Java8新特性Stream流
1、是什么?
- Stream(流)是一个来自数据源的元素队列并支持聚合操作
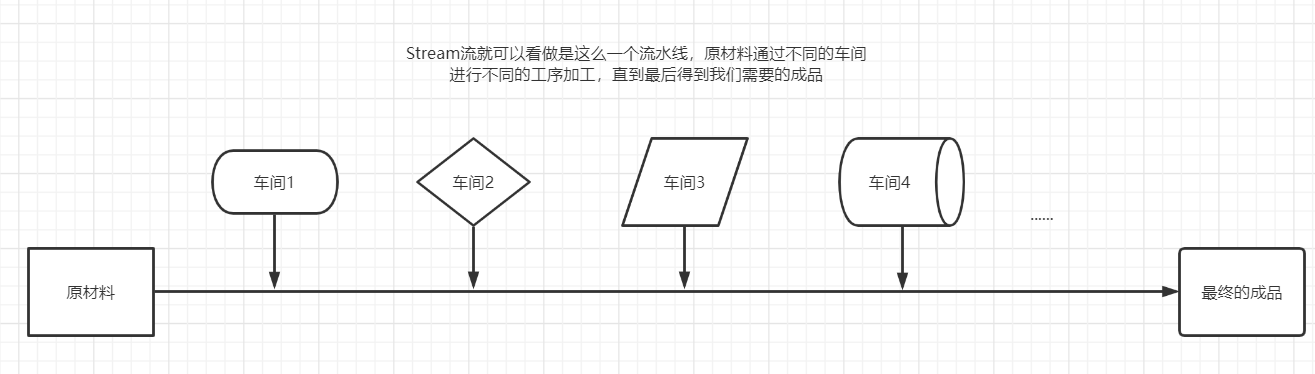
2、能干嘛?
- Stream流的元素是特定类型的对象,形成一个队列。
- Java中的Stream并不会存储元素,而是按需计算。
- 数据源,流的来源。
- 可以是集合,数组,I/O channel, generator等。
- 聚合操作,类似SQL语句一样的操作:
- 比如filter, map, reduce, find, match, sorted等。
- 和以前的Collection操作不同, Stream操作还有两个基础的特征:
- Pipelining: 中间操作都会返回流对象本身。 这样多个操作可以串联成一个管道, 如同流式风格(fluent style)。 这样做可以对操作进行优化, 比如延迟执行(laziness)和短路( short-circuiting)。
- 内部迭代: 以前对集合遍历都是通过Iterator或者For-Each的方式, 显式的在集合外部进行迭代, 这叫做外部迭代。 Stream提供了内部迭代的方式, 通过访问者模式(Visitor)实现。
3、怎么玩?
1、创建Stream的方式(原材料)
package com.qbb.threadpool;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* @author QiuQiu&LL (个人博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/qbbit)
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-07-23 20:19
* @Description:
*/
public class Java8NewFeatureStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建Stream方式一 : 通过集合
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
// 获取串行流
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
// 获取一个并行流
Stream<Integer> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();
// 创建Stream方式二 : 通过数组
String[] arr = new String[]{"a", "b", "c"};
Stream<String> arrStream = Arrays.stream(arr);
// 创建Stream方式三 : 通过Stream.of()
Stream<String> streamOf = Stream.of("x", "y", "z");
// 创建Stream方式四 : 通过Stream.iterate(),创建无限流(创建无限流必须要指定范围,不然会报错的)
Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.iterate(0, q -> q + 1).limit(5);
integerStream.forEach(System.out::println);
//生成10个随机数
Stream<Double> stream1 = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10);
stream1.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
2、中间操作(车间加工)
(1)fifter(Predicate<? super T> predicate) : 过滤,保留满足条件分元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
asList.stream()
.filter(q -> q % 2 ==0) // filter:过滤,保留符合条件的元素
.forEach(System.out::println); // forEach:内部迭代,终止操作输出每一个元素
}

(2) distinct () : 去除重复的元素
// 测试类
class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
return age == user.age && Objects.equals(name, user.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2, 5);
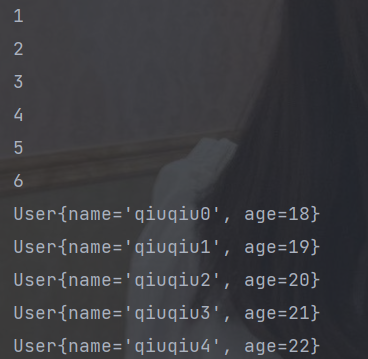
asList.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
// 测试一下对象类型
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
User user = new User("qiuqiu"+i,18+i);
userList.add(user);
}
User qiuqiu3 = new User("qiuqiu3", 21);
userList.add(qiuqiu3);
userList.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
}
(3)limit(long maxSize) : 获取指定maxSize个元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2, 5);
asList.stream().limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
}

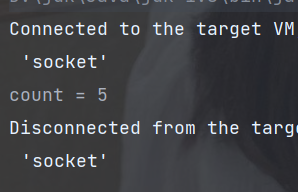
(4) skip(long n) : 跳过前n个元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 2, 5);
long count = asList.stream()
.skip(3) // 跳过前三个元素
// .findFirst() // 获取跳过操作后的第一个元素
// .findAny() // 获取跳过操作后的任意一个元素
.count(); // 获取剩余元素个数
// System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
(5) sorted()/sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator) : 排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(4, 5, 6, 2, 1, 2, 3, 5);
// 默认排序
asList.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("=======================================================");
// 指定比较器排序
// asList.stream().sorted((o1,o2) -> o1.compareTo(o2)).forEach(System.out::println);
asList.stream().sorted(Integer::compareTo).forEach(System.out::println);
}
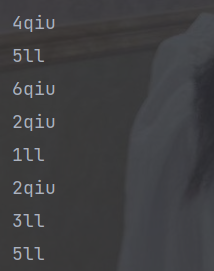
(6) map :接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(4, 5, 6, 2, 1, 2, 3, 5);
// map
asList.stream().map(q -> {
String str;
if(q%2 == 0){
str = q+"qiu";
}else {
str = q + "ll";
}
return str;
}).forEach(System.out::println);
}
- 其他的一些操作
mapToInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> mapper)mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T> mapper)mapToLong(ToLongFunction<? super T> mapper)flatMapToInt(Function<? super T, ? extends IntStream> mapper)flatMapToLong(Function<? super T, ? extends LongStream> mapper)flatMapToDouble(Function<? super T, ? extends DoubleStream> mapper)
(7) flatMap :接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
String[] arr = new String[]{"a,b,c","x,y,z"};
// flatMap
Arrays.stream(arr).flatMap(q -> {
String[] split = q.split(",");
// 把一个流拆分多个流然后又合并为一个流
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(split);
return stream;
}).forEach(System.out::println);
}
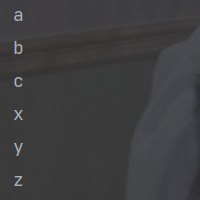
(8) peek :如同于map,能得到流中的每一个元素。但map接收的是一个Function表达式,有返回值;而peek接收的是Consumer表达式,没有返回值。
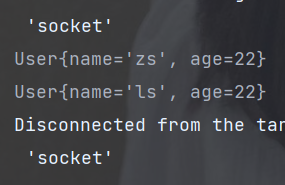
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
User zs = new User("zs", 18);
User ls = new User("ls", 28);
List<User> userList = Arrays.asList(zs, ls);
userList.stream()
.peek(q -> q.setAge(22))
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
当然还有其他的一些操作,这里就不一一演示了
3、终止操作
(1)匹配、聚合操作
allMatch :接收一个 Predicate 函数,当流中每个元素都符合该断言时才返回true,否则返回false
noneMatch :接收一个 Predicate 函数,当流中每个元素都不符合该断言时才返回true,否则返回false
anyMatch :接收一个 Predicate 函数,只要流中有一个元素满足该断言则返回true,否则返回false
findFirst :返回流中第一个元素
findAny :返回流中的任意元素
count :返回流中元素的总个数
max :返回流中元素最大值
min :返回流中元素最小值
forEach: 遍历流中的元素
forEachOrdered: 并行流下遍历流中的元素保证顺序
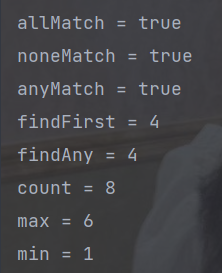
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(4, 5, 6, 2, 1, 2, 3, 5);
boolean allMatch = asList.stream().allMatch(q -> q > 0);
System.out.println("allMatch = " + allMatch);
boolean noneMatch = asList.stream().noneMatch(q -> q < 0);
System.out.println("noneMatch = " + noneMatch);
boolean anyMatch = asList.stream().anyMatch(q -> q % 2 == 0);
System.out.println("anyMatch = " + anyMatch);
Integer findFirst = asList.stream().findFirst().get();
System.out.println("findFirst = " + findFirst);
Integer findAny = asList.stream().findAny().get();
System.out.println("findAny = " + findAny);
// long count = asList.stream().count();
long count = asList.size();
System.out.println("count = " + count);
Integer max = asList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o)).get();
System.out.println("max = " + max);
Integer min = asList.stream().min(Integer::compareTo).get();
System.out.println("min = " + min);
String str = "my name is qiuqiu";
Stream.of(str.split(" ")).parallel().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
Stream.of(str.split(" ")).parallel().forEachOrdered(System.out::println);
}
(2) 规并操作
Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator) :第一次执行时,accumulator函数的第一个参数为流中的第一个元素,第二个参数为流中元素的第二个元素;第二次执行时,第一个参数为第一次函数执行的结果,第二个参数为流中的第三个元素;依次类推。
T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator) :流程跟上面一样,只是第一次执行时,accumulator函数的第一个参数为identity,而第二个参数为流中的第一个元素。
<U> U reduce(U identity,BiFunction<U, ? super T, U> accumulator,BinaryOperator<U> combiner) :在串行流(stream)中,该方法跟第二个方法一样,即第三个参数combiner不会起作用。在并行流(parallelStream)中,我们知道流被fork join出多个线程进行执行,此时每个线程的执行流程就跟第二个方法reduce(identity,accumulator)一样,而第三个参数combiner函数,则是将每个线程的执行结果当成一个新的流,然后使用第一个方法reduce(accumulator)流程进行规约。
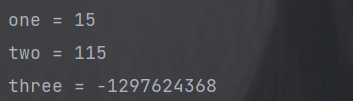
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流
List<Integer> asList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Integer one = asList.stream().reduce(Integer::sum).get();
System.out.println("one = " + one);
Integer two = asList.stream().reduce(100, Integer::sum);
System.out.println("two = " + two);
Integer three = asList.parallelStream().reduce(100,
Integer::sum,
(x, y) -> x * y);
System.out.println("three = " + three);
}
(3) 收集操作
collect :接收一个Collector实例,将流转化为其他形式,常用的List、Set、Map、Collection。
- 内部通过Collectors这个类进行相应的操作
(4) Collectors相关操作
toCollection toList() toSet() toMap : 将输入元素累积到一个集合中
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7);
list.replaceAll(q -> q > 5 ? q + 10 : q);
System.out.println("list = " + list);
list.sort((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
// 转Collection
Collection<Integer> collection = list.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
// 转List
List<Integer> integerList = list.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.toList());
// 转Set
Set<Integer> set = list.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
// 转Map
Map<Integer, Integer> map = list.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.toMap(item -> item, integer -> integer));
}
joining : 连接字符串
// joining
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g");
String result = list.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.joining(",", "[", "]"));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
mapping/flatMapping : 它将Function应用于输入元素,然后将它们累积到给定的Collector
Set<String> setStr = Stream.of("a", "a", "b")
.collect(Collectors.mapping(String::toUpperCase, Collectors.toSet()));
System.out.println(setStr); // [A, B]
Set<String> setStr1 = Stream.of("a", "a", "b")
.collect(Collectors.flatMapping(s -> Stream.of(s.toUpperCase()), Collectors.toSet()));
System.out.println(setStr1); // [A, B]
collectingAndThen : 返回一个收集器,该收集器将输入元素累积到给定的收集器中,然后执行其他完成功能
List<String> strList2 = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "10", "100", "20", "999");
List<String> unmodifiableList = strList2.parallelStream()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList));
System.out.println(unmodifiableList); // [1, 2, 10, 100, 20, 999]
counting : 计数
Long evenCount = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).filter(x -> x % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(evenCount); // 2
minBy : 根据给定的比较器返回最小元素
Optional<Integer> min = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.minBy((x, y) -> x - y));
System.out.println(min); // Optional[1]
maxBy : 它根据给定的比较器返回最大元素
Optional<Integer> max = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.maxBy((x, y) -> x - y));
System.out.println(max); // Optional[5]
summingInt/summingLong/summingDouble : 求总和
List<String> strList3 = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3", "4", "5");
Integer sum = strList3.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Integer::parseInt));
System.out.println(sum); // 15
Long sumL = Stream.of("12", "23").collect(Collectors.summingLong(Long::parseLong));
System.out.println(sumL); // 35
Double sumD = Stream.of("1e2", "2e3").collect(Collectors.summingDouble(Double::parseDouble));
System.out.println(sumD); // 2100.0
averagingInt/averagingLong/averagingDouble : 求平均值
List<String> strList4 = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3", "4", "5");
Double average = strList4.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Integer::parseInt));
System.out.println(average); // 3.0
Double averageL = Stream.of("12", "23").collect(Collectors.averagingLong(Long::parseLong));
System.out.println(averageL); // 17.5
Double averageD = Stream.of("1e2", "2e3").collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Double::parseDouble));
System.out.println(averageD); // 1050.0
groupingBy : 分组
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> mapGroupBy = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(x -> x * 10));
System.out.println(mapGroupBy); // {50=[5], 20=[2], 40=[4, 4], 10=[1], 30=[3, 3]}
groupingByConcurrent : 分组,是并发和无序的
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> mapGroupBy = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3).collect(Collectors.groupingByConcurrent(x -> x * 10));
System.out.println(mapGroupBy); // {50=[5], 20=[2], 40=[4, 4], 10=[1], 30=[3, 3]}
partitioningBy : 返回一个Collector,它根据Predicate对输入元素进行分区,并将它们组织成Map <Boolean,List >
Map<Boolean, List<Integer>> mapPartitionBy = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3).collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x -> x % 2 == 0));
System.out.println(mapPartitionBy); // {false=[1, 3, 5, 3], true=[2, 4, 4]}
BinaryOperator : 返回一个收集器,它在指定的BinaryOperator下执行其输入元素的减少。这主要用于多级缩减,例如使用groupingBy()和partitioningBy()方法指定下游收集器
Map<Boolean, Optional<Integer>> reducing = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3).collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(
x -> x % 2 == 0, Collectors.reducing(BinaryOperator.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Integer::intValue)))));
System.out.println(reducing); // {false=Optional[5], true=Optional[4]}
summarizingInt : 返回统计数据:min, max, average, count, sum
IntSummaryStatistics summarizingInt = Stream.of("12", "23", "35")
.collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Integer::parseInt));
System.out.println(summarizingInt);
//IntSummaryStatistics{count=3, sum=70, min=12, average=23.333333, max=35}
Java8新特性Stream流的更多相关文章
- 这可能是史上最好的 Java8 新特性 Stream 流教程
本文翻译自 https://winterbe.com/posts/2014/07/31/java8-stream-tutorial-examples/ 作者: @Winterbe 欢迎关注个人微信公众 ...
- Java8新特性 Stream流式思想(二)
如何获取Stream流刚开始写博客,有一些不到位的地方,还请各位论坛大佬见谅,谢谢! package cn.com.zq.demo01.Stream.test01.Stream; import org ...
- Java8新特性Stream流应用示例
Java8新特性介绍 过滤集合 List<String> newList = list.stream().filter(item -> item != null).collect(C ...
- java8 新特性Stream流的应用
作为一个合格的程序员,如何让代码更简洁明了,提升编码速度尼. 今天跟着我一起来学习下java 8 stream 流的应用吧. 废话不多说,直入正题. 考虑以下业务场景,有四个人员信息,我们需要根据性 ...
- Java8新特性 Stream流式思想(一)
遍历及过滤集合中的元素使用传统方式遍历及过滤集合中的元素package cn.com.zq.demo01.Stream.test01.Stream; import java.util.ArrayLis ...
- Java8新特性 Stream流式思想(三)
Stream接口中的常用方法 forEach()方法package cn.com.cqucc.demo02.StreamMethods.Test02.StreamMethods; import jav ...
- Java8 新特性 —— Stream 流式编程
本文部分摘自 On Java 8 流概述 集合优化了对象的存储,大多数情况下,我们将对象存储在集合是为了处理他们.使用流可以帮助我们处理对象,无需迭代集合中的元素,即可直接提取和操作元素,并添加了很多 ...
- Java8新特性——stream流
一.基本API初探 package java8.stream; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.IntSummaryStatistics; impo ...
- java8 新特性 Stream流 分组 排序 过滤 多条件去重
private static List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>(); public static void main(String[] ...
- Java8 新特性 Stream 无状态中间操作
无状态中间操作 Java8 新特性 Stream 练习实例 中间无状态操作,可以在单个对单个的数据进行处理.比如:filter(过滤)一个元素的时候,也可以判断,比如map(映射)... 过滤 fil ...
随机推荐
- CTFshow misc1-10
小提示:需要从图片上提取flag文字,可以通过截图翻译或者微信发送图片,这两个的ai图像识别挺好用的. misc1: 解压打开就能看见flag,提取出来就行 misc2: 记事本打开,看见 ng字符, ...
- 《SQL与数据库基础》04. SQL-DQL
目录 DQL 基础查询 条件查询 分组聚合 聚合函数 分组查询 结果排序 分页限制 总结 本文以 MySQL 为例 DQL 语法结构: SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表名列表 WHERE 条件列表 ...
- Redis系列21:缓存与数据库的数据一致性讨论
Redis系列1:深刻理解高性能Redis的本质 Redis系列2:数据持久化提高可用性 Redis系列3:高可用之主从架构 Redis系列4:高可用之Sentinel(哨兵模式) Redis系列5: ...
- C#结合OpenCVSharp4图片相似度识别
OpenCVSharp4图片相似度识别 需求背景:需要计算两个图片的相似度,然后将相似的图片进行归纳 1. 图片相似度算法 由于我是CRUD后端仔,对图像处理没什么概念.因此网上调研了几种相似度算法分 ...
- 利用BGP Anycast 实现DNS 服务的高可用测试
一.背景 根据当前某公司内部生产系统容器平台架构设计,在各生产线边缘机房部署容器平台,与数据中心容器平台形成纵向冗余,在此情况下,传统部署在数据中心机房的DNS系统成为容器平台业务服务的短板, ...
- selenium库浅析
selenium库浅析 基于4.3 pip install selenium安装好后,在sitepackages下 2个主要的目录,common和webdriver 1- common 该目录一共就一 ...
- DDMS查看Threads情况
有时候程序运行出现死锁或者信号量卡死是很纠结的问题,单看代码很难分析定位问题,这时候可以借助DDMS来查看threads的运行情况,一目了然. 手机连接上USB,确保adb连通,然后启动Eclipse ...
- 在 Rust 中实现 Repository 仓储模式
前言 单位上有个 Rust 项目,orm 选型很长时间都没定下来,故先设计了抽象的仓储层方便写业务逻辑. 设计抽象接口 抽象只读接口,仅读取使用,目前需求仅用查询 id.查询全部和按名称搜索,当然理应 ...
- 利用OpenXML获取Excel单元格背景色
利用OpenXML获取Excel单元格背景色 最近项目上遇到了关于Excel获取处理的问题,关于Excel单元格背景色的获取,水的文章都大同小异,都没注意到Excel单元格背景色是怎么赋值,这会导致出 ...
- Python网页应用开发神器fac 0.2.10版本新功能介绍
fac项目地址:https://github.com/CNFeffery/feffery-antd-components 欢迎star支持 大家好我是费老师,由我开源维护的Python网页通用组件库f ...
