ServletContext相关
简介
每个web工程都只有一个ServletContext对象。 说白了也就是不管在哪个servlet里面,获取到的这个类的对象都是同一个。
如何得到对象
//1. 获取对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();有什么作用
- 获取全局配置参数
- 获取web工程中的资源
- 存取数据,servlet间共享数据 域对象
1、获取全局配置参数
web.xml中设置参数
<context-param>
<param-name>name</param-name>
<param-value>朱俊伟</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>创建Servlet并配置Servlet并读取相应的参数
package com.zhujunwei.servletContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
*
* @author Administrator
* 创建ServletContext读取全局变量的值
*
*/
public class ServletContext01 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//读取全局变量的值
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
String name = context.getInitParameter("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}运行结果
朱俊伟2、获取web工程中的资源
如果在项目中存在配置文件想要读取(如config.properties),可采用如下三种方法:
config.properties文件所在目录
-WebContent
-file
-config.properties
-META-INF
-WEB-INFconfig.properties文件内容
name=zhujunwei读取的三种方法
package com.zhujunwei.servletContext;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
*
* @author Administrator
* 读取工程文件的三种方法
*
*/
public class ServletContext02 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
getProperty1();
getProperty2();
getProperty3();
}
/**
* 方法3:通过类加载器读取工程中的文件
* @throws IOException
*/
private void getProperty3() throws IOException {
// 1、创建属性对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2、指定载入的数据源
InputStream inStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("../../file/config.properties");
properties.load(inStream);
// 3、获取name属性的值
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
System.out.println("getProperty3():name=" + name);
}
/**
* 方法2:通过ServletContext中的getResourceAsStream方法读取文件
* @throws IOException
*/
private void getProperty2() throws IOException {
// 获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
// 1、创建属性对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2、指定载入的数据源
InputStream inStream = context.getResourceAsStream("file/config.properties");
properties.load(inStream);
// 3、获取name属性的值
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
System.out.println("getProperty2():name=" + name);
}
/**
* 方法1:通过ServletContext中的getRealPath方法读取文件
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws IOException
*/
private void getProperty1() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
// 获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
// 获取给定的文件在服务器上面的绝对路径
String path = context.getRealPath("file/config.properties");
// 1、创建属性对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 2、指定载入的数据源
InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(path);
properties.load(inStream);
// 3、获取name属性的值
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
System.out.println("getProperty1():name=" + name);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
配置Servlet,执行得到结果
getProperty1():name=zhujunwei
getProperty2():name=zhujunwei
getProperty3():name=zhujunwei3、存取数据,servlet间共享数据 域对象
思路分析
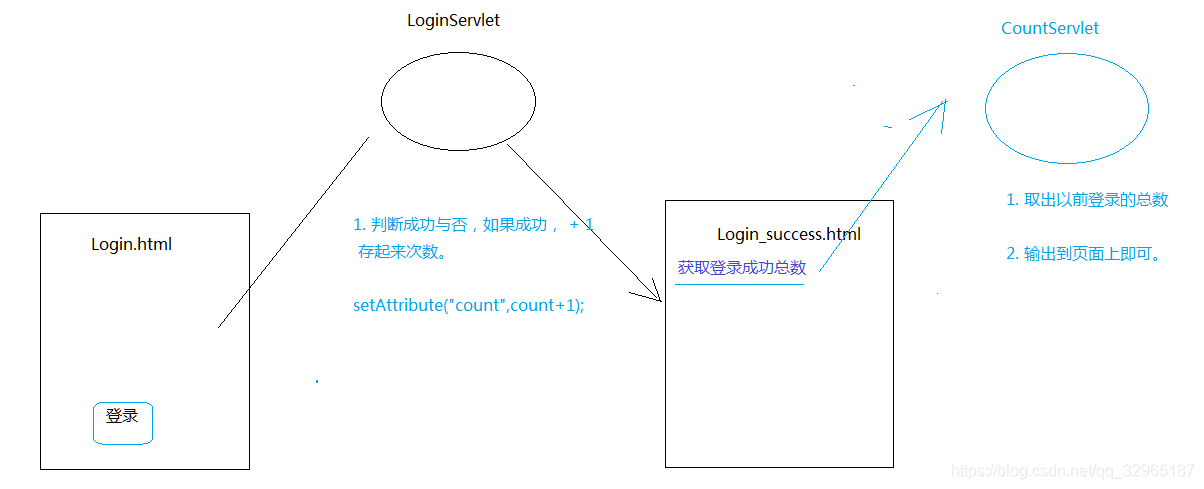
Login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>请输入账号密码登录</h2>
<form action="LoginServlet" method="get">
账号:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="text" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>LoginServlet
package com.zhujunwei.servletContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* 从客户端取得用户输入的账号和密码,经过校验后跳转到指定的页面
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取客户端输入的值
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
//对值进行校验并返回客户端
if("admin".equals(username)&&"123456".equals(password))
{
//1、成功次数的累加
//获取以前存的值,然后在旧的值基础上+1
Object obj = getServletContext().getAttribute("count");
//默认就是0次
int totalCount = 0;
if(obj!=null)
{
totalCount = (int) obj;
}
//给count赋新的值
getServletContext().setAttribute("count", totalCount+1);
//2、跳转到login_success.html
//设置状态码 :重新定位状态码
response.setStatus(302);
//定位跳转的位置是哪一个页面
response.setHeader("Location", "login_success.html");
}
else
{
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.write("login filed...");
}
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
login_success.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>登录成功</h2>
<a href="ServletContext04">查看网页登录成功的次数。</a>
</body>
</html>CountServlet
package com.zhujunwei.servletContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class CountServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//取值
int count = (int) getServletContext().getAttribute("count");
//输出到界面
response.getWriter().write("Login Success Count:"+count);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
运行结果



ServlerContext的生命周期
服务器启动的时候,会为托管的每一个web应用程序,创建一个ServletContext对象
从服务器移除托管,或者是关闭服务器。
ServletContext 的作用范围
只要在这个项目里面,都可以取。 只要同一个项目。 A项目存,在B项目取,是取不到的,因为ServletContext对象不同。
ServletContext相关的更多相关文章
- 与ServletContext相关的监听器
概述 与ServletContext相关的监听器有ServletContextListener与ServletContextAttributeListener. ServletContextListe ...
- 【Servlet】1、Servlet监听器及相关接口
Servlet监听器用于监听一些重要事件的发生,监听器对象可以在事情发生前.发生后可以做一些必要的处理. 接口: 目前Servlet2.4和JSP2.0总共有8个监听器接口和6个Event类,其中Ht ...
- Spring 的优秀工具类盘点
文件资源操作 文件资源的操作是应用程序中常见的功能,如当上传一个文件后将其保存在特定目录下,从指定地址加载一个配置文件等等.我们一般使用 JDK 的 I/O 处理类完成这些操作,但对于一般的应用程序来 ...
- 2015第30周三Spring常用工具类
文件资源操作 文件资源的操作是应用程序中常见的功能,如当上传一个文件后将其保存在特定目录下,从指定地址加载一个配置文件等等.我们一般使用 JDK 的 I/O 处理类完成这些操作,但对于一般的应用程序来 ...
- Spring 的优秀工具类盘点第 1 部分
文件资源操作 文件资源的操作是应用程序中常见的功能,如当上传一个文件后将其保存在特定目录下,从指定地址加载一个配置文件等等.我们一般使用 JDK 的 I/O 处理类完成这些操作,但对于一般的应用程序来 ...
- web.xml中的主要元素说明(listener, filter, servlet)
web.xml中加载的顺序为:context-param ---> listener ---> filter ---> servlet. listener:主要针对的是对象的操作,如 ...
- web.xml中listener作用及使用
一.WebContextLoaderListener 监听类 它能捕捉到server的启动和停止,在启动和停止触发里面的方法做对应的操作! 它必须在web.xml 中配置才干使用,是配置监听类的 二. ...
- web.xml在listener作用与用途
一.WebContextLoaderListener 监听类 它能捕捉到server的启动和停止,在启动和停止触发里面的方法做对应的操作! 它必须在web.xml 中配置才干使用,是配置监听类的 二. ...
- Servlet 应用程序事件、监听器
Web容器管理Servlet/JSP相关的生命周期,若对HttpServletRequest对象.HttpSession对象.ServletContxt对象在生成.销毁或相关属性设置发生的时机点有兴趣 ...
- SSM框架注解整合
一.web应用环境 1.ServletContext 对于一个web应用,其部署在web容器(比如:tomcat)中,web容器提供其一个全局的上下文环境,这个上下文就是ServletContext, ...
随机推荐
- 闲话 717 - LGV 引理的小应用
这是我们的某一天的联考题目: \(n\le 500\). 显然使用平面图完美匹配计数可以获得 \(O(n^6)\),但是有一种神秘的对路径的双射.当时我们都认为这是超级人类智慧,但是今天看书发现是书上 ...
- P6108 [Ynoi2009] rprsvq 积分题解
给 EI 题解写注 qwq.. 化简方差: \[\frac{1}{n}\sum(a_i-\overline a)^2\\ =\frac{1}{n}(\sum a_i^2-2\overline {a}\ ...
- 记一次CUDA报错
报错内容:CUDA error: device-side assert triggered 原因:使用ResNet50训练时使用了pretrained=True的模型,但实际类别数classes远超过 ...
- 手把手教你在个人电脑部署本地知识库(基于RAGFlow + DeepSeek [+ Ollama])
1. 实现方案及准备工作 按照教程一步一步操作,基本没有什么太大难度,稍显麻烦的可能就是因网络问题有些资源无法下载,对于镜像无法下载的问题,文中也提供了替代的方法,但是github访问不稳定这点 ...
- AI探索:通过宏脚本给小众编辑器EverEdit插上AI的翅膀!
1 AI探索:通过宏脚本给小众编辑器EverEdit插上AI的翅膀! 1.1 背景 在AI编程大行其道的背景下,各种AI编程工具:Cursor.VSCode的各种插件.Trae等等搞得不亦乐乎!您 ...
- Python 脚本编写指南:从框架到实践
一.引言 Python 作为一种强大且易于学习的编程语言,在各个领域都有着广泛的应用.编写 Python 脚本是实现各种功能和任务的常见方式. 二.Python 脚本框架的基本组成部分 导入必要的模块 ...
- ssh: connect to host github.com port 22: Connection timed out----git问题记录
今天使用git命令提交代码,git add .,git commit -m '',git push 一顿操作猛如虎啊,嘴角一勾,邪魅一笑像往常一样期待着等着进度条100%,然后直接出现ssh: con ...
- docker push image harbor http 镜像
前言 搭建的 harbor 仓库为 http 协议,在本地登录后,推送镜像发生如下报错: docker push 192.168.xx.xx/test/grafana:v10.1.1 The push ...
- Sa-Token v1.41.0 发布 🚀,来看看有没有令你心动的功能!
Sa-Token 是一个轻量级 Java 权限认证框架,主要解决:登录认证.权限认证.单点登录.OAuth2.0.微服务网关鉴权 等一系列权限相关问题. 目前最新版本 v1.41.0 已推送至 Mav ...
- BUUCTF---basic RSA
题目 给出一个RSA加密的密文,阐述了RSA,主要就是代码实现解密 代码 点击查看代码 import gmpy2 from Crypto.Util.number import * from binas ...
