self):
'''判断 a is True '''
a = True
self.assertTrue(a)
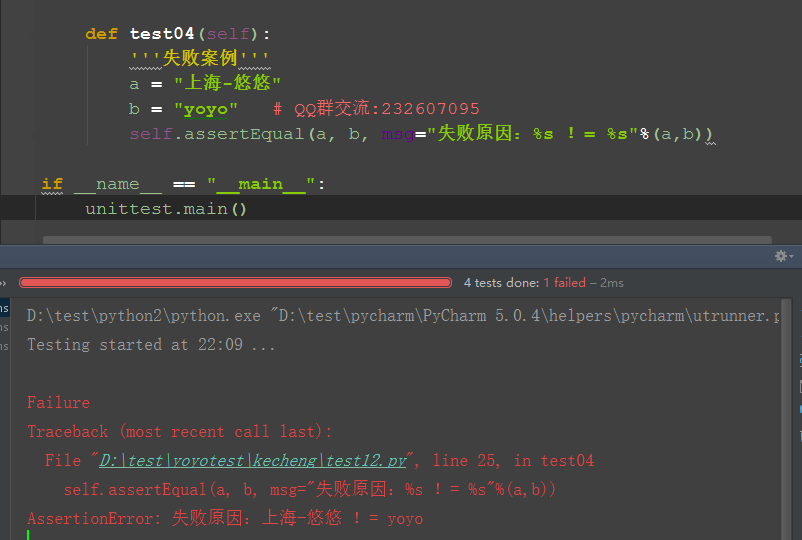
def test04(self):
'''失败案例'''
a = "上海-悠悠"
b = "yoyo"
self.assertEqual(a, b)
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()
2.执行结果如下
Failure
Expected :'\xe4\xb8\x8a\xe6\xb5\xb7-\xe6\x82\xa0\xe6\x82\xa0'
Actual :'yoyo'
<Click to see difference>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:\test\yoyotest\kecheng\test12.py", line 27, in test04
self.assertEqual(a, b)
AssertionError: '\xe4\xb8\x8a\xe6\xb5\xb7-\xe6\x82\xa0\xe6\x82\xa0' != 'yoyo'
3.执行的结果,中文编码不对,没正常显示中文,遇到这种情况,可以自定义异常输出
二、自定义异常
1.以assertEqual为例分析:
assertEqual(self, first, second, msg=None)
Fail if the two objects are unequal as determined by the '=='
operator.
2.翻译:如果两个对象不能相等,就返回失败,相当于return: first==second
3.这里除了相比较的两个参数first和second,还有第三个参数msg=None,这个msg参数就是遇到异常后自定义输出信息
三、unittest常用的断言方法
1.assertEqual(self, first, second, msg=None)
--判断两个参数相等:first == second
2.assertNotEqual(self, first, second, msg=None)
--判断两个参数不相等:first != second
3.assertIn(self, member, container, msg=None)
--判断是字符串是否包含:member in container
4.assertNotIn(self, member, container, msg=None)
--判断是字符串是否不包含:member not in container
5.assertTrue(self, expr, msg=None)
--判断是否为真:expr is True
6.assertFalse(self, expr, msg=None)
--判断是否为假:expr is False
7.assertIsNone(self, obj, msg=None)
--判断是否为None:obj is None
8.assertIsNotNone(self, obj, msg=None)
--判断是否不为None:obj is not None
四、unittest所有断言方法
1.下面是unittest框架支持的所有断言方法,有兴趣的同学可以慢慢看。
| assertAlmostEqual(self, first, second, places=None, msg=None, delta=None)
| Fail if the two objects are unequal as determined by their
| difference rounded to the given number of decimal places
| (default 7) and comparing to zero, or by comparing that the
| between the two objects is more than the given delta.
|
| Note that decimal places (from zero) are usually not the same
| as significant digits (measured from the most signficant digit).
|
| If the two objects compare equal then they will automatically
| compare almost equal.
|
| assertAlmostEquals = assertAlmostEqual(self, first, second, places=None, msg=None, delta=None)
|
| assertDictContainsSubset(self, expected, actual, msg=None)
| Checks whether actual is a superset of expected.
|
| assertDictEqual(self, d1, d2, msg=None)
|
| assertEqual(self, first, second, msg=None)
| Fail if the two objects are unequal as determined by the '=='
| operator.
|
| assertEquals = assertEqual(self, first, second, msg=None)
|
| assertFalse(self, expr, msg=None)
| Check that the expression is false.
|
| assertGreater(self, a, b, msg=None)
| Just like self.assertTrue(a > b), but with a nicer default message.
|
| assertGreaterEqual(self, a, b, msg=None)
| Just like self.assertTrue(a >= b), but with a nicer default message.
|
| assertIn(self, member, container, msg=None)
| Just like self.assertTrue(a in b), but with a nicer default message.
|
| assertIs(self, expr1, expr2, msg=None)
| Just like self.assertTrue(a is b), but with a nicer default message.
|
| assertIsInstance(self, obj, cls, msg=None)
| Same as self.assertTrue(isinstance(obj, cls)), with a nicer
| default message.
|
| assertIsNone(self, obj, msg=None)
| Same as self.assertTrue(obj is None), with a nicer default message.
|
| assertIsNot(self, expr1, expr2, msg=None)
| Just like self.assertTrue(a is not b), but with a nicer default message.
|
| assertIsNotNone(self, obj, msg=None)
| Included for symmetry with assertIsNone.
|
| assertItemsEqual(self, expected_seq, actual_seq, msg=None)
| An unordered sequence specific comparison. It asserts that
| actual_seq and expected_seq have the same element counts.
| Equivalent to::
|
| self.assertEqual(Counter(iter(actual_seq)),
| Counter(iter(expected_seq)))
|
| Asserts that each element has the same count in both sequences.
| Example:
| - [0, 1, 1] and [1, 0, 1] compare equal.
| - [0, 0, 1] and [0, 1] compare unequal.
|
| assertLess(self, a, b, msg=None)
| Just like self.assertTrue(a < b), but with a nicer default message.
|
| assertLessEqual(self, a, b, msg=None)
| Just like self.assertTrue(a <= b), but with a nicer default message.
|
| assertListEqual(self, list1, list2, msg=None)
| A list-specific equality assertion.
|
| Args:
| list1: The first list to compare.
| list2: The second list to compare.
| msg: Optional message to use on failure instead of a list of
| differences.
|
| assertMultiLineEqual(self, first, second, msg=None)
| Assert that two multi-line strings are equal.
|
| assertNotAlmostEqual(self, first, second, places=None, msg=None, delta=None)
| Fail if the two objects are equal as determined by their
| difference rounded to the given number of decimal places
| (default 7) and comparing to zero, or by comparing that the
| between the two objects is less than the given delta.
|
| Note that decimal places (from zero) are usually not the same
| as significant digits (measured from the most signficant digit).
|
| Objects that are equal automatically fail.
|
| assertNotAlmostEquals = assertNotAlmostEqual(self, first, second, places=None, msg=None, delta=None)
|
| assertNotEqual(self, first, second, msg=None)
| Fail if the two objects are equal as determined by the '!='
| operator.
|
| assertNotEquals = assertNotEqual(self, first, second, msg=None)
|
| assertNotIn(self, member, container, msg=None)
| Just like self.assertTrue(a not in b), but with a nicer default message.
|
| assertNotIsInstance(self, obj, cls, msg=None)
| Included for symmetry with assertIsInstance.
|
| assertNotRegexpMatches(self, text, unexpected_regexp, msg=None)
| Fail the test if the text matches the regular expression.
|
| assertRaises(self, excClass, callableObj=None, *args, **kwargs)
| Fail unless an exception of class excClass is raised
| by callableObj when invoked with arguments args and keyword
| arguments kwargs. If a different type of exception is
| raised, it will not be caught, and the test case will be
| deemed to have suffered an error, exactly as for an
| unexpected exception.
|
| If called with callableObj omitted or None, will return a
| context object used like this::
|
| with self.assertRaises(SomeException):
| do_something()
|
| The context manager keeps a reference to the exception as
| the 'exception' attribute. This allows you to inspect the
| exception after the assertion::
|
| with self.assertRaises(SomeException) as cm:
| do_something()
| the_exception = cm.exception
| self.assertEqual(the_exception.error_code, 3)
|
| assertRaisesRegexp(self, expected_exception, expected_regexp, callable_obj=None, *args, **kwargs)
| Asserts that the message in a raised exception matches a regexp.
|
| Args:
| expected_exception: Exception class expected to be raised.
| expected_regexp: Regexp (re pattern object or string) expected
| to be found in error message.
| callable_obj: Function to be called.
| args: Extra args.
| kwargs: Extra kwargs.
|
| assertRegexpMatches(self, text, expected_regexp, msg=None)
| Fail the test unless the text matches the regular expression.
|
| assertSequenceEqual(self, seq1, seq2, msg=None, seq_type=None)
| An equality assertion for ordered sequences (like lists and tuples).
|
| For the purposes of this function, a valid ordered sequence type is one
| which can be indexed, has a length, and has an equality operator.
|
| Args:
| seq1: The first sequence to compare.
| seq2: The second sequence to compare.
| seq_type: The expected datatype of the sequences, or None if no
| datatype should be enforced.
| msg: Optional message to use on failure instead of a list of
| differences.
|
| assertSetEqual(self, set1, set2, msg=None)
| A set-specific equality assertion.
|
| Args:
| set1: The first set to compare.
| set2: The second set to compare.
| msg: Optional message to use on failure instead of a list of
| differences.
|
| assertSetEqual uses ducktyping to support different types of sets, and
| is optimized for sets specifically (parameters must support a
| difference method).
|
| assertTrue(self, expr, msg=None)
| Check that the expression is true.
|
| assertTupleEqual(self, tuple1, tuple2, msg=None)
| A tuple-specific equality assertion.
|
| Args:
| tuple1: The first tuple to compare.
| tuple2: The second tuple to compare.
| msg: Optional message to use on failure instead of a list of
| differences.
Selenium2+python自动化56-unittest之断言(assert)【转载】的更多相关文章
- Selenium2+python自动化29-js处理多窗口【转载】
本篇转自博客:上海-悠悠 原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yoyoketang/tag/js/ 前言 在打开页面上链接的时候,经常会弹出另外一个窗口(多窗口情况前面这篇有讲解: ...
- Python单元测试框架unittest之断言(assert)
unittest中断言主要有三种类型: 1.基本的布尔断言,即:要么正确,要么错误的验证 2.比较断言,如比较两个变量的值(跟上面的布尔断言区别不大,主要是通过比较两个变量的值得出布尔值) 3.复杂断 ...
- Selenium2+python自动化(unittest)
# coding:utf-8from selenium import webdriverimport unittestimport timeclass Bolg(unittest.TestCase): ...
- Selenium2+python自动化63-简易项目搭建【转载】
前言 到unittest这里基本上可以搭建一个简易的项目框架了,我们可以用一条run_main.py脚本去控制执行所有的用例,并生成报告,发送邮件一系列的动作 一.新建工程 1.打开pycharm左上 ...
- Selenium2+python自动化2-pip降级selenium3.0【转载】
selenium版本安装后启动Firefox出现异常:'geckodriver' executable needs to be in PATH selenium默默的升级到了3.0,然而网上的教程都是 ...
- Selenium2+python自动化35-获取元素属性【转载】
前言 通常在做断言之前,都要先获取界面上元素的属性,然后与期望结果对比.本篇介绍几种常见的获取元素属性方法. 一.获取页面title 1.有很多小伙伴都不知道title长在哪里,看下图左上角. 2.获 ...
- Selenium2+python自动化27-查看selenium API【转载】
前言 前面都是点点滴滴的介绍selenium的一些api使用方法,那么selenium的api到底有多少呢?本篇就叫大家如何去查看selenium api,不求人,无需伸手找人要,在自己电脑就有. p ...
- Selenium2+python自动化18-加载Firefox配置【转载】
前言有小伙伴在用脚本启动浏览器时候发现原来下载的插件不见了,无法用firebug在打开的页面上继续定位页面元素,调试起来不方便 . 加载浏览器配置,需要用FirefoxProfile(profile_ ...
- Selenium2+python自动化76-Chrome配置加载【转载】
转至博客:上海-悠悠 一.加载Chrome配置 chrome加载配置方法,只需改下面一个地方,username改成你电脑的名字(别用中文!!!) '--user-data-dir=C:\Users\u ...
- Selenium2+python自动化68-html报告乱码问题【转载】
前言 python2用HTMLTestRunner生成测试报告时,有中文输出情况会出现乱码,这个主要是编码格式不统一,改下编码格式就行. 下载地址:http://tungwaiyip.info/sof ...
随机推荐
- python 调用RESTFul接口
本周需要将爬虫爬下来的数据入库,因为之前已经写好PHP的接口的,可以直接通过python调用PHP接口来实现,所以把方法总结一下. //python编码问题,因为好久用,所以很容易出现 # -*- c ...
- Java 无法初始化Connection的问题
通过断点调试捕获错误消息:The server time zone value '�й���ʱ��' is unrecognized or represents more than one time ...
- 关于org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter的学习
介绍 org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter 这是一个过滤器,是Spring在web请求中定义request和response的编 ...
- lintcode-109-数字三角形
109-数字三角形 给定一个数字三角形,找到从顶部到底部的最小路径和.每一步可以移动到下面一行的相邻数字上. 注意事项 如果你只用额外空间复杂度O(n)的条件下完成可以获得加分,其中n是数字三角形的总 ...
- linux下生成core dump文件方法
core 文件的简单介绍 当程序运行的过程中异常终止或崩溃,操作系统会将程序当时的内存状态记录下来,保存在一个文件中,这种行为就叫做Core Dump(中文有的翻译成“核心转储”).我们可以认为 co ...
- [剑指Offer] 28.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
[思路]将每个数字都存入map中作为key值,将它们出现的次数作为value值,当value超过一半时则返回其key值. class Solution { public: int MoreThanHa ...
- 【SQLAlchemy】SQLAlchemy技术文档(中文版)(中)
10.建立联系(外键) 是时候考虑怎样映射和查询一个和Users表关联的第二张表了.假设我们系统的用户可以存储任意数量的email地址.我们需要定义一个新表Address与User相关联. from ...
- 【bzoj4052】[Cerc2013]Magical GCD 暴力
题目描述 给出一个长度在 100 000 以内的正整数序列,大小不超过 10^12. 求一个连续子序列,使得在所有的连续子序列中,它们的GCD值乘以它们的长度最大. 样例输入 1 5 30 60 2 ...
- 【bzoj3224】Tyvj 1728 普通平衡树 01Trie姿势+平衡树的四种姿势 :splay,旋转Treap,非旋转Treap,替罪羊树
直接上代码 正所谓 人傻自带大常数 平衡树的几种姿势: AVL Red&Black_Tree 码量爆炸,不常用:SBT 出于各种原因,不常用. 常用: Treap 旋转 基于旋转操作和随机数 ...
- 两个数组的交集 II [ LeetCode - 350 ]
原题地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays-ii/description/ 给定两个数组,写一个方法来计算 ...
