Django(62)自定义认证类
前言
如果我们不用使用drf那套认证规则,我们想自定义认证类,那么我们首先要知道,drf本身是如何定义认证规则的,也就是要查看它的源码是如何写的
源码分析
源码的入口在APIView.py文件下的dispatch方法下的self.initial方法中的self.perform_authentication(request),点击查看后如下
def perform_authentication(self, request):
"""
Perform authentication on the incoming request.
Note that if you override this and simply 'pass', then authentication
will instead be performed lazily, the first time either
`request.user` or `request.auth` is accessed.
"""
request.user
返回了一个request的user方法,request代表的是drf的Request,所以我们进入drf的Request类中查找user方法属性,源码如下:
def user(self):
"""
Returns the user associated with the current request, as authenticated
by the authentication classes provided to the request.
"""
if not hasattr(self, '_user'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate()
return self._user
上述代码的意思是:返回与当前请求关联的用户,由提供给请求的身份验证类进行身份验证。如果没有用户,我们需要通过_authenticate方法验证,我们查看下它的源码
def _authenticate(self):
"""
尝试依次使用每个身份验证实例对请求进行身份验证。
"""
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self)
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise
if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple
return
self._not_authenticated()
我们可以看到self.authenticators验证器其实是调用父类APIView的authenticators,APIView的authenticators在源码initialize_request方法下的get_authenticators,我们查看源码
def get_authenticators(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of authenticators that this view can use.
"""
return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes]
再点击authentication_classes查看
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
我们就知道了drf默认的认证器在settings文件下的DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES类下面
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
],
我们发现drf默认有2个认证类一个基础的认证,另一个session认证,这两个认证类都继承自BaseAuthentication,我们来看下源码
class BaseAuthentication:
"""
所有的认证类都继承自BaseAuthentication.
"""
def authenticate(self, request):
"""
认证请求返回一个二元组(user, token),并且此方法必须重写,否则抛出异常
"""
raise NotImplementedError(".authenticate() must be overridden.")
def authenticate_header(self, request):
"""
Return a string to be used as the value of the `WWW-Authenticate`
header in a `401 Unauthenticated` response, or `None` if the
authentication scheme should return `403 Permission Denied` responses.
"""
pass
接下来我们看下BasicAuthentication如何写的,后续我们依葫芦画瓢
class BasicAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
"""
针对用户名密码的 HTTP 基本身份验证
"""
www_authenticate_realm = 'api'
def authenticate(self, request):
"""
如果使用 HTTP 基本身份验证提供了正确的用户名和密码,则返回“User”。否则返回“None”。
"""
# 获取请求头中`HTTP_AUTHORIZATION`,并进行分割
auth = get_authorization_header(request).split()
# 如果没有auth或者auth的第一个索引值的小写不等于basic,则返回None
if not auth or auth[0].lower() != b'basic':
return None
# auth列表的长度必须等于2,格式['basic', 'abc.xyz.123']
# 如果auth的长度等于1,则抛出异常
if len(auth) == 1:
msg = _('Invalid basic header. No credentials provided.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
# 如果长度大于2,也抛出异常
elif len(auth) > 2:
msg = _('Invalid basic header. Credentials string should not contain spaces.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
try:
try:
# auth[1]解码格式为utf-8
auth_decoded = base64.b64decode(auth[1]).decode('utf-8')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
auth_decoded = base64.b64decode(auth[1]).decode('latin-1')
auth_parts = auth_decoded.partition(':')
except (TypeError, UnicodeDecodeError, binascii.Error):
msg = _('Invalid basic header. Credentials not correctly base64 encoded.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
userid, password = auth_parts[0], auth_parts[2]
return self.authenticate_credentials(userid, password, request)
def authenticate_credentials(self, userid, password, request=None):
"""
Authenticate the userid and password against username and password
with optional request for context.
"""
credentials = {
get_user_model().USERNAME_FIELD: userid,
'password': password
}
user = authenticate(request=request, **credentials)
if user is None:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(_('Invalid username/password.'))
if not user.is_active:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(_('User inactive or deleted.'))
return (user, None)
def authenticate_header(self, request):
return 'Basic realm="%s"' % self.www_authenticate_realm
自定义认证类
- 创建继承BaseAuthentication的认证类
- 实现authenticate方法
- 实现体根据认证规则 确定 游客 正常用户 非法用户
- 进行全局或局部配置(一般采用全局配置)
认证规则
- 没有认证信息,返回
None(游客) - 有认证信息认证失败,抛异常(非法用户)
- 有认证信息认证成功,返回用户和认证信息的元组(合法用户)
我们创建一个文件夹authentications,写入如下代码
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed
from api.models import User
class MyAuthentications(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
# 前台在请求头携带认证信息
# 且默认规范用Authorization字段携带认证信息
# 后台固定在请求对象的META字段中的HTTP_AUTHORIZATION获取
auth = request.META.get('HTTP_AUTHORIZATION', None)
# 处理游客
if auth is None:
return None
auth_list = auth.split()
if not len(auth_list) == 2 and auth_list[0].lower() == "auth":
raise AuthenticationFailed("认证信息有误,非法用户")
# 合法的用户还需要从auth_list[1]中解析出来
# 注:假设一种情况,信息为xx.yy.zz,就可以解析出admin用户:实际开发,该逻辑一定是校验用户的正常逻辑
if auth_list[1] != 'xx.yy.zz': # 校验失败
raise AuthenticationFailed("用户校验失败,非法用户")
user = User.objects.filter(username='jkc').first()
print(user)
if not user:
raise AuthenticationFailed("用户数据有误,非法用户")
return user, None
然后在settings.py中配置全局的自定义认证类
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
'api.authentications.MyAuthentications'
],
}
最后写入视图函数
class TestView(APIView):
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return APIResponse(data_msg="drf get ok")
然后我们访问视图,在headers中不传Authorization 代表游客,游客可以访问成功
{
"statusCode": 0,
"message": "drf get ok"
}
接着我们在请求头中只传auth
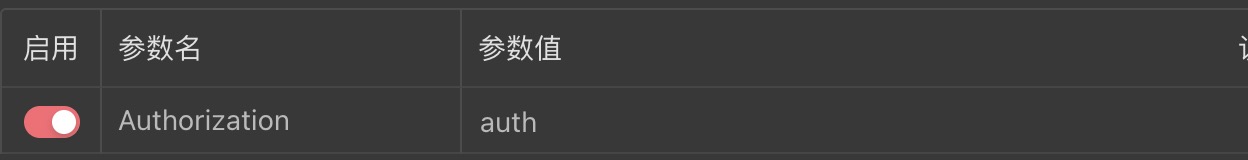
访问视图会抛出异常信息
{
"detail": "认证信息有误,非法用户"
}
然后我们在请求头中传入错误的认证,auth 111

访问视图会抛出异常信息
{
"detail": "用户校验失败,非法用户"
}
最后我们在请求头中传入正确的认证,auth xx.yy.zz,这次会得到正确的返回结果
{
"statusCode": 0,
"message": "drf get ok"
}
以上的测试,就代表我们自定义的认证类起作用了
Django(62)自定义认证类的更多相关文章
- DRF JWT的用法 & Django的自定义认证类 & DRF 缓存
JWT 相关信息可参考: https://www.jianshu.com/p/576dbf44b2ae DRF JWT 的使用方法: 1. 安装 DRF JWT # pip install djang ...
- 自定义user表签发token、自定义认证类、simpleui模块使用
今日内容概要 自定义User表,签发token 自定义认证类 simpleui的使用 多方式登陆接口(后面也写 内容详细 1.自定义User表,签发token # 如果项目中的User表使用auth的 ...
- [py][mx]django自定义认证类-实现邮箱作为用户名登录
创建自定义验证用户名密码类CustomBackend users/views.py from django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login from d ...
- django 实现自定义认证
1.Django自带用户认证系统 Django自带用户认证系统,这个系统支持访问控制.注册用户.关联创建者和内容等:在开发用户认证功能时的时候,可以使用Django自带用户认证系统实现: A.相关表 ...
- The Django Book(自定义ModelAdmi类)
默认的,管理界面下显示的东西只是 python2:def __unicode__(self): 和 python3:def __str__(self): 中返回的字段内容 想要让它更加的多元化的话 c ...
- Django:RestFramework之-------认证
3 restframework-认证 3.1APIView 认证: 认证是否已经登陆,如果已经登陆返回元组,如果没有登陆报错 源码流程: 执行dispatch方法: def dispatch(self ...
- Django REST framework —— 认证组件源码分析
我在前面的博客里已经讲过了,我们一般编写API的时候用的方式 class CoursesView(ViewSetMixin,APIView): pass 这种方式的有点是,灵活性比较大,可以根据自己的 ...
- drf三大认证:认证组件-权限组件-权限六表-自定义认证组件的使用
三大认证工作原理简介 认证.权限.频率 源码分析: from rest_framework.views import APIView 源码分析入口: 内部的三大认证方法封装: 三大组件的原理分析: 权 ...
- DRF认证、自定义认证和权限、自定义权限
源码分析 """ 1)APIView的dispath(self, request, *args, **kwargs) 2)dispath方法内 self.initial( ...
随机推荐
- 关于PHP动态的接收传递的GET,POST和COOKIE变量
0x01 我们知道 PHP 接收的变量最常用的是 GET,POST,COOKIE 这三个变量.GET变量是附在 url 后传输的,而 POST 变量是放在 http 包中传输的,COOKIE 则是浏览 ...
- 1.简单认识PHP和环境搭建
1.关于PHP PHP(Hypertext Perprocessor,超文本预处理器),是一种服务器端.跨平台.HTML嵌入式的脚本语言,其独特的语法混合了C.Java.和Perl语言的特点,是一种被 ...
- [CTF]当铺密码
[CTF]当铺密码 --------------------- 作者:adversity` 来源:CSDN 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40836553/articl ...
- C++将数值转换为string
std::to_string string to_string (int val); string to_string (long val); string to_string (long long ...
- Linux性能调优命令之free
功能说明 free 命令显示系统使用和空闲的内存情况,包括物理内存.交互区内存(swap)和内核缓冲区内存.共享内存将被忽略 语法 free [参数] 参数 -b : 以Byte为单位显示内存使用情况 ...
- [Django框架之视图层]
[Django框架之视图层] 视图层 Django视图层, 视图就是Django项目下的views.py文件,它的内部是一系列的函数或者是类,用来专门处理客户端访问请求后处理请求并且返回相应的数据,相 ...
- [DB] 数据库的连接
概述 集合运算:交,差,并,笛卡尔积 关系运算:选择,投影,连接,除 集合运算是关系运算的基础,关系运算可以用SQL语句表达 连接(join):从两个关系(表)的笛卡儿积中选取属性(列)间满足一定条件 ...
- 小甲鱼零基础入门学习python--课后作业
[小甲鱼零基础入门学习python--课后作业] 小甲鱼零基础入门学习python--课后作业 本章内容: 1.基础部分的作业 2.函数部分的作业 3.字典.集合.文件部分作业 4.异常 5.Easy ...
- RHEL sosreport
RHEL sosreport简介 sosreport对很多RedHat爱好者来说应该并不陌生! 它是一款在RedHat Linux下帮你收集系统信息打成一个tar包的工具,你可以将这个tar包发给供应 ...
- Python爬虫 小白[3天]入门笔记
笔记来源 Day-0 1.如果你还不了解Python的基础语法,可以移步|>>>Python 基础 小白 [7天] 入门笔记<<<|或自行学习. 简介 1.什么是爬 ...
