Objective-C:运行时runtime
通知在哪一个线程发的,那么对通知事件的处理就在同一个线程中进行;
1> runtime是一套底层的C语言API(包含很多强大实用的C语言数据类型、C语言函数)
2> 实际上,平时我们编写的OC代码,底层都是基于runtime实现的
* 也就是说,平时我们编写的OC代码,最终都是转成了底层的runtime代码(C语言代码)
runtime有啥用?
1> 能动态产生一个类、一个成员变量、一个方法
2> 能动态修改一个类、一个成员变量、一个方法
3> 能动态删除一个类、一个成员变量、一个方法
常见的函数、头文件
#import <objc/runtime.h> : 成员变量、类、方法
Ivar * class_copyIvarList : 获得某个类内部的所有成员变量
Method * class_copyMethodList : 获得某个类内部的所有方法
Method class_getInstanceMethod : 获得某个实例方法(对象方法,减号-开头)
Method class_getClassMethod : 获得某个类方法(加号+开头)
method_exchangeImplementations : 交换2个方法的具体实现
#import <objc/message.h> : 消息机制
objc_msgSend(….)
什么是iOS Swizzle? 利用运行时函数交换2个方法的实现
具体的距离如下:
1、测试运行时的消息机制:要在测试类头文件中导入<objc/message.h>
Person类:
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface Person : NSObject //<NSCoding>
@property (copy,nonatomic)NSString *name;
@property (assign,nonatomic)NSInteger age;
@property (assign,nonatomic)CGFloat height;
-(void)run;
@end #import "Person.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h> @implementation Person
-(void)run
{
NSLog(@"run-----");
} @end
测试类:
//测试运行时的消息机制
-(void)testMessage
{
//<objc/message.h>
Person *p = [[Person alloc]init]; p.age = ;
objc_msgSend(p, @selector(setAge:),); // <====> [p setAge:20]
NSLog(@"%zi",p.age); objc_msgSend(p, @selector(age)); //<======> [p age] [p run];
objc_msgSend(p, @selector(run)); // <====> [p run]
}
测试结果如下:
-- ::27.397 Runtime-运行时[:]
-- ::27.398 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::27.398 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::27.398 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::27.399 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
2、获取运行时的成员属性
//获取运行时的的成员属性
-(void)testRuntimeIvar
{
//<objc/runtime.h>
//Ivar:成员变量
unsigned int count = ;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([Person class], &count);
NSLog(@"%d",count); //取得成员变量的数量
for (int i=; i<count; i++)
{
//取得i位置的成员变量
Ivar ivar = ivars[i]; //const char *ivar_getName(Ivar v) 获取属性名称
const char *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivar); //const char *ivar_getTypeEncoding(Ivar v) 获取成员变量的类型
const char *ivarType = ivar_getTypeEncoding(ivar); NSLog(@"%d %s %s",i,ivarName,ivarType);
}
}
测试结果如下:
-- ::01.013 Runtime-运行时[:]
-- ::01.014 Runtime-运行时[:] _name @"NSString"
-- ::01.014 Runtime-运行时[:] _age q
-- ::01.014 Runtime-运行时[:] _height d
扩展:利用这个上面获取属性的这个方法,可以很轻松的实现对大量的类的属性进行归档和解归档
//归档
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)encoder
{
unsigned int count = ;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([Person class], &count);
for (int i=; i<count; i++)
{
Ivar ivar = ivars[i];
const char *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName]; [encoder encodeObject:[self valueForKey:key] forKey:key];
}
} //解归档
- (id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)decoder
{
self = [super init];
if (self)
{
unsigned int count = ;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([Person class], &count);
for (int i=; i<count; i++)
{
Ivar ivar = ivars[i];
const char *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivar);
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName];
key = [decoder decodeObjectForKey:key];
}
}
return self;
}
3、获得运行时的成员方法
//获取运行时的的成员方法
-(void)testRuntimeMethod
{
//<objc/runtime.h>
//Method: 成员方法
unsigned int count = ;
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList([Person class], &count);
NSLog(@"%d",count); //取得成员方法的数量
for (int i=; i<count; i++)
{
//取得i位置的成员方法
Method method = methods[i]; //SEL method_getName(Method m) 获取方法名称
SEL sel = method_getName(method);
const char *selName = sel_getName(sel);
NSLog(@"%s",selName); //const char *method_getTypeEncoding(Method m)
//Returns a string describing a method's parameter and return types
const char *methodType = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
NSLog(@"%s",methodType); //char *method_copyReturnType(Method m) 获取成员方法的返回值类型
char *method_return_type = method_copyReturnType(method);
NSLog(@"%s",method_return_type); //unsigned int method_getNumberOfArguments(Method m) 获取成员方法的参数个数
count = method_getNumberOfArguments(method);
NSLog(@"%zi",count);
}
}
测试结果如下:
-- ::33.081 Runtime-运行时[:]
-- ::33.081 Runtime-运行时[:] setAge:
-- ::33.081 Runtime-运行时[:] v24@:8q16
-- ::33.082 Runtime-运行时[:] v
-- ::33.082 Runtime-运行时[:]
-- ::33.082 Runtime-运行时[:] age
-- ::33.082 Runtime-运行时[:] q16@:
-- ::33.082 Runtime-运行时[:] q
-- ::33.082 Runtime-运行时[:]
4、获得运行时的协议
-(void)testRuntimeProtocol
{
//<objc/runtime.h>
//Protocol:协议
//unsigned int count = 0;
//Protocol * __unsafe_unretained *protocol = class_copyProtocolList([Person class], &count);
//.........................
}
5、在运行时中动态添加方法、属性、协议等
-(void)testRuntimeAdd
{
//动态添加方法
//BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp,const char *types) //动态替换方法
//IMP class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp,const char *types) //动态添加成员变量
//BOOL class_addIvar(Class cls, const char *name, size_t size,uint8_t alignment, const char *types) //动态添加协议
//BOOL class_addProtocol(Class cls, Protocol *protocol) //动态添加属性
//BOOL class_addProperty(Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount) //动态替换属性
//void class_replaceProperty(Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount) //........................
}
6、在运行时中动态的交换两个实现方法
-(void)testRuntimeChangedMethod
{
//什么是iOS Swizzle? 利用运行时函数交换2个方法的实现 //class_getClassMethod(__unsafe_unretained Class cls, SEL name) //类方法
//class_getInstanceMethod(__unsafe_unretained Class cls, SEL name) //实例方法
//method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2) //动态交换实现方法
}
下面我就来验证动态的交换两个实现方法:
例子一:动态交换类方法和实例方法的实现方法
<1>在Person类中声明和定义一个run方法
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface Person : NSObject
-(void)run;
@end #import "Person.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h> @implementation Person
-(void)run
{
NSLog(@"run-----");
}
<2>在Person类扩展中定义eat方法和加载内存时交换这两个方法的实现
#import "Person.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h> @implementation Person (Extension) //程序一运行就会加载
+(void)load
{
//获取实例方法和类方法
Method classMethod = class_getClassMethod([Person class], @selector(eat));
Method instanceMethod = class_getInstanceMethod([Person class], @selector(run)); //交换实例实现方法和类实现方法
method_exchangeImplementations(classMethod, instanceMethod);
} +(void)eat
{
NSLog(@"eat------");
Person *p = [[Person alloc]init]; //死循环
[p run];
}
@end
<3>测试如下:
Person *p = [[Person alloc]init];
[p run];
当Person类对象调用run方法时出现死循环:我只给出一部分结果
-- ::22.268 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::22.268 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::22.268 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::22.268 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::22.268 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::22.268 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::22.269 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
-- ::22.269 Runtime-运行时[:] eat------
解释原因:因为Person类一存在的时候,就会调用+(void)load方法,将run实例方法和eat类方法进行了交换,即实际上[p run]方法被没有执行,而是执行了[Person eat]方法,在[Person eat]中第一次输出NSLog(@"eat-------")后,紧接着又创建了一个新的Person对象,这个对象也调用了[p run]方法,就又调用了[Person eat]类方法,又一次输出
NSLog(@"eat-------"),一直如此循环下去...........
例子二:给OC内置的方法做手脚,用自定义的方法交换实现方法(以数组和可变数组为例)
<1>给NSObject、NSArray、NSMutableArray都创建扩展类。
在NSObejct扩展中创建两个类方法,用来交换实例方法和类方法
在NSArray扩展中创建两个方法,一个+(void)load方法实现交换,另一个是自定义的用来覆盖OC内置的方法ObjectAtIndex:
和NSMutableArray创建三个方法,一个+(void)load方法实现交换,一个是自定义的用来覆盖OC内置的方法ObjectAtIndex:,还有一个用来覆盖OC内置的方法addObject:
如下:
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import <objc/runtime.h> @implementation NSObject(Extension)
+(void)swizlleClassMethod:(Class)class originMethod:(SEL)originMethod otherMethod:(SEL)otherMethod
{
//获取实例方法
Method classMethod1 = class_getClassMethod(class, originMethod);
Method classMethod2 = class_getClassMethod(class, otherMethod); //交换实例实现方法
method_exchangeImplementations(classMethod1, classMethod2);
} +(void)swizlleInstanceMethod:(Class)class originMethod:(SEL)originMethod otherMethod:(SEL)otherMethod
{
//获取实例方法
Method instanceMethod1 = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originMethod);
Method instanceMethod2 = class_getInstanceMethod(class, otherMethod); //交换实例实现方法
method_exchangeImplementations(instanceMethod1, instanceMethod2);
}
@end @implementation NSArray(Extension) //程序一运行就会加载
+(void)load
{
[self swizlleInstanceMethod:NSClassFromString(@"__NSArrayI") originMethod:@selector(objectAtIndex:) otherMethod:@selector(Test_objectAtIndex:)];
}
-(id)Test_objectAtIndex:(NSUInteger)index
{
if (index < self.count)
{
//如果索引小于数组个数,就调用交换后的系统的objectAtIndex:方法返回该位置的值
return [self Test_objectAtIndex:index];
}
else
{
//超界,返回空值
return nil;
}
} @end @implementation NSMutableArray(Extension) //程序一运行就会加载
+(void)load
{
//获取实例方法
[self swizlleInstanceMethod:NSClassFromString(@"__NSArrayM") originMethod:@selector(addObject:) otherMethod:@selector(Test_addObject:)]; //交换实例实现方法
[self swizlleInstanceMethod:NSClassFromString(@"__NSArrayM") originMethod:@selector(objectAtIndex:) otherMethod:@selector(Test_objectAtIndex:)]; } -(void)Test_addObject:(id)object
{
if (object != nil)
{
//如果对象不为空,就调用交换后的系统的addObject:方法添加对象到可变数组中
[self Test_addObject:object];
}
} -(id)Test_objectAtIndex:(NSUInteger)index
{
if (index < self.count)
{
//如果索引小于数组个数,就调用交换后的系统的objectAtIndex:方法返回该位置的值
return [self Test_objectAtIndex:index];
}
else
{
//超界,返回空值
return nil;
}
}
@end
<2>测试:
声明数组:
@interface ViewController ()
@property (strong,nonatomic)NSMutableArray *names;
@property (strong,nonatomic)NSArray *books;
@end
NSArray:
self.books = @[@"水浒传",@"西游记"];
NSLog(@"%@",self.books[]); //[self.books objectAtIndex:1] --> [self.books Test_objectAtIndex:1]
NSLog(@"%@",self.books[]); //[self.books objectAtIndex:4] --> [self.books Test_objectAtIndex:4]
测试结果:
-- ::01.436 Runtime-运行时[:] 西游记
-- ::01.437 Runtime-运行时[:] (null)
解释原因:
因为程序一运行,就调用了+(void)load中的[self swizlleInstanceMethod:NSClassFromString(@"__NSArrayI") originMethod:@selector(objectAtIndex:) otherMethod:@selector(Test_objectAtIndex:)]方法,
所以交换后就成了这种情况: self.books[1]---> [self.books objectAtIndex:1] --> [self.books Test_objectAtIndex:1],
明显的,1小于数组个数2,调用[self.books Test_objectAtIndex:1]-->[self.books objectAtIndex:1],返回@"西游记";
同理,由于self.books[4]的索引4大于数组个数2,所以返回null.
NSMutableArray:
[self.names addObject:@"jack"];
[self.names addObject:nil];
[self.names addObject:nil];
[self.names addObject:@"rose"];
[self.names addObject:@"jim"];
NSLog(@"%@",self.names[]);
NSLog(@"%@",self.names);
测试结果:
-- ::45.785 Runtime-运行时[:] (null)
-- ::45.786 Runtime-运行时[:] (
jack,
rose,
jim
)
分析原理同上,这里说一点,明显的如果我们没有实现方法的交换,使用[self.name addobject:nil],程序肯定是会崩掉的,OC中是不允许向可变数组中添加空对象的,但是我们在这个方法上做一些手脚,换成自定义的方法后,可以消除这个bug,输出自己想要的结果;
最后还有一个知识,我们都知道,OC的分类中只能用来添加方法,是不能添加属性的。
但是有了运行时这个概念,动态的给分类添加属性也就不是事。
演示截图如下:
1.给分类添加属性:
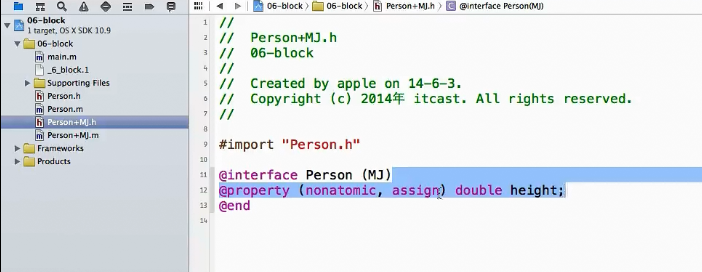
2.对象分类属性进行关联:

发现编译一下,不报错,okay,成了。
Objective-C:运行时runtime的更多相关文章
- Objective C运行时(runtime)
#import <objc/runtime.h> void setBeingRemoved(id __self, SEL _cmd) { NSLog(@"------------ ...
- iOS运行时Runtime浅析
运行时是iOS中一个很重要的概念,iOS运行过程中都会被转化为runtime的C代码执行.例如[target doSomething];会被转化成objc)msgSend(target,@select ...
- Deep Learning部署TVM Golang运行时Runtime
Deep Learning部署TVM Golang运行时Runtime 介绍 TVM是一个开放式深度学习编译器堆栈,用于编译从不同框架到CPU,GPU或专用加速器的各种深度学习模型.TVM支持来自Te ...
- CUDA运行时 Runtime(一)
CUDA运行时 Runtime(一) 一. 概述 运行时在cudart库中实现,该库通过静态方式链接到应用程序库cudart.lib和libcudart.a,或动态通过cuda ...
- CUDA运行时 Runtime(四)
CUDA运行时 Runtime(四) 一. 图 图为CUDA中的工作提交提供了一种新的模型.图是一系列操作,如内核启动,由依赖项连接,依赖项与执行分开定义.这允许定义一次图形,然后重复启动.将 ...
- CUDA运行时 Runtime(三)
CUDA运行时 Runtime(三) 一.异步并发执行 CUDA将以下操作公开为可以彼此并发操作的独立任务: 主机计算: 设备计算: 从主机到设备的内存传输: 从设备到主机的存储器传输: 在给定设备的 ...
- CUDA运行时 Runtime(二)
CUDA运行时 Runtime(二) 一. 概述 下面的代码示例是利用共享内存的矩阵乘法的实现.在这个实现中,每个线程块负责计算C的一个方子矩阵C sub,块内的每个线程负责计算Csub的一个元素.如 ...
- “ compiler-rt”运行时runtime库
" compiler-rt"运行时runtime库 编译器-rt项目包括: Builtins-一个简单的库,提供了代码生成和其他运行时runtime组件所需的特定于目标的低级接口. ...
- Objective C运行时(runtime)技术的几个要点总结
前言: Objective C的runtime技术功能非常强大,能够在运行时获取并修改类的各种信息,包括获取方法列表.属性列表.变量列表,修改方法.属性,增加方法,属性等等,本文对相 ...
- Objective C运行时(runtime)技术总结,好强大的runtime
前言: Objective C的runtime技术功能非常强大,能够在运行时获取并修改类的各种信息,包括获取方法列表.属性列表.变量列表,修改方法.属性,增加方法,属性等等,本文对相 ...
随机推荐
- bzoj 2190 线性生成欧拉函数表
首先我们知道,正方形内个是对称的,关于y=x对称,所以只需要算出来一半的人数 然后乘2+1就行了,+1是(1,1)这个点 开始我先想的递推 那么我们对于一半的三角形,一列一列的看,假设已经求好了第I- ...
- kickstart构建Live CD 添加文件问题
在构建自定义ISO的时候,有时候需要从母体机器拷贝文件到Live CD系统.比如拷贝/home/xiaoxiaoleo/hello 程序,在Kickstart配置文件里, post脚本添加--noch ...
- 【Sqlite3】SQLITE3使用总结(转)
原文转自 https://www.cnblogs.com/wenxp2006/archive/2012/06/04/2535169.html SQL语句操作 介绍如何用sqlite 执行标准 sql ...
- RabbitMQ消息队列(二): 工作队列
1. 工作队列: 对于资源密集型任务,我们等待其处理完成在很多情况下是不现实的,比如无法在http的短暂请求窗口中处理大量耗时任务, 为了达到主线程无需等待,任务异步执行的要求,我们可以将任务加入任务 ...
- gcc 簡單操作
gcc -c test.c 產出 test.o object file gcc -c test.c -o XXX 產出 XXX object file gcc test.c -o aaa 產出 aaa ...
- 创建第一个maven项目的那些坑
1.记事本方式: class所在的目录结构: class的代码书写: package com.imooc.maven01.mode1; public class HelloWorld { public ...
- [ 手记 ] 联想rd650服务器整列及系统安装
联想 RD650服务器 磁盘阵列:http://wenku.baidu.com/view/b364c2db5f0e7cd185253644.html?from=search 该服务器安装系统需要BIO ...
- JavaScript的7种继承模式
<JavaScript模式>一书中,对于JavaScript的几种继承模式讲解得很清楚,给我提供了很大帮助.总结一下,有如下7种模式. 继承模式1--设置原型(默认模式) 实现方式: // ...
- mysql 使用set names 解决乱码问题
引子: 最近查询公司线上表数据,返现在Xshell控制台打印的数据都是乱码,记得之前瞄过同事都是执行set names UTF8 , 解决的,特记录如下.
- GO语言的数据结构测试
用于docker了,go也慢慢看一些.. 推荐书籍<go语言实践>就是<Go in Action>的中文版,有文字版PDF的. package main import ( &q ...
