Mybatis拦截器实现原理深度分析
1.拦截器简介
拦截器可以说使我们平时开发经常用到的技术了,Spring AOP、Mybatis自定义插件原理都是基于拦截器实现的,而拦截器又是以动态代理为基础实现的,每个框架对拦截器的实现不完全相同,今天我们就来一起分析下Mybatis拦截器实现原理,其实也就是自定义插件的实现原理了。
2.Mybatis拦截器
2.1创建一个拦截器
在mybatis中提供了Interceptor接口,自己实现拦截器只需要实现Interceptor接口即可,下面来看一下接口定义:
public interface Interceptor {
//拦截方法,执行拦截器逻辑
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
//为目标对象创建代理并返回,通过调用Plugin.wrap(target, this)实现
Object plugin(Object target);
//设置属性
void setProperties(Properties properties);
}
下面来看一下我们常用的分页插件的实现:
//Intercepts注解表示这是一个拦截器,Signature注解描述具体拦截mybatis中四大对象中的哪一个,这里面只拦截Executor类型,
//只拦截Executor的query方法,因为query方法有多个,所以通过args标识拦截具体哪个query方法
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}))
public class PageHelper implements Interceptor { /**
* Mybatis拦截器方法
*
* @param invocation 拦截器入参
* @return 返回执行结果
* @throws Throwable 抛出异常
*/
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
//执行分页
return sqlUtil.processPage(invocation);
} /**
* 只拦截Executor
*
* @param target
* @return
*/
public Object plugin(Object target) {
if (target instanceof Executor) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
} else {
return target;
}
} /**
* 设置属性值
*
* @param p 属性值
*/
public void setProperties(Properties p) {
//MyBatis3.2.0版本校验
try {
Class.forName("org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.SqlNode");//SqlNode是3.2.0之后新增的类
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("您使用的MyBatis版本太低,MyBatis分页插件PageHelper支持MyBatis3.2.0及以上版本!");
}
//数据库方言
String dialect = p.getProperty("dialect");
sqlUtil = new SqlUtil(dialect);
sqlUtil.setProperties(p);
}
}
了解了怎样创建一个拦截器后,下面来看一下拦截器如何生效,也就是如何构建拦截器链
2.2拦截器链的构建
mybatis中的InterceptorChain类用来创建拦截器链,内部持有一个interceptors 的List,拦截器的顺序就是在配置文件中配置的拦截器的顺序,因为拦截器有顺序之分,所以这里用一个List维护。
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>();
//创建拦截器链,target为mybatis中的4大对象中的某个(ParameterHandler,StatementHandler,ResultSetHandler,Executor)
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
//通过jdk动态代理为目标创建代理对象,如果有多个拦截器,那么会出现代理对象再次被代理的情况,通过这样层层代理,构建拦截器链。注意:target的代理对象再次赋值给target,如果有多个拦截器,代理对象target将再次被代理!
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
既然pluginAll(target)方法是用来构建拦截器链的,那么,这个方法是在哪里被调用的呢,看下图
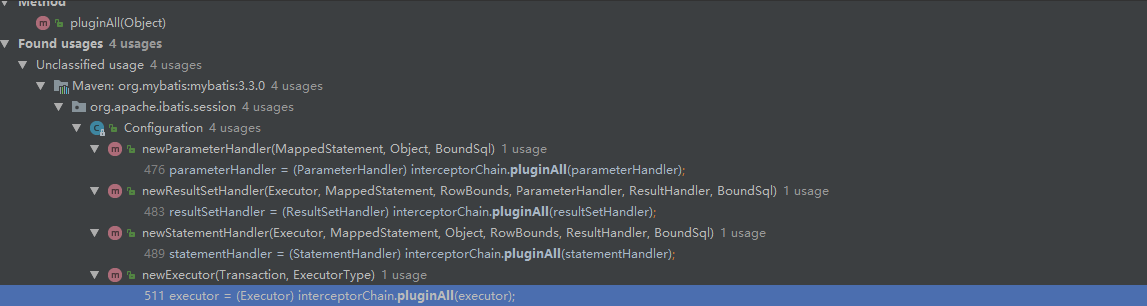
以Executor为例,继续看
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
由上面的代码可知在每次调用newExecutor()方法时将目标对象executor传入interceptorChain.pluginAll(),返回executor的代理对象,其实在这个代理对象的内部,拦截器链已经形成了。
要想搞清楚拦截器链怎样构建的,必须需要深入interceptor.plugin(target)方法的内部一探究竟
以上面的分页插件为例,如果target是Executor类型,则调用Plugin.wrap(target, this)方法,否则,直接返回传进来的target。
Plugin类是是mybatis中用来为目标对象创建代理对象的类,实现了InvocationHandler接口,所以对代理对象的所有调用都会调用Plugin类的invoke方法:
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
//目标对象,可能是一个代理对象,在第一次调用interceptor.plugin(target)时,target不是代理类,
//之后调用interceptor.plugin(target)时,这里的target就是代理对象了
private Object target;
//拦截器对象,因为之后要在invoke方法里面调用拦截器的拦截方法,所以这里需要持有引用
private Interceptor interceptor;
//拦截器方法签名map,在invoke方法内部判断如果调用的是拦截器支持拦截的方法,否则,直接调用目标对象的方法
private Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
//自己写的拦截器需要调用该方法对目标对象进行代理
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
//获取目标类的所有方法,包括从父接口继承的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,//注意这里第三个参数创建了一个当前类对象,并将目标对象、拦截器对象和方法签名的map传入
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
//不为空且拦截器支持对该方法进行拦截,则调用拦截器的拦截方法
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
//注意方法参数,创建一个Invocation并将目标对象、方法和参数传进去,所以在Invocation对象内部可以通过反射调用目标对象的方法
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
//直接调用目标对象的方法
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
// issue #251
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, Set<Method>>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type());
if (methods == null) {
methods = new HashSet<Method>();
signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods);
}
try {
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
}
}
对代理对象的方法调用会调用interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args),下面来看分页插件的intercept方法:
继续看processPage方法,processPage方法调用了_processPage方法:
public class SqlUtil implements Constant {
//...
/**
* Mybatis拦截器方法
*
* @param invocation 拦截器入参
* @return 返回执行结果
* @throws Throwable 抛出异常
*/
private Object _processPage(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
final Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2];
if (SqlUtil.getLocalPage() == null && rowBounds == RowBounds.DEFAULT) {
return invocation.proceed();
} else {
//忽略RowBounds-否则会进行Mybatis自带的内存分页
args[2] = RowBounds.DEFAULT;
//分页信息
Page page = getPage(rowBounds);
//pageSizeZero的判断
if ((page.getPageSizeZero() != null && page.getPageSizeZero()) && page.getPageSize() == 0) {
//执行正常(不分页)查询
Object result = invocation.proceed();
//得到处理结果
page.addAll((List) result);
//相当于查询第一页
page.setPageNum(1);
//这种情况相当于pageSize=total
page.setPageSize(page.size());
//仍然要设置total
page.setTotal(page.size());
//返回结果仍然为Page类型 - 便于后面对接收类型的统一处理
return page;
}
//获取原始的ms
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0];
SqlSource sqlSource = ms.getSqlSource();
//简单的通过total的值来判断是否进行count查询
if (page.isCount()) {
//将参数中的MappedStatement替换为新的qs
msUtils.processCountMappedStatement(ms, sqlSource, args);
//查询总数,继续调用目标对象(也可能是代理对象)的方法,但是此时修改了MappedStatement的参数,实际是查了数据的条数
Object result = invocation.proceed();
//设置总数
page.setTotal((Integer) ((List) result).get(0));
if (page.getTotal() == 0) {
return page;
}
}
//pageSize>0的时候执行分页查询,pageSize<=0的时候不执行相当于可能只返回了一个count
if (page.getPageSize() > 0 &&
((rowBounds == RowBounds.DEFAULT && page.getPageNum() > 0)
|| rowBounds != RowBounds.DEFAULT)) {
//将参数中的MappedStatement替换为新的ms,新的ms是原来传过来的ms+分页信息
msUtils.processPageMappedStatement(ms, sqlSource, page, args);
//执行分页查询
Object result = invocation.proceed();
//得到处理结果
page.addAll((List) result);
}
//返回结果
return page;
}
}
//...
}
上面的代码重点关注invocation.proceed()方法,第一次调用proceed()方法获取记录条数,第二次调用proceed()方法是执行原来目标对象的调用逻辑,但是此时的ms已经被修改(加上了分页信息),下面来看Invocation类的逻辑:
public class Invocation {
private Object target;
private Method method;
private Object[] args;
public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
this.target = target;
this.method = method;
this.args = args;
}
public Object getTarget() {
return target;
}
public Method getMethod() {
return method;
}
public Object[] getArgs() {
return args;
}
public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
return method.invoke(target, args);
}
}
Invocation类的代码非常简单,在拦截器中调用proceed()方法时,调用目标对象(也可能是代理对象)的方法,如果是目标对象,则直接调用目标对象方法的原有逻辑,如果是代理对象,则又会调用到 Plugin 类的invoke方法,知道最后调用目标对象的方法,完成拦截器链的调用,当然,这时,拦截器链还没有执行完成,当目标对象调用完成并返回,拦截器中interceptor方法层层返回,一次拦截器链的调用才算完成。
只看代码还是不够清晰,下面用时序的方式重新梳理一下拦截器链的构建与调用过程:
2.3拦截器链构建时序图
下面来看一下拦截器调用的时序图,为了形成拦截器链的效果,图中使用2个拦截器做演示:注意构建的时候先调用的MyInterceptor2,后调用的MyInterceptor1

需要注意的是上图中有2个Invocation对象,因为每调用一次interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args))方法就会创建一个新的Invocation对象
2.4拦截器链调用时序
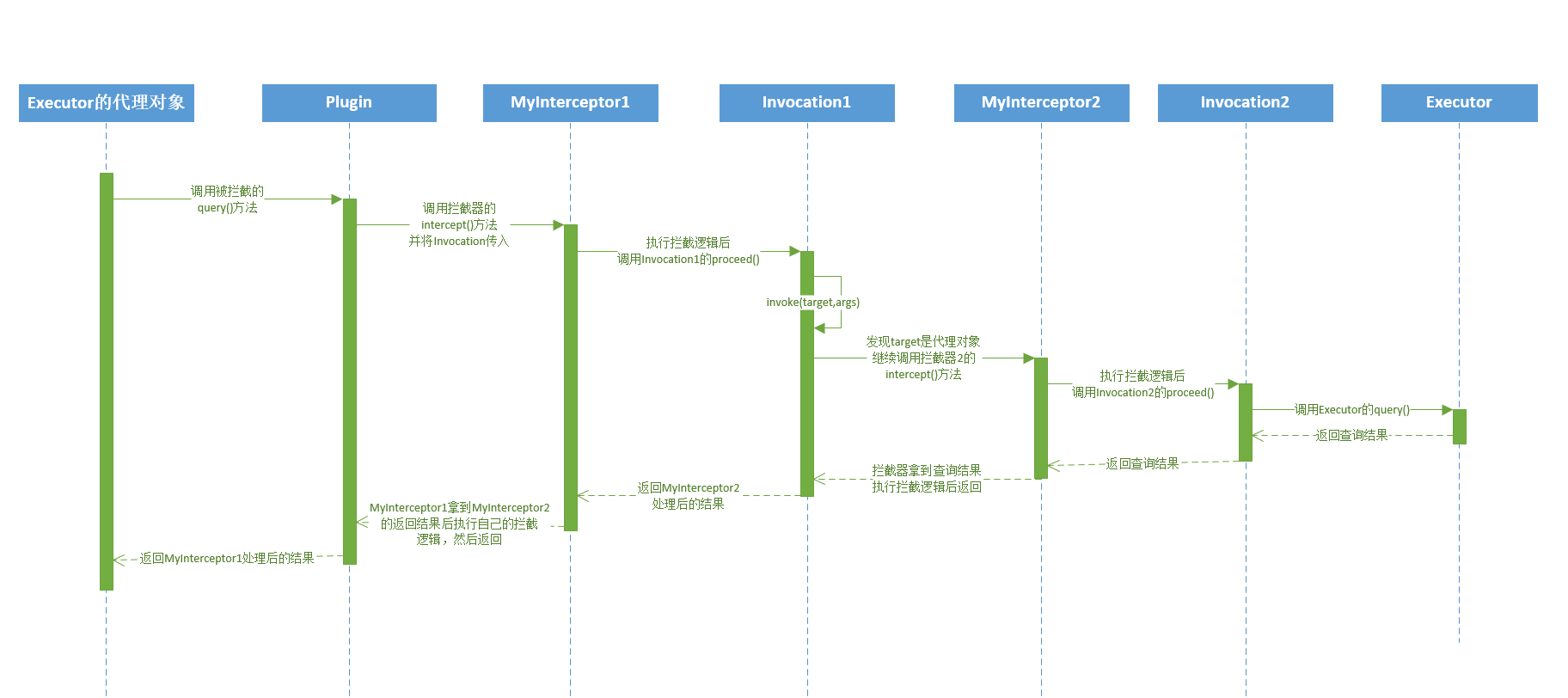
需要注意的是执行拦截器链时拦截器的调用顺序和构建的时候是相反的,构建中前面创建代理的拦截器后被调用,因为executor对象的代理对象被再次代理,只有调用executor代理对象的代理对象后,才能调用到更深层的executor代理对象,说起来比较绕,下面再简单画个图描述一下
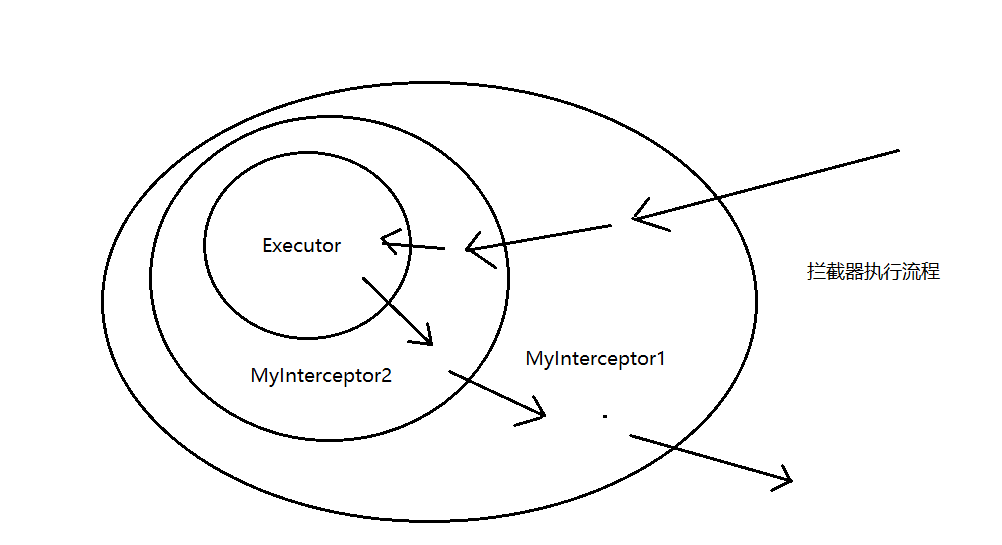
3.总结
mybatis中拦截器的设计还是非常巧妙的,可以说将jdk动态代理用到了极致,使用代理代理类的方法构建拦截器链。
构建拦截器链的3个核心对象:
InterceptorChain:持有所有拦截器的List,pluginAll()方法负责遍历拦截器集合,将创建的代理对象作为目标对象再次代理,形成拦截器链。
Interceptor(接口):实现了该接口的类就是一个拦截器,通过调用Plugin.wrap(target)方法获取目标类的代理对象,调用前需要先判断目标对象的类型是否是该拦截器需要拦截的对象,如果不是需要拦截的对象,则直接将原对象返回。
Plugin:负责创建目标对象的代理对象,该类实现了InvocationHandler接口,所以对目标类的所有调用都将调用该类的invoke方法。
拦截器执行中的3个核心对象:
Plugin:该类实现了InvocationHandler接口,在invoke方法中调用持有的Interceptor对象的intercetor()方法,同时传递创建的Invocation对象,以便拦截器内部调用Invocation对象的proceed()方法执行被代理对象的原有逻辑。
Interceptor(接口):实现了该接口的类就是一个拦截器,在intercept()方法内部完成拦截器的逻辑,调用Invocation对象的proceed()方法执行被代理对象的逻辑,注意:invocation.proceed()可以多次调用,分页插件中第一次调用proceed()方法查记录条数,第二次调用proceed()方法前通过invocation.getArgs()拿到调用目标对象的方法参数并修改sql实现分页功能。
Invocation:提供proceed()方法供拦截器调用,持有目标对象、调用的方法、方法参数并提供get方法,通过反射(method.invoke(target, args))实现对目标对象的调用。
以上就是mybatis拦截器原理的所有分析了。因个人能力有限,如果有错误之处,还请指出,谢谢!
Mybatis拦截器实现原理深度分析的更多相关文章
- MyBatis拦截器原理探究
MyBatis拦截器介绍 MyBatis提供了一种插件(plugin)的功能,虽然叫做插件,但其实这是拦截器功能.那么拦截器拦截MyBatis中的哪些内容呢? 我们进入官网看一看: MyBatis 允 ...
- 【公众号转载】MyBatis拦截器原理探究
MyBatis拦截器介绍 MyBatis提供了一种插件(plugin)的功能,虽然叫做插件,但其实这是拦截器功能.那么拦截器拦截MyBatis中的哪些内容呢? 我们进入官网看一看: MyBatis 允 ...
- Mybatis拦截器(插件实现原理)
在mybatis的mybatis.cfg.xml中插入: <plugins> <plugin interceptor="cn.sxt.util.PageIntercepto ...
- 【Mybatis】1、Mybatis拦截器学习资料汇总
MyBatis拦截器原理探究 http://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/mybatis-interceptor.html [myBatis]Mybatis中的拦截器 ...
- Mybatis拦截器介绍
拦截器的一个作用就是我们可以拦截某些方法的调用,我们可以选择在这些被拦截的方法执行前后加上某些逻辑,也可以在执行这些被拦截的方法时执行自己的逻辑而不再执行被拦截的方法.Mybatis拦截器设计的一个初 ...
- Mybatis拦截器实现分页
本文介绍使用Mybatis拦截器,实现分页:并且在dao层,直接返回自定义的分页对象. 最终dao层结果: public interface ModelMapper { Page<Model&g ...
- 基于Spring和Mybatis拦截器实现数据库操作读写分离
首先需要配置好数据库的主从同步: 上一篇文章中有写到:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuyiqing/p/10647133.html 为什么要进行读写分离呢? 通常的Web应用大多数 ...
- Spring异步调用原理及SpringAop拦截器链原理
一.Spring异步调用底层原理 开启异步调用只需一个注解@EnableAsync @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTI ...
- 通过spring抽象路由数据源+MyBatis拦截器实现数据库自动读写分离
前言 之前使用的读写分离的方案是在mybatis中配置两个数据源,然后生成两个不同的SqlSessionTemplate然后手动去识别执行sql语句是操作主库还是从库.如下图所示: 好处是,你可以人为 ...
随机推荐
- 一款用于绘制状态机转换图和流程图的web在线绘图工具
大型软件系统中离不开各类状态机的处理,日常工作中也涉及到各类事务处理流程:从表现力看文不如表,表不如图:因此日常工作中经常需要绘制各种状态机的状态转换图和流程图,以协助理解代码逻辑和各类事务处理流程等 ...
- SpringBoot正确打日志的姿势
前篇 Spring Boot 日志处理你还在用Logback? 本文简介 前篇侧重 Log4j2 的配置,本篇侧重统一日志处理的应用,以下包含 HTTP 请求的日志处理.Exception 异常日志处 ...
- how2heap 源码及输出
备个份,慢慢写总结 1 first_fit #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> i ...
- Redis过期--淘汰机制的解析和内存占用过高的解决方案
echo编辑整理,欢迎转载,转载请声明文章来源.欢迎添加echo微信(微信号:t2421499075)交流学习. 百战不败,依不自称常胜,百败不颓,依能奋力前行.--这才是真正的堪称强大!!! Red ...
- Hbase与Oracle的比较
http://blog.csdn.net/lucky_greenegg/article/details/47070565 转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/chay1227/arch ...
- python机器学习——感知器
最近在看机器学习相关的书籍,顺便把每天阅读的部分写出来和大家分享,共同学习探讨一起进步!作为机器学习的第一篇博客,我准备从感知器开始,之后会慢慢更新其他内容. 在实现感知器算法前,我们需要先了解一下神 ...
- m74 考试反思
这次不叫考试题解,叫做考试反思,为什么折磨说,因为这次犯的错误太多了! 事情还要从昨天晚上说起,昨晚放学,班主任来机房说我被子不合格,要停课反思 ###&&¥%#%¥@#%¥#@……% ...
- 2018年7月份JAVA开源软件TOP3
微信开发 Java SDK Weixin Java Tools 评分: 9.6 介绍: 信开发 Java 开发工具包(SDK),支持包括微信支付.微信开放平台.小程序.企业号/企业微信.公众号(包括服 ...
- SpringBoot RESTful api
一.REST简单介绍 REST代表Representational State Transfer,是一种URI风格,是一组架构约束条件和原则.REST风格服务调用就是解析URL请求,将请求由逻辑构建处 ...
- centos6的JDK安装
1. 通过如下命令查看当前操作系统是否存在JDK rpm -qa | grep java 如果出现以下内容说明你的操作系统存在jdk 2.那么依次通过如下命令进行删除它 rpm -e - -nodep ...
