Effective Java —— try-with-resources 优先于 try-finally
本文参考
本篇文章参考自《Effective Java》第三版第九条"Prefer try-with-resources to try-finally"
The code in both the try block and the finally block is capable of throwing exceptions.The second exception(in finally block) can completely obliterate the first one
try块和finally块都有可能抛出异常,若同时抛出异常,则finally块中的第二个异常将会覆盖try块的异常,使我们无法追踪到程序错误的根源,例如下面这段代码示例
@Test
public void tryFinallyTest() throws Exception {
try {
throw new Exception("try block Exception");
} finally {
throw new Exception("finally block Exception");
}
}
从执行结果中可以看出,try块中的异常没有显示
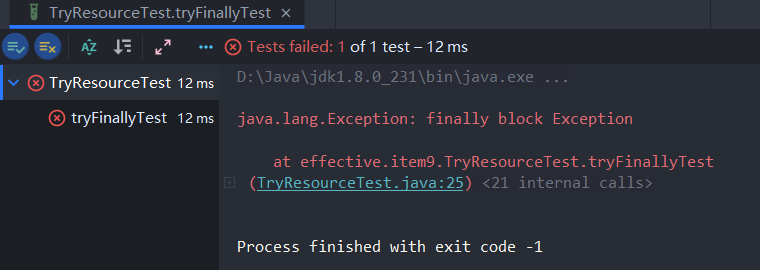
下面是一个更加实际的例子,BufferReader的readLine()方法和close()方法都会抛出IoException异常,close()抛出的异常可能会覆盖readLine()方法的异常
public void tryFinallyTest(String path) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
try {
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
} finally {
reader.close();
}
}
我们可以通过catch块捕获try块内的异常,这样finally块的异常就不会覆盖try块的异常
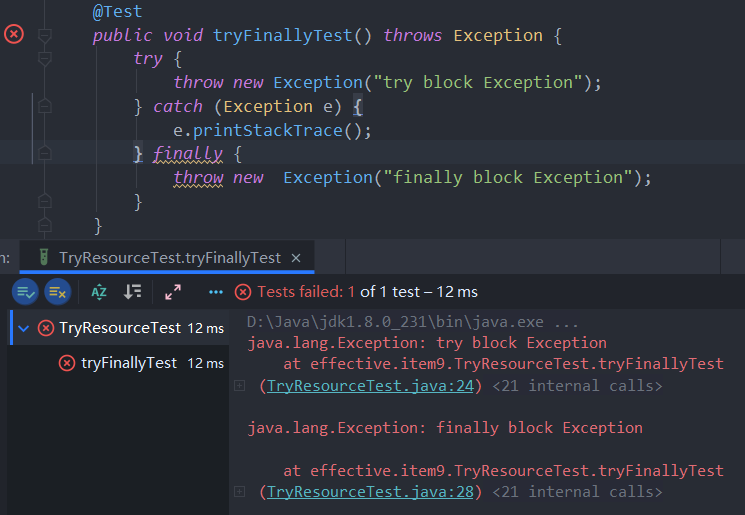
但是这未免有点"奇怪",因为当我们为方法加上throws Exception时,希望方法内产生的异常交由调用方或更上一级去处理,而不是在方法内部处理
这样一来,try块的异常由方法内部处理,而finally块的异常由调用方或更上一级处理,增加了我们对异常捕获的管理难度
Not only are the try-with-resources versions shorter and more readable than the originals, but they provide far better diagnostics
自java7开始加入了try-with-resource语法并引入了AutoCloseable接口,只要相关资源的类或接口实现或继承了这个接口,就可以不显式调用close()方法,自动关闭资源,并且不会有上述"异常覆盖"的情况发生
An object that may hold resources (such as file or socket handles) until it is closed. The close() method of an AutoCloseable object is called automatically when exiting a try-with-resources block for which the object has been declared in the resource specification header. This construction ensures prompt release, avoiding resource exhaustion exceptions and errors that may otherwise occur.
我们同时用两种形式的try语句来进行测试,throwException()方法累计抛出的异常
public class TryTest implements AutoCloseable {
private int count = 0;
@Test
public void tryResourceTest() throws Exception {
try(TryTest test = new TryTest()) {
test.throwException();
}
}
@Test
public void tryFinallyTest() throws Exception {
TryTest test = new TryTest();
try {
test.throwException();
} finally {
test.close();
}
}
public void throwException() throws Exception {
count++;
throw new Exception("the No." + count + " Exception occurs");
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
throwException();
}
}
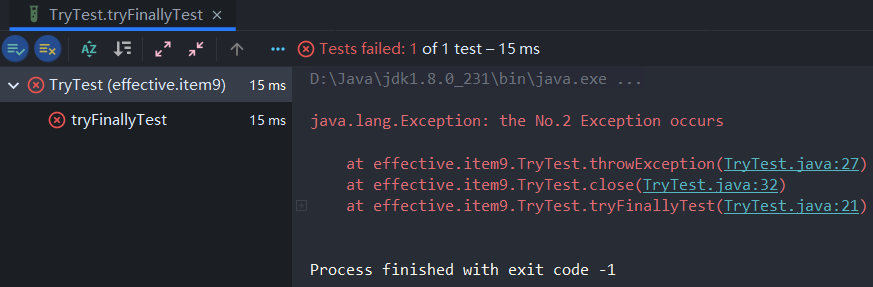
try-finally语句块的执行结果
try-with-resources语句块的执行结果
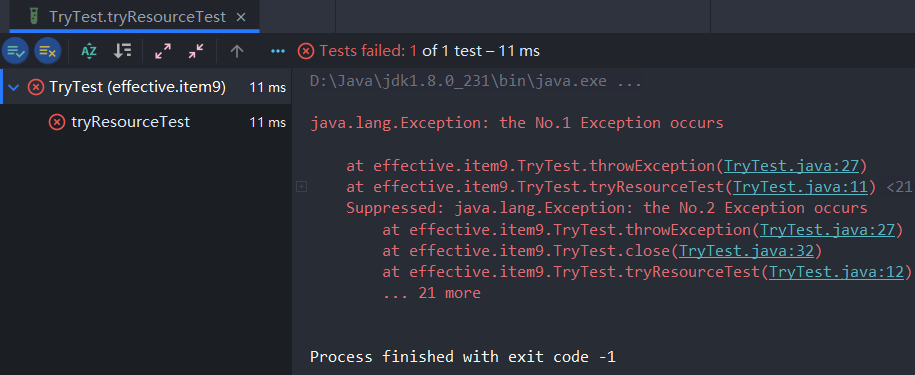
我们可以成功看到我们真正想要看到的第一个异常信息,第二个异常被标注为抑制
In fact, multiple exceptions may be suppressed in order to preserve the exception that you actually want to see. These suppressed exceptions are not merely discarded; they are printed in the stack trace with a notation saying that they were suppressed. You can also access them programmatically with the getSuppressed method, which was added to Throwable in Java 7
在try-with-resources语句块我们还是能够使用catch语句和finally语句,下面是一个更加实际的例子:
public void copy(String src, String dst) {
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dst)) {
byte[] buf = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int n;
while ((n = in.read(buf)) >= 0) out.write(buf, 0, n);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
因此在处理必须关闭的资源时,我们始终要优先考虑用 try-with-resources,而不是用try-finally,这样得到的代码将更加简洁、清晰,产生的异常也更有价值
Effective Java —— try-with-resources 优先于 try-finally的更多相关文章
- [Effective Java]第八章 通用程序设计
声明:原创作品,转载时请注明文章来自SAP师太技术博客( 博/客/园www.cnblogs.com):www.cnblogs.com/jiangzhengjun,并以超链接形式标明文章原始出处,否则将 ...
- EFFECTIVE JAVA 第十一章 系列化
EFFECTIVE JAVA 第十一章 系列化(将一个对象编码成一个字节流) 74.谨慎地实现Serializable接口 *实现Serializable接口付出的代价就是大大降低了“改变这个类 ...
- Effective Java通俗理解(下)
Effective Java通俗理解(上) 第31条:用实例域代替序数 枚举类型有一个ordinal方法,它范围该常量的序数从0开始,不建议使用这个方法,因为这不能很好地对枚举进行维护,正确应该是利用 ...
- 《Effective Java(中文第二版)》【PDF】下载
<Effective Java(中文第二版)>[PDF]下载链接: https://u253469.pipipan.com/fs/253469-230382186 Java(中文第二版)& ...
- 《Effective Java》 学习笔记 —— 并发
<Effective Java>第二版学习笔记之并发编程. 第66条 同步访问共享的可变数据 * 关键字synchronized可以保证在同一时刻只有一个线程可以执行某个方法或代码块. * ...
- [Java读书笔记] Effective Java(Third Edition) 第2章 创建和销毁对象
第 1 条:用静态工厂方法代替构造器 对于类而言,获取一个实例的方法,传统是提供一个共有的构造器. 类可以提供一个公有静态工厂方法(static factory method), 它只是一个返回类 ...
- 《Effective Java》笔记45-56:通用程序设计
将局部变量的作用域最小化,可以增强代码的可读性和可维护性,并降低出错的可能性. 要使用局部变量的作用域最小化,最有力的方法就是在第一次使用它的地方才声明,不要过早的声明. 局部变量的作用域从它被声明的 ...
- effective java 学习心得
目的 记录一下最主要学习心得,不然凭我这种辣鸡记忆力分分钟就忘记白看了... 用静态工厂方法代替构造器的最主要好处 1.不必每次都创建新的对象 Boolean.valueOf Long.valueOf ...
- effective java 读后感
think in java , effective java 这两本书一直都在java的生态圈中经久不衰.本来想着先翻过 think in java 这本大山,但是读到一半就放弃了.过长的篇幅,让 ...
随机推荐
- pycharm创建模板
用pycharm构造作者模板 模板,就是创建一个文件时自动生成模板内容. 这里用pycharm创建作者模板,步骤如下: File-->Settings Editor-->File and ...
- 在Mac上安装mysql并配置环境(详细篇)
在Mac上安装mysql并配置环境(详细篇) 1.下载mysql mysql官网 这一步根据自己电脑架构选择,分为arm和x86 下载完成之后打开就可以 接下来运行安装就可以,一直下一步,设置完密码就 ...
- C#调用带参数的python脚本
问题描述:使用C#调用下面的带参数的用python写的方法,并且想要获取返回值. def Quadratic_Equations(a,b,c): D=b**2-4*a*c ans=[] ans.app ...
- Neo4j入门日志(一)导入数据
本文主要来源于: neo4j的官方文档 使用的是neo4j官方提供的导入方式,即使用import,在cmd中进行导入. 1.导入的基本方式 bin/neo4j-admin import --datab ...
- MapReduce中一次reduce方法的调用中key的值不断变化
简单一句话总结就是:ReduceContextImpl类的RawKeyValueIterator input迭代器对象里面存储中着key-value对的元素, 以及一个只存储value的迭代器,然后每 ...
- Python:读取Excel 不带第一行标题
#根据第0到第1列进行重建 0-X 1-Y PX=sheet_name.col_values(0)[1:] PY=sheet_name.col_values(1)[1:] 读取的某一列后在后边加[1: ...
- pyinstaller打包exe文件,运行时一闪而过
pyinstaller打包exe文件出现命令窗口一闪而过 原因:exe运行过程中出错了,解决这些错误就可以了 解决方法: 通过 cd path >> xxx.exe 在命令行中运行exe文 ...
- (转载)《Three easy pieces 》虚拟化部分整体介绍
转载自知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37917910 一个程序在运行的时候发生了什么呢? 其实只是一些非常简单的事情:运行指令.处理器从内存中取出指令,译码然后执行. ...
- 动手学TCP——CS144实验感想
在Stanford CS144的课程实验Lab0~Lab4中,我们动手实现了一个自己的TCP协议,并且能够真的与互联网通信!此外,感谢Stanford开源本实验并提供了大量的优质测试用例,使得我们仅仅 ...
- XML序列化与反序列化接口对接实战,看这篇就够了
关键字:c# .NET XML 序列化 反序列化 本文为接口对接实践经验分享,不对具体的XML概念定义进行阐述:涉及工具类及处理方法已在生产环境使用多年,可放心使用.当然如果你发现问题,或有不同想法, ...
