Tensorflow[LSTM]
0.背景
通过对《tensorflow machine learning cookbook》第9章第3节"implementing_lstm"进行阅读,发现如下形式可以很方便的进行训练和预测,通过类进行定义,并利用了tf中的变量重用的能力,使得在训练阶段模型的许多变量,比如权重等,能够直接用在预测阶段。十分方便,不需要自己去做一些权重复制等事情。这里只是简单记录下这一小节的源码中几个概念性的地方。
# 定义LSTM模型
class LSTM_Model():
def __init__(self, embedding_size, rnn_size, batch_size, learning_rate,
training_seq_len, vocab_size, infer_sample=False):
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.rnn_size = rnn_size #LSTM单元隐层的神经元个数
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.infer_sample = infer_sample
self.learning_rate = learning_rate#学习率
if infer_sample:#如果是inference,则batch size设为1
self.batch_size = 1
self.training_seq_len = 1
else:
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.training_seq_len = training_seq_len
'''建立LSTM单元和初始化state'''
self.lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(self.rnn_size)
self.initial_state = self.lstm_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, tf.float32)
'''进行输入和输出的占位'''
self.x_data = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [self.batch_size, self.training_seq_len])
self.y_output = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [self.batch_size, self.training_seq_len])
with tf.variable_scope('lstm_vars'):
# Softmax 部分的权重
W = tf.get_variable('W', [self.rnn_size, self.vocab_size], tf.float32, tf.random_normal_initializer())
b = tf.get_variable('b', [self.vocab_size], tf.float32, tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
# Define Embedding
embedding_mat = tf.get_variable('embedding_mat', [self.vocab_size, self.embedding_size],
tf.float32, tf.random_normal_initializer())
embedding_output = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_mat, self.x_data)
rnn_inputs = tf.split(axis=1, num_or_size_splits=self.training_seq_len, value=embedding_output)
rnn_inputs_trimmed = [tf.squeeze(x, [1]) for x in rnn_inputs]
# If we are inferring (generating text), we add a 'loop' function
# Define how to get the i+1 th input from the i th output
def inferred_loop(prev, count):
# Apply hidden layer
prev_transformed = tf.matmul(prev, W) + b
# Get the index of the output (also don't run the gradient)
prev_symbol = tf.stop_gradient(tf.argmax(prev_transformed, 1))
# Get embedded vector
output = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_mat, prev_symbol)
return(output)
decoder = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.rnn_decoder
outputs, last_state = decoder(rnn_inputs_trimmed,
self.initial_state,
self.lstm_cell,
loop_function=inferred_loop if infer_sample else None)
# Non inferred outputs
output = tf.reshape(tf.concat(axis=1, values=outputs), [-1, self.rnn_size])
# Logits and output
self.logit_output = tf.matmul(output, W) + b
self.model_output = tf.nn.softmax(self.logit_output)
loss_fun = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example
loss = loss_fun([self.logit_output],[tf.reshape(self.y_output, [-1])],
[tf.ones([self.batch_size * self.training_seq_len])],
self.vocab_size)
self.cost = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / (self.batch_size * self.training_seq_len)
self.final_state = last_state
gradients, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(self.cost, tf.trainable_variables()), 4.5)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.learning_rate)
self.train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, tf.trainable_variables()))
def sample(self, sess, words=ix2vocab, vocab=vocab2ix, num=10, prime_text='thou art'):
state = sess.run(self.lstm_cell.zero_state(1, tf.float32))
word_list = prime_text.split()
for word in word_list[:-1]:
x = np.zeros((1, 1))
x[0, 0] = vocab[word]
feed_dict = {self.x_data: x, self.initial_state:state}
[state] = sess.run([self.final_state], feed_dict=feed_dict)
out_sentence = prime_text
word = word_list[-1]
for n in range(num):
x = np.zeros((1, 1))
x[0, 0] = vocab[word]
feed_dict = {self.x_data: x, self.initial_state:state}
[model_output, state] = sess.run([self.model_output, self.final_state], feed_dict=feed_dict)
sample = np.argmax(model_output[0])
if sample == 0:
break
word = words[sample]
out_sentence = out_sentence + ' ' + word
return(out_sentence)
上述代码就建立好了lstm的网络结构,其中想要说明的重点就是,如往常一样构建lstm结构,其中BasicLSTMCell中的权重和上述的lstm_vars一样是有variable_scope的
# 定义训练阶段的lstm
lstm_model = LSTM_Model(embedding_size, rnn_size, batch_size, learning_rate,
training_seq_len, vocab_size)
# 定义测试阶段的lstm
with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope(), reuse=True):
test_lstm_model = LSTM_Model(embedding_size, rnn_size, batch_size, learning_rate,
training_seq_len, vocab_size, infer_sample=True)
上述代码通过先建立一个训练的lstm结构,然后采用全局变量重用的形式,使得inference的lstm中的变量都方便的使用train阶段的变量。
下面是训练和inference的代码
# Train model
train_loss = []
iteration_count = 1
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Shuffle word indices
random.shuffle(batches)
# Create targets from shuffled batches
targets = [np.roll(x, -1, axis=1) for x in batches]
# Run a through one epoch
print('Starting Epoch #{} of {}.'.format(epoch+1, epochs))
# Reset initial LSTM state every epoch
state = sess.run(lstm_model.initial_state)
for ix, batch in enumerate(batches):
training_dict = {lstm_model.x_data: batch, lstm_model.y_output: targets[ix]}
'''每个batch的LSTM中初始化状态c和h,其状态被赋值为上一个batch的LSTM的最终状态的c和h '''
'''也就是前后相接 '''
c, h = lstm_model.initial_state
training_dict[c] = state.c
training_dict[h] = state.h
temp_loss, state, _ = sess.run([lstm_model.cost, lstm_model.final_state, lstm_model.train_op],
feed_dict=training_dict)
train_loss.append(temp_loss)
# Print status every 10 gens
if iteration_count % 10 == 0:
summary_nums = (iteration_count, epoch+1, ix+1, num_batches+1, temp_loss)
print('Iteration: {}, Epoch: {}, Batch: {} out of {}, Loss: {:.2f}'.format(*summary_nums))
if iteration_count % eval_every == 0:
for sample in prime_texts:
print(test_lstm_model.sample(sess, ix2vocab, vocab2ix, num=10, prime_text=sample))
iteration_count += 1
在后续的训练中只要正常训练和测试即可,其中inference阶段时候lstm中的权重,全都会自动的从训练阶段直接拿来用,在"site-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/rnn_cell_impl.py"的1240行:
scope = vs.get_variable_scope()
with vs.variable_scope(scope) as outer_scope:
weights = vs.get_variable(
_WEIGHTS_VARIABLE_NAME, [total_arg_size, output_size],
dtype=dtype,
initializer=kernel_initializer)
如上述代码中所示,当采用了全局变量重用功能之后,就无需手动去复制train好的权重到inference阶段了。

图0.1 graph图,左边红框是train的结构;右边红框是inference的结构
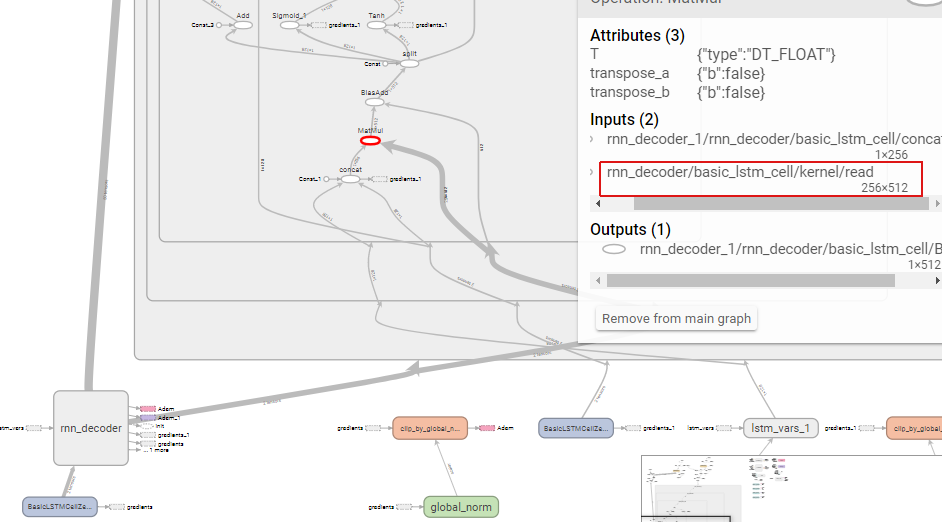
图0.2 基于图0.1的局部放大
Tensorflow[LSTM]的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow LSTM 注意力机制图解
TensorFlow LSTM Attention 机制图解 深度学习的最新趋势是注意力机制.在接受采访时,现任OpenAI研究主管的Ilya Sutskever提到,注意力机制是最令人兴奋的进步之一 ...
- TensorFlow-Bitcoin-Robot:一个基于 TensorFlow LSTM 模型的 Bitcoin 价格预测机器人
简介 TensorFlow-Bitcoin-Robot:一个基于 TensorFlow LSTM 模型的 Bitcoin 价格预测机器人. 文章包括一下几个部分: 1.为什么要尝试做这个项目? 2.为 ...
- Tensorflow LSTM实现
Tensorflow[LSTM] 0.背景 通过对<tensorflow machine learning cookbook>第9章第3节"implementing_lstm ...
- TensorFlow-Bitcoin-Robot:一个基于 TensorFlow LSTM 模型的 Bitcoin 价格预测机器人。
简介 TensorFlow-Bitcoin-Robot:一个基于 TensorFlow LSTM 模型的 Bitcoin 价格预测机器人. 文章包括一下几个部分: 1.为什么要尝试做这个项目? 2.为 ...
- 芝麻HTTP:TensorFlow LSTM MNIST分类
本节来介绍一下使用 RNN 的 LSTM 来做 MNIST 分类的方法,RNN 相比 CNN 来说,速度可能会慢,但可以节省更多的内存空间. 初始化 首先我们可以先初始化一些变量,如学习率.节点单元数 ...
- tflearn tensorflow LSTM predict sin function
from __future__ import division, print_function, absolute_import import tflearn import numpy as np i ...
- tensorflow LSTM+CTC使用详解
最近用tensorflow写了个OCR的程序,在实现的过程中,发现自己还是跳了不少坑,在这里做一个记录,便于以后回忆.主要的内容有lstm+ctc具体的输入输出,以及TF中的CTC和百度开源的warp ...
- TensorFlow——LSTM长短期记忆神经网络处理Mnist数据集
1.RNN(Recurrent Neural Network)循环神经网络模型 详见RNN循环神经网络:https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6509630.html 2. ...
- TensorFlow入门(五)多层 LSTM 通俗易懂版
欢迎转载,但请务必注明原文出处及作者信息. @author: huangyongye @creat_date: 2017-03-09 前言: 根据我本人学习 TensorFlow 实现 LSTM 的经 ...
随机推荐
- virtualenv的使用及pip常用命令
一.virtualenv 1.用途: virtualenv------用来建立一个虚拟的python环境,一个专属于项目的python环境.用virtualenv 来保持一个干净的环境非常有用. 例如 ...
- Chrome调试本地文件无法使用window.opener对象进行窗口间值传递
今天在百度BAE上建了个应用,svn上传后发现页面间互调有些问题,几经查询发现: (1)IE下正常的window.opener.object1.object2页面间对象访问方法在Chrome下不能使用 ...
- Java数据解析---PULL
安卓和JAVA解析xml文件的三种方式: 1.PULL解析 2.SAX解析 3.DOM解析 三者各有所长,依情况选择解析方式 1.PULL和SAX均采用流式解析,意味着只能从头读到底,无法像DOM解析 ...
- MIPS 安全相关paper阅读笔记
前言 论文来自 https://cyber-itl.org/2018/12/07/a-look-at-home-routers-and-linux-mips.html Linux_MIPS_mis ...
- Android手势密码--设置和校验
private void setGesturePassword() { toggleMore.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new CompoundButton.OnCheck ...
- (后端)注意hibernate中对象的set方法修改数据库
2017-10-16 公司里面其他人发现了一个问题,五粮液金品库存出现了问题,删除了库存也没还回来,一瓶一千多.而且在我的功能块,在我看出货详情的时候,诡异的事情发生了,第一眼看上去没问题呀,刷新了一 ...
- solr搜索引擎配置使用mongodb作为数据源
环境说明: 操作系统:由于是使用的docker直接拉取的镜像部署的,系统是LINUX环境 mongodb: 4.0.3 solr: 7.5.0 python: 3.5 配置mongodb 1.拉取mo ...
- maven(三):maven项目结构及其运行机制
在上一篇中讲了如何创建maven项目,现在回到那个项目 项目结构 src/main/java:java代码目录 src/main/resources:资源目录,比如spring.xml文件,prope ...
- python中remove的一些坑
前几天,使用python时遇到这么一个需求,删除一个列表中值为1的元素.我寻思着使用remove方法,但是remove方法只会删除第一个,于是我使用for循环去删除.代码和运行结果如下: 当时这个结果 ...
- Linux自制编译内核
今天我们来自己学习编译内核并使用它.自制内核是个人定制版,定制自己专属的内核环境. 我们先看看编译步骤有哪些: 步骤: 1.# tar xf linux-3.10.37.tar.xz -C /usr/ ...
