SNMP History and OID/MIB Tour
https://www.pei.com/snmp-history-oid-mib/
Description:
This document describes a bit of history and functionality of the SNMP protocol for monitoring.
SNMP Monitoring and Basic Architecture:
SNMP(Simple Network Management Protocol) was developed in the 80s by the IETF (Internet Engineer Task Force) as part of the IP(Internet Protocol Suite). There have been a few competitors developed by organizations, but over time SNMP has become the de-facto standard for monitoring network-connected devices. In addition to providing monitoring capabilities SNMP, also provides the ability for remote management to a variety of devices.
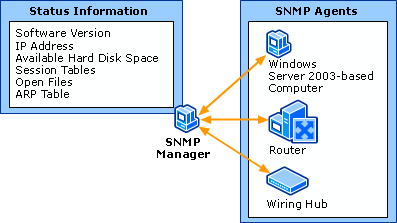
SNMP-based monitoring systems consist of Agents, which are installed on devices connected to networks and Network Management Systems/Stations(NMS), which are used to actively collect information from Agents as well as run tests against network-connected devices—usually for the purpose of determining health.
In addition to an SNMP agent serving out information about its device, it may also push notifications (known as traps) across the network to an NMS. This would be used for such information as that the device just started (known as coldstart).
In cases where SNMP is being utilized for remote management of devices, users would push changes across networks to Agents installed on devices, which then enact the prescribed changes.
SNMP OIDs:
Every piece of information an SNMP Agent serves out, and every type of trap that it supports, is associated with a unique identifier known as an OID (Object Identifier).
OID is a system created by the ITU and ISO organizations for international standardization of Data. It isn’t only used for network monitoring or SNMP, it is a standard used for all sorts of data. Examples of this are Hl7, which hass to do with electronic medical record taxonomy or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol(LDAP) protocol attributes and object classes. Think of it as an international standard for indexing data.
The OID system is heiarchical, which is to say, it is a tree structure. For instance, the OID .1.3.6, 6 would be part of .1.3 heiarchy, .3.6 would be part of the .1 hearchy etc… The root of the OID tree is only 2 values: .1 for ISO (which is where SNMP lives) and .0 for the ITU. Certain sections of the subtree for .1 are free-form, other sections are delegated to particular companies to use and yet other sections of three require that you register with ISO or the ITU. This includes goverments, large buisiness etc…
SNMP OIDs can start being found at OID .1.3.6.1
.1 - ISO assigned.
.1.3 - ISO identified organizations
.1.3.6 - The US Department of Defense
.1.3.6.1 - The InternetMost OIDs for business network devices and systems then fall under
.1.3.6.1.4.1 - IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) registered private enterprises.Under this hierarchy, you will see OIDs for all companies setting up custom OIDs for equipment. Here are some examples:
.1.3.6.1.4.1.9 - Cisco Systems (They embraced SNMP pretty early as you can see by their low number)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.2636 - Juniper
.1.3.6.1.4.1.311 - Microsoft.Now, say an NMS station wants to pull interface Output Queue drops from a router made by Cisco; it would make a request for the value of OID: .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.276.1.1.1.1.11
Which you can see is part of their tree at 1.3.6.1.4.9. Any custom statistic they develop should be registered under that portion of the OID tree.
MIBs and Enterprise Non-specific OIDs:
A MIB (Management Information Base), contains descriptions for every OID registered with either ISO or ITU. An MIB is an ASCII file, which is human readable and formatted in such a way as to work with what is called a MIB compiler. A MIB compiler simply builds a browsable tree of OIDs based descriptions of individual OIDs contained therein. The descriptions of OIDs contained in MIBs provide a short-name syntax for each OID used, the type of data allowed to be stored, and information on how that OID is used.
It is a common misconception that MIBs are necessary to enable functionality on SNMP Agents or devices. This is not true; loading MIBs into an agent simply allows that agent or client to provide more detailed information on the OIDs that it serves out or queries.
For instance, here is an SNMP client querying a server for all of it’s OIDs when the client has only the ISO MIB loaded:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING: "Linux PEI-HQ-NMS1 4.2.0-27-generic #32~14.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Fri Jan 22 15:32:26 UTC 2016 x86_64"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0 = OID: iso.3.6.1.4.1.8072.3.2.10
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 = Timeticks: (1223) 0:00:12.23
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0 = STRING: "root"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0 = STRING: "PEI-HQ-NMS1"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0 = STRING: "Unknown"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.8.0 = Timeticks: (0) 0:00:00.00
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.1 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.11.3.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.2 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.15.2.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.3 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.10.3.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.4 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.5 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.49
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.6 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.4
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.7 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.50
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.8 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.16.2.2.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.9 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.13.3.1.3Here is a similar query from a Sun system with the SNMPv2 MIB loaded on the client:
SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0 = STRING: ILOM machine custom description
SNMPv2-MIB::sysObjectID.0 = OID: SUN-ILOM-SMI-MIB::sunILOMSystems
DISMAN-EVENT-MIB::sysUpTimeInstance = Timeticks: (16439826) 1 day, 21:39:58.26
SNMPv2-MIB::sysContact.0 = STRING: set via snmp test
SNMPv2-MIB::sysName.0 = STRING: SUNSPHOSTNAME
SNMPv2-MIB::sysLocation.0 = STRING:
SNMPv2-MIB::sysServices.0 = INTEGER: 72
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORLastChange.0 = Timeticks: (14) 0:00:00.14
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.1 = OID: IF-MIB::ifMIB
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.2 = OID: SNMPv2-MIB::snmpMIB
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.3 = OID: TCP-MIB::tcpMIB
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.4 = OID: RFC1213-MIB::ip
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.5 = OID: UDP-MIB::udpMIB
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.6 = OID: SNMP-VIEW-BASED-ACM-MIB::vacmBasicGroup
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.7 = OID: SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB::snmpFrameworkMIBCompliance
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.8 = OID: SNMP-MPD-MIB::snmpMPDCompliance
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.9 = OID: SNMP-USER-BASED-SM-MIB::usmMIBComplianceAs you can see, the MIB is simply translating pieces of the OID into a more user-readable format. Instead of 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0, we see SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0, which for many things is easier to discern.
Mainly, MIBs contain lists of all OIDs by purpose.
Vendor Non-Specific OIDs/MIBs
Certain statistics aren’t vendor specific and have been around for a long time. Most NMS systems don’t poll for enterprise specific OIDs, but go after these long-hanging fruit that are common to all network connected devices. CPU Utilization, Disk drive utilization, and Network Utilization are all examples of types of stats that aren’t unique to a particular vendor. Most of these MIBS were created/maintained by the Internet Engineering Taskforce and are contained under:
.1.3.6.1.2.1 -> SNMP MIB2with .1.3.6.1.2 being the IETF management tree.
Here are some really handy MIBs under this heiarchy:
1.3.6.1.2.1.1 - SNMP MIB2 System: Contains system description, contact information etc...
1.3.6.1.2.1.2 - the IF-MIB, which contains a wide variety of network statistics information. Everything from number of Octets coming into an interface to a description of the interface.
1.3.6.1.2.1.25 - The Host-resources MIB, everything from disk utilization to CPU and Memory.
1.3.6.1.2.1.43 - The Printer MIB, which contains all general printer statistics.Mfuller, PEI
SNMP History and OID/MIB Tour的更多相关文章
- SNMP学习笔记之SNMP介绍,OID及MIB库
1.1. SNMP概览 SNMP的基本知识介绍简单网络管理协议(SNMP-Simple Network Management Protocol)是一个与网络设备交互的简单方法.该规范是由IETF ...
- SNMP介绍,OID及MIB库
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4502d59c0101fcy2.html
- Ubuntu 安装snmp报Unlinked OID in IPATM-IPMC-MIB: marsMIB ::= { mib-2 57 }错误
首先运行下面的脚本(脚本摘自:http://www.th7.cn/system/lin/201304/38800.shtml) #!/bin/bashfor i in /usr/share/mibs/ ...
- SNMP学习笔记之iReasoning MIB Browser
0x00 MIB Browser iReasoning MIB浏览器是一个强大和易于使用的工具由iReasoning SNMP API提供支持. MIB浏览器是工程师管理启用SNMP的网络设备和应用程 ...
- SNMP与MIB
简单网络管理协议(SNMP:Simple Network Management Protocol)是一套网络管理协议,注意,SNMP是一个强大的网络管理协议,而不是"简单"的.利用 ...
- Linux服务器SNMP常用OID (转)
原文地址:http://www.haiyun.me/archives/linux-snmp-oid.html 收集整理一些Linux下snmp常用的OID,用做服务器监控很不错. 服务器负载: 1 2 ...
- SNMP学习笔记之Linux服务器SNMP常用OID
收集整理一些Linux下snmp常用的OID,用做服务器监控很不错. 应用示例 查看服务器1分钟平均负载: snmpwalk -v1 -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.4.1. ...
- ubuntu snmp Error: unknown payload OID
ubuntu snmp Error: unknown payload OID 2013-11-12 15:51:48 标签:ubuntu Error snmp unknown payload OID ...
- (转)Linux服务器SNMP常用OID
原文:https://www.haiyun.me/archives/linux-snmp-oid.html 收集整理一些Linux下snmp常用的OID,用做服务器监控很不错.服务器负载: 1 2 3 ...
随机推荐
- 2.1.JVM的垃圾回收机制,判断对象是否死亡
因为热爱,所以坚持. 文章下方有本文参考电子书和视频的下载地址哦~ 这节我们主要讲垃圾收集的一些基本概念,先了解垃圾收集是什么.然后触发条件是什么.最后虚拟机如何判断对象是否死亡. 一.前言 我们 ...
- 在ES5实现ES6中的Object.is方法
ES6中对象的扩展里面添加了一个Object.is方法,用于比较两个值是否严格相等.内部计算与 === 行为基本一致.那么我们怎么在不支持这个方法的ES5中实现呢? 首先我们需要搞清楚两点,1:Obj ...
- PTA数据结构与算法题目集(中文) 7-43字符串关键字的散列映射 (25 分)
PTA数据结构与算法题目集(中文) 7-43字符串关键字的散列映射 (25 分) 7-43 字符串关键字的散列映射 (25 分) 给定一系列由大写英文字母组成的字符串关键字和素数P,用移位法定义 ...
- CentOS 6.5系统实现NFS文件共享
一台Linux server ip 192.168.1.254,一台Linux client ip 192.168.1.100操作系统:CentOS 6.5需求描述:1:将/root 共享给192.1 ...
- 安卓开发学习日记 DAY3——TextView,EditView,ImageView
今天学习了一些控件的使用方法,包括TextView,EditView,ImageView 1.TextView,输出一个文本呗 主要属性有 android:id 标志 android:layout_w ...
- Android 图片裁剪库 uCrop
引语 晚上好,我是猫咪,我的公众号「程序媛猫咪」会推荐 GitHub 上好玩的项目,挖掘开源的价值,欢迎关注我. 现在 Android 开发,离不开图片,必然也需要图片裁剪功能,这个实现可以调用系统的 ...
- CentOS Linux安装后扩充SWAP分区
1. 首先先查看目前swap分区大小: free -hm total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 11G 801M 10G 236K ...
- c++容器的底层数据结构
序列式容器 vector ->底层数据结构为数组,支持快速随机访问 list ->底层数据结构为双向链表,支持快速增加和删除 deque ->底层数据结构为一个中央控制器和多个缓冲区 ...
- Spring--开篇 (spring优缺点、模块组件、各个jar包详解)
Spring--开篇 分类: SSH&EJB2012-11-23 15:25 4369人阅读 评论(13) 收藏 举报 javaJavaJAVAspringSpringwebWebWEB框架 ...
- 数据结构和算法(Golang实现)(17)常见数据结构-树
树 树是一种比较高级的基础数据结构,由n个有限节点组成的具有层次关系的集合. 树的定义: 有节点间的层次关系,分为父节点和子节点. 有唯一一个根节点,该根节点没有父节点. 除了根节点,每个节点有且只有 ...
