strcpy&memcpy&memmove
strcpy
extern char *strcpy(char *dest,char *source);
{
assert((dest!=NULL)&&(source!=NULL));
char *address=dest;
while((*dest++=*source++)!='\0');
return address;
}
把source所指由NULL结束的字符串复制到dest所指的数组中。source和dest所指内存区域不可以重叠且dest必须有足够的空间来容纳source的字符串。返回指向dest的指针。
memcpy
void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *source, size_t count)//没有对内存重叠进行检查
{
assert((dest!=NULL)&&(source!=NULL));
char* tmpDest=(char*)dest;
char* tmpSource=(const char*)source;
while(count--)
*tmpDest++=*tmpSource++;
return tmpDest;
}
memmove
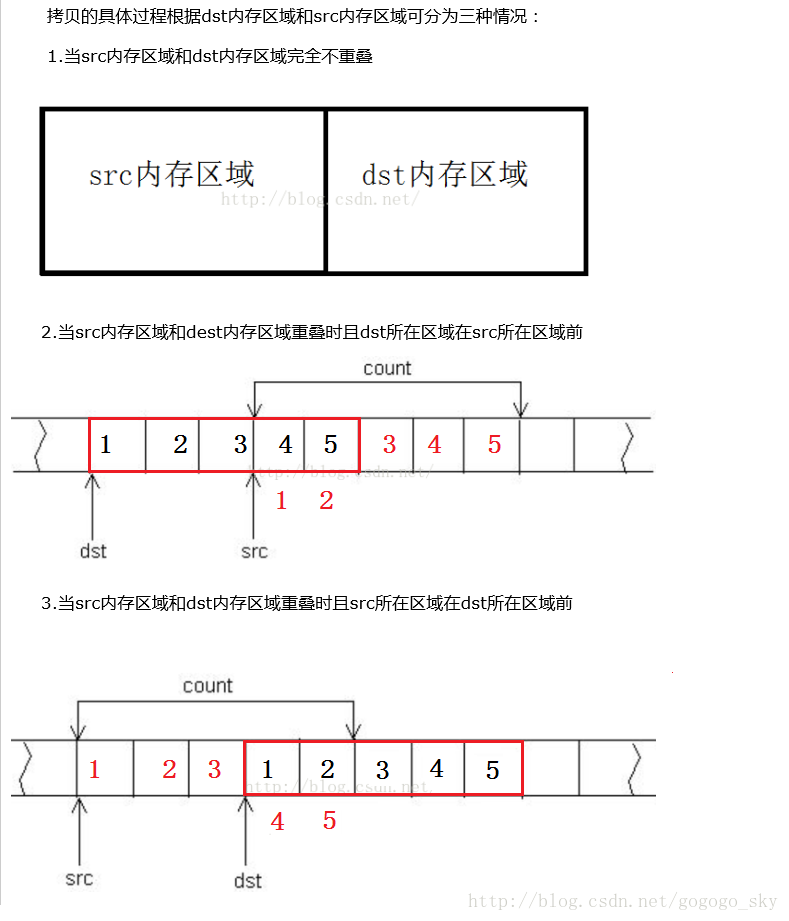
Copies the values of num bytes from the location pointed by source to the memory block pointed by destination. Copying takes place as if an intermediate buffer were used, allowing the destination and source to overlap
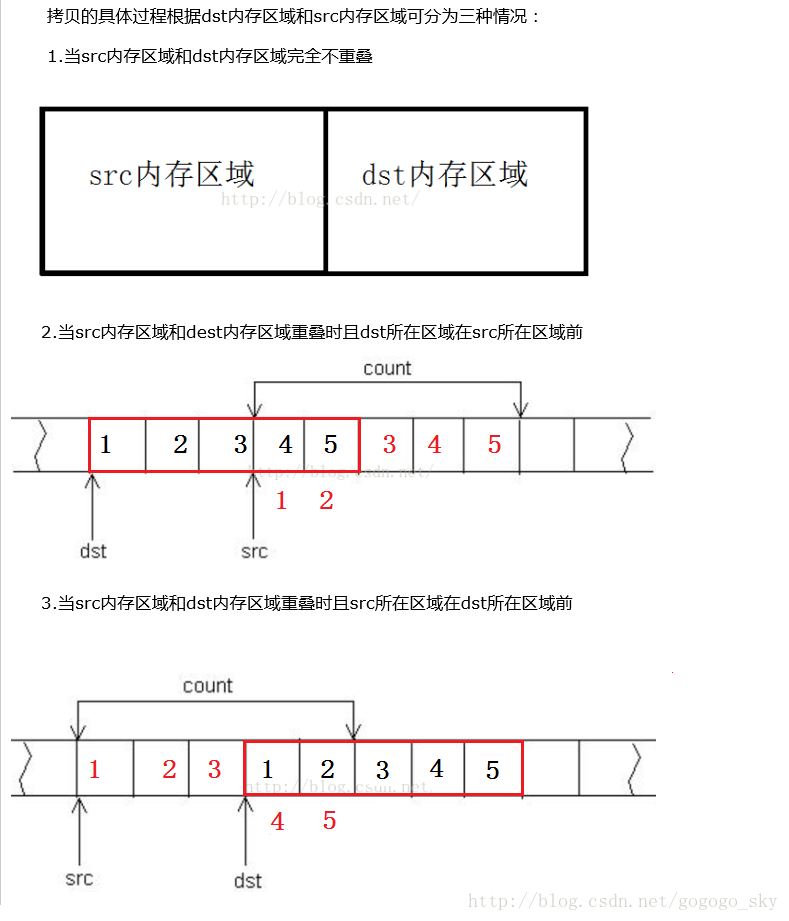
void* memmove(void* dest,const void* src,size_t num)
{
assert((dest!=NULL)&&(src!=NULL));
char* tmpDest=(char*)dest;
char* tmpSrc=(const char*)src;
if(src>dest||src+num<dest)
{
while(num--)
*tmpDest++=*tmpSrc++;
}
else
{
tmpDest=dest+num-;
tmpSrc=src+num-;
while(num--)
*tmpDest--=*tmpSrc--;
}
return dest;
}
strcpy&memcpy&memmove的更多相关文章
- strcpy,memcpy,memmove和内存重叠分析
一:strcpy函数用法和实现: /* GNU-C中的实现(节选): */ char* strcpy(char *d, const char *s) { char *r=d; while((*d++= ...
- strcpy, mencpy, memmove三者区别
首先来看strcpy,目的是实现字符串的复制,这里需要注意几个点: 1.判断指针的有效性 2.将复制后的指针地址返回,为了支持链式操作 3.不要忘记将字符串最后一个自负'\0'复制给dest 4.注意 ...
- 自己实现的库函数2(memset,memcmp,memcpy,memmove)
memset,memcmp,memcpy,memmove是对内存进行管理的库函数,为了更好的理解和使用这几个函数,自己用C语言实现一下~ //内存设置函数void* my_memset(void* d ...
- memset memcmp memcpy memmove 自己实现
memset memcmp memcpy memmove 自己实现 memset #include <stdio.h> #include <memory.h> #include ...
- memcpy/memmove?快速乘?
memcpy?memmove? //#pragma GCC optimize(2) #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ; ],b[n ...
- C的memset,memcpy,strcpy 的区别 及memset memcpy memmove源码
extern void *memcpy(void *dest,void *src,unsigned int count);#include <string.h> 功能:由src所指内存 ...
- strcpy和memcpy,memmove函数的区别
strcpy和memcpy的区别 strcpy和memcpy都是标准C库函数,它们有下面的特点. strcpy提供了字符串的复制.即strcpy只用于字符串复制,并且它不仅复制字符串内容之外,还会复制 ...
- strcpy, memcpy, memset函数
一. strcpy函数 原型声明:char *strcpy(char* dest, const char *src); 头文件:#include <string.h> 和 #inclu ...
- 访谈将源代码的函数 strcpy/memcpy/atoi/kmp/quicksort
一.社论 继上一次发表了一片关于參加秋招的学弟学妹们怎样准备找工作的博客之后,反响非常大.顾在此整理一下,以便大家复习.好多源自july的这篇博客,也有非常多是我自己整理的.希望大家可以一遍一遍的写. ...
随机推荐
- s3c2440裸机-UART编程(二、UART编程实现)
UART编程 1.初始化 我们的2440支持3个UART串口,以uart0为例讲解. 那么我们需要实现以下这几个函数完成串口的最基本功能: (1)uart0_init()用于初始化串口 (2)putc ...
- java8一些语法使用例子
package com.ladeng.jdk8; import com.google.common.collect.Lists;import java.util.*;import java.util. ...
- css3的新属性 新增的颜色--- 透明度---两种渐变---定义多张背景图--background-size
css31==>颜色的6种表示的方法有6种表示颜色的方法 关键字 rgb rgba(css3) 16进制 hsl hsla hsla h=>是色相,值为360, s=>饱和度,0%- ...
- Day7 - Python基础7 面向对象
本节内容: 1:概述 2:类.对象和方法的创建 3:面向对象三大特性,封装.继承和多态. 4:面向对象中高级篇:类成员:字段.方法.属性 5:类成员的修饰符 6:类的特殊成员 1.概述 面向过程:根据 ...
- 扩展KMP笔记
KMP能计算一个字符串的每个位置前最长公共前缀后缀 扩展KMP可以用来计算两个字符串间的最长公共前缀后缀的…… 不过为了计算这个需要绕些弯路 已知字符串$S$和$P$,$S$的长度为$n$,$P$的长 ...
- JDBC简介(一)
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity)是Java与数据库的接口规范,由Java 语言编写的类和接口组成,大致分为两类:针对Java程序员的JDBC API和针对数据库开发商的 ...
- LG3825/BZOJ4945/LOJ2305 「NOI2017」游戏 dfs+2-SAT
问题描述 LG3825 BZOJ4945 LOJ2305 题解 发现对于每个地图,如果没有\(A,B,C\)地图不可以使用\(a,b,c\),就是一个\(\mathrm{3-SAT}\)问题. 有了这 ...
- npm简单实用
npm包管理工具 npm可以理解为前端的maven,一个包的管理工具 1. 查看npm和node版本 node -v npm -v 2. 初始化项目 npm init 默认配置初始化项目 npm in ...
- 推荐|MathType的使用技巧
前言 持续更新中,敬请期待... 数学学科 制作新的数学符号 不包含于符号:输入$\not\subseteq,然后按回车键enter即可: 分式\(\cfrac{3-x}{2x-1}\)符号:输入$\ ...
- Codeforces Round #602 (Div. 2, based on Technocup 2020 Elimination Round 3) B. Box 贪心
B. Box Permutation p is a sequence of integers p=[p1,p2,-,pn], consisting of n distinct (unique) pos ...
