android界面布局
(一)LinearLayout界面编排模式
他的格式是按照线性顺序,由上往下或右左往右,逐一排列界面组件。
layout_width:中的“match_parent”表示要填满他所在的外框,而“wrap_content”表示它的大小只要满足内部所包含的界面组件即可。
android:orientation:“horizontal”表示排列方式为水平,而“vertical”表示排列方式为垂直
LinearLayout标签可以想象成一个外框,我们可以在其里面加入另外一个LinearLayout标签
我们将之前的婚姻建议程序改良一下,换成以下格式
第一层布局还是LinearLayout垂直布局,里面嵌套了一个LinearLayout水平布局,在该布局中包括性别TextView,和Spinner性别选择下拉框
再在第一层上嵌套一个LinearLayout水平布局,在该布局中包含年龄TextView和输入年龄框EditText
最后在第一层的布局上加入Button确定按钮和建议TextView
界面布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="@android:dimen/app_icon_size"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/sex"
android:textSize="25sp" />
<Spinner
android:id="@+id/spnSex"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:entries="@array/sex_list"
android:spinnerMode="dialog"
android:prompt="@string/spn_sex_list_prompt" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/age"
android:textSize="25sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edtAge"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:inputType="number"
android:hint="@string/edt_age_hint" />
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnOk"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="@string/btn_ok"
android:textSize="25sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtR"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="25sp" /> </LinearLayout>
页面截图:
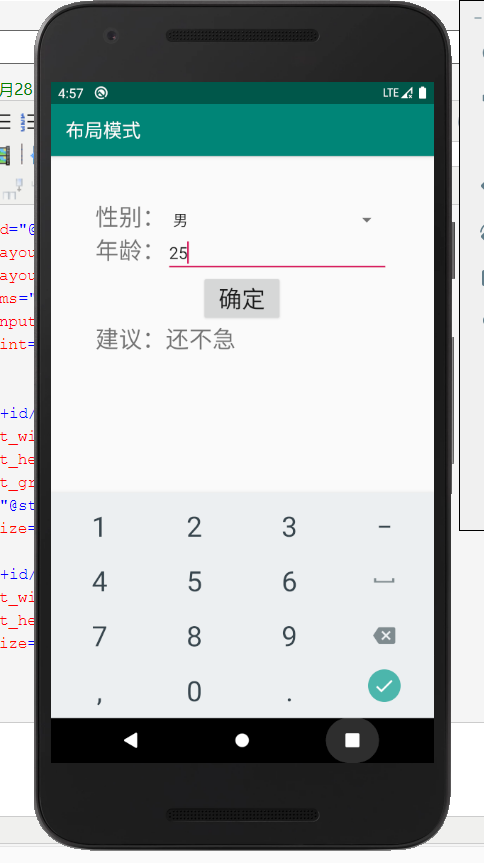
(二)TableLayout界面布局
顾名思义,tabel就是按照表格的形式来进行排列,也就是由上往下一行接着一行,而且每一个字段都上下对齐
每一行用标签用TableRow标签包裹起来,如果想让一个TableRow中的足见按照比例使用整个Table的宽度,可以借助android:layout_weight属性
例如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text="姓名:"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<TextView android:text="性别:"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<TextView android:text="生日:"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<EditText android:text="输入姓名"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<EditText android:text="输入性别"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<EditText android:text="输入生日"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</TableRow>
<Button android:text="确定"/>
</TableLayout>
程序截屏:
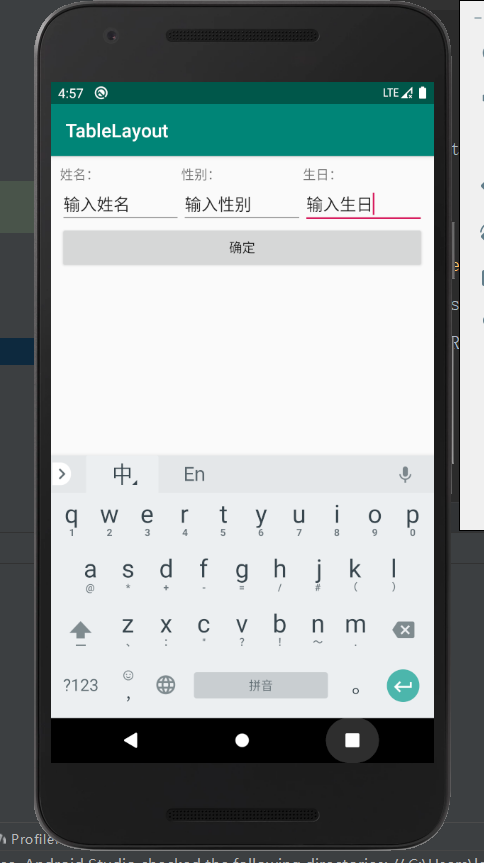
TableRow中的组件和上一个组件对齐,无法错开,就会形成如下图:
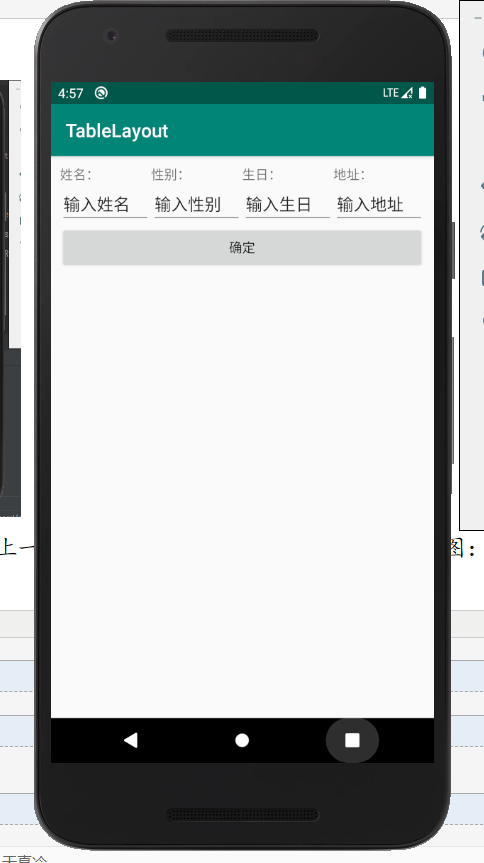
那么我们想要错开可以使用,在TableLayout标签中再增加一个TableLayout标签,这样就可以让不同行的字段错开
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TableLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text="姓名:"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<TextView android:text="性别:"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<TextView android:text="生日:"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<EditText android:text="输入姓名"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<EditText android:text="输入性别"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<EditText android:text="输入生日"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
<TableRow>
<TextView android:text="电话:" />
<TextView android:text="地址:" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<EditText android:text="请输入电话:"/>
<EditText android:text="请输入地址"/>
</TableRow>
<Button android:text="确定"/>
</TableLayout>
应用截图:
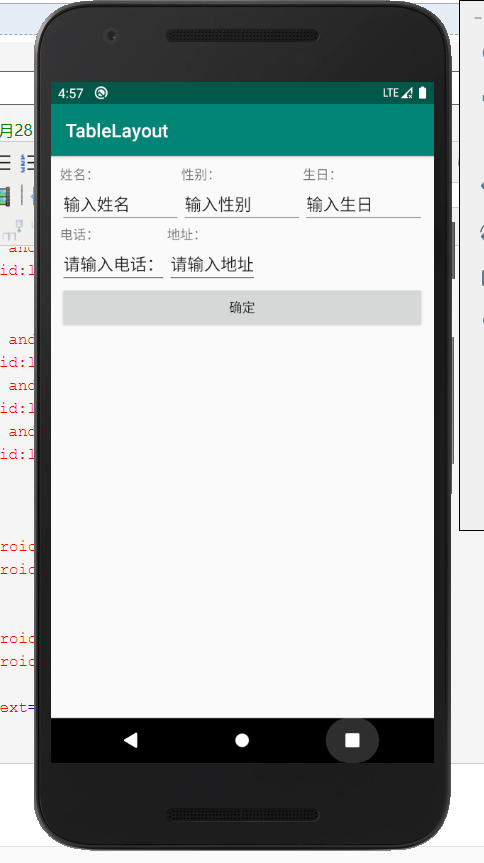
(三)RelativeLayout界面编排
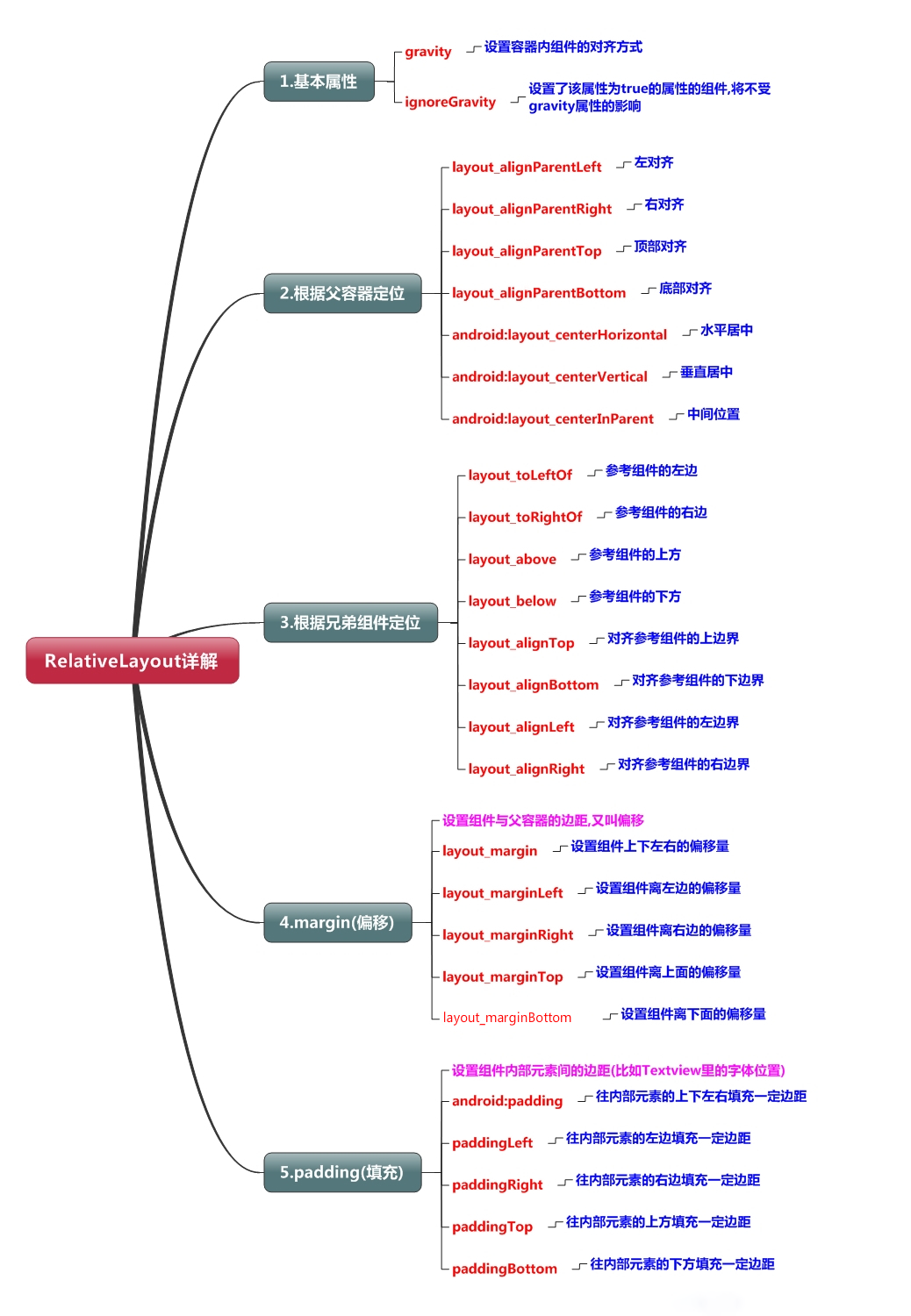
先做个小案例试试手:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/txt1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="txt1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="txt2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/txt1" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="edt1"
android:layout_below="@+id/txt1" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="edt2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/edt1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="btn1"
android:layout_below="@+id/edt1" />
</RelativeLayout>
程序截图:
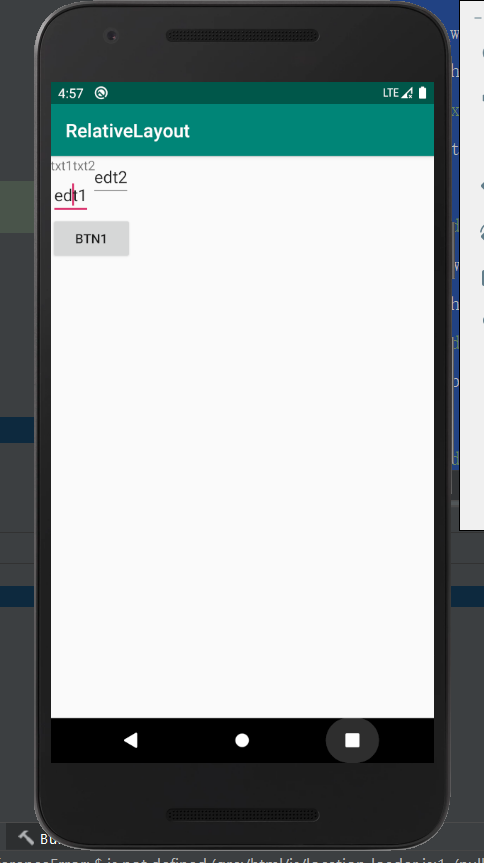
可以看到两个EditText出现一高一低,没有对齐。因此我们需要给edt2加上:android:layout_alighTop="@+id/edt1"
我们重新对其编排一下

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="400dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/txt1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="txt1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="txt2"
android:layout_above="@+id/edt2"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/edt2" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="edt1"
android:layout_below="@+id/txt1" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="edt2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/edt1"
android:layout_alignTop="@+id/edt1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="btn1"
android:layout_below="@+id/edt1" />
</RelativeLayout>
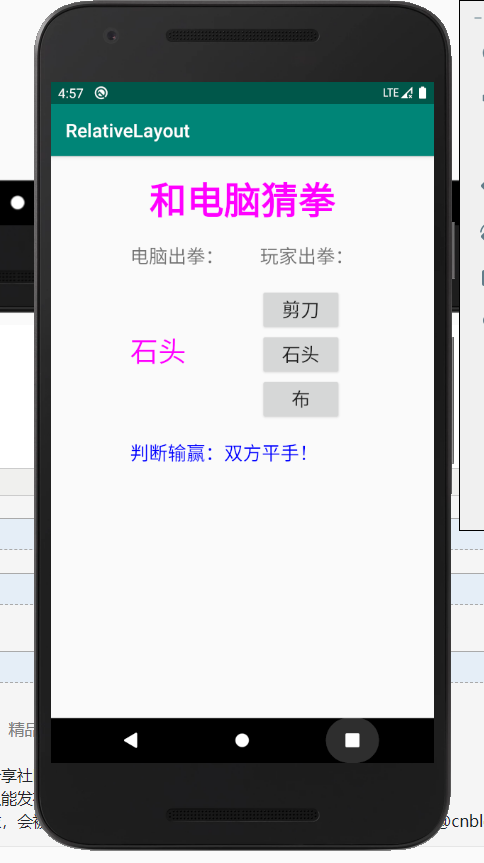
猜拳游戏:
界面布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="400dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/txtTitle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/prompt_title"
android:textColor="#FF00FF"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:paddingLeft="20dp"
android:paddingRight="20dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtCom"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/prompt_com_play"
android:layout_below="@+id/txtTitle"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txtTitle"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txtTitle" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtMyPlay"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/prompt_my_play"
android:layout_below="@id/txtTitle"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/txtTitle"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:layout_alignEnd="@id/txtTitle" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnScissors"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/play_scissors"
android:layout_below="@+id/txtMyPlay"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txtMyPlay"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:paddingLeft="15dp"
android:paddingRight="15dp"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txtMyPlay" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtComPlay"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/btnScissors"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txtCom"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:textColor="#FF00FF"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/txtCom" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnStone"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/play_stone"
android:layout_below="@id/btnScissors"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/btnScissors"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:paddingLeft="15dp"
android:paddingRight="15dp"
android:layout_alignStart="@id/btnScissors" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnPaper"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/play_paper"
android:layout_below="@id/btnStone"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/btnStone"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:paddingLeft="25dp"
android:paddingRight="25dp"
android:layout_alignStart="@id/btnStone" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtResult"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/result"
android:layout_below="@id/btnPaper"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/txtCom"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#0000FF"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_alignStart="@id/txtCom" /> </RelativeLayout>
字符串资源文件:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">RelativeLayout</string>
<string name="prompt_com_play">电脑出拳:</string>
<string name="prompt_my_play">玩家出拳:</string>
<string name="play_scissors">剪刀</string>
<string name="play_stone">石头</string>
<string name="play_paper">布</string>
<string name="player_win">恭喜,你赢了</string>
<string name="player_lose">很可惜,你输了</string>
<string name="player_draw">双方平手!</string>
<string name="prompt_title">和电脑猜拳</string>
<string name="result">判断输赢:</string>
</resources>
程序文件:
package com.example.relativelayout; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView; import org.w3c.dom.Text; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView mTxtComPlay,mTxtResult;
private Button mBtnScissors,mBtnStone,mBtnPaper;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mTxtComPlay=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txtComPlay);
mTxtResult=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txtResult);
mBtnScissors=(Button)findViewById(R.id.btnScissors);
mBtnPaper=(Button)findViewById(R.id.btnPaper);
mBtnStone=(Button)findViewById(R.id.btnStone); mBtnScissors.setOnClickListener(btnScissorsOnClick);
mBtnStone.setOnClickListener(btnStoneOnClick);
mBtnPaper.setOnClickListener(btnPaperOnClick);
} private Button.OnClickListener btnScissorsOnClick=new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int iComPlay=(int)(Math.random()*3+1);
//1.剪刀,2.石头,3.布
if(iComPlay==1)
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_scissors);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_draw));
}
else if(iComPlay==2)
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_stone);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_lose));
}
else
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_paper);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_win));
}
}
};
private Button.OnClickListener btnStoneOnClick=new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int iComPlay=(int)(Math.random()*3+1);
//1.剪刀,2.石头,3.布
if(iComPlay==1)
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_scissors);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_win));
}
else if(iComPlay==2)
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_stone);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_draw));
}
else
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_paper);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_lose));
}
}
};
private Button.OnClickListener btnPaperOnClick=new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int iComPlay=(int)(Math.random()*3+1);
//1.剪刀,2.石头,3.布
if(iComPlay==1)
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_scissors);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_lose));
}
else if(iComPlay==2)
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_stone);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_win));
}
else
{
mTxtComPlay.setText(R.string.play_paper);
mTxtResult.setText(getString(R.string.result)+getString(R.string.player_draw));
}
}
};
}
程序截图:
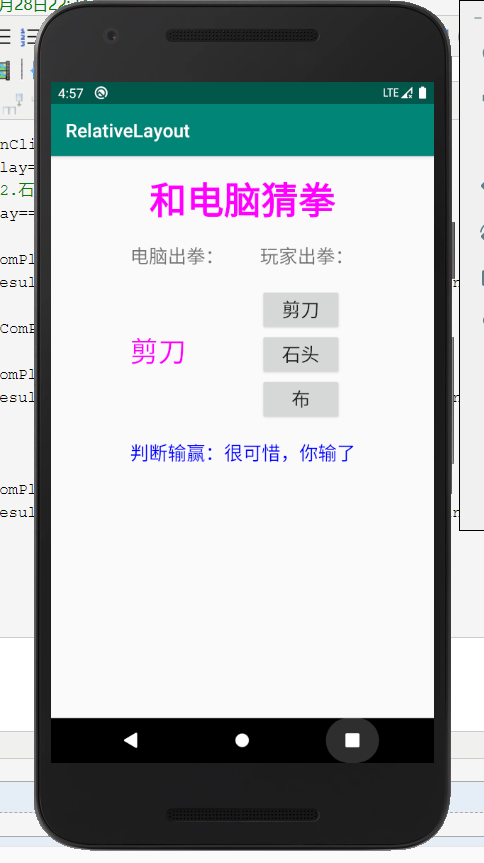
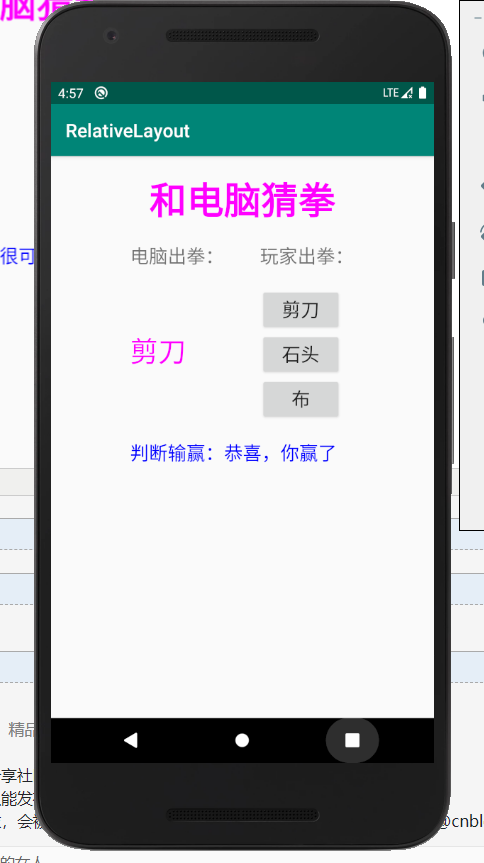
android界面布局的更多相关文章
- Android界面布局基本知识简述
Android手机操作系统在模拟器中进行相关的编写,可以帮助我们实现各种功能需求.尤其是在界面的操作方面显得更为突出.在这里我们就可以对Android界面布局的相关操作来对这方面的知识进行一个深入的了 ...
- iOS中xib与storyboard原理,与Android界面布局的异同
用文本标记语言来进行布局,用的最多的应该是HTML语言.HTML能够理解为有一组特殊标记的XML语言. 一.iOS中xib与storyboard显示原理 在iOS中基本的布置界面的方式有3种:代码.x ...
- Android界面布局学习总结
参考文章: http://blog.csdn.net/shakespeare001/article/details/7843460 http://www.cnblogs.com/w-y-f/p/412 ...
- 初识android界面布局
1.活动 活动是android开发中最基本的概念,也是最容易吸引用户的地方,是一种可以包含用户界面的组件. Activity类中定义了7个回调方法,覆盖了活动生命周期的每一个环节.具体如下: (1)o ...
- 解决Android界面布局添加EditText组件后界面无法预览
错误报告: Exception raised during rendering: java.lang.System.arraycopy([CI[CII)V Exception details are ...
- Android界面布局基本属性
在 android 中我们常用的布局方式有这么几种:1.LinearLayout ( 线性布局 ) :(里面只可以有一个控件,并且不能设计这个控件的位置,控件会放到左上角) ...
- 【android学习3】解决Android界面布局添加EditView之后无法预览问题
在设计登陆界面时,拖入一个EditView之后发现界面无法预览 问题分析: 进入xml源文件里发现一个警告,提示添加inputType或者hint元素,添加后界面仍然无法预览... 仔细查看了当前使用 ...
- android 界面布局 很好的一篇总结[转]
1.LinearLayout ( 线性布局 ) :(里面只可以有一个控件,并且不能设计这个控件的位置,控件会放到左上角) 线性布局分为水平线性和垂直线性二者的属性分别为:android:orienta ...
- android 界面布局
一.LinearLayout LinearLayout 又称作线性布局,是一种非常常用的布局,它所包含的控件在线性方向上依次排列. android:orientation="horizont ...
随机推荐
- CentOS 7 1810版本不能使用yum 命令
使用yum install httpd 命令安装Apache 提示错误 annot find a valid baseurl for repobase7x86_64 解决方法: 进入 ls命令寻找类似 ...
- 每天进步一点点------Allegro 建立封装的一般步骤
在制作封装之前,先确定你需要的焊盘,如果库中没有,那就要自己画了,(我就是自己画的) 制作二极管1N5822 SMD,实际尺寸:480milX520mil 一.添加元件焊盘 1 启动Allegro P ...
- 【做题笔记】UVA11988破损的键盘
本题可以在洛谷评测,但需要绑定账号 首先解释一下:Home键的作用是把光标移动,End键的作用是返回上次按Home键的地方 考虑朴素做法:输入为[时下一次插入在数组最前端,然后元素整体向后:同时令 l ...
- 解决Cannot download "https://github.com/sass/node-sass/releases/download/binding.nod的问题
npm i node-sass --sass_binary_site=https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node-sass/
- Django - DRF自带的token认证和JWT区别
问题重现 当查看DRF 文档时发现DRF内置的token是存储在数据库里,这和我在网上搜索资料时认识的token-based authentication有出入. from rest_framewor ...
- Java入门学习路线目录索引
原创 Java入门学习路线目录索引 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明. 本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/One_ ...
- 概率dp light 1321
题意:给定一张无向图,每条边都有一个通过的概率 ,如果无法通过,那么就要回到起点重新出发从起点到终点的时间固定为K,如果成功到达,又需要额外花费K的时间,问走S次的最小期望时间 思路:这道题分为两部分 ...
- 【音乐欣赏】《Siren》 - The Chainsmokers / Aazar
曲名:Siren 作者:The Chainsmokers . Aazar [00:00.00] 作曲 : Alex Pall/Andrew Taggart/Alexis Duvivier [00:01 ...
- 【Python redis】
目录 基本用法 连接池 基本命令 String Hash List set "下载:pip install redis @ *** 基本用法 redis库提供两个类,Redis和Strict ...
- console.log 如何打印对象
问题描述: var obj={a:1,b:2}; console.log(obj); 控制台返回的值是object. 解决方案: console.log(JSON.stringify(obj))
