解决OpenCV JavaCameraView相机preview方向问题
网上找了很多解决都是有问题的,研究了半天源码解决了这个问题。我是从整个相机启动和数据传输的过程着手的,这里捡重点介绍一下,最后会贴上修改后的两个源文件。
首先要知道一个概念。
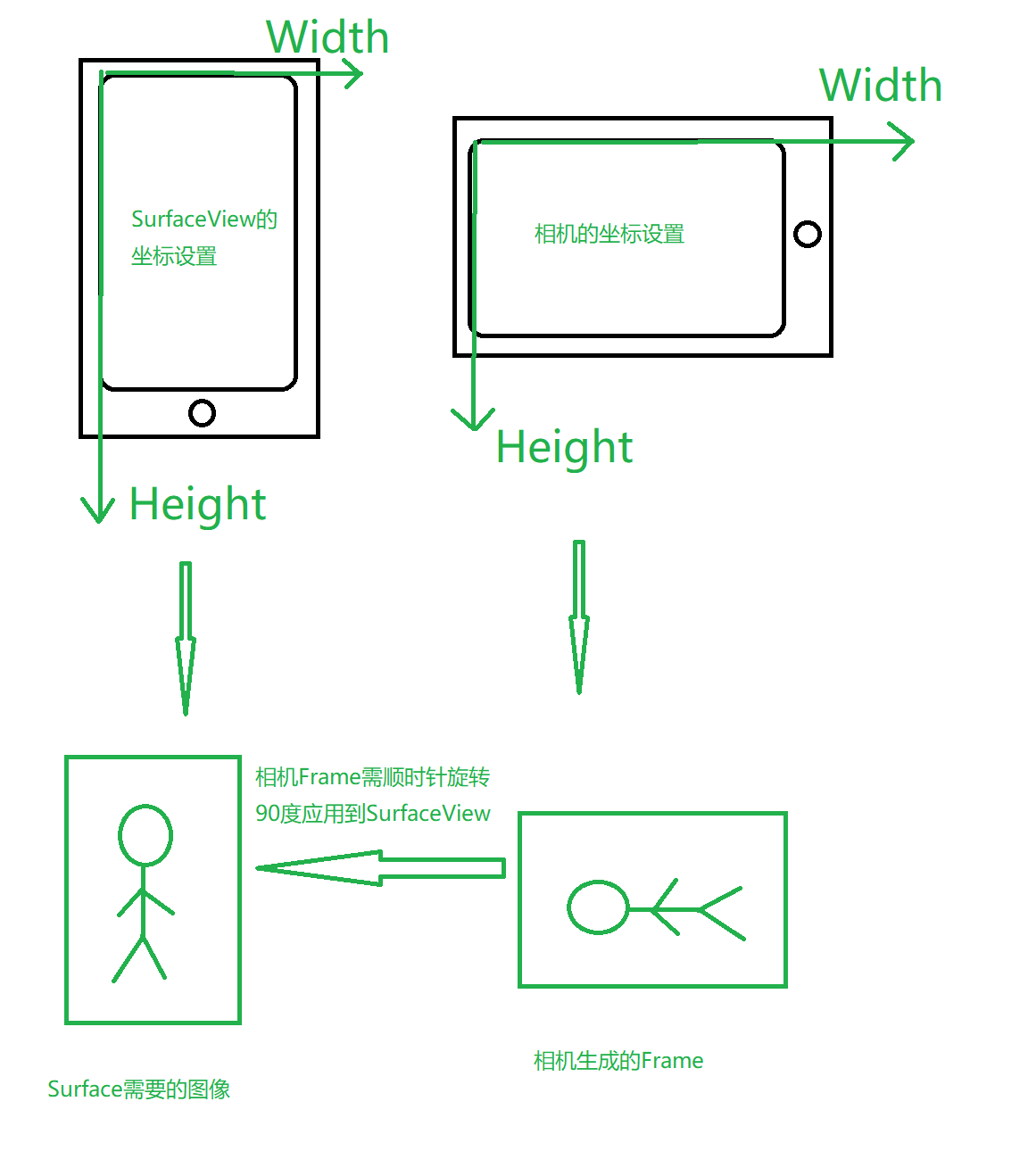
图里的小圆圈是Home按键,不是摄像头:)
现在问题就是在什么地方进行旋转,如何旋转。这就需要了解JavaCameraView类的工作流程了。JavaCameraView实现了父类CameraBridgeViewBase的抽象方法connectCamera,这个方法主要做两件事
1.初始化相机,包括选择启动哪个相机,选择preview的Frame大小等等。这个过程是在UI线程实现的,因此onPreviewFrame也是在UI线程调用,当相机启动后数据就会传至onPreviewFrame。onPreviewFrame不处理数据只是将数据存好然后通知另一个线程去处理。
2.就是启动那个处理onPreviewFrame存储数据的线程。
JavaCameraView类的问题就是在这第1,第2步骤里都没有区分SurfaceView和相机Frame的坐标是不同的。比如,在第1步骤里,选择相机preview大小时,preview的height最大不能超过SurfaceView的width,也就是说相机Frame的高对应着SurfaceView的宽而相机Frame的宽对应着SurfaceView的高。因此所有涉及到SurfaceView宽和高的地方都需要修改,因为源码都用的相机Frame的宽和高。最重要的就是第1步骤里会调用AllocateCache函数初始化一个Bitmap,之后在第2步骤里将相机Frame转为这个Bitmap,然后直接画到SurfaceView对应的画布上的。因此这个Bitmap的宽和高应该跟相机Frame的宽和高正好相反,因为相机Frame的数据是顺时针旋转90度后使用的。在第2步骤里,相机Frame转为Bitmap之前需要顺时针旋转相机Frame数据,旋转后相机Frame和Bitmap就一致了。这个旋转相机Frame的时机我选择在JavaCameraFrame类实现,这个类很简单它有一个Mat成员,onPreviewFrame每当有数据时就是存到这个成员里,这个Mat是Yuv420sp格式的。但是它实现了CvCameraViewFrame接口的gray,rgba方法,可直接返回Yuv420sp对应的灰度图和rgba图,此时返回的是相机Frame那个方向的。我在gray,rgba方法里对返回结果进行旋转。我认为这个时机很好,因为通过onCameraFrame传给JavaCameraView类的用户的数据就是JavaCameraFrame类型,在onCameraFrame函数里用户像往常一样直接调用gray,rgba方法就可得到方向正确的Mat,且这个时机在相机Frame转为Bitmap之前,当转换时相机Frame的数据已经被旋转到正确方向了。
水平一般,能力有限。说的可能不清楚,贴上代码,所有我修改的地方都注释了#Modified,修改的地方不是很多。
1.CameraBridgeViewBase
package org.opencv.android; import java.util.List; import org.opencv.BuildConfig;
import org.opencv.R;
import org.opencv.core.Mat;
import org.opencv.core.Size; import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView; /**
* This is a basic class, implementing the interaction with Camera and OpenCV library.
* The main responsibility of it - is to control when camera can be enabled, process the frame,
* call external listener to make any adjustments to the frame and then draw the resulting
* frame to the screen.
* The clients shall implement CvCameraViewListener.
*/
public abstract class CameraBridgeViewBase extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback { private static final String TAG = "CameraBridge";
private static final int MAX_UNSPECIFIED = -1;
private static final int STOPPED = 0;
private static final int STARTED = 1; private int mState = STOPPED;
private Bitmap mCacheBitmap;
private CvCameraViewListener2 mListener;
private boolean mSurfaceExist;
private final Object mSyncObject = new Object(); protected int mFrameWidth;
protected int mFrameHeight;
protected int mMaxHeight;
protected int mMaxWidth;
protected float mScale = 0;
protected int mPreviewFormat = RGBA;
protected int mCameraIndex = CAMERA_ID_ANY;
protected boolean mEnabled;
protected FpsMeter mFpsMeter = null; public static final int CAMERA_ID_ANY = -1;
public static final int CAMERA_ID_BACK = 99;
public static final int CAMERA_ID_FRONT = 98;
public static final int RGBA = 1;
public static final int GRAY = 2; public CameraBridgeViewBase(Context context, int cameraId) {
super(context);
mCameraIndex = cameraId;
getHolder().addCallback(this);
mMaxWidth = MAX_UNSPECIFIED;
mMaxHeight = MAX_UNSPECIFIED;
} public CameraBridgeViewBase(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs); int count = attrs.getAttributeCount();
Log.d(TAG, "Attr count: " + Integer.valueOf(count)); TypedArray styledAttrs = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CameraBridgeViewBase);
if (styledAttrs.getBoolean(R.styleable.CameraBridgeViewBase_show_fps, false))
enableFpsMeter(); mCameraIndex = styledAttrs.getInt(R.styleable.CameraBridgeViewBase_camera_id, -1); getHolder().addCallback(this);
mMaxWidth = MAX_UNSPECIFIED;
mMaxHeight = MAX_UNSPECIFIED;
styledAttrs.recycle();
} /**
* Sets the camera index
* @param cameraIndex new camera index
*/
public void setCameraIndex(int cameraIndex) {
this.mCameraIndex = cameraIndex;
} public interface CvCameraViewListener {
/**
* This method is invoked when camera preview has started. After this method is invoked
* the frames will start to be delivered to client via the onCameraFrame() callback.
* @param width - the width of the frames that will be delivered
* @param height - the height of the frames that will be delivered
*/
public void onCameraViewStarted(int width, int height); /**
* This method is invoked when camera preview has been stopped for some reason.
* No frames will be delivered via onCameraFrame() callback after this method is called.
*/
public void onCameraViewStopped(); /**
* This method is invoked when delivery of the frame needs to be done.
* The returned values - is a modified frame which needs to be displayed on the screen.
* TODO: pass the parameters specifying the format of the frame (BPP, YUV or RGB and etc)
*/
public Mat onCameraFrame(Mat inputFrame);
} public interface CvCameraViewListener2 {
/**
* This method is invoked when camera preview has started. After this method is invoked
* the frames will start to be delivered to client via the onCameraFrame() callback.
* @param width - the width of the frames that will be delivered
* @param height - the height of the frames that will be delivered
*/
public void onCameraViewStarted(int width, int height); /**
* This method is invoked when camera preview has been stopped for some reason.
* No frames will be delivered via onCameraFrame() callback after this method is called.
*/
public void onCameraViewStopped(); /**
* This method is invoked when delivery of the frame needs to be done.
* The returned values - is a modified frame which needs to be displayed on the screen.
* TODO: pass the parameters specifying the format of the frame (BPP, YUV or RGB and etc)
*/
public Mat onCameraFrame(CvCameraViewFrame inputFrame);
}; protected class CvCameraViewListenerAdapter implements CvCameraViewListener2 {
public CvCameraViewListenerAdapter(CvCameraViewListener oldStypeListener) {
mOldStyleListener = oldStypeListener;
} public void onCameraViewStarted(int width, int height) {
mOldStyleListener.onCameraViewStarted(width, height);
} public void onCameraViewStopped() {
mOldStyleListener.onCameraViewStopped();
} public Mat onCameraFrame(CvCameraViewFrame inputFrame) {
Mat result = null;
switch (mPreviewFormat) {
case RGBA:
result = mOldStyleListener.onCameraFrame(inputFrame.rgba());
break;
case GRAY:
result = mOldStyleListener.onCameraFrame(inputFrame.gray());
break;
default:
Log.e(TAG, "Invalid frame format! Only RGBA and Gray Scale are supported!");
}; return result;
} public void setFrameFormat(int format) {
mPreviewFormat = format;
} private int mPreviewFormat = RGBA;
private CvCameraViewListener mOldStyleListener;
}; /**
* This class interface is abstract representation of single frame from camera for onCameraFrame callback
* Attention: Do not use objects, that represents this interface out of onCameraFrame callback!
*/
public interface CvCameraViewFrame { /**
* This method returns RGBA Mat with frame
*/
public Mat rgba(); /**
* This method returns single channel gray scale Mat with frame
*/
public Mat gray();
}; /*
重载SurfaceHolder.Callback的方法
*/
/*
Access to the underlying surface is provided via the SurfaceHolder interface,
which can be retrieved by calling getHolder().
The Surface will be created for you while the SurfaceView's window is visible;
you should implement SurfaceHolder.Callback.surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder)
and SurfaceHolder.Callback.surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder) to discover when the
Surface is created and destroyed as the window is shown and hidden.
One of the purposes of this class is to provide a surface in which a secondary
thread can render into the screen. If you are going to use it this way,
you need to be aware of some threading semantics:
All SurfaceView and SurfaceHolder.Callback methods will be called from
the thread running the SurfaceView's window (typically the main thread of the application). They thus need to correctly synchronize with any state that is also touched by the drawing thread.
You must ensure that the drawing thread only touches the underlying Surface
while it is valid -- between SurfaceHolder.Callback.surfaceCreated()
and SurfaceHolder.Callback.surfaceDestroyed().
*/
/*
This is called immediately after any structural changes (format or size)
have been made to the surface. You should at this point update the imagery
in the surface. This method is always called at least once,
after surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder).
*/
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3) {
Log.d(TAG, "call surfaceChanged event");
synchronized(mSyncObject) {
if (!mSurfaceExist) {
mSurfaceExist = true;
checkCurrentState();
} else {
/** Surface changed. We need to stop camera and restart with new parameters */
/* Pretend that old surface has been destroyed */
mSurfaceExist = false;
checkCurrentState();
/* Now use new surface. Say we have it now */
mSurfaceExist = true;
checkCurrentState();
}
}
} /*
This is called immediately after the surface is first created.
Implementations of this should start up whatever rendering code they desire.
Note that only one thread can ever draw into a Surface,
so you should not draw into the Surface here if your normal rendering
will be in another thread.
*/
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
/* Do nothing. Wait until surfaceChanged delivered */
} /*
This is called immediately before a surface is being destroyed.
After returning from this call, you should no longer try to access this surface.
If you have a rendering thread that directly accesses the surface,
you must ensure that thread is no longer touching the Surface before returning
from this function.
*/
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
synchronized(mSyncObject) {
mSurfaceExist = false;
checkCurrentState();
}
} /**
* This method is provided for clients, so they can enable the camera connection.
* The actual onCameraViewStarted callback will be delivered only after both this method is called and surface is available
*/
public void enableView() {
synchronized(mSyncObject) {
mEnabled = true;
checkCurrentState();
}
} /**
* This method is provided for clients, so they can disable camera connection and stop
* the delivery of frames even though the surface view itself is not destroyed and still stays on the scren
*/
public void disableView() {
synchronized(mSyncObject) {
mEnabled = false;
checkCurrentState();
}
} /**
* This method enables label with fps value on the screen
*/
public void enableFpsMeter() {
if (mFpsMeter == null) {
mFpsMeter = new FpsMeter();
mFpsMeter.setResolution(mFrameWidth, mFrameHeight);
}
} public void disableFpsMeter() {
mFpsMeter = null;
} /**
*
* @param listener
*/ public void setCvCameraViewListener(CvCameraViewListener2 listener) {
mListener = listener;
} public void setCvCameraViewListener(CvCameraViewListener listener) {
CvCameraViewListenerAdapter adapter = new CvCameraViewListenerAdapter(listener);
adapter.setFrameFormat(mPreviewFormat);
mListener = adapter;
} /**
* This method sets the maximum size that camera frame is allowed to be. When selecting
* size - the biggest size which less or equal the size set will be selected.
* As an example - we set setMaxFrameSize(200,200) and we have 176x152 and 320x240 sizes. The
* preview frame will be selected with 176x152 size.
* This method is useful when need to restrict the size of preview frame for some reason (for example for video recording)
* @param maxWidth - the maximum width allowed for camera frame.
* @param maxHeight - the maximum height allowed for camera frame
*/
public void setMaxFrameSize(int maxWidth, int maxHeight) {
mMaxWidth = maxWidth;
mMaxHeight = maxHeight;
} public void SetCaptureFormat(int format)
{
mPreviewFormat = format;
if (mListener instanceof CvCameraViewListenerAdapter) {
CvCameraViewListenerAdapter adapter = (CvCameraViewListenerAdapter) mListener;
adapter.setFrameFormat(mPreviewFormat);
}
} /**
* Called when mSyncObject lock is held
*/
private void checkCurrentState() {
Log.d(TAG, "call checkCurrentState");
int targetState;
//enableView()将设置mEnabled为true,surfaceChanged()将设置mSurfaceExist
//getVisibility() == VISIBLE似乎总是成立的
//当surface准备好了且client设置enableView()时设置targetState为STARTED
if (mEnabled && mSurfaceExist && getVisibility() == VISIBLE) {
targetState = STARTED;
} else {
targetState = STOPPED;
} //mState初始值是STOPPED
//若目标状态与当前状态不同则退出当前状态进入目标状态
if (targetState != mState) {
/* The state change detected. Need to exit the current state and enter target state */
processExitState(mState);
mState = targetState;
processEnterState(mState);
}
} private void processEnterState(int state) {
Log.d(TAG, "call processEnterState: " + state);
switch(state) {
case STARTED:
//真正启动相机的地方
onEnterStartedState();
if (mListener != null) {
//进入STARTED状态后若CameraBridgeViewBase类的成员CvCameraViewListener2 mListener
//不为null则调用其onCameraViewStarted方法,通知mListener相机启动了
mListener.onCameraViewStarted(mFrameWidth, mFrameHeight);
}
break;
case STOPPED:
onEnterStoppedState();
if (mListener != null) {
//进入STOPPED状态后若CameraBridgeViewBase类的成员CvCameraViewListener2 mListener
//不为null则调用其onCameraViewStopped方法,通知mListener相机停止了
mListener.onCameraViewStopped();
}
break;
};
} private void processExitState(int state) {
Log.d(TAG, "call processExitState: " + state);
switch(state) {
case STARTED:
onExitStartedState();
break;
case STOPPED:
onExitStoppedState();
break;
};
} private void onEnterStoppedState() {
/* nothing to do */
} private void onExitStoppedState() {
/* nothing to do */
} // NOTE: The order of bitmap constructor and camera connection is important for android 4.1.x
// Bitmap must be constructed before surface
private void onEnterStartedState() {
Log.d(TAG, "call onEnterStartedState");
/* Connect camera */
//connectCamera的参数是CameraBridgeViewBase的width,height
if (!connectCamera(getWidth(), getHeight())) {
AlertDialog ad = new AlertDialog.Builder(getContext()).create();
ad.setCancelable(false); // This blocks the 'BACK' button
ad.setMessage("It seems that you device does not support camera (or it is locked). Application will be closed.");
ad.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEUTRAL, "OK", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
((Activity) getContext()).finish();
}
});
ad.show(); }
} private void onExitStartedState() {
disconnectCamera();
if (mCacheBitmap != null) {
mCacheBitmap.recycle();
}
} /*
onPreviewFrame在UI线程被调用,它存好数据后通知另一个线程处理
另一个线程就调用这个方法处理数据
onPreviewFrame相当于生产者,另一个线程相当于消费者
当使用JavaCameraView类时frame是JavaCameraFrame类型
其通过OpenCV实现了接口
*/
/**
* This method shall be called by the subclasses when they have valid
* object and want it to be delivered to external client (via callback) and
* then displayed on the screen.
* @param frame - the current frame to be delivered
*/
protected void deliverAndDrawFrame(CvCameraViewFrame frame) {
Mat modified; if (mListener != null) {
//CvCameraViewListener2 mListener是client指定的
//这里调用客户重载的接口方法且接收返回值
//这里都是在数据处理线程里执行的
modified = mListener.onCameraFrame(frame);
} else {
//若client没指定CvCameraViewListener2 mListener即client不准备处理preview数据
//则modified设置为
//onPreviewFrame传回的数据转换成的rgba Mat
modified = frame.rgba();
} //Log Mat的大小和Bitmap的大小
Log.d("FunnyAR","mScale: "+mScale+" modified.rows: "+modified.rows()
+" modified.cols: "+modified.cols()+" mCacheBitmap.getWidth(): "+
mCacheBitmap.getWidth()+" mCacheBitmap.getHeight() "+
mCacheBitmap.getHeight()); //标志modified转Bitmap是否成功
boolean bmpValid = true;
//若确实有modified则将其转为Bitmap
if (modified != null) {
try {
Utils.matToBitmap(modified, mCacheBitmap);
} catch(Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Mat type: " + modified);
Log.e(TAG, "Bitmap type: " + mCacheBitmap.getWidth() + "*" + mCacheBitmap.getHeight());
Log.e(TAG, "Utils.matToBitmap() throws an exception: " + e.getMessage());
bmpValid = false;
}
}
//转换成功通过画布画到surface里
if (bmpValid && mCacheBitmap != null) {
Canvas canvas = getHolder().lockCanvas();
if (canvas != null) {
canvas.drawColor(0, android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.CLEAR);
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG)
Log.d(TAG, "mStretch value: " + mScale); if (mScale != 0) {
canvas.drawBitmap(mCacheBitmap, new Rect(0,0,mCacheBitmap.getWidth(), mCacheBitmap.getHeight()),
new Rect((int)((canvas.getWidth() - mScale*mCacheBitmap.getWidth()) / 2),
(int)((canvas.getHeight() - mScale*mCacheBitmap.getHeight()) / 2),
(int)((canvas.getWidth() - mScale*mCacheBitmap.getWidth()) / 2 + mScale*mCacheBitmap.getWidth()),
(int)((canvas.getHeight() - mScale*mCacheBitmap.getHeight()) / 2 + mScale*mCacheBitmap.getHeight())), null);
} else {
canvas.drawBitmap(mCacheBitmap, new Rect(0,0,mCacheBitmap.getWidth(), mCacheBitmap.getHeight()),
new Rect((canvas.getWidth() - mCacheBitmap.getWidth()) / 2,
(canvas.getHeight() - mCacheBitmap.getHeight()) / 2,
(canvas.getWidth() - mCacheBitmap.getWidth()) / 2 + mCacheBitmap.getWidth(),
(canvas.getHeight() - mCacheBitmap.getHeight()) / 2 + mCacheBitmap.getHeight()), null);
} if (mFpsMeter != null) {
mFpsMeter.measure();
mFpsMeter.draw(canvas, 20, 30);
}
getHolder().unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas);
}
}
} /**
* This method is invoked shall perform concrete operation to initialize the camera.
* CONTRACT: as a result of this method variables mFrameWidth and mFrameHeight MUST be
* initialized with the size of the Camera frames that will be delivered to external processor.
* @param width - the width of this SurfaceView
* @param height - the height of this SurfaceView
*/
//具体启动相机的过程由子类实现
protected abstract boolean connectCamera(int width, int height); /**
* Disconnects and release the particular camera object being connected to this surface view.
* Called when syncObject lock is held
*/
protected abstract void disconnectCamera(); // NOTE: On Android 4.1.x the function must be called before SurfaceTexture constructor!
protected void AllocateCache()
{
//mCacheBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(mFrameWidth, mFrameHeight, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
//#Modified portrait step2
//为了方向正确mCacheBitmap存储的时相机frame旋转90度之后的数据
//旋转90度后mFrameWidth,mFrameHeight互换
int portraitWidth=mFrameHeight;
int portraitHeight=mFrameWidth;
mCacheBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(portraitWidth, portraitHeight, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
} public interface ListItemAccessor {
public int getWidth(Object obj);
public int getHeight(Object obj);
}; /**
* This helper method can be called by subclasses to select camera preview size.
* It goes over the list of the supported preview sizes and selects the maximum one which
* fits both values set via setMaxFrameSize() and surface frame allocated for this view
* @param supportedSizes
* @param surfaceWidth
* @param surfaceHeight
* @return optimal frame size
*/
protected Size calculateCameraFrameSize(List<?> supportedSizes, ListItemAccessor accessor, int surfaceWidth, int surfaceHeight) {
//选择一个相机frame大小
int calcWidth = 0;
int calcHeight = 0; //允许的最大width和height
//#Modified step4
//相机Frame的mMaxWidth应该与surface的surfaceHeight比
//相机Frame的mMaxHeight应该与surface的surfaceWidth比
//int maxAllowedWidth = (mMaxWidth != MAX_UNSPECIFIED && mMaxWidth < surfaceWidth)? mMaxWidth : surfaceWidth;
//int maxAllowedHeight = (mMaxHeight != MAX_UNSPECIFIED && mMaxHeight < surfaceHeight)? mMaxHeight : surfaceHeight;
int maxAllowedWidth = (mMaxWidth != MAX_UNSPECIFIED && mMaxWidth < surfaceHeight)? mMaxWidth : surfaceHeight;
int maxAllowedHeight = (mMaxHeight != MAX_UNSPECIFIED && mMaxHeight < surfaceWidth)? mMaxHeight : surfaceWidth; for (Object size : supportedSizes) {
int width = accessor.getWidth(size);
int height = accessor.getHeight(size); //在允许的范围内选择最大的size
//client是可通过设置小的mMaxWidth,mMaxHeight来选择低分辨率frame的
if (width <= maxAllowedWidth && height <= maxAllowedHeight) {
if (width >= calcWidth && height >= calcHeight) {
calcWidth = (int) width;
calcHeight = (int) height;
}
}
} return new Size(calcWidth, calcHeight);
}
}
2.JavaCameraView
package org.opencv.android; import java.util.List; import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.ImageFormat;
import android.graphics.SurfaceTexture;
import android.hardware.Camera;
import android.hardware.Camera.PreviewCallback;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams; import org.opencv.BuildConfig;
import org.opencv.core.Core;
import org.opencv.core.CvType;
import org.opencv.core.Mat;
import org.opencv.core.Size;
import org.opencv.imgproc.Imgproc; /**
* This class is an implementation of the Bridge View between OpenCV and Java Camera.
* This class relays on the functionality available in base class and only implements
* required functions:
* connectCamera - opens Java camera and sets the PreviewCallback to be delivered.
* disconnectCamera - closes the camera and stops preview.
* When frame is delivered via callback from Camera - it processed via OpenCV to be
* converted to RGBA32 and then passed to the external callback for modifications if required.
*/
public class JavaCameraView extends CameraBridgeViewBase implements PreviewCallback { private static final int MAGIC_TEXTURE_ID = 10;
private static final String TAG = "JavaCameraView"; private byte mBuffer[];
private Mat[] mFrameChain;
private int mChainIdx = 0;
private Thread mThread;
private boolean mStopThread; protected Camera mCamera;
protected JavaCameraFrame[] mCameraFrame;
private SurfaceTexture mSurfaceTexture;
private int mPreviewFormat = ImageFormat.NV21; public static class JavaCameraSizeAccessor implements ListItemAccessor { @Override
public int getWidth(Object obj) {
Camera.Size size = (Camera.Size) obj;
return size.width;
} @Override
public int getHeight(Object obj) {
Camera.Size size = (Camera.Size) obj;
return size.height;
}
} public JavaCameraView(Context context, int cameraId) {
super(context, cameraId);
} public JavaCameraView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
} //传入的是JavaCameraView的width,height
protected boolean initializeCamera(int width, int height) {
Log.d(TAG, "Initialize java camera");
boolean result = true;
synchronized (this){
mCamera = null;
//mCameraIndex是指定相机的类型,是应用里的设置不是指相机ID
//相机ID需根据类型找
//继承父类CameraBridgeViewBase
//初值为CAMERA_ID_ANY
if (mCameraIndex == CAMERA_ID_ANY) {
Log.d(TAG, "Trying to open camera with old open()");
try {
//先尝试不指定相机类型启动相机
mCamera = Camera.open();
}
catch (Exception e){
Log.e(TAG, "Camera is not available (in use or does not exist): " + e.getLocalizedMessage());
} if(mCamera == null && Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.GINGERBREAD) {
boolean connected = false;
for (int camIdx = 0; camIdx < Camera.getNumberOfCameras(); ++camIdx) {
Log.d(TAG, "Trying to open camera with new open(" + Integer.valueOf(camIdx) + ")");
try {
//若不指定相机类型启动相机失败则遍历所有相机ID一个个尝试启动,一旦成功
//就选择当前成功启动的相机
mCamera = Camera.open(camIdx);
connected = true;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Camera #" + camIdx + "failed to open: " + e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
if (connected) break;
}
}
} else {
//这里是指定相机类型的情况
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.GINGERBREAD) {
int localCameraIndex = mCameraIndex;
if (mCameraIndex == CAMERA_ID_BACK) {
Log.i(TAG, "Trying to open back camera");
Camera.CameraInfo cameraInfo = new Camera.CameraInfo();
//根据相机类型找此类型对应的相机ID
for (int camIdx = 0; camIdx < Camera.getNumberOfCameras(); ++camIdx) {
Camera.getCameraInfo( camIdx, cameraInfo );
if (cameraInfo.facing == Camera.CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_BACK) {
localCameraIndex = camIdx;
break;
}
}
} else if (mCameraIndex == CAMERA_ID_FRONT) {
Log.i(TAG, "Trying to open front camera");
Camera.CameraInfo cameraInfo = new Camera.CameraInfo();
for (int camIdx = 0; camIdx < Camera.getNumberOfCameras(); ++camIdx) {
Camera.getCameraInfo( camIdx, cameraInfo );
if (cameraInfo.facing == Camera.CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_FRONT) {
localCameraIndex = camIdx;
break;
}
}
}
if (localCameraIndex == CAMERA_ID_BACK) {
//localCameraIndex初赋值为CAMERA_ID_BACK类型,指定要启动背面相机
//若有背面相机此处localCameraIndex值已经被赋值为背面相机的相机ID了
Log.e(TAG, "Back camera not found!");
} else if (localCameraIndex == CAMERA_ID_FRONT) {
Log.e(TAG, "Front camera not found!");
} else {
Log.d(TAG, "Trying to open camera with new open(" + Integer.valueOf(localCameraIndex) + ")");
try {
//根据找到的相机ID启动相机
mCamera = Camera.open(localCameraIndex);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Camera #" + localCameraIndex + "failed to open: " + e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
}
}
} //若启动相机失败则返回false
if (mCamera == null)
return false; /* Now set camera parameters */
try {
Camera.Parameters params = mCamera.getParameters();
Log.d(TAG, "getSupportedPreviewSizes()");
List<android.hardware.Camera.Size> sizes = params.getSupportedPreviewSizes(); if (sizes != null) {
//选择预览size
/* Select the size that fits surface considering maximum size allowed */
Size frameSize = calculateCameraFrameSize(sizes, new JavaCameraSizeAccessor(), width, height);
//这里width,height是connectCamera(getWidth(), getHeight())传进来的
//是surfaceView的大小也是surface的大小
//Log相机frame大小和surface大小
Log.d("FunnyAR","surface width: "+width+" surface height: "+height+
"frameSize: "+frameSize.toString()); //选择预览格式
/* Image format NV21 causes issues in the Android emulators */
if (Build.FINGERPRINT.startsWith("generic")
|| Build.FINGERPRINT.startsWith("unknown")
|| Build.MODEL.contains("google_sdk")
|| Build.MODEL.contains("Emulator")
|| Build.MODEL.contains("Android SDK built for x86")
|| Build.MANUFACTURER.contains("Genymotion")
|| (Build.BRAND.startsWith("generic") && Build.DEVICE.startsWith("generic"))
|| "google_sdk".equals(Build.PRODUCT))
params.setPreviewFormat(ImageFormat.YV12); // "generic" or "android" = android emulator
else
params.setPreviewFormat(ImageFormat.NV21); //预览格式记录到成员变量里
mPreviewFormat = params.getPreviewFormat(); Log.d(TAG, "Set preview size to " + Integer.valueOf((int)frameSize.width) + "x" + Integer.valueOf((int)frameSize.height));
params.setPreviewSize((int)frameSize.width, (int)frameSize.height); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH && !android.os.Build.MODEL.equals("GT-I9100"))
params.setRecordingHint(true); //JavaCameraView的聚焦模式也是写定下的
List<String> FocusModes = params.getSupportedFocusModes();
if (FocusModes != null && FocusModes.contains(Camera.Parameters.FOCUS_MODE_CONTINUOUS_VIDEO))
{
params.setFocusMode(Camera.Parameters.FOCUS_MODE_CONTINUOUS_VIDEO);
} mCamera.setParameters(params);
params = mCamera.getParameters(); //设置frame大小
mFrameWidth = params.getPreviewSize().width;
mFrameHeight = params.getPreviewSize().height; //这里涉及到缩放
/*
#Modified portrait step1
为了在deliverAndDrawFrame里往画布上画时应用缩放
<JavaCameraView>里
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
若又想指定缩放后的大小可将<JavaCameraView>放在一个有大小的
LinearLayout里
且当方向是portrait时比率是
surface的width/相机frame的mFrameHeight
surface的height/相机frame的mFrameWidth
若不想设置<JavaCameraView>则这里直接去掉if语句应该也可
*/
if ((getLayoutParams().width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) && (getLayoutParams().height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT))
//mScale = Math.min(((float)height)/mFrameHeight, ((float)width)/mFrameWidth);
mScale = Math.min(((float)width)/mFrameHeight, ((float)height)/mFrameWidth);
else
mScale = 0; //Log缩放和相机Frame大小
Log.d("FunnyAR","mScale: "+mScale+" mFrameWidth: "+mFrameWidth+
" mFrameHeight: "+mFrameHeight); if (mFpsMeter != null) {
mFpsMeter.setResolution(mFrameWidth, mFrameHeight);
} //算frame的字节大小,设置相应大小的缓冲区接收数据
//像素个数
int size = mFrameWidth * mFrameHeight;
//像素个数x当前格式每个像素所需bit个数/一个字节8bit==frame所需byte数
size = size * ImageFormat.getBitsPerPixel(params.getPreviewFormat()) / 8;
mBuffer = new byte[size]; /*
Adds a pre-allocated buffer to the preview callback buffer queue.
Applications can add one or more buffers to the queue.
When a preview frame arrives and there is still at least
one available buffer, the buffer will be used and removed from the queue.
Then preview callback is invoked with the buffer.
If a frame arrives and there is no buffer left, the frame is discarded.
Applications should add buffers back when they finish processing the data
in them.
*/
/*
This method is only necessary when setPreviewCallbackWithBuffer(PreviewCallback)
is used. When setPreviewCallback(PreviewCallback) or
setOneShotPreviewCallback(PreviewCallback) are used,
buffers are automatically allocated.
When a supplied buffer is too small to hold the preview frame data,
preview callback will return null and the buffer will be removed from the
buffer queue.
*/
mCamera.addCallbackBuffer(mBuffer);
/*
Installs a callback to be invoked for every preview frame,
using buffers supplied with addCallbackBuffer(byte[]),
in addition to displaying them on the screen.
he callback will be repeatedly called for as long as preview is active
and buffers are available. Any other preview callbacks are overridden.
*/
mCamera.setPreviewCallbackWithBuffer(this); //一个Mat数组
//注意Yuv420sp格式
mFrameChain = new Mat[2];
mFrameChain[0] = new Mat(mFrameHeight + (mFrameHeight/2), mFrameWidth, CvType.CV_8UC1);
mFrameChain[1] = new Mat(mFrameHeight + (mFrameHeight/2), mFrameWidth, CvType.CV_8UC1); //继承的方法为继承的Bitmap mCacheBitmap初始化内存
AllocateCache(); //JavaCameraFrame内部有对Mat的引用
//mCameraFrame[0].mYuvFrameData就是Mat mFrameChain[0]
mCameraFrame = new JavaCameraFrame[2];
mCameraFrame[0] = new JavaCameraFrame(mFrameChain[0], mFrameWidth, mFrameHeight);
mCameraFrame[1] = new JavaCameraFrame(mFrameChain[1], mFrameWidth, mFrameHeight); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
mSurfaceTexture = new SurfaceTexture(MAGIC_TEXTURE_ID);
mCamera.setPreviewTexture(mSurfaceTexture);
} else
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(null); /* Finally we are ready to start the preview */
Log.d(TAG, "startPreview");
mCamera.startPreview();
}
else
result = false;
} catch (Exception e) {
result = false;
e.printStackTrace();
}
} return result;
} protected void releaseCamera() {
synchronized (this) {
if (mCamera != null) {
mCamera.stopPreview();
mCamera.setPreviewCallback(null); mCamera.release();
}
mCamera = null;
if (mFrameChain != null) {
mFrameChain[0].release();
mFrameChain[1].release();
}
if (mCameraFrame != null) {
mCameraFrame[0].release();
mCameraFrame[1].release();
}
}
} private boolean mCameraFrameReady = false; //重载父类的抽象方法,负责启动相机
@Override
protected boolean connectCamera(int width, int height) { /* 1. We need to instantiate camera
* 2. We need to start thread which will be getting frames
*/
/* First step - initialize camera connection */
Log.d(TAG, "Connecting to camera");
//用initializeCamera函数实现初始化相机连接
if (!initializeCamera(width, height))
return false; mCameraFrameReady = false; /* now we can start update thread */
Log.d(TAG, "Starting processing thread");
mStopThread = false;
mThread = new Thread(new CameraWorker());
mThread.start(); return true;
} @Override
protected void disconnectCamera() {
/* 1. We need to stop thread which updating the frames
* 2. Stop camera and release it
*/
Log.d(TAG, "Disconnecting from camera");
try {
mStopThread = true;
Log.d(TAG, "Notify thread");
synchronized (this) {
this.notify();
}
Log.d(TAG, "Waiting for thread");
if (mThread != null)
mThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
mThread = null;
} /* Now release camera */
releaseCamera(); mCameraFrameReady = false;
} /*
重载Camera.PreviewCallback onPreviewFrame方法
这里onPreviewFrame时在UI线程里被处理的,因为相机时在主线程里被启动的
但是数据将被另一个线程取走处理
*/
/*
Callback interface used to deliver copies of preview frames as they are displayed.
Called as preview frames are displayed. This callback is invoked
on the event thread Camera.open(int) was called from.
*/
@Override
public void onPreviewFrame(byte[] frame, Camera arg1) {
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG)
Log.d(TAG, "Preview Frame received. Frame size: " + frame.length);
synchronized (this) {
//mChainIdx在0,1间切换,由另一个线程负责管理
//OpenCV Java层特有的方法
//mFrameChain[mChainIdx]的大小是1.5height x 1.0width,将数据存进去
mFrameChain[mChainIdx].put(0, 0, frame);
//设置标志表示数据存好了
mCameraFrameReady = true;
//唤醒一个等待当前JavaCameraView.this的线程 this.notify();
}
/*
onPreviewFrame处理数据时addCallbackBuffer()的buffer将出队列被处理
处理完后为了下次onPreviewFrame需再次将buffer给回调
*/
if (mCamera != null)
mCamera.addCallbackBuffer(mBuffer);
} /*
JavaCameraFrame实现CvCameraViewFrame的rgba(),gray()方法
这个类型将通过deliverAndDrawFrame()里的mListener.onCameraFrame(frame)传给用户处理
在JavaCameraFrame的接口里实现Mat的旋转是最好的时机了
如此client通过gray(),rgba()获得的Mat就是方向portrait的了
#Modified portrait step3
*/
private class JavaCameraFrame implements CvCameraViewFrame {
@Override
public Mat gray() {
//返回Mat里的选定区域,这跟Yuv420sp格式紧密相关
//return mYuvFrameData.submat(0, mHeight, 0, mWidth);
//#Modified step3.1
Core.rotate(mYuvFrameData.submat(0, mHeight, 0, mWidth),
portrait_gray,Core.ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE);
return portrait_gray;
} @Override
public Mat rgba() {
if (mPreviewFormat == ImageFormat.NV21)
Imgproc.cvtColor(mYuvFrameData, mRgba, Imgproc.COLOR_YUV2RGBA_NV21, 4);
else if (mPreviewFormat == ImageFormat.YV12)
Imgproc.cvtColor(mYuvFrameData, mRgba, Imgproc.COLOR_YUV2RGB_I420, 4); // COLOR_YUV2RGBA_YV12 produces inverted colors
else
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Preview Format can be NV21 or YV12"); //#Modified step3.2
Core.rotate(mYuvFrameData.submat(0, mHeight, 0, mWidth),
portrait_rgba,Core.ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE); return portrait_rgba;
} public JavaCameraFrame(Mat Yuv420sp, int width, int height) {
super();
mWidth = width;
mHeight = height;
//#Modified
portrait_mHeight=mWidth;
portrait_mWidth=mHeight;
portrait_gray=new Mat(portrait_mHeight,portrait_mWidth,CvType.CV_8UC1);
portrait_rgba=new Mat(portrait_mHeight,portrait_mWidth,CvType.CV_8UC4);
mYuvFrameData = Yuv420sp;
mRgba = new Mat();
} public void release() {
mRgba.release();
} private Mat mYuvFrameData;
private Mat mRgba;
private int mWidth;
private int mHeight;
//#Modified
private int portrait_mHeight;
private int portrait_mWidth;
private Mat portrait_gray;
private Mat portrait_rgba;
}; private class CameraWorker implements Runnable { @Override
public void run() {
do {
boolean hasFrame = false;
synchronized (JavaCameraView.this) {
try {
//onPreviewFrame里frame准备好了会设置mCameraFrameReady为true然后唤醒此线程
//只要相机启动着mStopThread就为false
//当相机启动着且onPreviewFrame里frame没准备好时线程就等待
//等待语句放在while里防止条件没满足时线程被唤醒
while (!mCameraFrameReady && !mStopThread) {
JavaCameraView.this.wait();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//线程被唤醒是因为onPreviewFrame里frame准备好了
if (mCameraFrameReady)
{
//mChainIdx在0,1之间切换表示mCameraFrame当前的缓冲区
mChainIdx = 1 - mChainIdx;
//设置mCameraFrameReady为false用来等下次onPreviewFrame里frame准备好
mCameraFrameReady = false;
//表示当前有frame可用
hasFrame = true;
}
} //线程没停止且有frame可用
if (!mStopThread && hasFrame) {
//当前的缓冲区不为空则处理它
//mChainIdx初值为0,mChainIdx = 1 - mChainIdx设置其为1
//这里1 - mChainIdx为0
//之后mChainIdx值为1,mChainIdx = 1 - mChainIdx设置其为0
//这里1 - mChainIdx为1
//如此循环
//mCameraFrame[1 - mChainIdx].mYuvFrameData就是对mFrameChain[1 - mChainIdx]
//的引用,即JavaCameraFrame类里有对Mat的引用
if (!mFrameChain[1 - mChainIdx].empty())
deliverAndDrawFrame(mCameraFrame[1 - mChainIdx]);
}
} while (!mStopThread);
Log.d(TAG, "Finish processing thread");
}
}
}
3.这是layout文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <!-- 这里1080px,1440px是硬编码,适合redmi note4x屏幕 -->
<!--<org.opencv.android.JavaCameraView
android:id="@+id/javaCameraView"
android:layout_width="1080px"
android:layout_height="1440px" />--> <!--为了应用缩放-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="1080px"
android:layout_height="1440px"
android:orientation="vertical"> <org.opencv.android.JavaCameraView
android:id="@+id/javaCameraView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </LinearLayout> <TextView
android:layout_width="1080px"
android:layout_height="480px"
android:text="FunnyAR!" /> </LinearLayout>
解决OpenCV JavaCameraView相机preview方向问题的更多相关文章
- 使用OpenCV进行相机标定
1. 使用OpenCV进行标定 相机已经有很长一段历史了.但是,伴随着20世纪后期的廉价针孔照相机的问世,它们已经变成我们日常生活的一种常见的存在.不幸的是,这种廉价是由代价的:显著的变形.幸运的是, ...
- 【opencv】相机标定程序内存溢出
运行相机内参标定程序出现内存溢出的错误 opencv的alloc.cpp报cv::OutOfMemoryError 因为同时开了多个线程,每个线程标定一台相机,每个线程都会imread读入所有标定图片 ...
- 利用opencv进行相机标定程序
#include "Stafx.h" ; //棋盘上有13个格子,那么角点的数目12 ; ; //图片的总张数 int main(int argc, char** argv) { ...
- 解决OpenCV Error:Insufficient memory(Failed to allocate 1244164 bytes) in unknown function
从师兄那拷贝过来的代码,师兄的机器上可以运行,环境为Win7+OpenCV231,编译器为Debug Win32,拷贝到自己机器上运行时出现问题. 本机的运行环境为win10+OpenCV244,编译 ...
- 解决opencv和mfc同时使用导致memory leak
参考资料:http://blog.csdn.net/lujin0312/article/details/42214467 最彻底的解决办法就是把用到opencv的部分做成dll,且这个dll中不出现跟 ...
- 解决Opencv高低版本不兼容问题
目前OpenCV版本已更新到2.4...由此出现了一系列问题,解决如下: 1.cxcore.h等头文件找不到: 法一.将opencv1.0中的各种.h或者.lib文件拷到opencv2.3.1对应in ...
- 解决opencv无法读AVI视频的问题
原文来自:http://blog.csdn.net/yeqiu712/article/details/6220030 其实AVI只是一个外壳.里面的东西可不一样的! 问题:为什么我的电脑支持AVI或者 ...
- 触发bfc解决父子元素嵌套垂直方向margin塌陷问题
首先看一下问题案例 .wrapper{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-colo ...
- 解决QPainter::drawText修改文字方向
今天在绘制双坐标曲线的时候需要修改y轴文字提示 QPainter的drawText()函数提供了绘制文本的功能. 它有几种重载形式,我们使用了其中的一种,即制定文本的坐标然后绘制 正常我们的文字书写方 ...
随机推荐
- 【zookeeper】4、利用zookeeper,借助观察模式,判断服务器的上下线
首先什么是观察者模式,可以看看我之前的设计模式的文章 https://www.cnblogs.com/cutter-point/p/5249780.html 确定一下,要有观察者,要有被观察者,然后要 ...
- 使用C# (.NET Core) 实现简单工厂(Simple Factory) 和工厂方法设计模式 (Factory Method Pattern)
本文源自深入浅出设计模式. 只不过我是使用C#/.NET Core实现的例子. 前言 当你看见new这个关键字的时候, 就应该想到它是具体的实现. 这就是一个具体的类, 为了更灵活, 我们应该使用的是 ...
- hibernate框架(2)---Hibernate的核心API
Hibernate的核心API 一般我们通过hibernate进行操作的时候,都会遵循下面的流程,那么接下来我对每一个步骤进行讲解: 1 public void testInsert() { 2 // ...
- while true 死循环判断端口按顺序启动应用
需求:spring微服务应用启动较慢并且要求一个应用启完才能启第二个应用. 思路:加了个while true 死循环判断端口启动了才启下一个应用. 执行方式:/appupgrade/spring_cl ...
- Servlet & JSP系列文章总结
前言 谢谢大家的捧场,真心感谢我的阅读者. @all 下一期,重点在 数据结构和算法 ,希望给大家带来开心.已经出了几篇,大家爱读就是我的开心. Servlet & JSP系列总结 博客, ...
- Eureka客户端注册多网卡下IP选择问题
在使用Spring Cloud多人协作开发时有一个场景:我本机启动了Eureka注册中心,其他人机器需要将服务注册到我本机的Eureka.(服务端和客户端在不同机器上) 这时出现了一个问题:服务成功注 ...
- 《用OpenResty搭建高性能服务端》笔记
概要 <用OpenResty搭建高性能服务端>是OpenResty系列课程中的入门课程,主讲人:温铭老师.课程分为10个章节,侧重于OpenResty的基本概念和主要特点的介绍,包括它的指 ...
- python使用多进程
python多线程适合IO密集型场景,而在CPU密集型场景,并不能充分利用多核CPU,而协程本质基于线程,同样不能充分发挥多核的优势. 针对计算密集型场景需要使用多进程,python的multipro ...
- webservice的两种调用方式
如下 using ConsoleApplication1.TestWebService; using System; using System.Collections; using System.Co ...
- 使用 Synchronized 关键字
使用 Synchronized 关键字来解决并发问题是最简单的一种方式,我们只需要使用它修饰需要被并发处理的代码块.方法或字段属性,虚拟机自动为它加锁和释放锁,并将不能获得锁的线程阻塞在相应的阻塞队列 ...
