面试中常见的算法之Java中的递归
1、方法定义中调用方法本身的现象
2、递归注意实现
1) 要有出口,否则就是死递归
2) 次数不能太多,否则就内存溢出
3) 构造方法不能递归使用
3、递归解决问题的思想和图解:
分解和合并【先分解后合并】
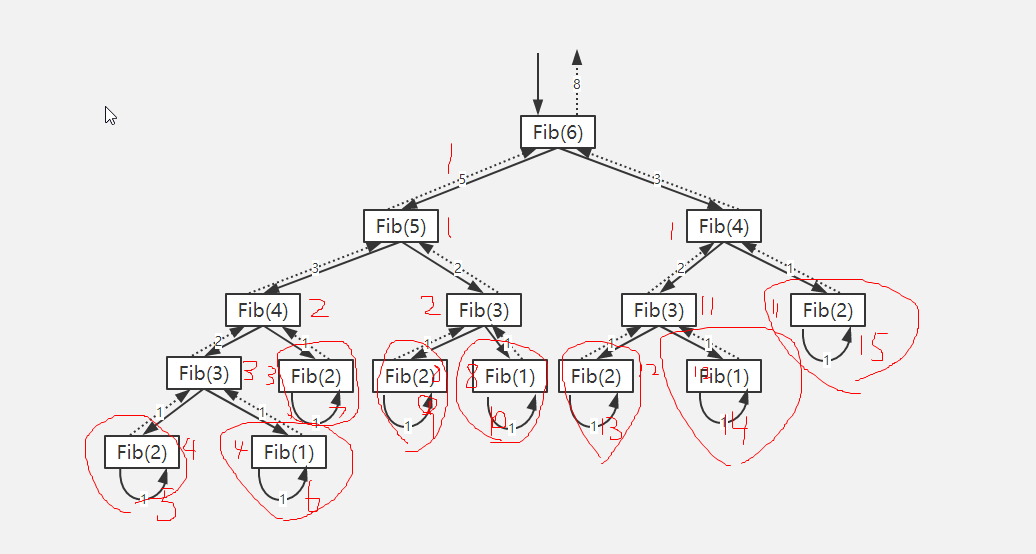
1. 常见的斐波那契数列
1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,...
特征: 从第三个数开始,每个数是前两个数的和。
int count = 0;
private int getFibo(int i) {
if (i == 1 || i == 2) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 并返回结果1" );
return 1;}
else
{
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 "+ "getFibo("+(i - 1)+")"+" + getFibo("+(i - 2)+")");
return getFibo(i - 1) + getFibo(i - 2);
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
int value = getFibo(6);
System.out.println(value);
}


2. 阶乘
10!= 10 * 9 * 8 * 7 * (... )* 1
9! = 9 * 8 * 7 * (... )* 1
8! = 8 * 7 * (... )* 1
特征:
9!=9* 8!
10! =10 * 9!
//阶乘
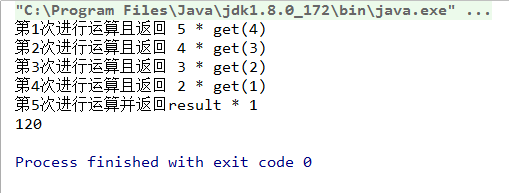
private int get(int i){
int result = 1;
if (i == 1) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 并返回结果* 1" );
result = result * 1;
}
else {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算" + "get(" +(i-1)+")" );
result = i * get(i-1);
}
return result; } @Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
System.out.println(get(5));
}

3. 加法实现1+2+3+4+5+...+100=
//求和
private int fsum(int i){ if (i <= 0) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算并返回0" );
return 0;
}
else {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算且返回 " + i +" + fsum(" +(i-1)+")" );
return (i + fsum(i-1)); } } @Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
//System.out.println(get(5));
System.out.println(fsum(10)); }
4. 实现打印乘法表
//打印乘法表
//for 循环实现
private void getByFor(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i+" * "+j+" = "+i*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//打印乘法表
//递归实现
public static void getByRecursion(int n) {//递归 实现
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("1 * 1 = 1 ");
}
else {
getByRecursion(n-1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
System.out.print(n+" * "+j+" = "+n*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
} @Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
//System.out.println(get(5));
//System.out.println(fsum(10)); getByFor(8);
getByRecursion(9); }
6. 汉诺塔游戏
三根木棒,n个依次增大的空心圈圈,每次移动一个圈圈到木棒上,且任何时候保证小的圈圈不能被大的圈圈压在下面。
2的n次方-1

//5. 汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题其实是印度的一个古老的传说
public int hanio(int n,char a,char b,char c) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println( n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);
count = count+1;
return count; } else {
count = count+1;
hanio(n - 1, a, c, b);//把上面n-1个盘子从a借助b搬到c
System.out.println("移动" + n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);//紧接着直接把n搬动c
hanio(n - 1, b, a, c);//再把b上的n-1个盘子借助a搬到c
return count;
} } @Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
//System.out.println(get(5));
//System.out.println(fsum(10)); //getByFor(8);
//getByRecursion(9); int count =hanio(3,'A','B','C');
System.out.println(count); }
代码:
package com.example.demo;
import org.junit.Test;
public class Test02 {
int count = 0;
//1. 斐波那契数列递归,用的时候请将count和输出System.Out去除
private int getFibo(int i) {
if (i == 1 || i == 2) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 并返回结果1" );
return 1;}
else
{
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算 "+ "getFibo("+(i - 1)+")"+" + getFibo("+(i - 2)+")");
return getFibo(i - 1) + getFibo(i - 2);
}
}
//2. 阶乘
private int get(int i){
int result = 1;
if (i == 1) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算并返回result * 1" );
result = result * 1;
}
else {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算且返回 " + i+" * get(" +(i-1)+")" );
result = i * get(i-1);
}
return result;
}
//3. 求和
private int fsum(int i){
if (i <= 0) {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算并返回0" );
return 0;
}
else {
count = count+1;
System.out.println("第" +count+"次进行运算且返回 " + i +" + fsum(" +(i-1)+")" );
return (i + fsum(i-1));
}
}
//打印乘法表
//for 循环实现
private void getByFor(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i+" * "+j+" = "+i*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//打印乘法表
//4. 递归实现
public void getByRecursion(int n) {//递归 实现
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("1 * 1 = 1 ");
}
else {
getByRecursion(n-1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
System.out.print(n+" * "+j+" = "+n*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//5. 汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题其实是印度的一个古老的传说
public int hanio(int n,char a,char b,char c) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println( n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);
count = count+1;
return count;
} else {
count = count+1;
hanio(n - 1, a, c, b);//把上面n-1个盘子从a借助b搬到c
System.out.println("移动" + n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);//紧接着直接把n搬动c
hanio(n - 1, b, a, c);//再把b上的n-1个盘子借助a搬到c
return count;
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
//System.out.println(getFibo(6));
//System.out.println(get(5));
//System.out.println(fsum(10));
//getByFor(8);
//getByRecursion(9);
int count =hanio(3,'A','B','C');
System.out.println(count);
}
}
package com.example.demo;
import org.junit.Test;
public class Test03 {
int count = 0;
//1. 斐波那契数列递归,用的时候请将count和输出System.Out去除
private int getFibo(int i) {
if (i == 1 || i == 2) {
return 1;}
else
{
return getFibo(i - 1) + getFibo(i - 2);
}
}
//2. 阶乘
private int get(int i){
int result = 1;
if (i == 1) {
result = result * 1;
}
else {
result = i * get(i-1);
}
return result;
}
//3. 求和
private int fsum(int i){
if (i <= 0) {
return 0;
}
else {
return (i + fsum(i-1));
}
}
//打印乘法表
//for 循环实现
private void getByFor(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i+" * "+j+" = "+i*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//打印乘法表
//4. 递归实现
public void getByRecursion(int n) {//递归 实现
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("1 * 1 = 1 ");
}
else {
getByRecursion(n-1);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
System.out.print(n+" * "+j+" = "+n*j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//5. 汉诺塔(又称河内塔)问题其实是印度的一个古老的传说
public int hanio(int n,char a,char b,char c) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println( n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);
count = count+1;
return count;
} else {
count = count+1;
hanio(n - 1, a, c, b);//把上面n-1个盘子从a借助b搬到c
System.out.println("移动" + n + "号盘子从" + a + "到" + c);//紧接着直接把n搬动c
hanio(n - 1, b, a, c);//再把b上的n-1个盘子借助a搬到c
return count;
}
}
@Test
public void test01() {
System.out.println(getFibo(6));
System.out.println(get(5));
System.out.println(fsum(10));
getByFor(8);
getByRecursion(8);
int count =hanio(3,'A','B','C');
System.out.println(count);
}
}
面试中常见的算法之Java中的递归的更多相关文章
- 常见排序算法(附java代码)
常见排序算法与java实现 一.选择排序(SelectSort) 基本原理:对于给定的一组记录,经过第一轮比较后得到最小的记录,然后将该记录与第一个记录的位置进行交换:接着对不包括第一个记录以外的其他 ...
- 常见排序算法总结 -- java实现
常见排序算法总结 -- java实现 排序算法可以分为两大类: 非线性时间比较类排序:通过比较来决定元素间的相对次序,由于其时间复杂度不能突破O(nlogn),因此称为非线性时间比较类排序. 线性时间 ...
- 正整数构成的线性表存放在单链表中,编写算法将表中的所有的奇数删除。(C语言)
/* 正整数构成的线性表存放在单链表中,编写算法将表中的所有的奇数删除 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef st ...
- iOS面试中常见的算法题目
一.前言 这里是在iOS求职中自己遇到的算法题,希望对大家有所帮助.不定期更新.如果大家想在线运行代码调试,可以将代码拷贝到这里.然后进行调试.下面就是常见的算法题目. 二.正文 1.就n的阶乘.(这 ...
- Java开发中常见的危险信号(中)
本文来源于我在InfoQ中文站原创的文章,原文地址是:http://www.infoq.com/cn/news/2013/12/common-red-flags-in-java-1 Dustin Ma ...
- 最近在准备面试,总结了几个java中面向对象的几个问题,问题本事还不够全面,要想知道还是要自己去找,但是在面试上应该是没多大问题了
Overload(重载)与Override(重写)的区别 重载:发生在一个类中,方法名称相同,参数列表不同,方法体不同(看对象类型) 重写:发生在父类中,方法名称相同,参数列表相同,方法体不同(看引用 ...
- 几种常见排序算法的java实现
一.几种常见的排序算法性能比較 排序算法 最好时间 平均时间 最坏时间 辅助内存 稳定性 备注 简单选择排序 O(n^2) O(n^2) O(n^2) O(1) 不稳定 n小时较好 直接插入排序 O( ...
- java中接口的简单运用&java中的一些异常(运用myeclipse)
package test;//创建一个名为test的包 public class A4paper implements Paper { public String getSize(){ return& ...
- .NET和JAVA中BYTE的区别以及JAVA中“DES/CBC/PKCS5PADDING” 加密解密在.NET中的实现
场景:java 作为客户端调用已有的一个.net写的server的webservice,输入string,返回字节数组. 问题:返回的值不是自己想要的,跟.net客户端直接调用总是有差距 分析:平台不 ...
随机推荐
- 在微信浏览器里使用js或jquery实现页面重新刷新
function refresh() { var random = Math.floor((Math.random() * 10000) + 1); var url = decodeURI(windo ...
- Java之"Mozilla Rhino"引擎(二)
在Java中使用Rhino, 能让你使用类似Groovy, ECMAScript...等等之类的不同动态脚本语言, 其中值得推荐的是ECMAScript, 它是Rhino的默认实现, 同时也在JDK1 ...
- [ 转]Node.js模块 require和 exports
什么是模块? node.js通过实现CommonJS的Modules/1.0标准引入了模块(module)概念,模块是Node.js的基本组成部分.一个node.js文件就是一个模块,也就是说文件和模 ...
- QRCode二维码生成方案及其在带LOGO型二维码中的应用(2)
原文:QRCode二维码生成方案及其在带LOGO型二维码中的应用(2) 续前:QRCode二维码生成方案及其在带LOGO型二维码中的应用(1) http://blog.csdn.net/johnsu ...
- PostSharp-5.0.26安装包_KeyGen发布_支持VS2017
PostSharp-5.0.26安装包_KeyGen发布_支持VS2017 请低调使用. PostSharp安装及注册步骤截图.rar 请把浏览器主页设置为以下地址支持本人.https://www.d ...
- PHP模拟单链表的数据结构
<?php /*** * 单链表 */ //节点,下标,节点名称,下一个节点的地址 class Node { public $id; public $name; public $next; pu ...
- PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(二)
PySide——Python图形化界面入门教程(二) ——交互Widget和布局容器 ——Interactive Widgets and Layout Containers 翻译自:http://py ...
- GIS基础软件及操作(十)
原文 GIS基础软件及操作(十) 练习十.网络分析 (1) 加深对网络分析基本原理.方法的认识:(2) 熟练掌握ARCGIS下进行道路网络分析的技术方法:(3) 结合实际.掌握利用网络分析方法解决地学 ...
- 微信小程序把玩(三十四)Audio API
原文:微信小程序把玩(三十四)Audio API 没啥可值得太注意的地方 重要属性: 1. wx.getBackgroundAudioPlayerState(object) 获取播放状态 2.wx.p ...
- UWP 设置控件样式四种方法
1.隐式方法,通过仅指定 Style 的 TargetType.(设置全部的Button样式) <Page.Resources > <Style TargetType="B ...
