SpringMVC流程源码分析及DispatcherServlet核心源码
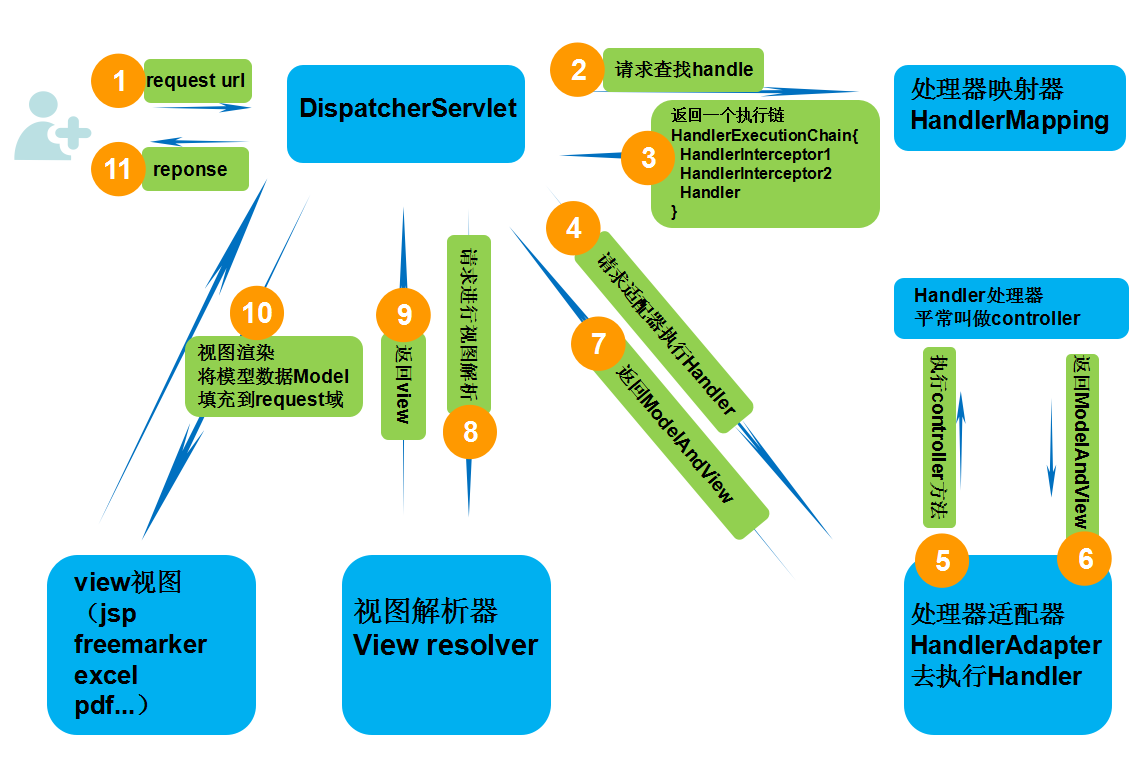
一、源码分析前还是需要一张流程图作为指导,如下:
二、简单介绍以及源码定位
DispatcherServlet其实就是一个HttpServlet,他是HttpServlet的子类,所以它和普通的HttpServlet在web.xml里同样的配置。
这个Servlet的doPost和doGet方法的实现是DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet中实现的,两个方法里都是调用processRequest方法。processRequest的实现是在FrameworkServlet中,此方法中最主要的操作就是调用doService方法。
doService方法的最终实现是在DispatcherServlet中,这样所有的Http请求(GET、POST、PUT和DELETE等)的最终操作就DispatcherServlet中实现了。
DispatcherServlet中doService的实现如下,对Request设置了一些全局属性,最终接下来的操作是在doDispatcher函数中实现了。
[java] view plain copy
//获取请求,设置一些request的参数,然后分发给doDispatch
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
/* 设置web应用上下文**/
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
/* 国际化本地**/
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
/* 样式**/
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
//设置样式资源
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
//请求刷新时保存属性
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
//Flash attributes 在对请求的重定向生效之前被临时存储(通常是在session)中,并且在重定向之后被立即移除
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
//FlashMap 被用来管理 flash attributes 而 FlashMapManager 则被用来存储,获取和管理 FlashMap 实体.
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
doDispatch()方法源码如下:
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Error err) {
triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err);
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}三、通过阅读源码总结分析流程如下:
1. web应用服务器接收到一个新请求是,读取web.xml中的配置,如果匹配DispatcherServlet的请求映射路径,web容器将该请求转发给DispatcherServlet进行处理
2. DispatcherServlet接收到请求后,执行doDispatch方法,此方法遍历DispatcherServlet中的HandlerMapping(处理器映射器)集合,根据请求的HttpServletRequest信息通过HandlerMapping对象方法找到HandlerExecutionChain(执行链,内含拦截器和处理器)。
3. DispatcherServlet继续执行doDispatch方法,根据得到的HandlerExecutionChain(执行链)中的handler遍历自己的HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器)集合,找到支持这个Handler的HandlerAdapter并返回。
4.继续doDispatch方法,把HandlerExecutionChain(执行链)内部的那些前置拦截器逻辑都执行完,然后再再通过得到的HandlerAdapter执行HandlerExecutionChain内部的处理器,会返回一个ModelAndView包含了视图逻辑名和模型数据信息
5.调用执行链的方法,执行拦截器的后置拦截器
6. ModelAndView中包含的是“逻辑视图名”,而非真正的视图对象,DispatcherServlet借助ViewResolver完成逻辑视图名到真实视图名对象的解析工作
7. 当得到真实的视图对象View后,DispatcherServlet就使用这个View对象对ModelAndView中的模型数据进行视图渲染
8. 最终客户端得到HTML页面什么的
SpringMVC流程源码分析及DispatcherServlet核心源码的更多相关文章
- Android版数据结构与算法(五):LinkedHashMap核心源码彻底分析
版权声明:本文出自汪磊的博客,未经作者允许禁止转载. 上一篇基于哈希表实现HashMap核心源码彻底分析 分析了HashMap的源码,主要分析了扩容机制,如果感兴趣的可以去看看,扩容机制那几行最难懂的 ...
- 并发编程之 SynchronousQueue 核心源码分析
前言 SynchronousQueue 是一个普通用户不怎么常用的队列,通常在创建无界线程池(Executors.newCachedThreadPool())的时候使用,也就是那个非常危险的线程池 ^ ...
- iOS 开源库系列 Aspects核心源码分析---面向切面编程之疯狂的 Aspects
Aspects的源码学习,我学到的有几下几点 Objective-C Runtime 理解OC的消息分发机制 KVO中的指针交换技术 Block 在内存中的数据结构 const 的修饰区别 block ...
- HashMap的结构以及核心源码分析
摘要 对于Java开发人员来说,能够熟练地掌握java的集合类是必须的,本节想要跟大家共同学习一下JDK1.8中HashMap的底层实现与源码分析.HashMap是开发中使用频率最高的用于映射(键值对 ...
- Java内存管理-掌握类加载器的核心源码和设计模式(六)
勿在流沙筑高台,出来混迟早要还的. 做一个积极的人 编码.改bug.提升自己 我有一个乐园,面向编程,春暖花开! 上一篇文章介绍了类加载器分类以及类加载器的双亲委派模型,让我们能够从整体上对类加载器有 ...
- 3 手写Java HashMap核心源码
手写Java HashMap核心源码 上一章手写LinkedList核心源码,本章我们来手写Java HashMap的核心源码. 我们来先了解一下HashMap的原理.HashMap 字面意思 has ...
- HTTP流量神器Goreplay核心源码详解
摘要:Goreplay 前称是 Gor,一个简单的 TCP/HTTP 流量录制及重放的工具,主要用 Go 语言编写. 本文分享自华为云社区<流量回放工具之 goreplay 核心源码分析> ...
- Netty 学习(六):创建 NioEventLoopGroup 的核心源码说明
Netty 学习(六):创建 NioEventLoopGroup 的核心源码说明 作者: Grey 原文地址: 博客园:Netty 学习(六):创建 NioEventLoopGroup 的核心源码说明 ...
- Backbone事件机制核心源码(仅包含Events、Model模块)
一.应用场景 为了改善酷版139邮箱的代码结构,引入backbone的事件机制,按照MVC的分层思想搭建酷版云邮局的代码框架.力求在保持酷版轻量级的基础上提高代码的可维护性. 二.遗留问题 1.b ...
随机推荐
- lambda表达式排序
lambda表达式排序简洁 1.给一个字符串数组: String[] atp = {"2016-06-28 08:00:00", "2017-12-05 19:17:32 ...
- Java Web总结(二)-- 上传和下载
在Web应用系统开发中,文件上传和下载功能是非常常用的功能,今天来讲一下JavaWeb中的文件上传和下载功能的实现. 对于文件上传,浏览器在上传的过程中是将文件以流的形式提交到服务器端的,如果直接 ...
- FreeSql (十六)分页查询
IFreeSql fsql = new FreeSql.FreeSqlBuilder() .UseConnectionString(FreeSql.DataType.MySql, "Data ...
- .Net基础篇_学习笔记_第六天_异常捕获复习及断点调试
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.T ...
- java使用FileSystem上传文件到hadoop文件系统
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URI; import org.ap ...
- JavaScript之数据类型转换
JavaScript中有多种数据类型,在实际工作中,不管是有意还是无意的,我们总能碰到不一样的数据类型值之间进行运算,或者我想从用户输入获得一个数字时,而用户却输入了一个字符串,这种时候就需要用到今天 ...
- Salesforce学习之路-admin篇(三)role hierarchy & sharing
1. Role Hierarchy 在私有或者混合模型中,如果在organization-wide defaults设置某个对象为Private,那么对象的记录只有拥有者可以查看.但是,role hi ...
- 从 HTTP/1 到 HTTP/2,以及即将到来的 HTTP/3
如今的生活中已经离不开互联网,智能家居.在线支付.网上购物都需要互联网的支持.互联网切切实实地给生活带来了诸多便利.有了互联网,我们可以呆在空调房里,一边刷着微博,一边等透心凉的西瓜送到手上,安安静静 ...
- 日志 logging 代码格式
日志logging 格式代码 import logging looger = logging.getLogger() #创建一个空架子 创建一个文件句柄,用来记录日志(文件流) fh = loggin ...
- java中的IO流和多线程
1.如何用file操作目录和文件? java对待目录和文件统一使用file来表示,在创建file对象时,使用isDictionary和isFile方法进行判断 package test; import ...