netty reactor线程模型分析
netty4线程模型
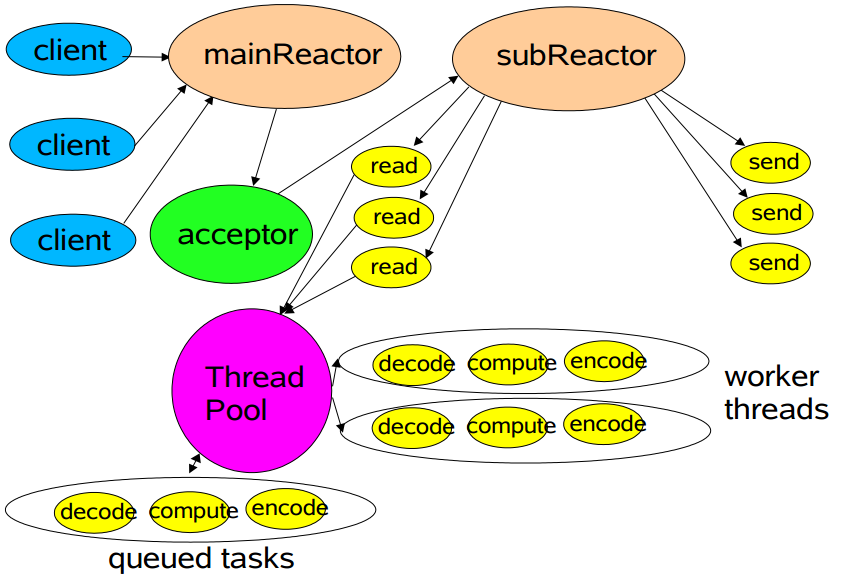
ServerBootstrap http示例
// Configure the server.
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup(); try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.channel(EpollServerSocketChannel.class);
b.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
b.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
// .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new HttpHelloWorldServerInitializer(sslCtx)); Channel ch = b.bind(PORT).sync().channel();
/* System.err.println("Open your web browser and navigate to " +
(SSL? "https" : "http") + "://127.0.0.1:" + PORT + '/');*/
ch.closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
绑定过程:
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.executor = channel.eventLoop();
}
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
});
return promise;
}
}
初始化过程:
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
final Channel channel = channelFactory().newChannel();
try {
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
ChannelFuture regFuture = group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
channel.close();
} else {
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
// If we are here and the promise is not failed, it's one of the following cases:
// 1) If we attempted registration from the event loop, the registration has been completed at this point.
// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now because the channel has been registered.
// 2) If we attempted registration from the other thread, the registration request has been successfully
// added to the event loop's task queue for later execution.
// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now:
// because bind() or connect() will be executed *after* the scheduled registration task is executed
// because register(), bind(), and connect() are all bound to the same thread.
return regFuture;
}
ServerBootStrap的初始化过程:
@Override
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = options();
synchronized (options) {
channel.config().setOptions(options);
} final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = attrs();
synchronized (attrs) {
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
AttributeKey<Object> key = (AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey();
channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue());
}
} ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline(); final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;
final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions;
final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs;
synchronized (childOptions) {
currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(childOptions.size()));
}
synchronized (childAttrs) {
currentChildAttrs = childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(childAttrs.size()));
} p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
接收器ServerBootstrapAcceptor
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg; child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler); for (Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object> e: childOptions) {
try {
if (!child.config().setOption((ChannelOption<Object>) e.getKey(), e.getValue())) {
logger.warn("Unknown channel option: " + e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to set a channel option: " + child, t);
}
} for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
} try {
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
ThreadPerChannelEventLoopGroup实现注册
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
if (channel == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("channel");
}
try {
EventLoop l = nextChild();
return l.register(channel, new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, l));
} catch (Throwable t) {
return new FailedChannelFuture(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE, t);
}
}
获取子eventLoop
private EventLoop nextChild() throws Exception {
if (shuttingDown) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("shutting down");
}
EventLoop loop = idleChildren.poll();
if (loop == null) {
if (maxChannels > 0 && activeChildren.size() >= maxChannels) {
throw tooManyChannels;
}
loop = newChild(childArgs);
loop.terminationFuture().addListener(childTerminationListener);
}
activeChildren.add(loop);
return loop;
}
产生新子eventLoop(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java)
/**
* Create a new instance
*
* @param parent the {@link EventExecutorGroup} which is the parent of this instance and belongs to it
* @param executor the {@link Executor} which will be used for executing
* @param addTaskWakesUp {@code true} if and only if invocation of {@link #addTask(Runnable)} will wake up the
* executor thread
*/
protected SingleThreadEventExecutor(EventExecutorGroup parent, Executor executor, boolean addTaskWakesUp) {
super(parent); if (executor == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("executor");
} this.addTaskWakesUp = addTaskWakesUp;
this.executor = executor;
taskQueue = newTaskQueue();
}
其执行方法(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java):
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
} boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
if (inEventLoop) {
addTask(task);
} else {
startThread();
addTask(task);
if (isShutdown() && removeTask(task)) {
reject();
}
} if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
启动处理线程(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java):
private void startThread() {
if (STATE_UPDATER.get(this) == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
doStartThread();
}
}
}
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception from an event executor: ", t);
} finally {
for (;;) {
int oldState = STATE_UPDATER.get(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this);
if (oldState >= ST_SHUTTING_DOWN || STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, oldState, ST_SHUTTING_DOWN)) {
break;
}
}
// Check if confirmShutdown() was called at the end of the loop.
if (success && gracefulShutdownStartTime == 0) {
logger.error("Buggy " + EventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + " implementation; " +
SingleThreadEventExecutor.class.getSimpleName() + ".confirmShutdown() must be called " +
"before run() implementation terminates.");
}
try {
// Run all remaining tasks and shutdown hooks.
for (;;) {
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
try {
cleanup();
} finally {
STATE_UPDATER.set(SingleThreadEventExecutor.this, ST_TERMINATED);
threadLock.release();
if (!taskQueue.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn(
"An event executor terminated with " +
"non-empty task queue (" + taskQueue.size() + ')');
}
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
}
}
});
}
其中的run方法由其子类(DefaultEventLoop,EpollEventLoop,NioEventLoop,ThreadPerChannelEventLoop)各种实现,以NioEventLoop为例:
@Override
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
boolean oldWakenUp = wakenUp.getAndSet(false);
try {
if (hasTasks()) {
selectNow();
} else {
select(oldWakenUp); // 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' is always evaluated
// before calling 'selector.wakeup()' to reduce the wake-up
// overhead. (Selector.wakeup() is an expensive operation.)
//
// However, there is a race condition in this approach.
// The race condition is triggered when 'wakenUp' is set to
// true too early.
//
// 'wakenUp' is set to true too early if:
// 1) Selector is waken up between 'wakenUp.set(false)' and
// 'selector.select(...)'. (BAD)
// 2) Selector is waken up between 'selector.select(...)' and
// 'if (wakenUp.get()) { ... }'. (OK)
//
// In the first case, 'wakenUp' is set to true and the
// following 'selector.select(...)' will wake up immediately.
// Until 'wakenUp' is set to false again in the next round,
// 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' will fail, and therefore
// any attempt to wake up the Selector will fail, too, causing
// the following 'selector.select(...)' call to block
// unnecessarily.
//
// To fix this problem, we wake up the selector again if wakenUp
// is true immediately after selector.select(...).
// It is inefficient in that it wakes up the selector for both
// the first case (BAD - wake-up required) and the second case
// (OK - no wake-up required). if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
} cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
processSelectedKeys();
runAllTasks();
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime(); processSelectedKeys(); final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
} if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception in the selector loop.", t); // Prevent possible consecutive immediate failures that lead to
// excessive CPU consumption.
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore.
}
}
}
}
运行所有任务(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java)
/**
* Poll all tasks from the task queue and run them via {@link Runnable#run()} method. This method stops running
* the tasks in the task queue and returns if it ran longer than {@code timeoutNanos}.
*/
protected boolean runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos) {
fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue();
Runnable task = pollTask();
if (task == null) {
return false;
} final long deadline = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime() + timeoutNanos;
long runTasks = 0;
long lastExecutionTime;
for (;;) {
try {
task.run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("A task raised an exception.", t);
} runTasks ++; // Check timeout every 64 tasks because nanoTime() is relatively expensive.
// XXX: Hard-coded value - will make it configurable if it is really a problem.
if ((runTasks & 0x3F) == 0) {
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();
if (lastExecutionTime >= deadline) {
break;
}
} task = pollTask();
if (task == null) {
lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();
break;
}
} this.lastExecutionTime = lastExecutionTime;
return true;
}
小结
本文从一个简单的示例程序,一步步分析netty4的线程模型,从ServerBootstrapAcceptor到SingleThreadEventExecutor的源码,环环相扣,可以根据上面的分析链理解
一个请求过来后,netty的处理流程。
netty reactor线程模型分析的更多相关文章
- Netty Reactor 线程模型笔记
引用: https://www.cnblogs.com/TomSnail/p/6158249.html https://www.cnblogs.com/heavenhome/articles/6554 ...
- 【Netty源码分析】Reactor线程模型
1. 背景 1.1. Java线程模型的演进 1.1.1. 单线程 时间回到十几年前,那时主流的CPU都还是单核(除了商用高性能的小机),CPU的核心频率是机器最重要的指标之一. 在Java领域当时比 ...
- Netty源码分析之Reactor线程模型详解
上一篇文章,分析了Netty服务端启动的初始化过程,今天我们来分析一下Netty中的Reactor线程模型 在分析源码之前,我们先分析,哪些地方用到了EventLoop? NioServerSocke ...
- 面试官:Netty的线程模型可不只是主从多Reactor这么简单
笔者看来Netty的内核主要包括如下图三个部分: 其各个核心模块主要的职责如下: 内存管理 主要提高高效的内存管理,包含内存分配,内存回收. 网通通道 复制网络通信,例如实现对NIO.OIO等底层JA ...
- 深入Netty逻辑架构,从Reactor线程模型开始
本文是Netty系列第6篇 上一篇文章我们从一个Netty的使用Demo,了解了用Netty构建一个Server服务端应用的基本方式.并且从这个Demo出发,简述了Netty的逻辑架构,并对Chann ...
- Netty高性能之Reactor线程模型
Netty是一个高性能.异步事件驱动的NIO框架,它提供了对TCP.UDP和文件传输的支持,作为一个异步NIO框架,Netty的所有IO操作都是异步非阻塞的,通过Future-Listener机制,用 ...
- Reactor 线程模型以及在netty中的应用
这里我们需要理解的一点是Reactor线程模型是基于同步非阻塞IO实现的.对于异步非阻塞IO的实现是Proactor模型. 一 Reactor 单线程模型 Reactor单线程模型就是指所有的IO操作 ...
- Netty是什么,Netty为什么速度这么快,线程模型分析
哈喽!大家好,我是小奇,一位热爱分享的程序员 小奇打算以轻松幽默的对话方式来分享一些技术,如果你觉得通过小奇的文章学到了东西,那就给小奇一个赞吧 文章持续更新 一.前言 书接上回,现在下着大雨看来是去 ...
- Netty IO线程模型学习总结
Netty框架的 主要线程是IO线程.线程模型的好坏直接决定了系统的吞吐量.并发性和安全性. Netty的线程模型遵循了Reactor的基础线程模型.以下我们先一起看下该模型 Reactor线程模型 ...
随机推荐
- 63.note.js之 Mongodb在Nodejs上的配置及session会话机制的实现
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/alvin_xp/p/4751784.html 1.第一步安装mongodb数据库,这直接官网下载,这里不介绍. 2.也可以使用npm实现直接下载 ...
- Kinect 开发 —— Kinect for windows SDK
开发 —— 基本的SDK和Windows 编程技巧(彩色图像视频流,深度图像视频流的采集,骨骼跟踪,音频处理,语音识别API) 深度数据,就是Kinect的精髓和灵魂,很多问题都转换为深度图像的模式识 ...
- mvn本地执行java程序
mvn -f pom.xml compile exec:java -Dexec.classpathScope=compile -Dexec.mainClass=storm.starter.WordCo ...
- HDU 4699 Editor 维护栈
维护两个栈,分别存光标前和光标后的数 再维护前缀和的栈 和 前缀和最大值的栈 注意一下左移,右移,删除到顶了就不操作了 5个操作 I x : 光标处插入x -----> s1.push(x) ...
- Vue给元素添加样式
Vue中使用样式 绑定css 数组 <style> .red{ color:red } .thin{ font-size:18px } </style> <h1 :cla ...
- chkconfig---检查设置系统服务
chkconfig命令 chkconfig命令检查.设置系统的各种服务.这是Red Hat公司遵循GPL规则所开发的程序,它可查询操作系统在每一个执行等级中会执行哪些系统服务,其中包括各类常驻服务 ...
- 清除celery 任务队列
celery 有密码的时候 清除任务 redis-cli -h host -p port -a password -n 11 ltrim transcode 0 196 没有密码的时候 redis-c ...
- Python-Flask项目开发--为什么需要搭建虚拟环境?
在使用python开发过程中,需要使用到某些工具包/框架等,需要联网下载. 例如,联网安装Flask框架flask-0.10.1版本:pip install flask==0.10.1 此时, ...
- Drupal 关于节点(nodes)的理解
在 Drupal 构建的站点中.全部的内容都是以节点形式存储的,一个节点能够是公布的不论什么一个内容,比方说一个单面(page).一个投票(Poll).一篇文章(article).论坛主题(forum ...
- 35.Node.js GET/POST请求
转自:http://www.runoob.com/nodejs/nodejs-module-system.html 在很多场景中,我们的服务器都需要跟用户的浏览器打交道,如表单提交. 表单提交到服务器 ...
