codeforces:818G Four Melodies分析
题目
题目大意是有一组自然数v1,...,vn,要求在其中找到四个非空子序列(从原来的自然数序列中挑选一部分数,并按原先后关系排序),这些子序列互不相交,且每个子序列中的前后元素的值要么差值的绝对值为1,要么对7取余的值相同。
输入自然数序列的长度n满足4<=n<=3000,而每个输入的自然数均不超过1e5。
求解所有满足以上条件的这样四个子序列的长度的总和的最大可能值。
预处理
这道题有点难度,考察的知识范围很大。我个人也是参考了codeforces上的tutorial。要解决这个问题必须掌握最短路径和网络流等多方面的基础知识,这些内容不会在本文中被一一讲解,需要读者自己去查阅。
先说明如何用已有的知识体系来解决。这个问题如果我们将每个序列中的自然数比作一个网络结点,而从这个结点向所有可以在同一子序列中作为后续数值的序列元素对应的结点蔓延出一条有向边,而这些有向边的费用均为-1,容量为1。这样求解4条子序列,就类似于求解从源点到汇点输送4单位流所花费最小费用,即最小费用网络流问题。当然这里没有限定每个结点只能被通过一次,可以将原来一个结点ak,拆分为ak.in和ak.out两个结点,其中原来所有以抵达ak的有向边(容量为无限)都转由抵达ak.in(入点),而从ak出发的有向边(容量为无限)则转由ak.out(出点)出发。而由一条从ak.in到ak.out的有向边(ak.in,ak.out)连接两个结点,且容量为1,费用为0。这样就能确保只有一单位的流能通过ak结点,对应与原问题中子序列互不相交的性质。这样我们就构建了一个网络N(A,E),其中A为2*n个顶点的集合,而E为创建的边,其数量不会超过|A|^2=O(n^2)。
但是最小费用最大流问题中拥有多项式时间复杂度的算法都拥很高的时间复杂度,比如minimun-mean-cycle-canceling算法,其时间复杂度更是有O(|A|^2*|E|^3)的时间复杂度,当E的数目最大时,取值O(n^2),则时间复杂度可以达到O(|A|^8)。What the fuck!当取n=3000时,需要执行将近6561000000000000000000000000*k次运算,其中k是一个有上界的数值,妥妥的有生之年系列。
为了避免上面这么尴尬的问题,我们需要继续深入理解条件。可以发现若j可以作为数值i的邻接后续元素,则必然满足i%7=j%7或者i=j-1或者i=j+1,且注意到i%7=j%7=k%7,则k也可以作为i的邻接后续元素,同样i+1=j=k或i-1=j=k,则k也可以作为作为i的邻接后续元素,即邻接后续关系实际上是一种传递关系。因此我们可以通过只连接结点at与后续第一个满足vi%7=vt%7的结点ai,以及连接结点at与后续第一个满足vj=vt+1的结点aj,以及连接结点at与后续第一个满足vk=vt-1的结点ak,这样借助与关系的传递性,我们就可以将一条包含多个中间结点的路径视为从开端到结尾结点的简单有向边。首先我们将结点at切分为四个子结点:m7,equal和occupy-in,occupy-out。其中m7子结点负责接受所有模7值,且允许以0费用转发给任意其它具有相同模7值的其它结点(序号高于t)的m7子结点;equal子结点允许以0费用转发给任意其它具有相同值的其它结点(序号高于t)的equal子结点。而occupy-in和occupy-out负责标志结点被占领,通过一条费用为-1的边(occupy-in,occupy-out)。而occupy-out连接下一个拥有相同模7值的结点的m7子结点,以及下一个值为vt-1的结点的equal子结点,以及下一个值为vt+1的结点的equal子结点,而所有结点的子结点m7和equal都连接到同一个结点中的occupy-in。上面提到的所有边若没有显示说明费用,则表示 费用为0。所有费用为0的边的容量都是无穷的,而其它边的容量均为1。这样我们就利用等价关系构建了一个压缩图。此时A'=4|A|=4n,E'=5|A|=5n
上面整个过程可以在O(n)的时间内完成,即在O(n)的时间内创建这样一个图。这个过程可以通过创建一个大的数组来实现订阅功能,或者通过散列算法来实现,这里不再赘述。
尽管压缩了图,但是时间复杂度依旧维持在O(|A|^5),在|A|=3000的情况下,依旧是不现实的。
算法实现
首先讲述一个最小费用网络流中的定义:假设x为满足容量守恒的任意流,V(x):=从源点发出送入到汇点中的流量。
接着讲述最小费用网络流中的基本定理:若x是图N(A,E)中的所有容量为V(x)的流中费用最小的流,而y是图N(A,E)关联于流x的残存网络N(A,E(x))中容量为V(y)的费用最小的流,那么x和y合并后的流z是图N(A,E)中所有容量为V(z)=V(x)+V(y)的流中费用最小的流。
这个定理的证明非常简单,假设还存在一个比z费用更小的流f,满足V(f)=V(z)。记f'=f-x。我们知道每一个网络中的流均可以被分解为至多|A|个从源点到汇点的路径和|E|个从循环圈的复合。而显然f'中是不包含负费用循环圈,因为假如存在,那么在x中就存在对应的有残余容量的负费循环圈,那么我们就可以通过增广x中这些负费循环圈构建费用比x更低,但是V不变的新流x',这与x是图N(A,E)中所有容量为V(x)的流中费用最小的流这一前提相悖。而所有出现在f'中的从源点到汇点的路径上的分支流f'1,f'2,...,f'k的总流量与y一致,而由于y是所有N(A,E(x))中容量为V(y)的费用最小的流,因此y的费用一定低于f'1,f'2,...,f'k的加总。而由于费用可以直接加总,因此cost(x+y)=cost(x)+cost(y)<=cost(x)+cost(f')<=cost(x+f'),因此假设不成立,z确实是所有容量为V(z)的N(A,E)中的流中的费用最小的流。
因此我们只需要连续四次在前面汇总流的残余网络中找到下一个容量V为一单位的最小费用流,并添加到原来的汇总流上。重复四次,就可以得到我们最终的结果。但是如何在一个费用网络中找到最小费用路径是一个困难的问题。
这里可以采用加权的方案。我们为每个结点v分配一个加权值p(v),并且我们称b(u,v)=c(u,v)+p(u)-p(v)为边(u,v)的加权费用,其中c(u,v)表示边(u,v)的原始费用(按照预处理阶段的结果为-1或0)。注意对于任意路径(v0,v1,...,vk),其加权费用(即出现的各条边的加权费用的汇总)为b(v0,v1)+b(v1,v2)+...+b(vk-1,vk)=c(v0,v1)+c(v1,v2)+...+c(vk-1,vk)+p(v0)-p(vk)。即从u出发,终点为v的路径的加权费用为原始费用+p(u)-p(v),这也意味着所有从u出发,终点为v的路径在原始费用上的偏序关系在加权费用得到了保持,因此最小加权费用路径与原始费用下的最小费用路径在同一张图中是同一条路径。因此如果我们能使得每一条在N(A,E(x))中的边的加权费用都为非负,那么就可以利用最短路径算法(比如广度优先搜索,dijkstra算法)计算出从源点到汇点加权费用最低的路径(相当于用加权费用代替最短路径问题中的边长),即原始费用最低的路径,这也就解决了如何在一个费用网络中找到最小费用路径这一难题。
当然现在的难题是如何找到这样的一组加权值使得残余网络中每一条边的费用均非负。首先保证原始网络的加权值,为了使b(u,v)=c(u,v)+p(u)-p(v)>=0,即p(u)+c(u,v)>=p(v),这是不是很类似与最短路径算法中的路径关系,我们这里可以令源点的加权值为0,而其余点v则为
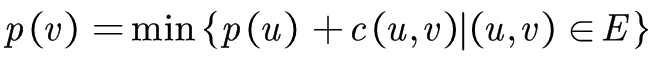
由于原始网络中是不包含任何环的,因此这个方案可以保证能为每个结点u都分配到合适的权值,且任意以u为出发点的边的加权费用必定非负。之后我们执行一次最短路径算法找到从源到汇点的最小费用路径,之后沿着这条路径传入一单位的流,这样得到了我们流量为1的最小费用路径x1。对于i=1,2,3,由于每次沿着xi的增广操作都可能会导致N(A,E(xi))中xi上的反向边的出现(拥有与正向边相反原始费用和加权费用),甚至可能导致原来的单向边变作双向边。这就意味着我们必须重新修改权值以保证残余边的加权费用非负。该如何进行修改呢,其实双向边的出现已经给予了我们提示,由于正向边的费用c和反向边的费用cr恒为相反数,即-c=cr,因此c>=0且cr>=0就意味着c=cr=0。因此我们只要保证所有xi上的边全部被赋予0加权值,而其余非xi上的边全部被赋予非0加权值就可以保证N(A,E(xi))所有的边都有非负费用。b'(u,v)=b(u,v)+p'(u)-p'(v)>=0,即b(u,v)+p'(u)>=p'(v),这与最短路径算法中核心部分是一致的,即我们令p'(u)表示从源点到点u,以p为加权函数得到的最短路径长度(最小加权费用)。这样也能保证所有在最短路径xi上的边(u,v)满足b(u,v)+p'(u)=p'(v),即b'(u,v)=0。b'(u,v)=b(u,v)+p'(u)-p'(v)=>b'(u,v)=c(u,v)+(p(u)+p'(u))-(p(v)-p'(v)),因此u的新权重为p(u)+p'(u)。
到此,所有难点都已经被克服了,下面说明一下整个流程的时间复杂度。利用动态规划,我们可以在O(|E|+|A|)=O(n)时间内重新计算每个结点的权值,而同样在每次迭代中(共4次),利用dijkstra算法计算从源点到所有其它点的最短路径(最小加权费用),其时间复杂度为O((|E|+n)logn)=O(nlogn),因此每次迭代的总费用为‘计算每个结点的权值’+‘计算单源最短路径’=O(|E|+|A|)+O(|E|+nlogn)=O(nlogn)。而总共四次迭代,故总费用为4*O(nlogn)=O(nlogn)。加上预处理阶段的O(n)的时间复杂度,其最终时间复杂度为O(n)+O(nlogn)=O(nlogn)。
代码实现
不好意思,最近晚上加班,周末才有空写这段代码(代码分4部分,与题目相关的主程序,用于dijkstra算法的最小堆,以及Acm专用的输入流,用于表示网络流的图):

package cn.dalt.codeforces;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PushbackInputStream;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Created by dalt on 2017/7/29.
*/
public class FourMelodies {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AcmInputReader reader = new AcmInputReader(System.in);
int n = reader.nextInteger();
ResidualNet net = new ResidualNet(2 + n * 4);
{
List<Integer>[] m7registries = new List[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
m7registries[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
m7registries[i].add(0);
}
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> equalRegistries = new TreeMap<>();
int inf = 100000000;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int input = reader.nextInteger();
int m7 = i * 4 + 2;
int equal = m7 + 1;
int occupy_in = m7 + 2;
int occupy_out = m7 + 3;
//Clear the registry
int m7Value = input % 7;
for (int src : m7registries[m7Value]) {
net.buildEdge(src, m7, inf, 0);
}
m7registries[m7Value].clear();
List<Integer> registry = equalRegistries.get(input);
if (registry == null) {
registry = new LinkedList<>();
equalRegistries.put(input, registry);
}
for (Integer src : registry) {
net.buildEdge(src, equal, inf, 0);
}
registry.clear();
//Build inner edge
net.buildEdge(m7, occupy_in, 1, 0);
net.buildEdge(equal, occupy_in, 1, 0);
net.buildEdge(occupy_in, occupy_out, 1, -1);
//Register for some slots
m7registries[m7Value].add(m7);
m7registries[m7Value].add(occupy_out);
registry.add(equal);
registry = equalRegistries.get(input - 1);
if (registry == null) {
registry = new LinkedList<>();
equalRegistries.put(input - 1, registry);
}
registry.add(occupy_out);
registry = equalRegistries.get(input + 1);
if (registry == null) {
registry = new LinkedList<>();
equalRegistries.put(input + 1, registry);
}
registry.add(occupy_out);
}
//Redirect all remain registries into sink point
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
for (int src : m7registries[i]) {
if (src != 0) {
net.buildEdge(src, 1, inf, 0);
}
}
}
for (List<Integer> list : equalRegistries.values()) {
for (int src : list) {
net.buildEdge(src, 1, inf, 0);
}
}
}
//Now we have build the net graph successfully
//Then we should do preparation for append flow
prepare(net);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//validate(net);
sendMinCostOneUnitFlow(net);
}
int totalPrice = net.totalPrice();
System.out.println(-totalPrice);
}
public static void validate(ResidualNet net) {
for (ResidualNet.INetNode node : net.getAllNodes()) {
for (ResidualNet.INetEdge edge : node.getEdges()) {
if (edge.valid() && edge.weightedPrice() < 0) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
}
}
public static void prepare(ResidualNet net) {
ResidualNet.INetNode[] nodes = net.getAllNodes();
nodes[0].setWeight(0);
for (ResidualNet.INetNode src : nodes) {
int srcWeight = src.getWeight();
for (ResidualNet.INetEdge edge : src.getEdges()) {
if (!edge.valid()) {
continue;
}
ResidualNet.INetNode target = edge.targetNode();
int targetWeight = edge.targetNode().getWeight();
int newWeight = srcWeight + edge.unitPrice();
if (newWeight < targetWeight) {
target.setWeight(newWeight);
}
}
}
}
public static void sendMinCostOneUnitFlow(ResidualNet net) {
//First step, build a min heap
ResidualNet.INetNode[] nodes = net.getAllNodes();
KeyHeap.Key[] keyOutput = new KeyHeap.Key[nodes.length];
Pair<Integer, ResidualNet.INetNode>[] shortestDistanceFromSrc = new Pair[nodes.length];
int inf = 100000000;
Integer infPack = Integer.valueOf(inf);
shortestDistanceFromSrc[0] = new Pair<>(Integer.valueOf(0), nodes[0]);
ResidualNet.INetEdge[] parentEdges = new ResidualNet.INetEdge[nodes.length];
for (int i = 1, bound = nodes.length; i < bound; i++) {
shortestDistanceFromSrc[i] = new Pair<>(infPack, nodes[i]);
}
KeyHeap heap = new KeyHeap(shortestDistanceFromSrc, keyOutput, new Comparator<Object>() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((Pair<Integer, ResidualNet.INetNode>) o1).key.compareTo(((Pair<Integer, ResidualNet.INetNode>) o2).key);
}
});
//Then pop all nodes from shortestDistanceFromSrc
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
Pair<Integer, ResidualNet.INetNode> pair = (Pair<Integer, ResidualNet.INetNode>) heap.pop();
if (pair.key.intValue() < inf) {
shortestDistanceFromSrc[pair.value.getId()] = pair;
//Reduce the shortest distance to all node follow edges whose source is pair.value
for (ResidualNet.INetEdge edge : pair.value.getEdges()) {
if (!edge.valid()) {
continue;
}
int newDistance = edge.weightedPrice() + pair.key;
ResidualNet.INetNode targetNode = edge.targetNode();
KeyHeap.Key targetKey = keyOutput[targetNode.getId()];
if (((Pair<Integer, ResidualNet.INetNode>) targetKey.getValue()).key > newDistance) {
targetKey.update(new Pair<Integer, ResidualNet.INetNode>(newDistance, edge.targetNode()));
parentEdges[targetNode.getId()] = edge;
}
}
} else {
break;
}
}
//Now we have find all the shortest distance to each node, we should expand the flow in the shortest distance road from src to sink
ResidualNet.INetEdge edge = parentEdges[1];
while (edge != null) {
edge.appendFlow(1);
edge = parentEdges[edge.sourceNode().getId()];
}
//Then recalculate all weight
for (int i = 0, bound = nodes.length; i < bound; i++) {
int newWeight = nodes[i].getWeight() + shortestDistanceFromSrc[i].key;
nodes[i].setWeight(Math.min(newWeight, inf));
}
}
public static class Pair<K, V> {
public final K key;
public final V value;
public Pair(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
/**
* Created by dalt on 2017/7/29.
*/
public static class KeyHeap {
private Comparator<Object> comparator;
private Key[] keys;
private int remain;
public KeyHeap(Object[] data, Key[] keyOutput, Comparator<Object> comparator) {
remain = data.length;
this.comparator = comparator;
if (data == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if (comparator == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
keys = new Key[data.length];
for (int i = 0, bound = data.length; i < bound; i++) {
keys[i] = new Key(data[i], i);
}
if (keyOutput != null) {
System.arraycopy(keys, 0, keyOutput, 0, Math.min(keys.length, keyOutput.length));
}
Arrays.sort(keys, new Comparator<Key>() {
@Override
public int compare(Key o1, Key o2) {
return comparator.compare(o1.getValue(), o2.getValue());
}
});
}
public KeyHeap(int capacity, Comparator<Object> comparator) {
if (capacity < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if (comparator == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
keys = new Key[capacity];
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public Object peek() {
if (remain <= 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
return keys[0].value;
}
public int size() {
return remain;
}
public Object pop() {
if (remain <= 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
Key result = keys[0];
remain--;
inject(keys[remain], 0);
keys[remain] = null;
downward(0);
return result.value;
}
public Key push(Object value) {
if (remain == keys.length) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
Key newKey = new Key(value, remain);
keys[remain] = newKey;
remain++;
upward(newKey.index);
return newKey;
}
public void clear() {
for (int i = 0; i < remain; i++) {
keys[i].removed = true;
keys[i] = null;
}
remain = 0;
}
private void downward(int target) {
if(target < 0 || target >= remain)
{
return;
}
Key targetKey = keys[target];
while (true) {
int lindex = target << 1;
int rindex = (target << 1) | 1;
if (lindex >= remain) {
break;
}
if (rindex >= remain) {
rindex = lindex;
}
Key left = keys[lindex];
Key right = keys[rindex];
if (comparator.compare(left.value, right.value) < 0) {
if (comparator.compare(left.value, targetKey.value) < 0) {
inject(left, target);
target = lindex;
} else {
break;
}
} else {
if (comparator.compare(right.value, targetKey.value) < 0) {
inject(right, target);
target = rindex;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
inject(targetKey, target);
}
private void inject(Key key, int i) {
keys[i] = key;
key.index = i;
}
private void upward(int target) {
if(target < 0 || target >= remain)
{
return;
}
Key targetKey = keys[target];
while (target > 0) {
int pindex = target >> 1;
Key parent = keys[pindex];
if (comparator.compare(targetKey.value, parent.value) < 0) {
inject(parent, target);
target = pindex;
} else {
break;
}
}
inject(targetKey, target);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return remain == 0;
}
private void remove(int index) {
keys[index].removed = true;
keys[index] = keys[--remain];
keys[remain] = null;
downward(index);
}
public class Key {
boolean removed = false;
private int index;
private Object value;
public Key(Object value, int index) {
this.value = value;
this.index = index;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
public void remove() {
if (removed) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
KeyHeap.this.remove(index);
}
public void update(Object value) {
if (removed) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
int cmp = comparator.compare(value, this.value);
this.value = value;
if (cmp < 0) {
upward(index);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
downward(index);
}
}
}
}
/**
* @author dalt
* @see java.lang.AutoCloseable
* @since java1.7
*/
private static class AcmInputReader implements AutoCloseable {
private PushbackInputStream in;
/**
* 创建读取器
*
* @param input 输入流
*/
public AcmInputReader(InputStream input) {
in = new PushbackInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(input));
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
in.close();
}
private int nextByte() throws IOException {
return in.read() & 0xff;
}
/**
* 如果下一个字节为b,则跳过该字节
*
* @param b 被跳过的字节值
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public void skipByte(int b) throws IOException {
int c;
if ((c = nextByte()) != b) {
in.unread(c);
}
}
/**
* 如果后续k个字节均为b,则跳过k个字节。这里{@literal k<times}
*
* @param b 被跳过的字节值
* @param times 跳过次数,-1表示无穷
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public void skipByte(int b, int times) throws IOException {
int c;
while ((c = nextByte()) == b && times > 0) {
times--;
}
if (c != b) {
in.unread(c);
}
}
/**
* 类似于{@link #skipByte(int, int)}, 但是会跳过中间出现的空白字符。
*
* @param b 被跳过的字节值
* @param times 跳过次数,-1表示无穷
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public void skipBlankAndByte(int b, int times) throws IOException {
int c;
skipBlank();
while ((c = nextByte()) == b && times > 0) {
times--;
skipBlank();
}
if (c != b) {
in.unread(c);
}
}
/**
* 读取下一块不含空白字符的字符块
*
* @return 下一块不含空白字符的字符块
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public String nextBlock() throws IOException {
skipBlank();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int c = nextByte();
while (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c = nextByte()] != AsciiMarksLazyHolder.BLANK_MARK) {
sb.append((char) c);
}
in.unread(c);
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* 跳过输入流中后续空白字符
*
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
private void skipBlank() throws IOException {
int c;
while ((c = nextByte()) <= 32) ;
in.unread(c);
}
/**
* 读取下一个整数(可正可负),这里没有对溢出做判断
*
* @return 下一个整数值
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public int nextInteger() throws IOException {
skipBlank();
int value = 0;
boolean positive = true;
int c = nextByte();
if (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.SIGN_MARK) {
positive = c == '+';
} else {
value = '0' - c;
}
c = nextByte();
while (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.NUMERAL_MARK) {
value = (value << 3) + (value << 1) + '0' - c;
c = nextByte();
}
in.unread(c);
return positive ? -value : value;
}
/**
* 判断是否到了文件结尾
*
* @return true如果到了文件结尾,否则false
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public boolean isMeetEOF() throws IOException {
int c = nextByte();
if (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.EOF) {
return true;
}
in.unread(c);
return false;
}
/**
* 判断是否在跳过空白字符后抵达文件结尾
*
* @return true如果到了文件结尾,否则false
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public boolean isMeetBlankAndEOF() throws IOException {
skipBlank();
int c = nextByte();
if (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.EOF) {
return true;
}
in.unread(c);
return false;
}
/**
* 获取下一个用英文字母组成的单词
*
* @return 下一个用英文字母组成的单词
*/
public String nextWord() throws IOException {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(16);
skipBlank();
int c;
while ((AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[(c = nextByte())] & AsciiMarksLazyHolder.LETTER_MARK) != 0) {
sb.append((char) c);
}
in.unread(c);
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* 读取下一个长整数(可正可负),这里没有对溢出做判断
*
* @return 下一个长整数值
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
skipBlank();
long value = 0;
boolean positive = true;
int c = nextByte();
if (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.SIGN_MARK) {
positive = c == '+';
} else {
value = '0' - c;
}
c = nextByte();
while (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.NUMERAL_MARK) {
value = (value << 3) + (value << 1) + '0' - c;
c = nextByte();
}
in.unread(c);
return positive ? -value : value;
}
/**
* 读取下一个浮点数(可正可负),浮点数是近似值
*
* @return 下一个浮点数值
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public float nextFloat() throws IOException {
return (float) nextDouble();
}
/**
* 读取下一个浮点数(可正可负),浮点数是近似值
*
* @return 下一个浮点数值
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public double nextDouble() throws IOException {
skipBlank();
double value = 0;
boolean positive = true;
int c = nextByte();
if (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.SIGN_MARK) {
positive = c == '+';
} else {
value = c - '0';
}
c = nextByte();
while (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.NUMERAL_MARK) {
value = value * 10.0 + c - '0';
c = nextByte();
}
if (c == '.') {
double littlePart = 0;
double base = 1;
c = nextByte();
while (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.NUMERAL_MARK) {
littlePart = littlePart * 10.0 + c - '0';
base *= 10.0;
c = nextByte();
}
value += littlePart / base;
}
in.unread(c);
return positive ? value : -value;
}
/**
* 读取下一个高精度数值
*
* @return 下一个高精度数值
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public BigDecimal nextDecimal() throws IOException {
skipBlank();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append((char) nextByte());
int c = nextByte();
while (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.NUMERAL_MARK) {
sb.append((char) c);
c = nextByte();
}
if (c == '.') {
sb.append('.');
c = nextByte();
while (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.NUMERAL_MARK) {
sb.append((char) c);
c = nextByte();
}
}
in.unread(c);
return new BigDecimal(sb.toString());
}
/**
* 读取下一个大整数数值
*
* @return 下一个大整数数值
* @throws IOException if 输入流读取错误
*/
public BigInteger nextBigInteger() throws IOException {
skipBlank();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append((char) nextByte());
int c = nextByte();
while (AsciiMarksLazyHolder.asciiMarks[c] == AsciiMarksLazyHolder.NUMERAL_MARK) {
sb.append((char) c);
c = nextByte();
}
in.unread(c);
return new BigInteger(sb.toString());
}
private static class AsciiMarksLazyHolder {
public static final byte BLANK_MARK = 1;
public static final byte SIGN_MARK = 1 << 1;
public static final byte NUMERAL_MARK = 1 << 2;
public static final byte UPPERCASE_LETTER_MARK = 1 << 3;
public static final byte LOWERCASE_LETTER_MARK = 1 << 4;
public static final byte LETTER_MARK = UPPERCASE_LETTER_MARK | LOWERCASE_LETTER_MARK;
public static final byte EOF = 1 << 5;
public static byte[] asciiMarks = new byte[256];
static {
for (int i = 0; i <= 32; i++) {
asciiMarks[i] = BLANK_MARK;
}
asciiMarks['+'] = SIGN_MARK;
asciiMarks['-'] = SIGN_MARK;
for (int i = '0'; i <= '9'; i++) {
asciiMarks[i] = NUMERAL_MARK;
}
for (int i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i++) {
asciiMarks[i] = LOWERCASE_LETTER_MARK;
}
for (int i = 'A'; i <= 'Z'; i++) {
asciiMarks[i] = UPPERCASE_LETTER_MARK;
}
asciiMarks[0xff] = EOF;
}
}
}
private static class ResidualNet {
private WeightedNetNode[] nodes;
/**
* Build a residual net with nodeNum nodes. The source node will be allocated id 0, and the target node will be allocated id 1.
* Other nodes follow the sequence.
*
* @param nodeNum the total node num of this residual net work.
*/
public ResidualNet(int nodeNum) {
nodes = new WeightedNetNode[nodeNum];
for (int i = 0; i < nodeNum; i++) {
nodes[i] = new WeightedNetNode(i);
}
}
public INetNode[] getAllNodes() {
return nodes;
}
public void buildEdge(int from, int to, int capcity, int unitPrice) {
if (from == 1 || to == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal source node for " + from + " with target node for " + to + " to build a edge");
}
if (from == to) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You can't build an edge between same node");
}
INetEdge edge = new ObeyNetEdge(nodes[from], nodes[to], unitPrice, capcity);
nodes[from].addEdge(edge);
nodes[to].addEdge(edge.reverseEdge());
}
public int totalPrice() {
int totalPrice = 0;
for (WeightedNetNode node : nodes) {
for (INetEdge edge : node.getEdges()) {
totalPrice += edge.totalPrice();
}
}
return totalPrice;
}
public static interface INetEdge {
public INetNode sourceNode();
public INetNode targetNode();
public int unitPrice();
public int totalPrice();
public int weightedPrice();
public INetEdge reverseEdge();
public int capacity();
public int flow();
public void appendFlow(int inc);
public int remain();
public boolean valid();
}
public static interface INetNode {
public int getId();
public Iterable<INetEdge> getEdges();
public int getWeight();
public void setWeight(int weight);
}
public static abstract class AbstractNetEdge implements INetEdge {
public int weightedPrice() {
return unitPrice() + sourceNode().getWeight() - targetNode().getWeight();
}
@Override
public boolean valid() {
return remain() > 0;
}
public int flow() {
return capacity() - remain();
}
@Override
public int totalPrice() {
return unitPrice() * flow();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("to %d, price %d, flow %d, remain %d", targetNode().getId(), weightedPrice(), flow(), remain());
}
}
public static class ObeyNetEdge extends AbstractNetEdge {
private INetNode source;
private INetNode target;
private int price;
private int capacity;
private int remain;
private RevoltedNetEdge revoltedGEdge = new RevoltedNetEdge(this);
public ObeyNetEdge(INetNode source, INetNode target, int price, int capacity) {
this.source = source;
this.target = target;
this.price = price;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.remain = capacity;
}
@Override
public void appendFlow(int inc) {
this.remain -= inc;
}
@Override
public INetNode sourceNode() {
return source;
}
@Override
public INetNode targetNode() {
return target;
}
@Override
public int unitPrice() {
return price;
}
@Override
public INetEdge reverseEdge() {
return revoltedGEdge;
}
@Override
public int capacity() {
return capacity;
}
@Override
public int remain() {
return remain;
}
}
public static class RevoltedNetEdge extends AbstractNetEdge {
private ObeyNetEdge edge;
public RevoltedNetEdge(ObeyNetEdge edge) {
this.edge = edge;
}
@Override
public INetNode sourceNode() {
return edge.targetNode();
}
@Override
public void appendFlow(int inc) {
edge.appendFlow(-inc);
}
@Override
public INetNode targetNode() {
return edge.sourceNode();
}
@Override
public int unitPrice() {
return -edge.unitPrice();
}
@Override
public INetEdge reverseEdge() {
return edge;
}
@Override
public int capacity() {
return edge.capacity();
}
@Override
public int remain() {
return edge.flow();
}
@Override
public int flow() {
return 0;
}
}
public static class WeightedNetNode implements INetNode {
private LinkedList<INetEdge> edges;
private int id;
private int weight;
public WeightedNetNode(int id) {
this.id = id;
edges = new LinkedList<INetEdge>();
}
public void addEdge(INetEdge edge) {
edges.add(edge);
}
@Override
public Iterable<INetEdge> getEdges() {
return edges;
}
@Override
public int getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
@Override
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(id);
}
}
}
}
codeforces:818G Four Melodies分析的更多相关文章
- 【Codeforces 1110D】Jongmah FST分析
Codeforces 1110 D FST分析 dotorya.FizzyDavid.MofK.gamegame.matthew99.chokudai.eddy1021.DBradac.Happy_N ...
- CodeForces 835D - Palindromic characteristics | Codeforces Round #427 (Div. 2)
证明在Tutorial的评论版里 /* CodeForces 835D - Palindromic characteristics [ 分析,DP ] | Codeforces Round #427 ...
- CF510E. Fox And Dinner
CF510E. Fox And Dinner https://codeforces.com/contest/510 分析: 由于\(a_i>2\), 相邻两个数一定一奇一偶,按奇偶建立二分图. ...
- CSUST 8.4 早训
## Problem A A - Memory and Crow CodeForces - 712A 题意: 分析可得bi=ai+ai+1 题解: 分析可得bi=ai+ai+1 C++版本一 #inc ...
- codeforces:MEX Queries分析和实现
首先说明一下MEX,设S是自然数集合N的一个子集,那么S的MEX则为min(N\S),即不包含于S的最小自然数. 题目大意是存在一个空集S,提供n组输入(n<10^5),每组输入对应下面的一个指 ...
- Codeforces 718A Efim and Strange Grade 程序分析
Codeforces 718A Efim and Strange Grade 程序分析 jerry的程序 using namespace std; typedef long long ll; stri ...
- Codeforces 679E - Bear and Bad Powers of 42(线段树+势能分析)
Codeforces 题目传送门 & 洛谷题目传送门 这个 \(42\) 的条件非常奇怪,不过注意到本题 \(a_i\) 范围的最大值为 \(10^{14}\),而在值域范围内 \(42\) ...
- Two Melodies CodeForces - 813D (DP,技巧)
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/813/D dp[i][j] = 一条链以i结尾, 另一条链以j结尾的最大值 关键要保证转移时两条链不能相交 #in ...
- codeforces:855D Rowena Ravenclaw's Diadem分析和实现
题目大意: 提供n个对象,分别编号为1,...,n.每个对象都可能是某个编号小于自己的对象的特例或是成分.认为某个对象的特例的特例依旧是该对象的特例,即特例关系传递,同样一个对象的成分的成分依旧是该对 ...
随机推荐
- Python基础学习----参数和返回值
# 函数的参数和返回值 # 4种组合方式 # 1.无参无返 # def methodone(): # 2.无参有返 def methodtwo(): a=10 return a # 3.有参无返 # ...
- Linux系统下 MYSQL数据库中的数据库文件在本机内迁移 (需暂停服务的方式)
Linux系统下 MYSQL数据库中的数据库文件在本机内迁移 本机采用Ubuntu16.04系统,tar方式安装MySQL5.7.21 数据库安装文件夹为 /home/devil/mysql 现 ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》 示例 Example 9.16
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- python 获取excel文件内sheet名称列表
xl = pd.ExcelFile('foo.xls') xl.sheet_names # see all sheet names xl.parse(sheet_name) # read a spec ...
- chrom调试javascript
上面的文章已经大致介绍了一下console对象具体有哪些方面以及基本的应用,下面简单介绍一下如何利用好chrome控制台这个神器好好调试javascript代码(这个才是我们真正能用到实处的地方) 1 ...
- Python中定时任务框架APScheduler
前言 大家应该都知道在编程语言中,定时任务是常用的一种调度形式,在Python中也涌现了非常多的调度模块,本文将简要介绍APScheduler的基本使用方法. 一.APScheduler介绍 APSc ...
- {转载}需要同时设置 noatime 和 nodiratime 吗?
相信对性能.优化这些关键字有兴趣的朋友都知道在 Linux 下面挂载文件系统的时候设置 noatime 可以显著提高文件系统的性能.默认情况下,Linux ext2/ext3 文件系统在文件被访问.创 ...
- C# zedgraph 怎么设置初始时坐标轴的比例??
http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390872329 已解决,,,我问是刷新图用的,,我以为mypane.YAxis.Scale.Min=0; mypane.YAxis.Scale ...
- java用double和float进行小数计算精度不准确
java用double和float进行小数计算精度不准确 大多数情况下,使用double和float计算的结果是准确的,但是在一些精度要求很高的系统中或者已知的小数计算得到的结果会不准确,这种问题是非 ...
- 使用Amoeba实现mysql读写分离机制
Amoeba的实用指南 http://docs.hexnova.com/amoeba/ 如何实现mysql读写分离 : 通常来说有两种方式: 1,应用程序层实现 2,中间件层实现 应用层实现 应用层实 ...
