浅谈Python之sys.argv
(1)sys.argv是什么
sys模块为进入解释器维护或使用的变量,以及与解释器相关的函数提供了途径。sys.argv在脚本程序中扮演了这样一个角色:将命令行输入的参数作为一个list传入脚本程序,即我们可以在cmd命令形式驱动程序方法下,将设定的参数传入脚本,argv[0]是驱动脚本的名字(由操作系统来决定是否是全路径的名字),如果cmd中,将-c传入,那么argv[0]就是-c,
分界线中的内容为cmd驱动脚本的详细解释,而关于cmd,-c传入的栗子,本文不再赘述 详见https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/03b2f78c3b38f05ea237ae05.html
在解释中,我们看到py [launcher-args] [python-args] script [script-args],这里script是脚本名字,而其后的[script-args]正是要传入脚本中sys.argv的列表,从argv[1]开始。下面举个简单的例子:
import sys
a=sys.argv[0]
b=sys.argv[1]
c=sys.argv[2]
print('argv0:%s'% a)
print('argv1:%s'% b)
print('argv2:%s'%c)
以上代码命名为sys_argvTest.py
然后在cmd中运行:
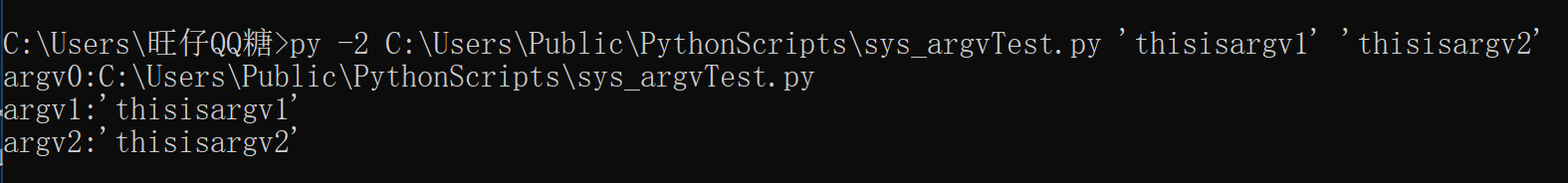
可以看到在脚本名字 后面的'thisisargv1' 'thisisargv2'分别传入了脚本中的sys.argv[1],sys.argv[2]中
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------这是一道华丽的分界线--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
py [launcher-args] [python-args] script [script-args]
-3 : Launch the latest Python 3.x version
-X.Y : Launch the specified Python version
The above all default to 64 bit if a matching 64 bit python is present.
-X.Y-32: Launch the specified 32bit Python version
-X-32 : Launch the latest 32bit Python X version
-X.Y-64: Launch the specified 64bit Python version
-X-64 : Launch the latest 64bit Python X version
-0 --list : List the available pythons
-0p --list-paths : List with paths
-b : issue warnings about str(bytes_instance), str(bytearray_instance)
and comparing bytes/bytearray with str. (-bb: issue errors)
-B : don't write .pyc files on import; also PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=x
-c cmd : program passed in as string (terminates option list)
-d : debug output from parser; also PYTHONDEBUG=x
-E : ignore PYTHON* environment variables (such as PYTHONPATH)
-h : print this help message and exit (also --help)
-i : inspect interactively after running script; forces a prompt even
if stdin does not appear to be a terminal; also PYTHONINSPECT=x
-I : isolate Python from the user's environment (implies -E and -s)
-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list)
-O : remove assert and __debug__-dependent statements; add .opt-1 before
.pyc extension; also PYTHONOPTIMIZE=x
-OO : do -O changes and also discard docstrings; add .opt-2 before
.pyc extension
-q : don't print version and copyright messages on interactive startup
-s : don't add user site directory to sys.path; also PYTHONNOUSERSITE
-S : don't imply 'import site' on initialization
-u : force the stdout and stderr streams to be unbuffered;
this option has no effect on stdin; also PYTHONUNBUFFERED=x
-v : verbose (trace import statements); also PYTHONVERBOSE=x
can be supplied multiple times to increase verbosity
-V : print the Python version number and exit (also --version)
when given twice, print more information about the build
-W arg : warning control; arg is action:message:category:module:lineno
also PYTHONWARNINGS=arg
-x : skip first line of source, allowing use of non-Unix forms of #!cmd
-X opt : set implementation-specific option
--check-hash-based-pycs always|default|never:
control how Python invalidates hash-based .pyc files
file : program read from script file
- : program read from stdin (default; interactive mode if a tty)
arg ...: arguments passed to program in sys.argv[1:]
PYTHONSTARTUP: file executed on interactive startup (no default)
PYTHONPATH : ';'-separated list of directories prefixed to the
default module search path. The result is sys.path.
PYTHONHOME : alternate <prefix> directory (or <prefix>;<exec_prefix>).
The default module search path uses <prefix>\python{major}{minor}.
PYTHONCASEOK : ignore case in 'import' statements (Windows).
PYTHONIOENCODING: Encoding[:errors] used for stdin/stdout/stderr.
PYTHONFAULTHANDLER: dump the Python traceback on fatal errors.
PYTHONHASHSEED: if this variable is set to 'random', a random value is used
to seed the hashes of str, bytes and datetime objects. It can also be
set to an integer in the range [0,4294967295] to get hash values with a
predictable seed.
PYTHONMALLOC: set the Python memory allocators and/or install debug hooks
on Python memory allocators. Use PYTHONMALLOC=debug to install debug
hooks.
PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the locale
coercion behavior. Use PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE=warn to request display of
locale coercion and locale compatibility warnings on stderr.
PYTHONBREAKPOINT: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the default
debugger. It can be set to the callable of your debugger of choice.
PYTHONDEVMODE: enable the development mode.
浅谈Python之sys.argv的更多相关文章
- 开发技术--浅谈Python函数
开发|浅谈Python函数 函数在实际使用中有很多不一样的小九九,我将从最基础的函数内容,延伸出函数的高级用法.此文非科普片~~ 前言 目前所有的文章思想格式都是:知识+情感. 知识:对于所有的知识点 ...
- 浅谈Python时间模块
浅谈Python时间模块 今天简单总结了一下Python处理时间和日期方面的模块,主要就是datetime.time.calendar三个模块的使用.希望这篇文章对于学习Python的朋友们有所帮助 ...
- Python中 sys.argv[]的用法
Python中 sys.argv[]的用法 因为是看书自学的python,开始后不久就遇到了这个引入的模块函数,且一直在IDLE上编辑了后运行,试图从结果发现它的用途,然而结果一直都是没结果,也在网上 ...
- 浅谈Python在信息学竞赛中的运用及Python的基本用法
浅谈Python在信息学竞赛中的运用及Python的基本用法 前言 众所周知,Python是一种非常实用的语言.但是由于其运算时的低效和解释型编译,在信息学竞赛中并不用于完成算法程序.但正如LRJ在& ...
- 31 Python中 sys.argv[]的用法简明解释(转)
Python中 sys.argv[]的用法简明解释 因为是看书自学的python,开始后不久就遇到了这个引入的模块函数,且一直在IDLE上编辑了后运行,试图从结果发现它的用途,然而结果一直都是没结果, ...
- python argparse sys.argv
python argparse sys.argv class WeiLearningArgumentParser(argparse.ArgumentParser): def __init__(self ...
- python关于sys.argv列表的应用场景
python关于sys.argv列表的应用场景 1.需求很简单: 使用 sys.argv 获取命令行参数(即要判断的文件名),然后判断文件是否存在,文件存在再进一步判断是否有读权限 2.分析: (1) ...
- 浅谈python字符串存储形式
http://blog.csdn.net/zhonghuan1992 钟桓 2014年8月31日 浅谈python字符串存储形式 记录一下自己今的天发现疑问而且给出自己现有知识有的回答. 长话短说,用 ...
- 开发技术--浅谈python数据类型
开发|浅谈python数据类型 在回顾Python基础的时候,遇到最大的问题就是内容很多,而我的目的是回顾自己之前学习的内容,进行相应的总结,所以我就不玩基础了,很多在我实际生活中使用的东西,我会在文 ...
随机推荐
- 吴裕雄--天生自然HADOOP操作实验学习笔记:单节点伪分布式安装
实验目的 了解java的安装配置 学习配置对自己节点的免密码登陆 了解hdfs的配置和相关命令 了解yarn的配置 实验原理 1.Hadoop安装 Hadoop的安装对一个初学者来说是一个很头疼的事情 ...
- JavaScript中的变量在内存中的具体存储形式
栈内存和堆内存 JavaScript中的变量分为基本类型和引用类型 基本类型是保存在栈内存中的简单数据段,它们的值都有固定的大小,保存在栈空间,通过按值访问 引用类型是保存在堆内存中的对象,值大小不固 ...
- 在linux中安装redis
1.安装gcc环境: yum install gcc-c++ 2.下载redis的源码包,把源码包上传到linux服务器 3.解压源码包 : tar -zxvf redis-3.0.0.tar.gz ...
- String类与StringBuffer类
String类与StringBuffer类 一.String类和StringBuffer类的区别 String类是不可变类,新建的对象为不可变对象(String类的内容和长度是固定的),一旦被创建 ...
- 074、Java面向对象之构造方法重载
01.代码如下: package TIANPAN; class Book { // 定义一个新的类 private String title; // 书的名字 private double price ...
- POJ 3050 Hopscotch 四方向搜索
Hopscotch Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 6761 Accepted: 4354 Descrip ...
- ES6中 ,var,let和const的区别
var的特点 没有代码块的概念,全局范围内都有效 存在“变量提升”现象,即变量可以在声明之前使用,值为undefined let的特点 声明的变量仅在块级作用域内有效,存在了代码块的概念 不存在“变量 ...
- 今日份学习: Spring中使用AOP并实现redis缓存?
笔记 在Spring中如何使用AOP? Spring是如何切换JDK动态代理和CGLIB的? spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true (在下方第二个链接中,原生doc中提 ...
- Kubernetes 集群日志管理【转】
Kubernetes 开发了一个 Elasticsearch 附加组件来实现集群的日志管理.这是一个 Elasticsearch.Fluentd 和 Kibana 的组合.Elasticsearch ...
- XmlBeanDefinitionReader
