iOS关于RunLoop和Timer
RunLoop这个东西,其实我们一直在用,但一直没有很好地理解它,或者甚至没有知道它的存在。RunLoop可以说是每个线程都有的一个对象,是用来接受事件和分配任务的loop。永远不要手动创建一个runloop,它是跟随着每个线程的。一个RunLoop接收两种source的事件:input source和timer source。同时必须知道的是,input source,runloop是异步交付的,而timer source是同步交付的。每个runloop都有一个RunLoop Modes,代表它以何种方式执行。
我们为什么从来没有感觉到runloop的存在呢,是因为当程序启动,系统默认帮我们启动了一个主线程的runloop,并且一直在运行,直到程序退出。而用户创建的子线程,runloop是需要手动启动的,所以在线程里启动timer或者调用performSelector: withObject:afterDelay:inModes: 是需要启动runloop的。在后面我会介绍到怎么启动。
关于input source :一般来说,input source基本我们用的就是下面几种方式调用的:
|
Methods |
Description |
performSelectorOnMainThread: withObject: performSelectorOnMainThread: withObject: |
Performs the specified selector on the application’s main thread during that thread’s next run loop cycle. These methods give you the option of blocking the current thread until the selector is performed. |
performSelector: onThread:withObject: performSelector: onThread:withObject: |
Performs the specified selector on any thread for which you have an NSThread object. These methods give you the option of blocking the current thread until the selector is performed. |
performSelector: withObject: afterDelay: performSelector: withObject: |
Performs the specified selector on the current thread during the next run loop cycle and after an optional delay period. Because it waits until the next run loop cycle to perform the selector, these methods provide an automatic mini delay from the currently executing code. Multiple queued selectors are performed one after another in the order they were queued. |
cancelPreviousPerformRequestsWithTarget: cancelPreviousPerformRequestsWithTarget: |
Lets you cancel a message sent to the current thread using the performSelector: withObject: afterDelay: or performSelector: withObject: afterDelay:inModes: method. |
这是系统帮我们封装了一层,非常容易调用。用户可以创建自己的Port-based input sources,用来监听某个端口的事件跟其他线程通信:
- (void)addPort:(NSPort *)aPort forMode:(NSString *)mode; - (void)removePort:(NSPort *)aPort forMode:(NSString *)mode;
就是利用NSPort对象进行的消息传递和delegate,我们一般用不了,有兴趣可以看看NSPort的介绍。
关于timer source:就是我们平时用到的NSTimer了。
至于我们什么时候需要用到runloop呢,主要是下面几种情况:
1.需要用到NSPort或者其他input source跟其他线程通信。
2.在线程启动timer。
3.在线程里调用performSelector...这类函数去调用。
下面我简单用一个例子怎么在线程里启动timer或者performSelector...如下:
-(void)testMain
{
//开启一个测试子线程
[NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(threadMethod) toTarget:self withObject:nil];
}
-(void)threadMethod
{
//没用的timer
//NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:.2 target:self selector:@selector(timerDone) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
//真正启动了timer
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimerscheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:.2target:selfselector:@selector(timerDone) userInfo:nilrepeats:YES];
[[NSRunLoopcurrentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
[[NSRunLoopcurrentRunLoop] run];
//同理,调用performSelector也一样
//[self performSelector:@selector(timerDone) withObject:nil afterDelay:.2];
//[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] run];
}
-(void)timerDone
{
NSLog(@"Timer Run");
}
NStimer,几乎每个做iOS开发的程序员都用过,但是有一个关于Timer的介绍估计很多人都不知道:timer是不一定准时的,是有可能被delay的,每次间隔的时间是不一定一样的。
A repeating timer reschedules itself automatically based on the scheduled firing time, not the actual firing time. For example, if a timer is scheduled to fire at a particular time and every 5 seconds after that, the scheduled firing time will always fall on the original 5 second time intervals, even if the actual firing time gets delayed. If the firing time is delayed so much that it misses one or more of the scheduled firing times, the timer is fired only once for the missed time period. After firing for the missed period, the timer is rescheduled for the next scheduled firing time.
简单解读一下:就是说一个repeat的timer,它在创建的时候就把每次的执行时间算好了,而不是真正启动的时候才计算下次的执行时间。举个例子,假如一个timer在一个特定的时间t激活,然后以间隔5秒的时间重复执行。那么它的执行操作的时间就应该为t, t+5, t+10,... 假如它被延迟了,例如实际上timer在t+2的时候才启动,那么它下次执行的时间还是t+5,而并不是t+2+5,如果很不幸地在t+5还没有启动,那么它理应该在t执行的操作就跟下一次t+5的操作合为一个了。至于为什么会延迟呢,这就跟当前线程的操作有关,因为timer是同步交付的,所以假如当前线程在执行很复杂的运算时,那必须等待运算的完成才能调用timer,这就导致了timer的延迟。
我们就用一个例子来看看效果吧,代码为:
//这里创建timer以每隔1秒执行
[NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval: target:self selector:@selector(timerDone) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
//这里在第3秒的时候模拟一个复杂运算
[self performSelector:@selector(busyDone) withObject:nil afterDelay:]; -(void)busyDone
{
//这里模拟线程复杂的运算
for(NSInteger i = ; i< 0xffffffff;i++){ }
NSLog(@"BusgDone");
} -(void)timerDone
{
NSLog(@"Timer Run");
}
执行结果为:
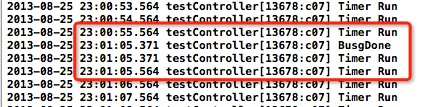
可以看到,timer本来都是以每隔1秒执行,毫秒都是.564,然后在进行复杂的运算时候,timer直接被delay了,当执行完BusyDone之后,立即执行了TimerRun,然后又在.564执行了TimerRun,而不是距离上次执行时间的1秒。
仅供参考。
iOS关于RunLoop和Timer的更多相关文章
- iOS多线程-RunLoop简介
什么是RunLoop? 从字面上来看是运行循环的意思. 内部就是一个do{}while循环,在这个循环里内部不断的处理各种任务(比如:source/timer/Observer) RunLoop的存在 ...
- ios之runloop笔记
网上关于runloop的文章不计其数,再此,贴个自认为讲的比较简单明了的文章 http://www.jianshu.com/p/536184bfd163 个人理解: ios的runloop应该是类似于 ...
- iOS开发RunLoop学习:四:RunLoop的应用和RunLoop的面试题
一:RunLoop的应用 #import "ViewController.h" @interface ViewController () /** 注释 */ @property ( ...
- iOS - OC RunLoop 运行循环/消息循环
1.RunLoop 1)运行循环: 运行循环在 iOS 开发中几乎不用,但是概念的理解却非常重要. 同一个方法中的代码一般都在同一个运行循环中执行,运行循环监听 UI 界面的修改事件,待本次运行循环结 ...
- iOS开发RunLoop
最近处于离职状态,时间也多了起来,但是学习还是不能放松,今天总结一下RunLoop,RunLoop属于iOS系统层的东西,还是比较重要的. 一.什么是RunLoop 字面意思看是跑圈,也可以看作运行循 ...
- iOS之RunLoop
RunLoop是iOS线程相关的比较重要的一个概念,无论是主线程还是子线程,都对应一个RunLoop,如果没有RunLoop,线程会马上被系统回收. 本文主要CFRunLoop的源码解析,并简单阐述一 ...
- iOS开发-Runloop详解(简书)
不知道大家有没有想过这个问题,一个应用开始运行以后放在那里,如果不对它进行任何操作,这个应用就像静止了一样,不会自发的有任何动作发生,但是如果我们点击界面上的一个按钮,这个时候就会有对应的按钮响应事件 ...
- iOS开发RunLoop学习:一:RunLoop简单介绍
一:RunLoop的简单介绍 #import "ViewController.h" @interface ViewController () @end @implementatio ...
- iOS开发 - RunLoop理解
RunLoop概念 运行循环,一个 run loop 就是一个事件处理的循环,用来不停的调度工作以及处理事件 作用 保持程序的持续运行 监听处理App中的各种事件(触摸事件,定时器事件,selecto ...
随机推荐
- crawler_爬虫开发的准备工作【工具】
俗话说工欲善其事必先利其器,做java网络爬虫开发分析网页的分析工具,抓包工具比不可少,一下是个人常用的几个工具. 1.firefox低版本是为了支持httpwather , ie各个版本都支持htt ...
- MVC 插件化框架支持原生MVC的Area和路由特性
.NET MVC 插件化框架支持原生MVC的Area和路由特性 前面开放的源码只是简单的Plugin的实现,支持了插件的热插拔,最近晚上偶然想到,原生的MVC提供Areas和RouteAtrribut ...
- mysql_MYSQL远程登录权限设置
Mysql默认关闭远程登录权限,如下操作允许用户在任意地点登录: 1. 进入mysql,GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY ...
- 程序员的Scala
C#程序员的Scala之路第九章(Scala的层级) 摘要: 1.Scala的类层级Scala里类的顶端是Any所有的类都继承Any类,Any包括以下几个通用方法:final def ==(that: ...
- SSAS系列——【08】多维数据(程序展现Cube)
原文:SSAS系列--[08]多维数据(程序展现Cube) 1.引用DLL? 按照之前安装的MS SQLServer的步骤安装完成后,发现在新建的项目中“Add Reference”时居然找不到Mic ...
- 登录记住账号和密码小Demo
读取 // 1.读取沙盒中plist文件 // 1.1.获得沙盒根路径 NSString *home = NSHomeDirectory(); // 1.2.拼接Documents路径 NSStrin ...
- perconaXTRADB Cluster在Redhat Linux上的安装
installing-perconaXTRADB Cluster 5.6 For Redhat 6.4 一.server版本号查看 Root# cat /etc/redhat-release Red ...
- hdu - 3049 - Data Processing(乘法逆元)
题意:N(N<=40000)个数n1, n2, ..., nN (ni<=N),求(2 ^ n1 + 2 ^ n2 + ... + 2 ^nN) / N % 1000003. 题目链接:h ...
- Robotium源码分析之运行原理
从上一章<Robotium源码分析之Instrumentation进阶>中我们了解到了Robotium所基于的Instrumentation的一些进阶基础,比如它注入事件的原理等,但Rob ...
- 如何实现TWaver 3D颜色渐变
一般而言,须要实现3D物体的渐变,通常的思路就是通过2D绘制一张渐变canvas图片作为3D对象的贴图.这样的方式是能够解决这类问题的.只是对于一般用户而言,通过2D生成一张渐变的图片.有一定的难度, ...
