模拟FCFS调度算法(先来先服务)
文章目录
一、FCFS的介绍
先来先服务的调度算法:最简单的调度算法,既可以用于作业调度 ,也可以用于程序调度,当作业调度中采用该算法时,系统将按照作业到达的先后次序来进行调度,优先从后备队列中,选择一个或多个位于队列头部的作业,把他们调入内存,分配所需资源、创建进程,然后放入“就绪队列”,直到该进程运行到完成或发生某事件堵塞后,进程调度程序才将处理机分配给其他进程。
简单了说就是如同名字 “先来先服务” ;
二、代码演示
package com.zsh.blog;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:抱着鱼睡觉的喵喵
* @date:2021/3/19
* @description:
*/
public class SimulateSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
SimulateFCFS simulateFCFS = new SimulateFCFS();
boolean flag = true;
char at = ' ';
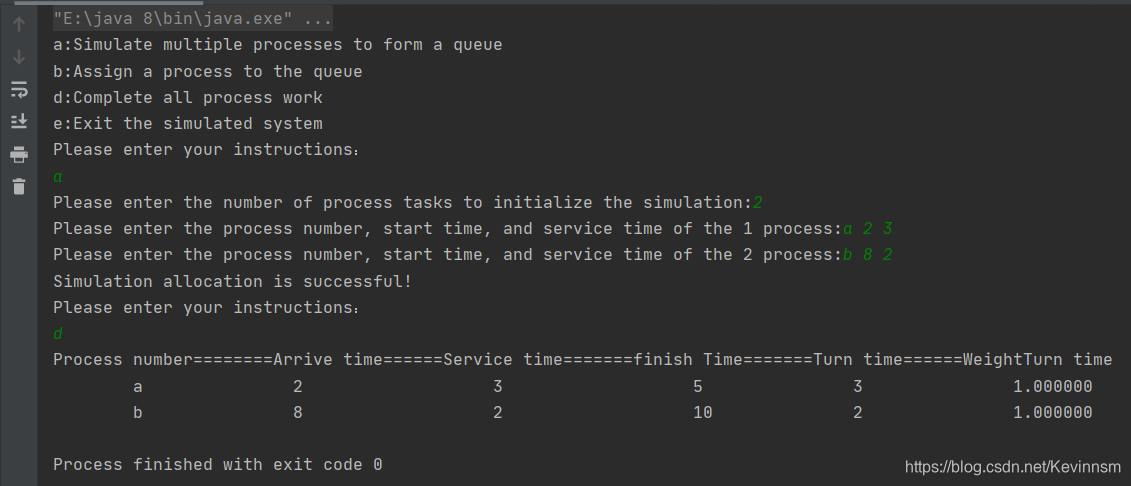
System.out.println("a:Simulate multiple processes to form a queue");
System.out.println("b:Assign a process to the queue");
System.out.println("d:Complete all process work");
System.out.println("e:Exit the simulated system");
while (flag) {
System.out.println("Please enter your instructions:");
at = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (at) {
case 'a':
simulateFCFS.createQueue();
break;
case 'b':
simulateFCFS.assignProcess();
break;
case 'd':
simulateFCFS.finishAllProcessTask();
return;
case 'e':
System.out.println("Simulated is end~");
return;
default:
System.out.println("Your input is wrong, please re-enter!");
break;
}
}
}
}
class Queue {
int arrTime; //timeOfArrival
int serviceTime; //timeOfService
int finishTime; //timeOfComplish
int turnTime; //timeOfTurnaround
double weightTurnTime; //timeOfWeightTurnaround
String processName; //process number
Queue next;
public Queue(int arrTime, int serviceTime, String processName) {
this.arrTime = arrTime;
this.serviceTime = serviceTime;
this.processName = processName;
}
public Queue() {
}
}
/**
* Simulate FCFS algorithm class
*/
class SimulateFCFS {
private Queue head = new Queue(-1, -1, null);
private int timer = 0;
private Queue tail = head;
public void createQueue() {
Queue arr = null;
Queue temp = head;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.printf("Please enter the number of process tasks to initialize the simulation:");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.printf("Please enter the process number, start time, and service time of the %d process:",i);
arr = new Queue();
keyBordInput(arr, scanner);
calTime(arr);
temp.next = arr;
temp = arr;
}
this.tail = arr;
System.out.println("Simulation allocation is successful!");
}
/**
* Completion time of calculation process - Turnaround time - Weighted turnaround time
* @param arr
*/
public void calTime(Queue arr) {
Queue temp = arr;
if (this.timer < temp.arrTime) {
this.timer = arr.arrTime;
} else {
if (timer == 0) {
this.timer = temp.arrTime;
}
}
temp.finishTime = temp.serviceTime + this.timer;
temp.turnTime = temp.finishTime - temp.arrTime;
temp.weightTurnTime = (temp.turnTime * 1.0) / (temp.serviceTime * 1.0);
this.timer += temp.serviceTime;
}
/**
* Process number,arrival time,service time entered from the keyboard
* @param arr
* @param scanner
*/
public void keyBordInput(Queue arr, Scanner scanner) {
arr.processName = scanner.next();
arr.arrTime = scanner.nextInt();
arr.serviceTime = scanner.nextInt();
}
/**
* Assign a process to the queue
*/
public void assignProcess() {
Queue newProcess = new Queue();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.printf("Please enter the add process number,start time,and service time of the process:");
keyBordInput(newProcess, scanner);
calTime(newProcess);
this.tail.next = newProcess;
this.tail = newProcess;
}
/**
* Complish a task of process from the queue
*/
// public void finishProcessTask() {
// Queue workingProcess = head;
//
// }
/**
* Complish all task of process from the queue
*/
public void finishAllProcessTask() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Queue cur = head.next;
System.out.println("Process number========Arrive time======Service time=======finish Time=======Turn time======WeightTurn time");
while (true) {
System.out.printf("\t\t%s\t\t\t\t%d\t\t\t\t\t%d\t\t\t\t\t%d\t\t\t\t%d\t\t\t\t%f",cur.processName,cur.arrTime,cur.serviceTime,cur.finishTime,cur.turnTime,cur.weightTurnTime);
System.out.println();
if (cur.next == null) {
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("Queue is null!");
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
三、代码分析
1.使用节点模拟进程
因为需要计算完成时间、周转时间、带权周转时间,所以需要事先给出每个进程到达时间和服务时间
模拟时至少需要以下几个属性(Queue类对象模拟进程)
class Queue {
int arrTime; //timeOfArrival
int serviceTime; //timeOfService
int finishTime; //timeOfComplish
int turnTime; //timeOfTurnaround
double weightTurnTime; //timeOfWeightTurnaround
String processName; //process number
Queue next;
public Queue(int arrTime, int serviceTime, String processName) {
this.arrTime = arrTime;
this.serviceTime = serviceTime;
this.processName = processName;
}
public Queue() {
}
}
2.SimulateFCFS(核心模拟FCFS类)
以下分析核心模拟类
3.创建一个节点为n的队列(模拟就绪队列)
public void createQueue() {
Queue arr = null;
Queue temp = head;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.printf("Please enter the number of process tasks to initialize the simulation:");
int n = scanner.nextInt(); //创建节点数为n的队列
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.printf("Please enter the process number, start time, and service time of the %d process:",i);
arr = new Queue();
keyBordInput(arr, scanner);//这个自定义的函数主要用来输入进程的到达时间和服务时间
calTime(arr); //该自定义函数用来计算完成时间、周转时间、带权周转时间
temp.next = arr;
temp = arr; //进行节点连接
}
this.tail = arr;
System.out.println("Simulation allocation is successful!");
}
4.核心计算分析
(如果是第一个进程) 完成时间 = 服务时间 + 到达时间
如果是n>1的进程就要考虑前面进程所花费的时间和该进程到达时间的长短问题。如果前面所花费的完成时间大于该进程的到达进程,则(完成时间 = 服务时间+上一个进程的完成时间)
反之则是 (完成时间= 服务时间+到达时间)
//timer是全局变量,用来计算完成时间(解决上面的问题)
public void calTime(Queue arr) {
Queue temp = arr;
if (this.timer < temp.arrTime) {
this.timer = arr.arrTime;
} else {
if (timer == 0) {
this.timer = temp.arrTime;
}
}
temp.finishTime = temp.serviceTime + this.timer;
temp.turnTime = temp.finishTime - temp.arrTime;
temp.weightTurnTime = (temp.turnTime * 1.0) / (temp.serviceTime * 1.0);
this.timer += temp.serviceTime;
}
5.输入到达时间和服务时间(模拟进程到达和服务)
public void keyBordInput(Queue arr, Scanner scanner) {
arr.processName = scanner.next();
arr.arrTime = scanner.nextInt();
arr.serviceTime = scanner.nextInt();
}
6.出队列(模拟完成所有进程工作)
public void finishAllProcessTask() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Queue cur = head.next;
System.out.println("Process number========Arrive time======Service time=======finish Time=======Turn time======WeightTurn time");
while (true) {
System.out.printf("\t\t%s\t\t\t\t%d\t\t\t\t\t%d\t\t\t\t\t%d\t\t\t\t%d\t\t\t\t%f",cur.processName,cur.arrTime,cur.serviceTime,cur.finishTime,cur.turnTime,cur.weightTurnTime);
System.out.println();
if (cur.next == null) {
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
模拟FCFS调度算法(先来先服务)的更多相关文章
- 《操作系统_FCFS和SJF》
先来先服务FCFS和短作业优先SJF进程调度 转自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34374664/article/details/73231072 一.概念介绍和案例解析 FCF ...
- python基础(31):进程(一)
1. 什么是进程 进程(Process)是计算机中的程序关于某数据集合上的一次运行活动,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位,是操作系统结构的基础.在早期面向进程设计的计算机结构中,进程是程序的基本执行 ...
- OS作业模拟SJF和FCFS
一个OS的作业, 用于模拟短作业优先 和 先来先服务两种作业调度方式. #!/usr/bin/python3.5 ## Modify the SJF and FCFS algorithm in the ...
- FCFS,SSTF,SCAN,FIFO,LRO考点题解
四.应用题 ( 本大题共5 小题,50 分 ) 1. 假设某系统中有五个进程,每个进程的执行时间(单位:ms)和优先数如下表所示(优先数越小,其优先级越高). 进程 执行时间 优先数 P1 P2 P3 ...
- Linux 常见的进程调度算法
1.在介绍进程调度之前,先对进程的状态的概念应该有所了解,下面是关于进程状态的一些基本概念:进程的状态分为三种,分别为: 1).运行态:该状态表明进程在实际占用CPU 2).就绪态: 该状态下进程可以 ...
- Linux - 进程调度算法
进程调度: 无论是在批处理系统还是分时系统中,用户进程数一般都多于处理机数.这将导致它们互相争夺处理机.另外,系统进程也同样需要使用处理机. 这就要求进程调度程序按一定的策略,动态地把处理机分配给处于 ...
- 操作系统常用调度算法(转载https://www.cnblogs.com/kxdblog/p/4798401.html)
操作系统常用调度算法 在操作系统中存在多种调度算法,其中有的调度算法适用于作业调度,有的调度算法适用于进程调度,有的调度算法两者都适用.下面介绍几种常用的调度算法. 先来先服务(FCFS)调度算法 ...
- s5-2 Cpu调度算法
调度程序采用什么算法选择一个进程(作业)? 如何评价调度算法的性能? 调度准则 CPU利用率 – 使CPU尽可能的忙碌 吞吐量 – 单位时间内运行完的进程数 周转时间 – 进程从提交到运行结束的全部时 ...
- Python 调度算法 死锁 静动态链接 分页分段
1 select poll epoll的区别基本上select有3个缺点: 连接数受限查找配对速度慢数据由内核拷贝到用户态poll改善了第一个缺点 epoll改了三个缺点. (1)select,pol ...
随机推荐
- const 对象的属性能否修改
const保证的并不是变量的值不能改动,而是变量指向的那个内存地址不能改动. 对于基本类型的数据(数值.字符串.布尔值),其值就保存在变量指向的那个内存地址,因此等同于常量. 对于引用类型的数据(主要 ...
- LGP4229题解
某位寄吧的故事 下文的 \(m\) 即为题面中的 \(Q\). 离散化,把序列变成 \(O(2m)\) 个部分,然后对这 \(O(2m)\) 个部分把最大值求出来,每次把最大值相同的部分拉出来,再把限 ...
- 如何写好B端产品的技术方案?
B端产品为企业提供协同办公的工具,帮助企业解决某类经营管理问题,核心价值在于为企业增加收入.降本提效.管控风险,企业级SaaS产品也是B端产品中的一类. B端产品有以下特点: 客户是一个群体:B端产 ...
- 面向服务开发(SOA)
面向服务的体系结构是一个组件模型,它将应用程序的不同功能单元(称为服务)通过这些服务之间定义良好的接口和契约联系起来.接口是采用中立的方式进行定义的,它应该独立于实现服务的硬件平台.操作系统和编程语言 ...
- IBM QRadar Advisor 安全限制绕过漏洞
受影响系统:IBM QRadar Advisor 1.0.0 -2.4.0描述:CVE(CAN) ID: CVE-2019-4556 IBM QRadar Advisor是一套安全威胁分析解决方案. ...
- Java 代码注意细节
代码优化的目标是: 1.减小代码的体积 2.提高代码运行的效率 代码优化细节 1.尽量指定类.方法的final修饰符 带有final修饰符的类是不可派生的.在Java核心API中,有许多应用final ...
- Django基础必会
Django基础必会 Django项目目录 mysite -mysite -__init__.py -urls.py(函数和函数的对应关系) -settings.py(Django项目的配置信息) - ...
- 6月11日 python学习总结 框架理论
Web框架本质及第一个Django实例 Web框架本质 我们可以这样理解:所有的Web应用本质上就是一个socket服务端,而用户的浏览器就是一个socket客户端. 这样我们就可以自己实现Web ...
- 解决metasploit的module load fail
解决metasploit的module load fail 在exploits文件夹下面新建一个文件夹test 把你要用的rb文件放进去 reload_all 就行了
- session 会话机制以及变量覆盖
session会话机制介绍如下 http是无状态协议.服务器靠cookie和session来记住用户.$_SESSION 和 $_GET等一样,是超全局变量. 后台脚本里面会写: session() ...
