自动化运维之SaltStack初探
1.1、基础环境
linux-node1(master服务端) 192.168.31.46 CentOS 6.6 X86_64
linux-node2(minion客户端) 192.168.31.47 CentOS 6.8 X86_64
1.2、SaltStack三种运行模式
Local 本地
Master/Minion 传统运行方式(server端跟agent端)
Salt SSH SSH
1.3、SaltStack三大功能
●远程执行
●配置管理
●云管理
1.4、SaltStack安装基础环境准备
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS release 6.6 (Final)
[root@linux-node1 ~]# getenforce
Disabled
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables stop
iptables: Setting chains to policy ACCEPT: filter [ OK ]
iptables: Flushing firewall rules: [ OK ]
iptables: Unloading modules: [ OK ]
[root@linux-node1 ~]# ifconfig eth0 |awk -F '[: ]+' 'NR==2{print $4}'
192.168.31.46
[root@linux-node1 ~]# hostname
linux-node1.mage.com
[root@linux-node1 ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-6.repo
--2019-04-17 16:37:01-- http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-6.repo
Resolving mirrors.aliyun.com... 115.223.37.229, 115.223.37.231, 115.223.37.228, ...
Connecting to mirrors.aliyun.com|115.223.37.229|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 664 [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: “/etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo” 100%[===================================================================================================================================================>] 664 --.-K/s in 0s 2019-04-17 16:37:01 (77.1 MB/s) - “/etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo” saved [664/664] [root@linux-node1 ~]# ls /etc/yum.repos.d/
CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Vault.repo epel.repo
1.5、安装Salt
服务端:
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum -y install salt-master salt-minion
[root@linux-node1 ~]# chkconfig salt-master on
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /etc/init.d/salt-master start
Starting salt-master daemon: [ OK ] [root@linux-node1 /]# grep '^[a-z]' /etc/salt/minion
master: 192.168.31.46
[root@linux-node1 /]# tail -2 /etc/hosts
192.168.31.46 linux-node1.mage.com
192.168.31.47 linux-node2.mage.com
[root@linux-node1 /]# ping linux-node1.mage.com
PING linux-node1.mage.com (192.168.31.46) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from linux-node1.mage.com (192.168.31.46): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.062 ms
^C
--- linux-node1.mage.com ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 410ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.062/0.062/0.062/0.000 ms
[root@linux-node1 /]# ping linux-node2.mage.com
PING linux-node2.mage.com (192.168.31.47) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from linux-node2.mage.com (192.168.31.47): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.412 ms
^C
--- linux-node2.mage.com ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 638ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.412/0.412/0.412/0.000 ms
启动客户端
[root@linux-node1 /]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion start
Starting salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
客户端:
[root@linux-node2 ~]# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-6.repo
[root@linux-node2 ~]# yum -y install salt-minion
[root@linux-node2 ~]# chkconfig salt-minion on
[root@linux-node2 ~]# grep '^[a-z]' /etc/salt/minion
master: 192.168.31.46
[root@linux-node2 ~]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion restart
Stopping salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
Starting salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
1.6、Salt密钥认证设置
1.6.1 在使用salt-kes -a linux*命令之前在目录/etc/salt/pki/master目录结构如下:
[root@linux-node1 master]# tree /etc/salt/pki/master/
/etc/salt/pki/master/
├── master.pem
├── master.pub
├── minions
├── minions_autosign
├── minions_denied
├── minions_pre
│ ├── linux-node1.mage.com
│ └── linux-node2.mage.com
└── minions_rejected 5 directories, 4 files [root@linux-node1 master]# salt-key
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
linux-node1.mage.com ---->被拒绝的密钥
linux-node2.mage.com ---->被拒绝的密钥
Rejected Keys:
1.6.2 使用salt-kes -a linux*命令将密钥通过允许,随后minions_pre下的文件会转移到minions目录下
[root@linux-node1 master]# salt-key -a linux*
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
linux-node1.mage.com
linux-node2.mage.com
Proceed? [n/Y] Y
Key for minion linux-node1.mage.com accepted.
Key for minion linux-node2.mage.com accepted. [root@linux-node1 master]# salt-key
Accepted Keys:
linux-node1.mage.com
linux-node2.mage.com
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
1.6.3 此时目录机构变化成如下:
[root@linux-node1 master]# tree /etc/salt/pki/master/
/etc/salt/pki/master/
├── master.pem
├── master.pub
├── minions
│ ├── linux-node1.mage.com
│ └── linux-node2.mage.com
├── minions_autosign
├── minions_denied
├── minions_pre
└── minions_rejected 5 directories, 4 files minions_pre目录为空,转移到minions目录下。
1.6.4 并且伴随着客户端/etc/salt/pki/minion/目录下有master公钥生成
[root@linux-node2 ~]# tree /etc/salt/pki/
/etc/salt/pki/
└── minion
├── minion_master.pub
├── minion.pem
└── minion.pub 1 directory, 3 files
1.7 salt远程执行命令详解
1.7.1 salt '*' test.ping 命令 命令说明:test.ping的含义是,test是一个模块,ping是模块内的方法
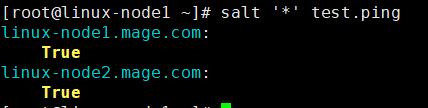
1.7.2 salt '*' cmd.run 'uptime' 命令

1.8、saltstack配置管理
1.8.1 编辑配置文件/etc/salt/master,将file_roots注释去掉
[root@linux-node1 master]# vim /etc/salt/master
406 # file_roots:
407 # base:
408 # - /srv/salt/
409 # dev:
410 # - /srv/salt/dev/services
411 # - /srv/salt/dev/states
412 # prod:
413 # - /srv/salt/prod/services
414 # - /srv/salt/prod/states
415 #
416 file_roots:
417 base:
418 - /srv/salt
将416-418行注释去掉;
1.8.2 saltstack远程执行如下命令
[root@linux-node1 master]# ls /srv/
[root@linux-node1 master]# mkdir /srv/salt
[root@linux-node1 master]# /etc/init.d/salt-master restart
Stopping salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
Starting salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
进入到/srv/salt/目录下创建
[root@linux-node1 /]# cd /srv/salt/
[root@linux-node1 salt]# cat apache.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- names:
- httpd
- httpd-devel apache-service:
service.running:
- name: httpd
- enable: True
- reload: True
最后成功执行如下:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt '*' state.sls apache
linux-node1.mage.com:
----------
ID: apache-install
Function: pkg.installed
Name: httpd
Result: True
Comment: The following packages were installed/updated: httpd
Started: 19:42:29.044800
Duration: 13895.126 ms
Changes:
----------
apr:
----------
new:
1.3.9-5.el6_9.1
old:
apr-util:
----------
new:
1.3.9-3.el6_0.1
old:
apr-util-ldap:
----------
new:
1.3.9-3.el6_0.1
old:
httpd:
----------
new:
2.2.15-69.el6.centos
old:
httpd-tools:
----------
new:
2.2.15-69.el6.centos
old:
mailcap:
----------
new:
2.1.31-2.el6
old:
----------
ID: apache-install
Function: pkg.installed
Name: httpd-devel
Result: True
Comment: The following packages were installed/updated: httpd-devel
Started: 19:42:42.942793
Duration: 10862.807 ms
Changes:
----------
apr-devel:
----------
new:
1.3.9-5.el6_9.1
old:
apr-util-devel:
----------
new:
1.3.9-3.el6_0.1
old:
cyrus-sasl:
----------
new:
2.1.23-15.el6_6.2
old:
2.1.23-15.el6
cyrus-sasl-devel:
----------
new:
2.1.23-15.el6_6.2
old:
cyrus-sasl-lib:
----------
new:
2.1.23-15.el6_6.2
old:
2.1.23-15.el6
expat:
----------
new:
2.0.1-13.el6_8
old:
2.0.1-11.el6_2
expat-devel:
----------
new:
2.0.1-13.el6_8
old:
httpd-devel:
----------
new:
2.2.15-69.el6.centos
old:
openldap:
----------
new:
2.4.40-16.el6
old:
2.4.39-8.el6
openldap-devel:
----------
new:
2.4.40-16.el6
old:
----------
ID: apache-service
Function: service.running
Name: httpd
Result: True
Comment: Service httpd has been enabled, and is running
Started: 19:42:53.808407
Duration: 331.765 ms
Changes:
----------
httpd:
True Summary
------------
Succeeded: 3 (changed=3)
Failed: 0
------------
Total states run: 3
linux-node2.mage.com:
----------
ID: apache-install
Function: pkg.installed
Name: httpd
Result: True
Comment: The following packages were installed/updated: httpd
Started: 19:17:39.705974
Duration: 18610.497 ms
Changes:
----------
apr:
----------
new:
1.3.9-5.el6_9.1
old:
apr-util:
----------
new:
1.3.9-3.el6_0.1
old:
apr-util-ldap:
----------
new:
1.3.9-3.el6_0.1
old:
httpd:
----------
new:
2.2.15-69.el6.centos
old:
httpd-tools:
----------
new:
2.2.15-69.el6.centos
old:
mailcap:
----------
new:
2.1.31-2.el6
old:
----------
ID: apache-install
Function: pkg.installed
Name: httpd-devel
Result: True
Comment: The following packages were installed/updated: httpd-devel
Started: 19:17:58.320077
Duration: 15078.914 ms
Changes:
----------
apr-devel:
----------
new:
1.3.9-5.el6_9.1
old:
apr-util-devel:
----------
new:
1.3.9-3.el6_0.1
old:
cyrus-sasl-devel:
----------
new:
2.1.23-15.el6_6.2
old:
db4:
----------
new:
4.7.25-22.el6
old:
4.7.25-20.el6_7
db4-cxx:
----------
new:
4.7.25-22.el6
old:
db4-devel:
----------
new:
4.7.25-22.el6
old:
db4-utils:
----------
new:
4.7.25-22.el6
old:
4.7.25-20.el6_7
expat:
----------
new:
2.0.1-13.el6_8
old:
2.0.1-11.el6_2
expat-devel:
----------
new:
2.0.1-13.el6_8
old:
httpd-devel:
----------
new:
2.2.15-69.el6.centos
old:
openldap:
----------
new:
2.4.40-16.el6
old:
2.4.40-12.el6
openldap-devel:
----------
new:
2.4.40-16.el6
old:
----------
ID: apache-service
Function: service.running
Name: httpd
Result: True
Comment: Service httpd has been enabled, and is running
Started: 19:18:13.453671
Duration: 407.064 ms
Changes:
----------
httpd:
True Summary
------------
Succeeded: 3 (changed=3)
Failed: 0
------------
Total states run: 3
1.8.3 验证使用saltstack安装httpd是否成功
Linux-node1:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# lsof -i :80
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
httpd 5961 root 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 5963 apache 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 5964 apache 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 5965 apache 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 5966 apache 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 5967 apache 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 5968 apache 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 5969 apache 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 5970 apache 4u IPv6 32751 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
Linux-node2:
[root@linux-node2 ~]# lsof -i :80
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
httpd 1966 root 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 1968 apache 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 1969 apache 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 1970 apache 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 1971 apache 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 1972 apache 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 1973 apache 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 1974 apache 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
httpd 1975 apache 4u IPv6 23627 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
2.1、 SaltStack之Grains数据系统
●Grains
●Pillar
2.1.1 使用salt命令查看系统版本:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node1*' grains.ls
linux-node1.mage.com:
- SSDs
- cpu_flags
- cpu_model
- cpuarch
- domain
- fqdn
- fqdn_ip4
- fqdn_ip6
- gpus
- host
- hwaddr_interfaces
- id
- init
- ip4_interfaces
- ip6_interfaces
- ip_interfaces
- ipv4
- ipv6
- kernel
- kernelrelease
- locale_info
- localhost
- lsb_distrib_codename
- lsb_distrib_id
- lsb_distrib_release
- machine_id
- master
- mdadm
- mem_total
- nodename
- num_cpus
- num_gpus
- os
- os_family
- osarch
- oscodename
- osfinger
- osfullname
- osmajorrelease
- osrelease
- osrelease_info
- path
- ps
- pythonexecutable
- pythonpath
- pythonversion
- saltpath
- saltversion
- saltversioninfo
- selinux
- server_id
- shell
- virtual
- zmqversion
2.1.2 系统版本相关信息:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node1*' grains.items
linux-node1.mage.com:
----------
SSDs:
cpu_flags:
- fpu
- vme
- de
- pse
- tsc
- msr
- pae
- mce
- cx8
- apic
- sep
- mtrr
- pge
- mca
- cmov
- pat
- pse36
- clflush
- dts
- mmx
- fxsr
- sse
- sse2
- ss
- ht
- nx
- rdtscp
- lm
- constant_tsc
- arch_perfmon
- pebs
- bts
- xtopology
- tsc_reliable
- nonstop_tsc
- aperfmperf
- unfair_spinlock
- pni
- pclmulqdq
- ssse3
- cx16
- pcid
- sse4_1
- sse4_2
- x2apic
- popcnt
- tsc_deadline_timer
- aes
- xsave
- avx
- hypervisor
- lahf_lm
- ida
- arat
- epb
- pln
- pts
- dts
cpu_model:
Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E31230 @ 3.20GHz
cpuarch:
i686
domain:
mage.com
fqdn:
linux-node1.mage.com
fqdn_ip4:
- 192.168.31.46
fqdn_ip6:
gpus:
|_
----------
model:
SVGA II Adapter
vendor:
unknown
host:
linux-node1
hwaddr_interfaces:
----------
eth0:
00:0c:29:c2:08:ef
lo:
00:00:00:00:00:00
id:
linux-node1.mage.com
init:
upstart
ip4_interfaces:
----------
eth0:
- 192.168.31.46
lo:
- 127.0.0.1
ip6_interfaces:
----------
eth0:
- fe80::20c:29ff:fec2:8ef
lo:
- ::1
ip_interfaces:
----------
eth0:
- 192.168.31.46
- fe80::20c:29ff:fec2:8ef
lo:
- 127.0.0.1
- ::1
ipv4:
- 127.0.0.1
- 192.168.31.46
ipv6:
- ::1
- fe80::20c:29ff:fec2:8ef
kernel:
Linux
kernelrelease:
2.6.32-573.26.1.el6.i686
locale_info:
----------
defaultencoding:
UTF8
defaultlanguage:
en_US
detectedencoding:
UTF-8
localhost:
linux-node1.mage.com
lsb_distrib_codename:
Final
lsb_distrib_id:
CentOS
lsb_distrib_release:
6.6
machine_id:
618afc16402c42bc00e491e600000022
master:
192.168.31.46
mdadm:
mem_total:
498
nodename:
linux-node1.mage.com
num_cpus:
2
num_gpus:
1
os:
CentOS
os_family:
RedHat
osarch:
i686
oscodename:
Final
osfinger:
CentOS-6
osfullname:
CentOS
osmajorrelease:
6
osrelease:
6.6
osrelease_info:
- 6
- 6
path:
/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin
ps:
ps -efH
pythonexecutable:
/usr/bin/python2.6
pythonpath:
- /usr/bin
- /usr/lib/python26.zip
- /usr/lib/python2.6
- /usr/lib/python2.6/plat-linux2
- /usr/lib/python2.6/lib-tk
- /usr/lib/python2.6/lib-old
- /usr/lib/python2.6/lib-dynload
- /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages
- /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/setuptools-0.6c11-py2.6.egg-info
pythonversion:
- 2
- 6
- 6
- final
- 0
saltpath:
/usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/salt
saltversion:
2015.5.10
saltversioninfo:
- 2015
- 5
- 10
- 0
selinux:
----------
enabled:
False
enforced:
Disabled
server_id:
82870161
shell:
/bin/bash
virtual:
VMware
zmqversion:
3.2.5
2.1.3 系统版本相关信息:
[root@linux-node1 salt]#
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node1*' grains.item fqdn
linux-node1.mage.com:
----------
fqdn:
linux-node1.mage.com
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node1*' grains.get fqdn
linux-node1.mage.com:
linux-node1.mage.com
2.1.4 查看node1、node2所有ip地址:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node1*' grains.get ip_interfaces:eth0
linux-node1.mage.com:
- 192.168.31.46
- fe80::20c:29ff:fec2:8ef
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node2*' grains.get ip_interfaces:eth0
linux-node2.mage.com:
- 192.168.31.47
- fe80::20c:29ff:fec8:3e5c
2.1.5 使用Grains收集系统信息:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node1*' grains.get os
linux-node1.mage.com:
CentOS
收集登录信息:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt -G os:CentOS cmd.run 'w' # -G:代表使用Grains收集,使用w命令,查看登录信息
linux-node1.mage.com:
19:55:03 up 3:57, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.05, 0.10
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root pts/0 192.168.10.35 15:57 1.00s 0.77s 0.42s /usr/bin/python
linux-node2.mage.com:
19:30:13 up 3:55, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.02, 0.05
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root pts/0 192.168.10.35 15:35 6:15 0.19s 0.19s -bash
2.1.5 使用Grains规则匹配到memcache的主机上运行
[root@linux-node1 salt]# vim /etc/salt/minion #编辑minion配置文件,取消如下几行注释
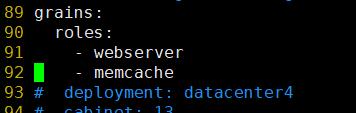
[root@linux-node1 salt]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion restart
Stopping salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
Starting salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt -G 'roles:memcache' cmd.run 'echo mage'
linux-node1.mage.com:
mage
#使用grains匹配规则是memcache的客户端机器,然后输出命令
2.1.6 也可以通过创建新的配置文件/etc/salt/grains文件来配置规则
[root@linux-node1 salt]# cat /etc/salt/grains
web: nginx
[root@linux-node1 salt]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion restart
Stopping salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
Starting salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt -G web:nginx cmd.run 'w' #使用grains匹配规则为web:nginx的主机运行命令w
linux-node1.mage.com:
20:16:46 up 4:19, 1 user, load average: 0.15, 0.08, 0.07
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root pts/0 192.168.10.35 15:57 1.00s 0.82s 0.42s /usr/bin/python
grains的用法:
1、收集底层系统信息
2、远程执行里面匹配minion
3、top.sls里面匹配minion
2.1.7 也可以/srv/salt/top.sls 配置文件匹配minion
[root@linux-node1 salt]# cat /srv/salt/top.sls
base:
'web:nginx':
- match: grain
- apache
2.2 SaltStack之Pillar数据系统
2.2.1 首先在master配置文件552行打开pillar开关
[root@linux-node1 salt]# grep '^[a-z]' /etc/salt/master
file_roots:
pillar_opts: True
[root@linux-node1 salt]# /etc/init.d/salt-master restart
Stopping salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
Starting salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt '*' pillar.items ##使用如下命令验证##
打开如下529--531行注释:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# vim /etc/salt/master 521 #
522 ##### Pillar settings #####
523 ##########################################
524 # Salt Pillars allow for the building of global data that can be made selectively
525 # available to different minions based on minion grain filtering. The Salt
526 # Pillar is laid out in the same fashion as the file server, with environments,
527 # a top file and sls files. However, pillar data does not need to be in the
528 # highstate format, and is generally just key/value pairs.
529 pillar_roots:
530 base:
531 - /srv/pillar
[root@linux-node1 salt]# mkdir /srv/pillar
[root@linux-node1 salt]# /etc/init.d/salt-master restart
Stopping salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
Starting salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
[root@linux-node1 salt]# vim /srv/pillar/apache.sls
[root@linux-node1 salt]#
[root@linux-node1 salt]# cat /srv/pillar/apache.sls
{%if grains['os'] == 'CentOS' %}
apache: httpd
{% elif grains['os'] == 'Debian' %}
apache: apache2
{% endif %}
接着指定哪个minion可以看到:
[root@linux-node1 salt]# cat /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'*':
- apache
修改完成之后,验证该命令:
[root@linux-node1 pillar]# salt '*' pillar.items
linux-node2.mage.com:
----------
apache:
httpd linux-node1.mage.com:
----------
apache:
httpd
2.2.1 使用Pillar定位主机
[root@linux-node1 pillar]# salt -I 'apache:httpd' test.ping
linux-node2.mage.com:
Minion did not return. [No response]
linux-node1.mage.com:
Minion did not return. [No response]
报错:Minion did not return. [No response]
需要执行刷新命令:
[root@linux-node1 pillar]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
linux-node2.mage.com:
True
linux-node1.mage.com:
True
再次测试:
[root@linux-node1 pillar]# salt -I 'apache:httpd' test.ping
linux-node1.mage.com:
True
linux-node2.mage.com:
True
2.3、SaltStack数据系统区别介绍
|
名称 |
存储位置 |
数据类型 |
数据采集更新方式 |
应用 |
|
Grains |
Minion端 |
静态数据 |
minion启动时收集,也可以使用saltutil.sync_grains进行刷新 |
存储minion基本数据,比如用于匹配minion,自身数据可以用来做资产管理等。 |
|
Pillar |
Master端 |
动态数据 |
在master端定义,指定给对应的minion,可以使用saltutil.refresh_pillar刷新 |
存储Master指定的数据,只有指定的minion可以看到,用于敏感数据保存。 |
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/hackerer/p/6617301.html
自动化运维之SaltStack初探的更多相关文章
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑩SaltStack二次开发初探
saltstack自动化运维系列⑩SaltStack二次开发初探 1.当salt运行在公网或者网络环境较差的条件下,需要配置timeout时间vim /etc/salt/master timeout: ...
- 1、自动化运维之SaltStack实践
自动化运维之SaltStack实践 1.1.环境 linux-node1(master服务端) 192.168.0.15 linux-node2(minion客户端) 192.168.0.16 1.2 ...
- 自动化运维之Saltstack
第三十八课 自动化运维之Saltstack 目录 一.自动化运维介绍 二. saltstack安装 三. 启动saltstack服务 四. saltstack配置认证 五. saltstack远程执行 ...
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑧SaltStack实践配置管理安装nginx-1.10.3
saltstack自动化运维系列⑧SaltStack实践配置管理安装nginx-1.10.3 安装nginx-1.10.3.tar.gz # mkdir -p /srv/salt/prod/pkg / ...
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑦SaltStack实践配置管理安装zabbix
saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践配置管理安装zabbix 1.添加管理zabbix的sls文件# vim /srv/salt/base/init/zabbix_agent.sl ...
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践安装配置HAproxy的Keepalived
saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践安装配置HAproxy的Keepalived 安装配置Keepalived 1.编写功能模块 #创建keepalived目录# mkdir -p ...
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践安装配置HAproxy
saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践安装配置HAproxy 下载haproxy1.6.2.tar.gz下载地址:http://www.haproxy.org/download/1. ...
- 自动化运维工具 SaltStack 搭建
原文地址:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-devops-saltstack-in-cloud/index.html#N10072 ...
- 自动化运维工具SaltStack详细部署【转】
==========================================================================================一.基础介绍==== ...
随机推荐
- pytest-html 测试报告
前言 上一篇文章pytest简介中,执行测试用例后,在 pycharm 控制台(方式一)或 Terminal(方式二)中可以查看测试结果.但是在实际的接口自动化项目中一般需要生成直观的测试报告,这个测 ...
- python多版本切换
环境:Macbook MacOS自带的python2.7,在命令行中输入python后会显示2.7版本 如何切换成新版本? 一.修改用户配置环境变量~/.bash_profile 确定新版本的安装位置 ...
- 海康PTZ云台摄像头调试之直接控制云台(C#)
众所周知,海康的摄像头sdk较为完善,但是对于新手来说还是有点麻烦. 今天写一篇随笔给大家展示下怎么控制海康摄像头的云台(前提是有ptz云台设备) 1.sdk准备 本文基于C#的frame来开发一个p ...
- Elasticsearch笔记2
1 搜索所有文档中还有某个字段的方法: localhost:9200/get-together/group/_search?pretty { "query": { "qu ...
- Redis 竟然能用 List 实现消息队列
分布式系统中必备的一个中间件就是消息队列,通过消息队列我们能对服务间进行异步解耦.流量消峰.实现最终一致性. 目前市面上已经有 RabbitMQ.RochetMQ.ActiveMQ.Kafka等,有人 ...
- [LeetCode]14.最长公共前缀(Java)
原题地址: longest-common-prefix 题目描述: 编写一个函数来查找字符串数组中的最长公共前缀. 如果不存在公共前缀,返回空字符串 "". 示例 1: 输入:st ...
- python-关键字驱动接口框架中,接口关联字段进行值替换的实现方式
前言 编写关键字驱动的接口自动化测试框架中,通过不同的取值方式,将需要关联的字段以及取出的值放到一个空字典中,需要将关联的字段进行值替换,下面是替换的实现方式 实现思路 import re temp_ ...
- 渗透测试之本地文件包含(LFI)
一.本地文件包含 本地文件包含漏洞指的是包含本地的php文件,而通过PHP文件包含漏洞入侵网站,可以浏览同服务器所有文件,并获得webshell. 看见?page=标志性注入点,提示我们输入?=pag ...
- Java泛型的那些事
1.泛型概述 1.1.为什么使用泛型 没有泛型,在编写代码时只能使用具体类型或Object类型,无法做到使用者想要使用什么类型就是类型.比如:创建一个方法,形参需要指定需要使用的数据类型,在创建方法之 ...
- “百度杯”CTF比赛 九月场Upload
首先生成一个php文件以下源代码: <script language="PHP">$fh=fopen("../flag.".strtolower(& ...
