MyBatis-Cache
一、一级缓存
/**
* 一级缓存(本地缓存):SqlSession 级别。一级缓存是默认开启的,为 SqlSession 级别的一个Map
* 与数据库同一次会话期间查询到的数据会放在本地缓存中,以后如果需要获取相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取。
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); MyUserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(MyUserMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
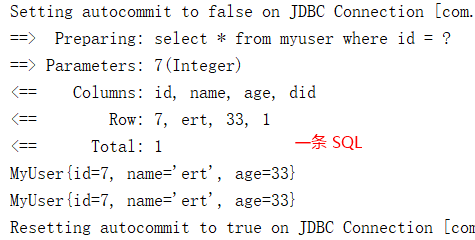
一级缓存失效的几种情况,相同的查询也会向数据库发送SQL
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
MyUserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(MyUserMapper.class);
// sqlSession 不同
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
mapper = session.getMapper(MyUserMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
// sqlSession 相同,查询条件不同(当前一级缓存中还没有这个数据)
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(8));
// sqlSession 相同,两次查询之间执行了增删改操作(这次增删改可能对当前数据有影响)
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
mapper.updateMyUser(new MyUser(10,"xasx",24,null));
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
// sqlSession 相同,手动清除了一级缓存
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
session.clearCache();
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
} finally {
session.close();
}
}

二、二级缓存
1.开启二级缓存 mybatis-config.xml
<settings>
<!-- 开启全局二级缓存 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 自动映射有三种模式,NONE、PARTIAL、FULL。NONE 不启用自动映射,PARTIAL 只对非嵌套的 resultMap 进行自动映射,FULL 表示对所有的 resultMap 都进行自动映射。默认为 PARTIAL -->
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/>
<!-- 数据库字段下划线转Bean字段的驼峰命名 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!-- 控制台打印SQL -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" /> <!-- 延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置fetchType属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。默认false -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。否则,每个属性会按需加载。默认false (true in ≤3.4.1) -->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>
2.配置二级缓存 xxxMapper.xml
<!-- namespace 对应接口文件的全路径 -->
<mapper namespace="com.dao.MyUserMapper">
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" readOnly="false" size="1024"></cache>
<!-- eviction:缓存的回收策略:默认的是 LRU
• LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
• FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
• SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
• WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
flushInterval:缓存刷新间隔,缓存多长时间清空一次,默认不清空,设置一个毫秒值
readOnly:缓存中的数据是否只读
true:只读,会将数据在缓存中的引用交给用户。数据可能被修改,不安全,速度快
false:非只读,会利用序列化和反序列的技术克隆一份新的数据返回。安全,速度慢
size:缓存存放多少元素
type:指定自定义缓存的全类名,实现 org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache 接口 -->
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultType="myUser">
select * from myuser where id = #{id}
</select>
3.实体类实现序列化接口 Serializable
public class MyUser implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Dept dept;
4.测试
/**
* 二级缓存(全局缓存):基于 namespace 级别的缓存,一个 namespace 对应一个二级缓存(map)
*
* 创建会话:查询一条数据,这个数据就会被放在当前会话的一级缓存中
* 会话关闭:一级缓存中的数据会被保存到二级缓存中;新的会话查询信息,会先找二级缓存中的内容,没有就找一级缓存,再没有就会发送 SQL 查询数据库
* 效果:数据会从二级缓存中获取,查出的数据都会被默认先放在一级缓存中。只有会话提交或者关闭以后,一级缓存中的数据才会转移到二级缓存中
* 使用:
* 1)、在全局配置中开启二级缓存:<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
* 2)、在 xxxMapper.xml 中配置二级缓存:<cache/>
* 3)、POJO 实现序列化接口 Serializable
*/
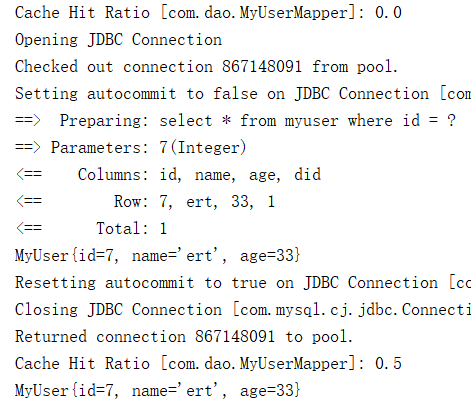
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); MyUserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(MyUserMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7)); // 关闭 session 让一级缓存中类容提交到二级缓存
session.close(); // 重新获取 sqlSession
session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
mapper = session.getMapper(MyUserMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
} finally {
session.close();
}
}

三、缓存相关配置
代码配置
// 只清除当前 session 的一级缓存
session.clearCache();
全局设置
<settings>
<!-- 二级缓存设置,不影响一级缓存 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="false"/>
<!-- 本地(一级)缓存作用域,默认 SESSION,会缓存一个会话(SqlSession)中执行的所有查询。 设置为 STATEMENT,会话仅作用在语句执行上,对 SqlSession 的调用将不会共享数据,可认为是禁用一级缓存 -->
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
</settings>
SQL 映射文件配置
<!-- flushCache:将其设置为 true,任何时候只要 SQL 被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空,默认值:true(对应插入、更新和删除语句),false(对应查询语句)。
useCache:将其设置为 true,将会导致本条 SQL 的结果被二级缓存(不影响一级),默认值:对 select 元素为 true -->
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultType="myUser" useCache="true" flushCache="false">
select * from myuser where id = #{id}
</select>
也可以在接口上配置
@Options(flushCache = Options.FlushCachePolicy.FALSE, useCache = true)
public MyUser selectMyUserById(Integer id);
四,使用第三方缓存(二级)
以 ehcache 为例
1.导入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-nop</artifactId>
<version>1.7.26</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies> <build>
<plugins>
<!-- 指定jdk -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2.添加缓存配置文件 ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache>
<!-- 磁盘保存路径 -->
<diskStore path="D:\ehcache" /> <!--
diskStore:指定数据在磁盘中的存储位置。
defaultCache:当借助CacheManager.add("demoCache")创建Cache时,EhCache便会采用<defalutCache/>指定的的管理策略 以下是必须属性:
maxElementsInMemory - 在内存中缓存的element的最大数目
maxElementsOnDisk - 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目,若是0表示无穷大
eternal - 设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断
overflowToDisk - 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上 以下是可选属性:
timeToIdleSeconds - 当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds的属性取值时,这些数据便会删除,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大
timeToLiveSeconds - 缓存element的有效生命期,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB - 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小.默认是30MB.每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区.
diskPersistent - 在VM重启的时候是否启用磁盘保存EhCache中的数据,默认是false。
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds - 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每个120s,相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy - 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出)
-->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
3.修改缓存配置,xxxMapper.xml
<!-- namespace 对应接口文件的全路径 -->
<mapper namespace="com.dao.MyUserMapper">
<!-- 引用缓存:namespace:指定和哪个名称空间下的缓存一样 -->
<!--<cache-ref namespace="com.dao.Dept"/>--> <!--使用自定义缓存-->
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
<select id="selectMyUserById" resultType="myUser" useCache="true" flushCache="false">
select * from myuser where id = #{id}
</select>
5.测试
/**
* 使用第三方缓存:
* 1)、导入依赖;
* 2)、xxxMapper.xml 中使用自定义缓存 <cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
MyUserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(MyUserMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7)); session.close(); session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
mapper = session.getMapper(MyUserMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectMyUserById(7));
} finally {
if (session != null) {
session.close();
}
}
}
http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html#cache
http://www.mybatis.org/ehcache-cache/index.html
MyBatis-Cache的更多相关文章
- MyBatis Cache配置
@(MyBatis)[Cache] MyBatis Cache配置 MyBatis提供了一级缓存和二级缓存 配置 全局配置 配置 说明 默认值 可选值 cacheEnabled 全局缓存的开关 tru ...
- SmartSql = Dapper + MyBatis + Cache(Memory | Redis) + ZooKeeper + R/W Splitting + ......
SmartSql Why 拥抱 跨平台 DotNet Core,是时候了. 高性能.高生产力,超轻量级的ORM.156kb (Dapper:168kb) So SmartSql TargetFrame ...
- Mybatis Cache 缓存策略
Mybatis Cache 缓存策略 正如大多数持久层框架一样,MyBatis 同样提供了一级缓存和二级缓存的支持 一级缓存: 基于PerpetualCache 的 HashMap本地缓存,其存储作用 ...
- MyBatis源码分析(五):MyBatis Cache分析
一.Mybatis缓存介绍 在Mybatis中,它提供了一级缓存和二级缓存,默认的情况下只开启一级缓存,所以默认情况下是开启了缓存的,除非明确指定不开缓存功能.使用缓存的目的就是把数据保存在内存中,是 ...
- MyBatis源码分析(4)—— Cache构建以及应用
@(MyBatis)[Cache] MyBatis源码分析--Cache构建以及应用 SqlSession使用缓存流程 如果开启了二级缓存,而Executor会使用CachingExecutor来装饰 ...
- MyBatis源码分析(3)—— Cache接口以及实现
@(MyBatis)[Cache] MyBatis源码分析--Cache接口以及实现 Cache接口 MyBatis中的Cache以SPI实现,给需要集成其它Cache或者自定义Cache提供了接口. ...
- 笔记:MyBatis Mapper XML文件详解 - Cache
缓存(Cache) 从数据库中加载的数据缓存到内存中,是很多应用程序为了提高性能而采取的一贯做法.MyBatis对通过映射的SELECT语句加载的查询结果提供了内建的缓存支持.默认情况下,启用一级缓存 ...
- Mybatis 拦截器
Mybatis定义了四种拦截器: Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, ...
- mybatis入门基础(八)-----查询缓存
一.什么是查询缓存 mybatis提供查询缓存,用于减轻数据压力,提高数据库性能. mybaits提供一级缓存,和二级缓存. 1.1. 一级缓存是sqlSession级别的缓存.在操作数据库时需要构造 ...
- Mybatis映射文件
Mapper XML 文件 MyBatis 的真正强大在于它的映射语句,也是它的魔力所在.由于它的异常强大,映射器的 XML 文件就显得相对简单.如果拿它跟具有相同功能的 JDBC 代码进行对比,你会 ...
随机推荐
- Sublime Text ——3200破解补丁
声明 该资源来源于网络,只为学习交流使用,侵权联系删除.长期使用和觉得sublime text 不错的话,还望购买授权码,多多支持正版!!! 重要的事情说三遍 请支持正版!!! 请支持正版!!! 请支 ...
- 继承&派生 属性查找
# 在单继承背景下,无论是新式类还是经典类属性查找顺序都一样 # 先object->类->父类->... 实例: class Foo: def f1(self): print('Fo ...
- 【XSY2669】归并排序 树状数组 简单组合数学
题目描述 有一个长度为\(n\)的排列\(n=2^k\),你要把这个数组归并排序.但是在长度为\(2\)的时候有\(\frac{1}{2}\)的概率会把两个数交换(就是有\(\frac{1}{2}\) ...
- IDEA调试技巧之条件断点
调试的时候,在循环里增加条件判断,可以极大的提高效率,心情也能愉悦.以下介绍下IDEA使用条件[Condition]断点的方法 1.编写一段样例代码 /** * @author jiashubing ...
- stm32使用rt-thread在文件《stm32f1xx_hal.h》中头文件包含顺序引出的错误
@2019-01-24 [小记] 在学习 rt-thread BSP制作过程中,发现文件<stm32f1xx_hal.h>中 Env工具生成的原始顺序 1. #include " ...
- NOIP2017题解
T1小凯的疑惑 小凯手中有两种面值的金币,两种面值均为正整数且彼此互素.每种金币小凯都有 无数个.在不找零的情况下,仅凭这两种金币,有些物品他是无法准确支付的.现在小 凯想知道在无法准确支付的物品中, ...
- django rest framework ViewSets & Routers
Using viewsets views.py from rest_framework import viewsets from rest_framework import mixins from r ...
- mysql慢查询,死锁解决方案
1. 先使用root用户登录到MySQL中 2. 使用show processlist查看其查询速率 +----+------+-----------------+------+---------+- ...
- ElasticSearch启动错误处理方法
在配置完elasticsearch,启动程序会包如下错误: [elk@localhost bin]$ ./elasticsearch ... ... ERROR: [3] bootstrap chec ...
- kafka为什么这么优秀!
kafka为什么这么优秀! 阿飞的博客 匠心零度 今天 1.动机2.持久化3.效率4.生产者4.1负载均衡4.2异步发送5.消费者Push vs. Pull消费者位置离线数据加载 1.动机 kafka ...
