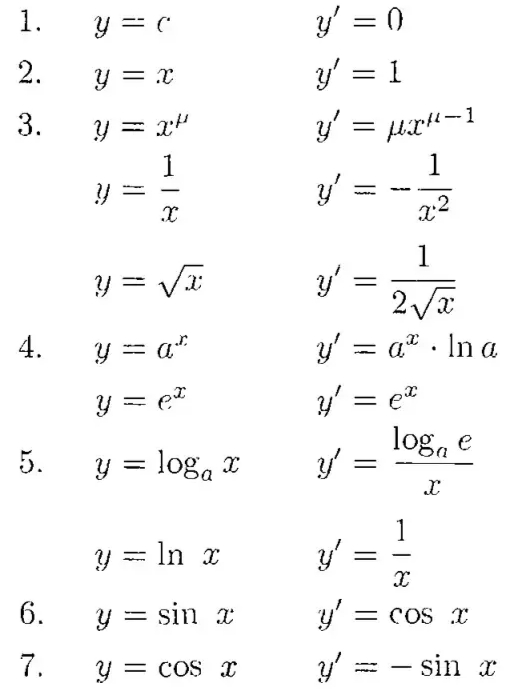SciTech-Mathmatics-Analysis-Calculus: Difference+Derivative+Integral+Limit:极限(变化测度与量化,高阶)+Series无穷级数+Field:Closure+Theories{RealTheory:Continuity+Measure:Metric+Set(Countability,Set Vs. Element-Wise)}
SciTech-Mathmatics-Analysis
Mathematical Thinking
数学思维:集合论,数和数域,运算符号,函数关系,数形结合;
导数、微分、积分的奥秘就在(例如变形:同一公式换一种形式表达, 就是另一种用途):
- 微分升幂:将"静态/结果"的 "点值"/"线段"和"维度函数(定义域:整个数轴+零点偏移)" 变换为 "动态/过程" 的 "无穷级数".
- 求导降幂:将 "动态/过程" 的 "点值"/"线段"和"维度函数(定义域:整个数轴+零点偏移)" 分解出 静态/结果 的规律.
\(\large f'(x) = dy / dx\)
\(\large dy = f'(x) dx\)
the Definite Difference:
\(\large \begin{array}{rll} \int_{a}^{b}{f'(x) dx} =& \underset{n \rightarrow \infty}{\lim} \overset{ n }{\underset{k=1}{\sum}} { \Delta{f(x_k)} } & \leftarrow \ 微分划分形 \\
=& \underset{n \rightarrow \infty}{\lim} \overset{n}{\underset{k=1}{\sum}} { ( f'(x_k) \cdot \Delta{x_k} ) } & \leftarrow \ Riemman's\ Sum\ Form \\
=& f(b) - f(a) & \leftarrow \ 积分化差形 \\
\end{array}\)the Indefinite Integral:
\(\large \begin{array}{rll} \\
\int{f'(x) dx} &= f(x) + C & \ f'(x)dx 整体是被积表达式;\ f'(x)只是被积函数. & \\
Definite &\rightarrow Indefinite & [a,b]扩展到[-\infty, +\infty]; 积分值由f(b) - f(a), 变换为 f(x) + C(不定常数). & \\
\end{array}\)导数与微分:
\(\large f'(x) = dy / dx\) 即 \(\large dy = f'(x) dx\)升幂:
将“点值”、“线段”和“整个数轴+零点偏移”用“无穷级数”形式表示。- \(\large dN= 0 dx\), \(\large y = X,\ X \in R\)
常数函数的 导函数的值总是0 - \(\large dx = 1 dx\), \(\large y = kx + b,\ k \in R, \ b \in R\)
线性函数 的导函数的值为常数 \(\large k\)
更特别是\(\large y = x\)的导数值为1 - \(\large d{x^n} = n x^{n- 1}dx\)
幂函数每乘一次\(\large dx\) 可以升幂指数一级
- \(\large dN= 0 dx\), \(\large y = X,\ X \in R\)
\(\large d{e^x} = e^x dx\), $\large d{n^x} = d{e^{x ln{n}}} = e^{x ln{n}} d({x ln{n}}) = n^x\ ln{n}\ dx $
自然数 指数函数 的导函数值为其本身, 自然数 指数函数\(\large d({ln {x}}) = \frac{1}{x} dx\),
自然数 对数函数 的导函数为\(\large \frac{1}{x}\), 自然数为底数的 对数函数。常用函数,及其导函数表
![]()
Calculus: 微积分
变化: relation, measurement度量,规律:
数学分析:“无穷无尽”是研究对象,“极限”是“研究方法”;
用 "n项数列(n是可变项数)" 和 "无穷级数", 在"确定项数" 与 "无穷或不确定的项数"之间,
用"极限"建立"量变与质变"的"函数关系"。Difference微分 与 Derivative导数:
measurement, 极限, approximationDerivative导数 与 Integral积分 互为逆运算:
- 由“导数”求“原函数” ;
- 由“原函数”求“导数”;
多重微分 Vs. 积分角度:
多重微分 是 将 一维的函数值域(常为R)分解到 "确定的多维度自变量域"上的 "函数(关系与测度)表示"
多重积分 是 用 "多维度的自变量域"的 "函数(关系与测度)表示" 合成一维的函数值域(常为R).
Derivative导数
\(\large \begin{array}{rl} \\
f'(x) &= \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim}{ \frac{\Delta{y}}{\Delta{x}} } \\
&= \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim}{ \frac{ f(x + \Delta{x}) - f(x) }{\Delta{x}} } \\
&= \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim}{( f'(x)+ O(\Delta{x}) )} \\
&= f'(x) \\
\end{array}\)
常用函数及其导函数:
\(\large \begin{array}{rl} \\
f(x)=x^n, & f'(x) = n x^{n-1} \\
f(x)=e^x, & f'(x) = e^x \\
f(x)=ln{x}, & f'(x) = \frac{1}{x} \\
f(x)=\sin{x}, & f'(x) = \cos{x} \\
f(x)=\cos{x}, & f'(x) = - \sin{x} \\
\end{array}\)
Difference微分:
- 一重微分
\(\large \begin{array}{rl} \\
\Delta{y} &= \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim}{ f(x + \Delta{x}) - f(x) } \\
&= \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim}{ f'(x) \cdot \Delta{x} + O(\Delta{x}) } \\
&= \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim}{ f'(x) \cdot \Delta{x} } \\
\end{array}\) - N重微分
多重微分 是 将 一维的函数值域(常为R)分解到 "确定的正交多维度自变量域"上的 "函数(关系与测度)表示";
例如求不规则体的体积:是微分到(x, y, z)三个纬度上;
Integral积分
一重积分:
Riemman Integral 定积分:
\(\large \begin{array}{rl} \\
\int_{a}^{b}{f'(x) dx} =& f(b) - f(a) \\
=& \underset{n \rightarrow \infty}{\lim} \overset{ n }{\underset{k=1}{\sum}} { ( f'(x_k) \cdot \Delta{x_k} ) }, 黎曼和形式\\
=& \underset{n \rightarrow \infty}{\lim} \overset{ n }{\underset{k=1}{\sum}} { \Delta{f(x_k)} } \\
=& \underset{n \rightarrow \infty}{\lim} \overset{ n }{\underset{k=1}{\sum}} {( f(x_{k}) - f(x_{(k-1)}) )} \\
=& \underset{n \rightarrow \infty}{\lim} ( f(x_{1}) - f(a) + f(x_{2}) - f(x_{1}) + \cdots + f(b) - f(x_{n-1}) ) \\
where: & \\
k \in & [1, n] \\
\end{array}\)不定积分:
\(\large \begin{array}{rl} \\
\int{f'(x) dx} =& f(x) + C \\
where: & \\
C :& 是一积分常数; \\
\int :& 积分号; \\
x :& 积分变量; \\
f'(x) :& 被积函数; \\
f'(x)dx :& 被积表达式; \\
\end{array}\)
多重积分:
多重积分 是 用 "正交多维度的自变量域"上的 "函数(关系与测度)表示" 合成一维的函数值域(常为R)。
Limit:极限(变化的测度与量化,高阶 )
数学分析: 变化与无穷 是 研究对象, 函数与极限 是“研究方法”
用 "n项数列(n是可变项数)" 和 "无穷级数", 在"确定项数" 与 "无穷或不确定的项数"之间,
用"极限"建立"量变与质变"的"函数关系"。
例如: \(\large f'(x) = \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim}{ \frac{\Delta{y}}{\Delta{x}} } = \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim}{ \frac{ f(x + \Delta{x}) - f(x) }{\Delta{x}} }\)- 在 \(\large \Delta{x}\rightarrow 0\)时,$\large \Delta{y} $ 与 $\large \Delta{x} $ 都是变化量;
- 变化的“快慢”是Relatively Measurable, and can be Quantified by Derivatives, High-order Derivatives and High-order Differences.
导数值就是value of relatively mesurement , 规律性。
导函数则是,总体的“变化快慢”的度量函数;高阶无穷小: $\large \underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow 0}{\lim} { O(\Delta{x}) } = 0 $
- 高阶无穷小 在“自变量取极限时”为0,规律性。
- "0(是在Real line上任取一点设置为0)",
- "无穷小\(\large \epsilon\)"的度量, 函数关系\(\large \delta\), 运算法则(线性) 以及 极限;
- 类似,无穷小的倒数则是 $\large \infty $
- 无穷小 的运算规律。
- 高阶无穷小 在“自变量取极限时”为0,规律性。
Series数列/无穷级数:
- 数, a point in real line, can be represented as an infinity series.
- 数列, 等差,等比,求和公式;
- 无穷级数;
- Cauchy Series
Field:数域(Closure),
- Rational Number,
- 稠密性:任两个不同Rationals之间有无尽的Rationals
例如 c = (a+b)/2; - 阿基米德性
- 稠密性:任两个不同Rationals之间有无尽的Rationals
- Real Number:
- FOC(field, order, continuity) Axioms
- Continuity(Completeness)
- Complex Number,
- \(\large i = \sqrt{-1}\),
- 迪莫佛定理: $\large e^{i\alpha} \cdot e^ {i\beta} = e ^{i(\alpha+\beta)} $,
- Euler's Equation: \(\large e^{i\theta} = \cos{\theta} + i \cdot \sin{\theta},\ \theta \in \bm{C}\),
\(\large let\ \theta = \pi,\ then\ e^{i\pi} + 1 = 0\), - Taylor equation in Complex Field.
- Rational Number,
Number Theory数论:
- Primes:
\(\large Euler's\ proof\) for "\(\large \text{ There are infinite number of Primes. }\)":
\(\large (P_1 \cdot P_2 \cdot \cdots \cdot P_n + 1) \ is\ a\ prime, if\ P_i \ are\ continued\ primes\ serie\ from\ 1, \ i \in [1,\ n]\) - Factorization(因式分解):
$\large \forall\ i \in N, \exists\ unique\ representation\ i = P_1^{n_1} \cdot P_2^{n_2} \cdot P_k^{n_k} $ - Functions: 121 mapping, bijection;
- Primes:
RealNumberTheory:实数理论
- 连续Continuity/完备Completeness:
- Dedkind Split: 不空、不漏、不乱
- 闭区间套
- fractions(小数论):
- Rational fractions: 最小数域;
- Irrational fractions: 无理数, 无限不循环小数;\(\large \pi,\ e,\ \sqrt{2}\)
- 连续Continuity/完备Completeness:
Probability Theory概率论
ProbabilityMeasureTheory测度论
Triangle Equation
MetricSetTheory集合论(Countable/Uncountable, 可列可加)
- Set Vs. Element:
- Set/Collection is collective object, or a "line, circle, square, rectangle"
- Element is considered as individual object. or a "point";
- Operations:
- Set-wise operations is cooresponding to and driving by Element-wise operations.
- Set Vs. Element:
SciTech-Mathmatics-Analysis-Calculus: Difference+Derivative+Integral+Limit:极限(变化测度与量化,高阶)+Series无穷级数+Field:Closure+Theories{RealTheory:Continuity+Measure:Metric+Set(Countability,Set Vs. Element-Wise)}的更多相关文章
- A. Difference Row
A. Difference Row time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- dedeCMS中单独调用子栏目模板和子栏目的文章时修改源代码给channel和chanenartllist加上limit
在网站文件中找到include-taglib-chanel.lib.php,和chaneartllist.lib.php 下载用php的IDE打开, chanel.php加入limit属性修改如下 & ...
- 《python for data analysis》第五章,pandas的基本使用
<利用python进行数据分析>一书的第五章源码与读书笔记 直接上代码 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# <python for data analysis>第五 ...
- PCA(Principal Component Analysis)主成分分析
PCA的数学原理(非常值得阅读)!!!! PCA(Principal Component Analysis)是一种常用的数据分析方法.PCA通过线性变换将原始数据变换为一组各维度线性无关的表示,可 ...
- Stat2—主成分分析(Principal components analysis)
最近在猛撸<R in nutshell>这本课,统计部分涉及的第一个分析数据的方法便是PCA!因此,今天打算好好梳理一下,涉及主城分析法的理论以及R实现!come on…gogogo… 首 ...
- amortized analysis
w https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amortized_analysis In computer science, amortized analysis is a meth ...
- 独立成分分析(Independent Component Analysis)
ICA是一种用于在统计数据中寻找隐藏的因素或者成分的方法.ICA是一种广泛用于盲缘分离的(BBS)方法,用于揭示随机变量或者信号中隐藏的信息.ICA被用于从混合信号中提取独立的信号信息.ICA在20世 ...
- 学习笔记之Machine Learning Crash Course | Google Developers
Machine Learning Crash Course | Google Developers https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/c ...
- 斯坦福CS课程列表
http://exploredegrees.stanford.edu/coursedescriptions/cs/ CS 101. Introduction to Computing Principl ...
- [C4] Andrew Ng - Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization
About this Course This course will teach you the "magic" of getting deep learning to work ...
随机推荐
- GitLab——重置(reset)和还原(revert)
Git 命令 reset 和 revert 的区别 - 知乎 (zhihu.com) 总结: git reset --hard 9201d9b19dbf5b4ceaf90f92fd4e4019b685 ...
- ModelForm验证实例
程序目录 models.py from django.db import models# Create your models here.class UserType(models.Model): ...
- 5 easybr指纹浏览器内存修改教程
目的 navigator.deviceMemory可以暴露设备的物理内存和运行状态,被用于设备唯一性识别或判断设备等级. 通过伪造这类信息,可以增强防关联.防追踪能力. easybr指纹浏览器提供演示 ...
- Friend Circles(dfs)——LeetCode进阶路
原题链接https://leetcode.com/problems/friend-circles/ 题目描述 There are N students in a class. Some of them ...
- SpringBoot启动类没有启动按钮,java文件变为灰色的解决策略
今天在查看Spring Boot项目的时候发现自己的项目变成了上面这个样子,无法执行main函数. 解决方法(上述操作可以忽略):选择我们项目的pom文件,然后右键选择 Add as Maven ...
- Web前端入门第 61 问:JavaScript 各种对象定义与对象取值方法
曾经有人说 JS 语言中万物皆对象,虽然这种说法不一定完全准确,但也有一定的道理.原因是 JS 的语法看起来所有的数据类型都像是一个对象,包括原始类型. const a = 1.234; consol ...
- 邮件收件、读取邮件API-批量导入-支持代理-开放HTTP接口
简介 大恩邮箱收件平台,支持读取收件箱.垃圾箱的邮件.支持批量导入各大邮箱平台的账号(例如微软.谷歌.网易.QQ等),采用pop3.imap协议收件,支持配置代理IP.验证码截取规则等,同时提供了HT ...
- MyAuthWeb TianYe版预览
- FFmpeg开发笔记(六十四)使用国产的RedPlayer播放器观看网络视频
RedPlayer是小红书基于FFmpeg4.3研发并开源的国产播放器,它可运行于Android和iOS系统,既支持播放本地视频文件,也支持播放网络上的流媒体链接.有关FFmpeg在Android平 ...
- (各种数组之间的互相转换)int 数组与List互相转换,object数组转换int数组
Stream流之List.Integer[].int[]相互转化 一.int[ ] 1.1.int[ ] 转 Integer[ ] public static void main(String[] a ...