Codeforces 931.F Teodor is not a liar!
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Young Teodor enjoys drawing. His favourite hobby is drawing segments with integer borders inside his huge [1;m] segment. One day Teodor noticed that picture he just drawn has one interesting feature: there doesn't exist an integer point, that belongs each of segments in the picture. Having discovered this fact, Teodor decided to share it with Sasha.
Sasha knows that Teodor likes to show off so he never trusts him. Teodor wants to prove that he can be trusted sometimes, so he decided to convince Sasha that there is no such integer point in his picture, which belongs to each segment. However Teodor is lazy person and neither wills to tell Sasha all coordinates of segments' ends nor wills to tell him their amount, so he suggested Sasha to ask him series of questions 'Given the integer point xi, how many segments in Fedya's picture contain that point?', promising to tell correct answers for this questions.
Both boys are very busy studying and don't have much time, so they ask you to find out how many questions can Sasha ask Teodor, that having only answers on his questions, Sasha can't be sure that Teodor isn't lying to him. Note that Sasha doesn't know amount of segments in Teodor's picture. Sure, Sasha is smart person and never asks about same point twice.
First line of input contains two integer numbers: n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100 000) — amount of segments of Teodor's picture and maximal coordinate of point that Sasha can ask about.
ith of next n lines contains two integer numbers li and ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ m) — left and right ends of ith segment in the picture. Note that that left and right ends of segment can be the same point.
It is guaranteed that there is no integer point, that belongs to all segments.
Single line of output should contain one integer number k – size of largest set (xi, cnt(xi)) where all xi are different, 1 ≤ xi ≤ m, and cnt(xi) is amount of segments, containing point with coordinate xi, such that one can't be sure that there doesn't exist point, belonging to all of segments in initial picture, if he knows only this set(and doesn't know n).
2 4
1 2
3 4
4
4 6
1 3
2 3
4 6
5 6
5
First example shows situation where Sasha can never be sure that Teodor isn't lying to him, because even if one knows cnt(xi) for each point in segment [1;4], he can't distinguish this case from situation Teodor has drawn whole [1;4] segment.
In second example Sasha can ask about 5 points e.g. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, still not being sure if Teodor haven't lied to him. But once he knows information about all points in [1;6] segment, Sasha can be sure that Teodor haven't lied to him.
题目大意:有一条线段,上面的点被若干条线段覆盖着. Sasha想知道是否存在一个整点被所有的线段覆盖,她每次可以任选一个点,Teodor会告诉她这个点被多少个线段覆盖,但是Sasha不知道有多少条线段.求Sasha最多猜多少次还不知道这个问题的答案. 也就是说,如果你最多猜n次能知道答案,那么输出n-1.如果猜不到答案就输出n.
分析:这种题目把图一画,各种情况考虑一下就能做出来了.
什么情况下Sasha能知道答案呢? 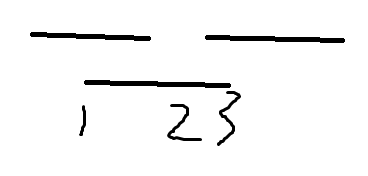 在这幅图中,1,2,3都被猜过了,覆盖2的线段数小于覆盖1,3的,而线段是连续的,说明有线段到2这个点就中断了,自然就没有整点被所有的线段给覆盖了. 同样的,如果覆盖2的线段数大于覆盖1,3的,也是能够猜出来的. 为了使猜的次数最多,把1,3全都猜完就行了.
在这幅图中,1,2,3都被猜过了,覆盖2的线段数小于覆盖1,3的,而线段是连续的,说明有线段到2这个点就中断了,自然就没有整点被所有的线段给覆盖了. 同样的,如果覆盖2的线段数大于覆盖1,3的,也是能够猜出来的. 为了使猜的次数最多,把1,3全都猜完就行了.
所以究竟是求什么呢? 要求猜的数组成的子序列中不能有两个凸起的部分,只能一边是单调函数,另一边也是单调函数.那么就是要求一个最长的单峰子序列.树状数组扫两次就好了.
小细节:树状数组查询,修改的数不能是0,而这道题中可能存在点没有被线段覆盖,所以要默认有一条线段覆盖了所有点.
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = ;
int n,m,c1[maxn],c2[maxn],a[maxn],sum,f1[maxn],f2[maxn],ans; int add1(int x,int v)
{
while (x <= n)
{
c1[x] = max(c1[x],v);
x += x & (-x);
}
} int query1(int x)
{
int res = ;
while (x)
{
res = max(res,c1[x]);
x -= x & (-x);
}
return res;
} int add2(int x,int v)
{
while (x <= n)
{
c2[x] = max(c2[x],v);
x += x & (-x);
}
} int query2(int x)
{
int res = ;
while (x)
{
res = max(res,c2[x]);
x -= x & (-x);
}
return res;
} int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++)
{
int l,r;
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
a[l]++;
a[r + ]--;
}
for (int i = ; i <= m; i++)
{
sum += a[i];
a[i] = sum + ;
}
for (int i = ; i <= m; i++)
{
f1[i] = query1(a[i]) + ;
add1(a[i],f1[i]);
}
for (int i = m; i >= ; i--)
{
f2[i] = query2(a[i]) + ;
add2(a[i],f2[i]);
}
for (int i = ; i <= m; i++)
ans = max(ans,f1[i] + f2[i] - );
printf("%d\n",ans); return ;
}
Codeforces 931.F Teodor is not a liar!的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 931F - Teodor is not a liar!
931F - Teodor is not a liar! 思路: 最长上升子序列 先差分数组染色 如果存在一个点,被所有区间包含,那么这张图一定是山峰状,如下图: 那么只要分别从前和从后找一个最长非严 ...
- Codeforces 959 F. Mahmoud and Ehab and yet another xor task
\(>Codeforces\space959 F. Mahmoud\ and\ Ehab\ and\ yet\ another\ xor\ task<\) 题目大意 : 给出一个长度为 \ ...
- Codeforces 835 F. Roads in the Kingdom
\(>Codeforces\space835 F. Roads in the Kingdom<\) 题目大意 : 给你一棵 \(n\) 个点构成的树基环树,你需要删掉一条环边,使其变成一颗 ...
- Codeforces 731 F. Video Cards(前缀和)
Codeforces 731 F. Video Cards 题目大意:给一组数,从中选一个数作lead,要求其他所有数减少为其倍数,再求和.问所求和的最大值. 思路:统计每个数字出现的个数,再做前缀和 ...
- Codeforces 931 C. Laboratory Work
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/931/C 题意: 给定一个数列,要求构造一个等长的数列,使得数列的平均值等于给定数列,并且使得构造出的数列中与原数列 ...
- Codeforces 797 F Mice and Holes
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/797/F F. Mice and Holes time limit per test 1.5 ...
- Codeforces 622 F. The Sum of the k-th Powers
\(>Codeforces \space 622\ F. The\ Sum\ of\ the\ k-th\ Powers<\) 题目大意 : 给出 \(n, k\),求 \(\sum_{i ...
- Codeforces 379 F. New Year Tree
\(>Codeforces \space 379 F. New Year Tree<\) 题目大意 : 有一棵有 \(4\) 个节点个树,有连边 \((1,2) (1,3) (1,4)\) ...
- Codeforces 538 F. A Heap of Heaps
\(>Codeforces \space 538 F. A Heap of Heaps<\) 题目大意 :给出 \(n\) 个点,编号为 \(1 - n\) ,每个点有点权,将这些点构建成 ...
随机推荐
- iOS 播放音频文件
// 播放音乐 NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"1670" ofType:@&qu ...
- HWI的安装
一.安装的过程 hwi的安装过程: 1.解压src源码包:tar -zvxf apache-hive-1.2.2-src.tar.gz 2.进到HWI目录下:cd /home/bigdata/apac ...
- Python基础灬函数补充(作用域,迭代器,生成器)
变量作用域 函数里面操作外部变量时,作用域仅限于函数里面. var1 = 123 def func(): var1 = 456 print("函数里:", var1) func() ...
- 记因内核版本错误导致U盘不能识别的问题解决
U盘插上电脑,发现没有自动挂载.然后运行sudo fdisk -l一看,发现并没有U盘所对应的设备,也就是U盘不能识别了!以前从没在Linux上遇到这种问题,通过查资料得知,要识别U盘,需要装载usb ...
- 第四次ScrumMeeting博客
第四次ScrumMeeting博客 本次会议于10月28日(六)22时整在3公寓725房间召开,持续15分钟. 与会人员:刘畅.辛德泰.窦鑫泽.张安澜.赵奕. 1. 每个人的工作(有Issue的内容和 ...
- HttpServlet 详解(基础)
HttpServlet详解 大家都知道Servlet,但是不一定很清楚servlet框架,这个框架是由两个Java包组成:javax.servlet和javax.servlet.http. 在java ...
- CSS中水平居中设置的几种方式
1.行内元素: 如果被设置元素为文本.图片等行内元素时,水平居中是通过给父元素设置 text-align:center 来实现的. <body> <div class="t ...
- 【IdentityServer4文档】- 术语&演示服务器和测试
术语 你需要了解一下,规范.文档和对象模型使用的术语有哪些. IdentityServer IdentityServer 是一个 OpenID Connect 提供程序 - 它实现了 OpenID C ...
- UIView maskView属性
给View1的maskView 赋值View2 1.View2不会显示在View1上: 2.View2 的alpha通道会体现在View1上. 关于maskView,Apple的解释: An opti ...
- 使用qemu-img创建虚拟磁盘文件
# 安装qemu-img yum install -y qemu-img # 获取帮助 qemu-img --help # 支持的虚拟磁盘文件格式 Supported formats: vvf ...
