HDU - 3407 - String-Matching Automata
先上题目:
String-Matching Automata
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 215 Accepted Submission(s): 140
Σ is the input alphabet (a finite nonempty set of symbols).
S is a finite nonempty set of states.
s0 is an element in S designated as the initial state.
δ is a function δ: S × Σ → S known as the transition function.
F is a (possibly empty) subset of S whose elements are designated as the final states.
An FSA with the above description operates as follows:
At the beginning, the automaton starts in the initial state s0.
The automaton continuously reads symbols from its input, one symbol at a time, and transits between states according to the transition function δ. To be specific, let s be the current state and w the symbol just read, the automaton moves to the state given by δ(s, w).
When the automaton reaches the end of the input, if the current state belongs to F, the string consisting sequentially of the symbols read by the automaton is declared accepted, otherwise it is declared rejected.
Just as the name implies, a string-matching automaton is a FSA that is used for string matching and is very efficient: they examine each character exactly once, taking constant time per text character. The matching time used (after the automaton is built) is therefore Θ(n). However, the time to build the automaton can be large.
Precisely, there is a string-matching automaton for every pattern P that you search for in a given text string T. For a given pattern of length m, the corresponding automaton has (m + 1) states {q0, q1, …, qm}: q0 is the start state, qm is the only final state, and for each i in {0, 1, …, m}, if the automaton reaches state qi, it means the length of the longest prefix of P that is also a suffix of the input string is i. When we reaches state qm, it means P is a suffix of the currently input string, which suggest we find an occurrence of P.
The following graph shows a string-matching automaton for the pattern “ababaca”, and illustrates how the automaton works given an input string “abababacaba”.
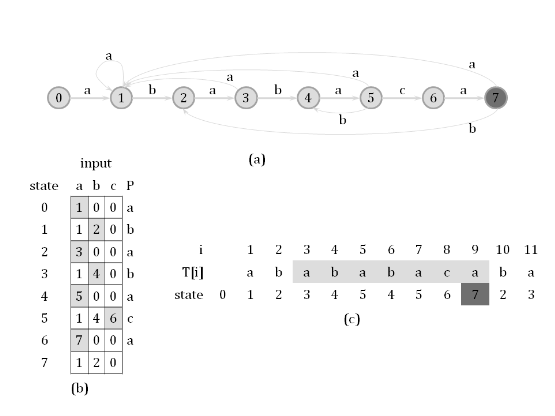
Apparently, the matching process using string-matching automata is quite simple (also efficient). However, building the automaton efficiently seems to be tough, and that’s your task in this problem.
0
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define MAX 10002
using namespace std; struct Trie{
int next[MAX][],fail[MAX],end[MAX],num[MAX][];
int root,L; int newnode(){
for(int i=;i<;i++){ next[L][i]=-; num[L][i]=;}
end[L++]=;
return L-;
}
void init(){
L=; root=newnode();
} void insert(char buf[]){
int len=strlen(buf);
int now = root;
for(int i=;i<len;i++){
if(next[now][buf[i]-'a']==-){
next[now][buf[i]-'a']=newnode(); }
now=next[now][buf[i]-'a'];
}
end[now]++;
} void build(){
queue<int> Q;
fail[root]=root;
for(int i=;i<;i++){
if(next[root][i]==-) next[root][i]=root;
else{
fail[next[root][i]]=root;
Q.push(next[root][i]);
}
}
while(!Q.empty()){
int now=Q.front();
Q.pop();
for(int i=;i<;i++){
if(next[now][i]==-) next[now][i]=next[fail[now]][i];
else{
fail[next[now][i]]=next[fail[now]][i];
Q.push(next[now][i]);
}
}
}
} void print(char buf[]){
int len=strlen(buf);
int now=root;
for(int i=;i<=len;i++){
printf("%d",i);
for(int j=;j<;j++) printf(" %d",next[now][j]);
printf("\n");
now=next[now][buf[i]-'a'];
}
}
}; Trie ac;
char s[MAX]; int main()
{
//freopen("data.txt","r",stdin);
while(scanf("%s",s),strcmp(s,"")){
ac.init();
ac.insert(s);
ac.build();
ac.print(s);//printf("\n");
}
return ;
}
/*3407*/
HDU - 3407 - String-Matching Automata的更多相关文章
- Binary String Matching
问题 B: Binary String Matching 时间限制: 3 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB提交: 4 解决: 2[提交][状态][讨论版] 题目描述 Given two strin ...
- NYOJ之Binary String Matching
Binary String Matching 时间限制:3000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:3 描述 Given two strings A and B, whose a ...
- ACM Binary String Matching
Binary String Matching 时间限制:3000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:3 描述 Given two strings A and B, whose alp ...
- 南阳OJ----Binary String Matching
Binary String Matching 时间限制:3000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:3 描述 Given two strings A and B, whose alp ...
- Binary String Matching(kmp+str)
Binary String Matching 时间限制:3000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:3 描述 Given two strings A and B, whose alp ...
- Aho - Corasick string matching algorithm
Aho - Corasick string matching algorithm 俗称:多模式匹配算法,它是对 Knuth - Morris - pratt algorithm (单模式匹配算法) 形 ...
- [POJ] String Matching
String Matching Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 4074 Accepted: 2077 D ...
- String Matching Content Length
hihocoder #1059 :String Matching Content Length 时间限制:10000ms 单点时限:1000ms 内存限制:256MB 描述 We define the ...
- HDU 3374 String Problem (KMP+最大最小表示)
HDU 3374 String Problem (KMP+最大最小表示) String Problem Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory ...
随机推荐
- bzoj1202: [HNOI2005]狡猾的商人(并查集 差分约束)
1202: [HNOI2005]狡猾的商人 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 4127 Solved: 1981[Submit][Sta ...
- knockout 和mvc4结合使用
Knockout (或者Knockout.js ,KnockoutJS)是一个开源的JavaScript库,网址为www.knockoutjs.com.Knockout语法简洁.可读性好,能轻松实现与 ...
- Linux学习系列八:操作网口
一些相对高性能的单片机会带以太网接口,网口在MCU里算是比较复杂的外设了,因为它涉及到网络协议栈,通常情况下网络协议栈会运行在一个RTOS中,所以对普通单片机开发者来说网口使用起来相对难度较大一些.在 ...
- linux守护进程的编写
linux监控一个进程进行 代码如下: #!/bin/sh cd /home/autoprocess/ auto=`pgrep -f autoProcessNew.php | wc -l` if [ ...
- c语言 error C4996: 'strupr': The POSIX name for this item is deprecated. Instead, use the ISO C and C++ conformant name
问题: 在使用visual studio 2013,进行调试执行代码时,出现如下错误: error C4996: 'strupr': The POSIX name for this item is d ...
- 线段树+树状数组+贪心 HDOJ 5338 ZZX and Permutations
题目传送门 /* 题意:不懂... 线段树+树状数组+贪心:贪心从第一位开始枚举,一个数可以是循环节的末尾或者在循环节中,循环节(循环节内部是后面的换到前面,最前面的换到最后面).线段树维护最大值,树 ...
- spring controller接口中,用pojo对象接收页面传递的参数,发现spring在对pojo对象赋值时,有一定顺序的问题
1.我的项目中的实体类都继承了基类entityBase,里面封装了分页的一些属性,pageindex.pagesize.pagerownum等. 2.思路是页面可以灵活的传递分页参数,比如当前页pag ...
- 367 Valid Perfect Square 有效的完全平方数
给定一个正整数 num,编写一个函数,如果 num 是一个完全平方数,则返回 True,否则返回 False.注意:不要使用任何内置的库函数,如 sqrt.示例 1:输入: 16输出: True示例 ...
- jquery中有关cookie的使用简要说明
jquery.cookie.js 的配置 首先包含jQuery的库文件,在后面包含 jquery.cookie.js 的库文件. <script type="text/javascri ...
- 关于sql的case when用法简述
刚入手公司项目,需要添加一个功能,用到了SQL的case when以及concat SELECT eve.cc, eve.sc, case concat(cc,sc) ' THEN '' ' THEN ...
