第六章 dubbo源码解析目录
从 9.1 客户端发起请求源码 的客户端请求总体流程图中,截取部分如下:
//代理发出请求
proxy0.sayHello(String paramString)
-->InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
-->new RpcInvocation(method, args)
-->MockClusterInvoker.invoke(Invocation invocation)//服务降级的地方
dubbo就是通过MockClusterInvoker来实现服务降级的。
一、示例
1 public interface DemoService {
2 // String sayHello(String name);
3 Car sayHello(String name);
4 }
将dubbo-demo中的服务接口定义一个返回模型Car。提供者实现如下:

1 public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
2 public Car sayHello(String name) {
3 Car car = new Car();
4 car.setCarNum("浙A10000");
5 car.setGoMile(100);
6 return car;
7 }
8 }

消费者使用如下:

1 public class Consumer {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"META-INF/spring/dubbo-demo-consumer.xml"});
4 context.start();
5 DemoService demoService = (DemoService) context.getBean("demoService"); // get remote service proxy
6
7 while (true) {
8 try {
9 Thread.sleep(1000);
10 Car hello = demoService.sayHello("world"); // call remote method
11 System.out.println(hello.getCarNum() + "-" + hello.getGoMile()); // get result
12 } catch (Throwable throwable) {
13 throwable.printStackTrace();
14 }
15 }
16 }
17 }

二、使用方式
实际使用中,会通过直接在dubbo-admin中设置服务降级策略,这里使用dubbo用户手册中的方式来更清晰的看一下服务降级的配置(实际上就是进行配置覆盖)
配置规则:
1、使用自定义mock类(接口名+Mock)
- mock = default => DemoServiceMock
- mock = true => DemoServiceMock
- mock = fail => DemoServiceMock
- mock = force => DemoServiceMock
2、先普通执行,执行失败之后再执行相应的mock逻辑
- mock = fail:throw => throw new RpcException(" mocked exception for Service degradation. ");
- mock = fail:throw XxxException => throw new RpcException(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION, XxxException);
- mock = fail:return => return null
- mock = fail:return xxx => return xxx
- mock = fail:return empty => return new Car()
3、直接执行相应的mock逻辑
- mock = force:throw => throw new RpcException(" mocked exception for Service degradation. ");
- mock = force:throw XxxException => throw new RpcException(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION, XxxException);
- mock = force:return => return null
- mock = force:return xxx => return xxx
- mock = force:return empty => return new Car()
进行配置:

1 public class DegradeTest {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 RegistryFactory registryFactory = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(RegistryFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
4 Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(URL.valueOf("zookeeper://10.211.55.5:2181"));
5 // return null;
6 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:return"));
7 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:return+null"));
8 // return 空对象;
9 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:return+empty"));
10 // return value;
11 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:return+hello"));
12 // throw exception
13 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:throw"));
14 // throw custom-msg exception
15 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:throw+com.alibaba.dubbo.Test.MyRuntimeException"));
16 // 执行mock类
17 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoServiceMock"));
18 }
19 }

上述需要注意的是需要配置为“force:return+null”的格式而非“force:return null”。(实际上空格的url encode就是+号),上述代码的执行,实际上是在zk上创建configurators的子节点:

关于覆盖配置:http://dubbo.io/books/dubbo-user-book/demos/config-rule.html
override://表示数据采用覆盖方式,支持override和absent,可扩展,必填。0.0.0.0表示对所有 IP 地址生效,如果只想覆盖某个 IP 的数据,请填入具体 IP,必填。com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoServicecategory=configurators表示该数据为动态配置类型,必填。dynamic=false表示该数据为持久数据,当注册方退出时,数据依然保存在注册中心,必填。enabled=true覆盖规则是否生效,可不填,缺省生效。application=demo-consumer表示只对指定应用生效,可不填,表示对所有应用生效。mock=force:return+nulloverride的 URL 参数上。
三、源码分析

1 public class MockClusterInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
2 private final Directory<T> directory; //RegistryDirectory:存储invoker列表
3 private final Invoker<T> invoker; //FailoverClusterInvoker:容错策略
4
5 public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
6 Result result = null;
7
8 String value = directory.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
9 if (value.length() == 0 || value.equalsIgnoreCase("false")) {
10 //no mock
11 result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
12 } else if (value.startsWith("force")) {
13 ...
14 //force:direct mock
15 result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null);
16 } else {
17 //fail-mock
18 try {
19 result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
20 } catch (RpcException e) {
21 if (e.isBiz()) {
22 throw e;
23 } else {
24 ...
25 result = doMockInvoke(invocation, e);
26 }
27 }
28 }
29 return result;
30 }
31 }

首先去获取mock参数,
- 如果没有配置,则直接使用FailoverClusterInvoker去正常的向provider发出请求;
- 如果配置为以force开头的,则直接执行doMockInvoke(Invocation invocation, RpcException e),不再向provider发送请求;
- 如果配置为以fail开头的,则先使用FailoverClusterInvoker去正常的向provider发出请求,如果失败抛出了非业务异常,则执行doMockInvoke(Invocation invocation, RpcException e);

1 private Result doMockInvoke(Invocation invocation, RpcException e) {
2 Result result = null;
3 Invoker<T> minvoker;
4
5 List<Invoker<T>> mockInvokers = selectMockInvoker(invocation); //获取mock类型的Invoker
6 if (mockInvokers == null || mockInvokers.size() == 0) {
7 minvoker = (Invoker<T>) new MockInvoker(directory.getUrl()); //如果没有配置mock类型的Invoker,则自己创建一个MockInvoker
8 } else {
9 minvoker = mockInvokers.get(0);
10 }
11 try {
12 result = minvoker.invoke(invocation); //执行MockInvoker的invoke(Invocation invocation)方法
13 } catch (RpcException me) {
14 if (me.isBiz()) {
15 result = new RpcResult(me.getCause());
16 } else { //非业务异常
17 throw new RpcException(me.getCode(), getMockExceptionMessage(e, me), me.getCause());
18 }
19 } catch (Throwable me) {
20 throw new RpcException(getMockExceptionMessage(e, me), me.getCause());
21 }
22 return result;
23 }

从RegistryDirectory中获取MockInvoker:

1 /**
2 * Return MockInvoker
3 * Contract:
4 * directory.list() will return a list of normal invokers if Constants.INVOCATION_NEED_MOCK is present in invocation, otherwise, a list of mock invokers will return.
5 * if directory.list() returns more than one mock invoker, only one of them will be used.
6 *
7 * @param invocation
8 * @return
9 */
10 private List<Invoker<T>> selectMockInvoker(Invocation invocation) {
11 List<Invoker<T>> invokers = null;
12 //TODO generic invoker?
13 if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
14 //Note the implicit contract (although the description is added to the interface declaration, but extensibility is a problem. The practice placed in the attachement needs to be improved)
15 ((RpcInvocation) invocation).setAttachment(Constants.INVOCATION_NEED_MOCK, Boolean.TRUE.toString());
16 //directory will return a list of normal invokers if Constants.INVOCATION_NEED_MOCK is present in invocation, otherwise, a list of mock invokers will return.
17 try {
18 invokers = directory.list(invocation);
19 } catch (RpcException e) {
20 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
21 logger.info("Exception when try to invoke mock. Get mock invokers error for service:"
22 + directory.getUrl().getServiceInterface() + ", method:" + invocation.getMethodName()
23 + ", will contruct a new mock with 'new MockInvoker()'.", e);
24 }
25 }
26 }
27 return invokers;
28 }

首先使用RegistryDirectory获取出方法名为sayHello的Invoker列表,之后使用MockInvokersSelector(Router)选取出MockInvoker。

1 public class MockInvokersSelector implements Router {
2
3 public <T> List<Invoker<T>> route(final List<Invoker<T>> invokers,
4 URL url, final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
5 if (invocation.getAttachments() == null) {
6 return getNormalInvokers(invokers);
7 } else {
8 String value = invocation.getAttachments().get(Constants.INVOCATION_NEED_MOCK);
9 if (value == null)
10 return getNormalInvokers(invokers);
11 else if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
12 return getMockedInvokers(invokers);
13 }
14 }
15 return invokers;
16 }
17
18 private <T> List<Invoker<T>> getMockedInvokers(final List<Invoker<T>> invokers) {
19 if (!hasMockProviders(invokers)) {
20 return null;
21 }
22 List<Invoker<T>> sInvokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(1);
23 for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
24 if (invoker.getUrl().getProtocol().equals(Constants.MOCK_PROTOCOL)) {
25 sInvokers.add(invoker);
26 }
27 }
28 return sInvokers;
29 }
30
31 private <T> boolean hasMockProviders(final List<Invoker<T>> invokers) {
32 boolean hasMockProvider = false;
33 for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
34 if (invoker.getUrl().getProtocol().equals(Constants.MOCK_PROTOCOL)) {
35 hasMockProvider = true;
36 break;
37 }
38 }
39 return hasMockProvider;
40 }
41 }

这里获取到的是空列表。
所以会先创建一个MockInvoker对象,之后执行其invoker方法。
MockInvoker:

1 public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
2 String mock = getUrl().getParameter(invocation.getMethodName() + "." + Constants.MOCK_KEY); //sayHello.mock
3 if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
4 ((RpcInvocation) invocation).setInvoker(this);
5 }
6 if (StringUtils.isBlank(mock)) {
7 mock = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.MOCK_KEY); //mock
8 }
9
10 if (StringUtils.isBlank(mock)) {
11 throw new RpcException(new IllegalAccessException("mock can not be null. url :" + url));
12 }
13 mock = normallizeMock(URL.decode(mock));
14 if (Constants.RETURN_PREFIX.trim().equalsIgnoreCase(mock.trim())) { // return
15 RpcResult result = new RpcResult();
16 result.setValue(null);
17 return result;
18 } else if (mock.startsWith(Constants.RETURN_PREFIX)) { // return value(包括return null)
19 mock = mock.substring(Constants.RETURN_PREFIX.length()).trim();
20 mock = mock.replace('`', '"');
21 try {
22 Type[] returnTypes = RpcUtils.getReturnTypes(invocation);
23 Object value = parseMockValue(mock, returnTypes);
24 return new RpcResult(value);
25 } catch (Exception ew) {
26 throw new RpcException("mock return invoke error. method :" + invocation.getMethodName() + ", mock:" + mock + ", url: " + url, ew);
27 }
28 } else if (mock.startsWith(Constants.THROW_PREFIX)) { // throw xxx
29 mock = mock.substring(Constants.THROW_PREFIX.length()).trim();
30 mock = mock.replace('`', '"');
31 if (StringUtils.isBlank(mock)) {// throw
32 throw new RpcException(" mocked exception for Service degradation. ");
33 } else { // user customized class : throw xxx
34 Throwable t = getThrowable(mock);
35 throw new RpcException(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION, t);
36 }
37 } else { //impl mock: 自定义mock类
38 try {
39 Invoker<T> invoker = getInvoker(mock);
40 return invoker.invoke(invocation);
41 } catch (Throwable t) {
42 throw new RpcException("Failed to create mock implemention class " + mock, t);
43 }
44 }
45 }

首先获取到mock配置,例如:mock=force:return+null,之后进行url解码为mock=force:return null,最后进行处理为mock=return null,然后根据规则走分支。
mock参数的处理函数:

1 /**
2 * 一、使用自定义mock类
3 * mock = default => DemoServiceMock
4 * mock = true => DemoServiceMock
5 * mock = fail => DemoServiceMock
6 * mock = force => DemoServiceMock
7 *
8 * 二、先普通执行,执行失败之后再执行相应的mock逻辑
9 * mock = fail:throw => throw new RpcException(" mocked exception for Service degradation. ");
10 * mock = fail:throw XxxException => throw new RpcException(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION, XxxException);
11 * mock = fail:return => return null
12 * mock = fail:return xxx => return xxx
13 *
14 * 三、直接执行相应的mock逻辑
15 * mock = force:throw => throw new RpcException(" mocked exception for Service degradation. ");
16 * mock = force:throw XxxException => throw new RpcException(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION, XxxException);
17 * mock = force:return => return null
18 * mock = force:return xxx => return xxx
19 *
20 * @param mock
21 * @return
22 */
23 private String normallizeMock(String mock) {
24 if (mock == null || mock.trim().length() == 0) {
25 return mock;
26 } else if (ConfigUtils.isDefault(mock) || "fail".equalsIgnoreCase(mock.trim()) || "force".equalsIgnoreCase(mock.trim())) {
27 mock = url.getServiceInterface() + "Mock";
28 }
29 if (mock.startsWith(Constants.FAIL_PREFIX)) {
30 mock = mock.substring(Constants.FAIL_PREFIX.length()).trim();
31 } else if (mock.startsWith(Constants.FORCE_PREFIX)) {
32 mock = mock.substring(Constants.FORCE_PREFIX.length()).trim();
33 }
34 return mock;
35 }

我们这里来看一下自定义mock类。消费端编写:

1 public class DemoServiceMock implements DemoService {
2
3 @Override
4 public Car sayHello(String name) {
5 Car car = new Car();
6 car.setCarNum("mock中");
7 car.setGoMile(666);
8 return car;
9 }
10 }

配置覆盖:
1 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoServiceMock"));
MockInvoker.invoke
1 try {
2 Invoker<T> invoker = getInvoker(mock);
3 return invoker.invoke(invocation);
4 } catch (Throwable t) {
5 throw new RpcException("Failed to create mock implemention class " + mock, t);
6 }

1 private Invoker<T> getInvoker(String mockService) {
2 Invoker<T> invoker = (Invoker<T>) mocks.get(mockService);
3 if (invoker != null) {
4 return invoker;
5 } else {
6 Class<T> serviceType = (Class<T>) ReflectUtils.forName(url.getServiceInterface());
7 if (ConfigUtils.isDefault(mockService)) {
8 mockService = serviceType.getName() + "Mock";
9 }
10
11 Class<?> mockClass = ReflectUtils.forName(mockService);
12 if (!serviceType.isAssignableFrom(mockClass)) {
13 throw new IllegalArgumentException("The mock implemention class " + mockClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + serviceType.getName());
14 }
15
16 if (!serviceType.isAssignableFrom(mockClass)) {
17 throw new IllegalArgumentException("The mock implemention class " + mockClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + serviceType.getName());
18 }
19 try {
20 T mockObject = (T) mockClass.newInstance(); // 获取自定义mock类实例
21 invoker = proxyFactory.getInvoker(mockObject, (Class<T>) serviceType, url); // 和普通类一样创建Invoker
22 if (mocks.size() < 10000) {
23 mocks.put(mockService, invoker);
24 }
25 return invoker;
26 } catch (InstantiationException e) {
27 throw new IllegalStateException("No such empty constructor \"public " + mockClass.getSimpleName() + "()\" in mock implemention class " + mockClass.getName(), e);
28 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
29 throw new IllegalStateException(e);
30 }
31 }
32 }

上边看了return和自定义mock类,最后来看一下throw异常。
默认抛出RpcException,异常信息:mocked exception for Service degradation. 也可以自定义异常,例如:

1 public class MyRuntimeException extends RuntimeException {
2 private String msg;
3
4 public MyRuntimeException(String msg){
5 this.msg = msg;
6 }
7 }

自定义异常必须具有单参构造器且参数为String。
配置覆盖:
MockInvoker.invoke
1 registry.register(URL.valueOf("override://0.0.0.0/com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService?category=configurators&dynamic=false&application=demo-consumer&mock=force:throw+com.alibaba.dubbo.Test.MyRuntimeException"));

1 private Throwable getThrowable(String throwstr) {
2 Throwable throwable = (Throwable) throwables.get(throwstr);
3 if (throwable != null) {
4 return throwable;
5 } else {
6 Throwable t = null;
7 try {
8 Class<?> bizException = ReflectUtils.forName(throwstr);
9 Constructor<?> constructor;
10 constructor = ReflectUtils.findConstructor(bizException, String.class);
11 t = (Throwable) constructor.newInstance(new Object[]{" mocked exception for Service degradation. "});
12 if (throwables.size() < 1000) {
13 throwables.put(throwstr, t);
14 }
15 } catch (Exception e) {
16 throw new RpcException("mock throw error :" + throwstr + " argument error.", e);
17 }
18 return t;
19 }
20 }

服务降级结束!!!
dubbo提供了三种结果缓存机制:
- lru:基于最近最少使用原则删除多余缓存,保持最热的数据被缓存
- threadlocal:当前线程缓存
- jcache:可以桥接各种缓存实现
一、使用方式
1 <dubbo:reference id="demoService" check="false" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService">
2 <dubbo:method name="sayHello" timeout="60000" cache="lru"/>
3 </dubbo:reference>
添加cache配置。
注意:dubbo结果缓存有一个bug,https://github.com/alibaba/dubbo/issues/1362,当cache="xxx"配置在服务级别时,没有问题,当配置成方法级别的时候,不管怎么配置,都睡使用LruCache。
二、LRU缓存源码解析

1 /**
2 * CacheFilter
3 * 配置了cache配置才会加载CacheFilter
4 */
5 @Activate(group = {Constants.CONSUMER, Constants.PROVIDER}, value = Constants.CACHE_KEY)
6 public class CacheFilter implements Filter {
7 private CacheFactory cacheFactory;
8
9 public void setCacheFactory(CacheFactory cacheFactory) {
10 this.cacheFactory = cacheFactory;
11 }
12
13 public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
14 if (cacheFactory != null && ConfigUtils.isNotEmpty(invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.CACHE_KEY))) {
15 // 使用CacheFactory$Adaptive获取具体的CacheFactory,然后再使用具体的CacheFactory获取具体的Cache对象
16 Cache cache = cacheFactory.getCache(invoker.getUrl().addParameter(Constants.METHOD_KEY, invocation.getMethodName()));
17 if (cache != null) {
18 // 缓存对象的key为arg1,arg2,arg3,...,arg4
19 String key = StringUtils.toArgumentString(invocation.getArguments());
20 // 获取缓存value
21 Object value = cache.get(key);
22 if (value != null) {
23 return new RpcResult(value);
24 }
25 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
26 // 响应结果没有exception信息,则将相应结果的值塞入缓存
27 if (!result.hasException()) {
28 cache.put(key, result.getValue());
29 }
30 return result;
31 }
32 }
33 return invoker.invoke(invocation);
34 }
35 }

从@Activate(group = {Constants.CONSUMER, Constants.PROVIDER}, value = Constants.CACHE_KEY)中我们可以看出,consumer端或provider端配置了cache="xxx",则会走该CacheFilter。
首先获取具体Cache实例:CacheFilter中的cacheFactory属性是CacheFactory$Adaptive实例。

1 public class CacheFactory$Adaptive implements com.alibaba.dubbo.cache.CacheFactory {
2 public com.alibaba.dubbo.cache.Cache getCache(com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg0) {
3 if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
4 com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0;
5 String extName = url.getParameter("cache", "lru");
6 if (extName == null)
7 throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.cache.CacheFactory) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([cache])");
8 // 获取具体的CacheFactory
9 com.alibaba.dubbo.cache.CacheFactory extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.cache.CacheFactory) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.cache.CacheFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
10 // 使用具体的CacheFactory获取具体的Cache
11 return extension.getCache(arg0);
12 }
13 }

这里extName使我们配置的lru,如果不配置,默认也是lru。这里获取到的具体的CacheFactory是LruCacheFactory。

1 @SPI("lru")
2 public interface CacheFactory {
3 @Adaptive("cache")
4 Cache getCache(URL url);
5 }
6
7 public abstract class AbstractCacheFactory implements CacheFactory {
8 private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> caches = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Cache>();
9
10 public Cache getCache(URL url) {
11 String key = url.toFullString();
12 Cache cache = caches.get(key);
13 if (cache == null) {
14 caches.put(key, createCache(url));
15 cache = caches.get(key);
16 }
17 return cache;
18 }
19
20 protected abstract Cache createCache(URL url);
21 }
22
23 public class LruCacheFactory extends AbstractCacheFactory {
24 protected Cache createCache(URL url) {
25 return new LruCache(url);
26 }
27 }

调用LruCacheFactory.getCache(URL url)方法,实际上调用的是其父类AbstractCacheFactory的方法。逻辑是:创建一个LruCache实例,之后存储在ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> caches中,key为url.toFullString()。
再来看LruCache的创建:

1 public interface Cache {
2 void put(Object key, Object value);
3 Object get(Object key);
4 }
5
6 public class LruCache implements Cache {
7 private final Map<Object, Object> store;
8
9 public LruCache(URL url) {
10 final int max = url.getParameter("cache.size", 1000);
11 this.store = new LRUCache<Object, Object>(max);
12 }
13
14 public void put(Object key, Object value) {
15 store.put(key, value);
16 }
17
18 public Object get(Object key) {
19 return store.get(key);
20 }
21 }

默认缓存存储的最大个数为1000个。之后创建了一个LRUCache对象。

1 public class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
2 private static final long serialVersionUID = -5167631809472116969L;
3
4 private static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
5
6 private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_CAPACITY = 1000;
7 private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
8 private volatile int maxCapacity;
9
10 public LRUCache(int maxCapacity) {
11 /**
12 * 注意:
13 * LinkedHashMap 维护着一个运行于所有Entry的双向链表:此链表定义了迭代顺序,该迭代顺序可以是插入顺序或者是访问顺序
14 * 而真正存储的数据结构还是其父类HashMap的那个Entry[]数组,上述的双向链表仅用于维护迭代顺序(帮助实现lru算法等)
15 *
16 * LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder)
17 * 第三个参数accessOrder:false(插入顺序),true(访问顺序)
18 */
19 super(16, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, true);
20 this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
21 }
22
23 /**
24 * 是否需要删除最老的数据(即最近没有被访问的数据)
25 * @param eldest
26 * @return
27 */
28 @Override
29 protected boolean removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
30 return size() > maxCapacity;
31 }
32
33 @Override
34 public V get(Object key) {
35 try {
36 lock.lock();
37 return super.get(key);
38 } finally {
39 lock.unlock();
40 }
41 }
42
43 @Override
44 public V put(K key, V value) {
45 try {
46 lock.lock();
47 return super.put(key, value);
48 } finally {
49 lock.unlock();
50 }
51 }
52
53 @Override
54 public V remove(Object key) {
55 try {
56 lock.lock();
57 return super.remove(key);
58 } finally {
59 lock.unlock();
60 }
61 }
62
63 @Override
64 public int size() {
65 try {
66 lock.lock();
67 return super.size();
68 } finally {
69 lock.unlock();
70 }
71 }
72 ...
73 }

注意:
- LinkedHashMap维护着一个运行于所有Entry的双向链表:此链表定义了迭代顺序,该迭代顺序可以是插入顺序或者是访问顺序(真正存储的数据结构还是其父类HashMap的那个Entry[]数组,上述的双向链表仅用于维护迭代顺序)
- 当指定了LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder)第三个参数accessOrder=true时,每次执行get(Object key)时,获取出来的Entry都会被放到尾节点,也就是说双向链表的header节点是最久以前访问的,当执行put(Object key, Object value)的时候,就执行removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry<K, V> eldest)来判断是否需要删除这个header节点。(这些是LinkedHashMap实现的,具体源码分析见 https://yikun.github.io/2015/04/02/Java-LinkedHashMap%E5%B7%A5%E4%BD%9C%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E5%8F%8A%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0/ http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/java-collection/linkedhashmap.html)
三、ThreadLocal缓存源码解析
根据文章开头提到的bug,cache=""只能配置在服务级别。
1 <dubbo:reference id="demoService" check="false" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" cache="threadlocal"/>

1 public class ThreadLocalCacheFactory extends AbstractCacheFactory {
2 protected Cache createCache(URL url) {
3 return new ThreadLocalCache(url);
4 }
5 }
6
7 public class ThreadLocalCache implements Cache {
8 private final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> store;
9
10 public ThreadLocalCache(URL url) {
11 this.store = new ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>>() {
12 @Override
13 protected Map<Object, Object> initialValue() {
14 return new HashMap<Object, Object>();
15 }
16 };
17 }
18
19 public void put(Object key, Object value) {
20 store.get().put(key, value);
21 }
22
23 public Object get(Object key) {
24 return store.get().get(key);
25 }
26 }

ThreadLocalCache的实现是HashMap。
监控总体图:
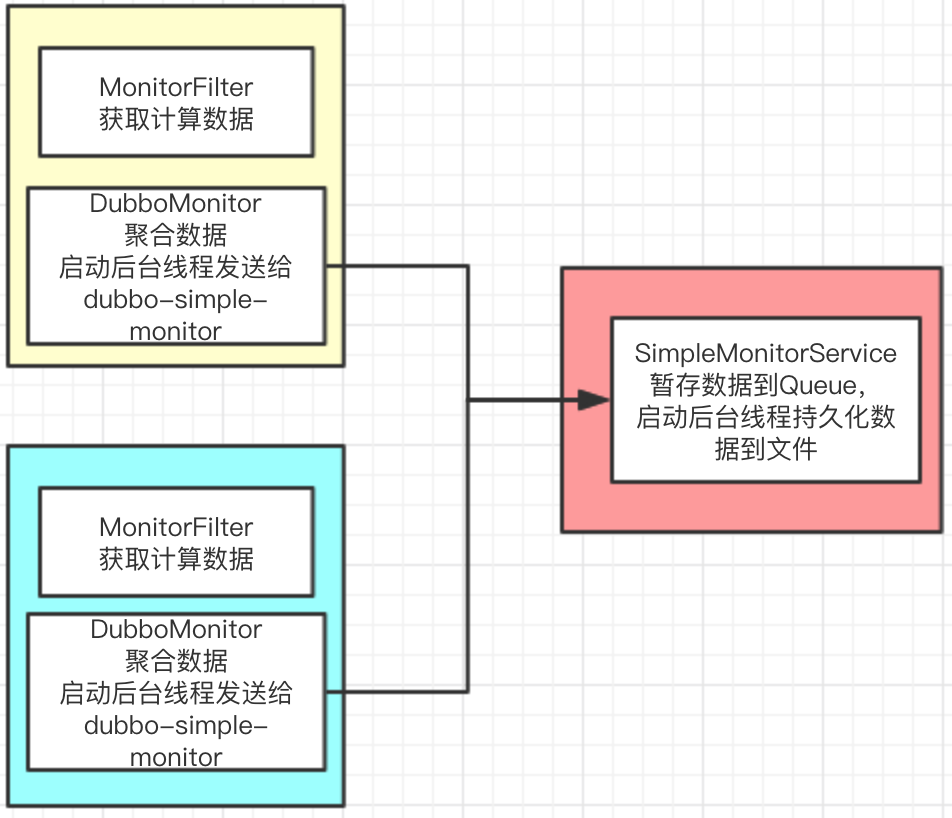
红色:监控中心 - dubbo-simple-monitor
黄色:provider
蓝色:consumer
统计总体流程:
- MonitorFilter向DubboMonitor发送数据
- DubboMonitor将数据进行聚合后(默认聚合1min中的统计数据)暂存到ConcurrentMap<Statistics, AtomicReference<long[]>> statisticsMap,然后使用一个含有3个线程(线程名字:DubboMonitorSendTimer)的线程池每隔1min钟,调用SimpleMonitorService遍历发送statisticsMap中的统计数据,每发送完毕一个,就重置当前的Statistics的AtomicReference<long[]>
- SimpleMonitorService将这些聚合数据塞入BlockingQueue<URL> queue中(队列大写为100000)
- SimpleMonitorService使用一个后台线程(线程名为:DubboMonitorAsyncWriteLogThread)将queue中的数据写入文件(该线程以死循环的形式来写)
- SimpleMonitorService还会使用一个含有1个线程(线程名字:DubboMonitorTimer)的线程池每隔5min钟,将文件中的统计数据画成图表
注意:
- SimpleMonitorService理解为一个服务提供者;而provider和consumer都是一个服务消费者,所以二者的DubboMonitor中的MonitorService实例都是一个代理实例。
- dubbo-monitor计数监控不支持异步调用下的数据监控
一、dubbo-monitor使用
在配置文件中添加:
1 <dubbo:monitor address="10.211.55.5:9090" />
即开启了monitor监控,并且指定了监控中心服务器为“10.211.55.5:9090”。
9090端口是Prometheus的默认端口,dubbo提供的监控中心比较简陋,我们后续会使用Prometheus作为监控中心来存储监控数据。
二、服务端加载monitor配置
doExportUrlsFor1Protocol(ProtocolConfig protocolConfig, List<URL> registryURLs)中:

1 if (!Constants.SCOPE_LOCAL.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(scope)) {
2 ...
3 if (registryURLs != null && registryURLs.size() > 0) {
4 for (URL registryURL : registryURLs) {
5 ...
6 URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(registryURL);
7 if (monitorUrl != null) {
8 url = url.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, monitorUrl.toFullString());
9 }
10 ...
11 }
12 } else {
13 ...
14 }
15 }

其中loadMonitor(URL registryURL)方法主要用于创建MonitorConfig对象(如果monitor配置在dubbo.properties中的话),并且设置属性,之后设置到数据总线Url中。

1 protected URL loadMonitor(URL registryURL) {
2 if (monitor == null) {
3 String monitorAddress = ConfigUtils.getProperty("dubbo.monitor.address");
4 String monitorProtocol = ConfigUtils.getProperty("dubbo.monitor.protocol");
5 if ((monitorAddress == null || monitorAddress.length() == 0) && (monitorProtocol == null || monitorProtocol.length() == 0)) {
6 return null;
7 }
8
9 monitor = new MonitorConfig();
10 if (monitorAddress != null && monitorAddress.length() > 0) {
11 monitor.setAddress(monitorAddress);
12 }
13 if (monitorProtocol != null && monitorProtocol.length() > 0) {
14 monitor.setProtocol(monitorProtocol);
15 }
16 }
17 appendProperties(monitor);
18 ...
19 }

三、消费端加载monitor配置
createProxy(Map<String, String> map)中:

1 List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false);
2 if (us != null && us.size() > 0) {
3 for (URL u : us) {
4 URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u);
5 if (monitorUrl != null) {
6 map.put(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString()));
7 }
8 ...
9 }
10 }

四、MonitorFilter收集监控数据
consumer端在发起调用之前会先走filter链;provider端在接收到请求时也是先走filter链,然后才进行真正的业务逻辑处理。默认情况下,在consumer和provider的filter链中都会有Monitorfilter。

1 /**
2 * MonitorFilter. (SPI, Singleton, ThreadSafe)
3 */
4 @Activate(group = {Constants.PROVIDER, Constants.CONSUMER})
5 public class MonitorFilter implements Filter {
6
7 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MonitorFilter.class);
8
9 // key: 接口名.方法名 value: 当前的并发数
10 private final ConcurrentMap<String, AtomicInteger> concurrents = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, AtomicInteger>();
11
12 private MonitorFactory monitorFactory;// MonitorFactory$Adaptive
13
14 public void setMonitorFactory(MonitorFactory monitorFactory) {
15 this.monitorFactory = monitorFactory;
16 }
17
18 // intercepting invocation
19 public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
20 if (invoker.getUrl().hasParameter(Constants.MONITOR_KEY)) {// 开启了monitor监控
21 RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext(); // provider must fetch context before invoke() gets called
22 String remoteHost = context.getRemoteHost();
23 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // record start timestamp
24 getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).incrementAndGet(); // 并发数+1
25 try {
26 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); // proceed invocation chain
27 collect(invoker, invocation, result, remoteHost, start, false);// 收集统计数据
28 return result;
29 } catch (RpcException e) {
30 collect(invoker, invocation, null, remoteHost, start, true);// 发生异常时收集统计数据
31 throw e;
32 } finally {
33 getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).decrementAndGet(); // 并发数-1
34 }
35 } else {
36 return invoker.invoke(invocation);
37 }
38 }
39
40 // collect info
41 private void collect(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation, Result result, String remoteHost, long start, boolean error) {
42 try {
43 // ---- service statistics ----
44 long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; // 此次调用花费的时间
45 int concurrent = getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).get(); // current concurrent count
46 String application = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.APPLICATION_KEY);
47 String service = invoker.getInterface().getName(); // service name
48 String method = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation); // method name
49 URL url = invoker.getUrl().getUrlParameter(Constants.MONITOR_KEY);
50 Monitor monitor = monitorFactory.getMonitor(url);//根据monitorUrl获取Monitor实现(默认使用DubboMonitor)
51 if (monitor == null) {
52 return;
53 }
54 int localPort;
55 String remoteKey;
56 String remoteValue;
57 if (Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE.equals(invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.SIDE_KEY))) {
58 // ---- for service consumer ----
59 localPort = 0;
60 remoteKey = MonitorService.PROVIDER;
61 remoteValue = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
62 } else {
63 // ---- for service provider ----
64 localPort = invoker.getUrl().getPort();
65 remoteKey = MonitorService.CONSUMER;
66 remoteValue = remoteHost;
67 }
68 String input = "", output = "";
69 if (invocation.getAttachment(Constants.INPUT_KEY) != null) {
70 input = invocation.getAttachment(Constants.INPUT_KEY);
71 }
72 if (result != null && result.getAttachment(Constants.OUTPUT_KEY) != null) {
73 output = result.getAttachment(Constants.OUTPUT_KEY);
74 }
75 monitor.collect(new URL(Constants.COUNT_PROTOCOL,
76 NetUtils.getLocalHost(), localPort,
77 service + "/" + method,
78 MonitorService.APPLICATION, application,
79 MonitorService.INTERFACE, service,
80 MonitorService.METHOD, method,
81 remoteKey, remoteValue,
82 error ? MonitorService.FAILURE : MonitorService.SUCCESS, "1",// 成功失败数
83 MonitorService.ELAPSED, String.valueOf(elapsed),// 调用消耗的时间
84 MonitorService.CONCURRENT, String.valueOf(concurrent),// 并发数
85 Constants.INPUT_KEY, input,
86 Constants.OUTPUT_KEY, output));
87 } catch (Throwable t) {
88 logger.error("Failed to monitor count service " + invoker.getUrl() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
89 }
90 }
91
92 // concurrent counter
93 private AtomicInteger getConcurrent(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
94 String key = invoker.getInterface().getName() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
95 AtomicInteger concurrent = concurrents.get(key);
96 if (concurrent == null) {
97 concurrents.putIfAbsent(key, new AtomicInteger());
98 concurrent = concurrents.get(key);
99 }
100 return concurrent;
101 }
102
103 }

调用之前,记录调用开始时间、并发数,之后进行调用,最后进行统计数据收集:
- 获取计算各种统计数据(调用消耗时间、调用成功/错误数等)
- 使用MonitorFactory获取Monitor
- 将统计数据构造成url
- 使用Monitor收集这些统计数据
获取Monitor的源码后续再说。这里获取到的是DubboMonitor实例。
五、DubboMonitor聚合监控数据

1 private static final int LENGTH = 10;
2 private final ConcurrentMap<Statistics, AtomicReference<long[]>> statisticsMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Statistics, AtomicReference<long[]>>();
3
4 // 聚合统计数据
5 public void collect(URL url) {
6 // data to collect from url
7 int success = url.getParameter(MonitorService.SUCCESS, 0);
8 int failure = url.getParameter(MonitorService.FAILURE, 0);
9 int input = url.getParameter(MonitorService.INPUT, 0);
10 int output = url.getParameter(MonitorService.OUTPUT, 0);
11 int elapsed = url.getParameter(MonitorService.ELAPSED, 0);
12 int concurrent = url.getParameter(MonitorService.CONCURRENT, 0);
13 // init atomic reference
14 Statistics statistics = new Statistics(url);
15 AtomicReference<long[]> reference = statisticsMap.get(statistics);
16 if (reference == null) {
17 statisticsMap.putIfAbsent(statistics, new AtomicReference<long[]>());
18 reference = statisticsMap.get(statistics);
19 }
20 // use CompareAndSet to sum
21 long[] current;
22 long[] update = new long[LENGTH];
23 do {
24 current = reference.get();
25 if (current == null) {
26 update[0] = success;
27 update[1] = failure;
28 update[2] = input;
29 update[3] = output;
30 update[4] = elapsed;
31 update[5] = concurrent;
32 update[6] = input;
33 update[7] = output;
34 update[8] = elapsed;
35 update[9] = concurrent;
36 } else {
37 update[0] = current[0] + success;
38 update[1] = current[1] + failure;
39 update[2] = current[2] + input;
40 update[3] = current[3] + output;
41 update[4] = current[4] + elapsed;
42 update[5] = (current[5] + concurrent) / 2;
43 update[6] = current[6] > input ? current[6] : input;
44 update[7] = current[7] > output ? current[7] : output;
45 update[8] = current[8] > elapsed ? current[8] : elapsed;
46 update[9] = current[9] > concurrent ? current[9] : concurrent;
47 }
48 } while (!reference.compareAndSet(current, update));
49 }

实际上这里聚合了1min钟的统计数据到statisticsMap中。
六、Monitor使用MonitorService存储数据到队列

1 private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3, new NamedThreadFactory("DubboMonitorSendTimer", true));
2 private final ScheduledFuture<?> sendFuture;
3 private final long monitorInterval;
4
5 public DubboMonitor(Invoker<MonitorService> monitorInvoker, MonitorService monitorService) {
6 this.monitorInvoker = monitorInvoker;
7 this.monitorService = monitorService;
8 this.monitorInterval = monitorInvoker.getUrl().getPositiveParameter("interval", 60000);
9 // collect timer for collecting statistics data
10 sendFuture = scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
11 public void run() {
12 // collect data
13 try {
14 send();
15 } catch (Throwable t) {
16 logger.error("Unexpected error occur at send statistic, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
17 }
18 }
19 }, monitorInterval, monitorInterval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
20 }


1 public void send() {
2 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
3 logger.info("Send statistics to monitor " + getUrl());
4 }
5 String timestamp = String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis());
6 for (Map.Entry<Statistics, AtomicReference<long[]>> entry : statisticsMap.entrySet()) {
7 // get statistics data
8 Statistics statistics = entry.getKey();
9 AtomicReference<long[]> reference = entry.getValue();
10 long[] numbers = reference.get();
11 long success = numbers[0];
12 long failure = numbers[1];
13 long input = numbers[2];
14 long output = numbers[3];
15 long elapsed = numbers[4];
16 long concurrent = numbers[5];
17 long maxInput = numbers[6];
18 long maxOutput = numbers[7];
19 long maxElapsed = numbers[8];
20 long maxConcurrent = numbers[9];
21
22 // send statistics data
23 URL url = statistics.getUrl()
24 .addParameters(MonitorService.TIMESTAMP, timestamp,
25 MonitorService.SUCCESS, String.valueOf(success),
26 MonitorService.FAILURE, String.valueOf(failure),
27 MonitorService.INPUT, String.valueOf(input),
28 MonitorService.OUTPUT, String.valueOf(output),
29 MonitorService.ELAPSED, String.valueOf(elapsed),
30 MonitorService.CONCURRENT, String.valueOf(concurrent),
31 MonitorService.MAX_INPUT, String.valueOf(maxInput),
32 MonitorService.MAX_OUTPUT, String.valueOf(maxOutput),
33 MonitorService.MAX_ELAPSED, String.valueOf(maxElapsed),
34 MonitorService.MAX_CONCURRENT, String.valueOf(maxConcurrent)
35 );
36 monitorService.collect(url);
37
38 // reset
39 long[] current;
40 long[] update = new long[LENGTH];
41 do {
42 current = reference.get();
43 if (current == null) {
44 update[0] = 0;
45 update[1] = 0;
46 update[2] = 0;
47 update[3] = 0;
48 update[4] = 0;
49 update[5] = 0;
50 } else {
51 update[0] = current[0] - success;
52 update[1] = current[1] - failure;
53 update[2] = current[2] - input;
54 update[3] = current[3] - output;
55 update[4] = current[4] - elapsed;
56 update[5] = current[5] - concurrent;
57 }
58 } while (!reference.compareAndSet(current, update));
59 }
60 }

- 首先从聚合数据存储器statisticsMap中获取相关统计数据并存储到数据总线Url中
- 之后调用MonitorService(这里是SimpleMonitorService),将统计数据存储到一个BlockingQueue中
注意:这里有一个改进点
- 由于monitorService.collect(url)是远程调用,这里在for循环体中执行远程调用,实际上是不合适的,我们可以将所有的url先暂存在一个List<URL>中,最后,使用一次monitorService.collect(urlList)即可 - 此时,可适当缩短数据发送时间。
SimpleMonitorService:

1 private final BlockingQueue<URL> queue;
2
3 public void collect(URL statistics) {
4 queue.offer(statistics);
5 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
6 logger.info("collect statistics: " + statistics);
7 }
8 }

七、MonitorService将数据写入本地文件

1 private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, new NamedThreadFactory("DubboMonitorTimer", true));
2 private final ScheduledFuture<?> chartFuture;
3 private final Thread writeThread;
4 private final BlockingQueue<URL> queue;
5 private String statisticsDirectory = "statistics";
6 private String chartsDirectory = "charts";
7 private volatile boolean running = true;
8
9 public SimpleMonitorService() {
10 queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<URL>(Integer.parseInt(ConfigUtils.getProperty("dubbo.monitor.queue", "100000")));
11 writeThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
12 public void run() {
13 while (running) {
14 try {
15 write(); // write statistics
16 } catch (Throwable t) {
17 logger.error("Unexpected error occur at write stat log, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
18 try {
19 Thread.sleep(5000); // retry after 5 secs
20 } catch (Throwable t2) {
21 }
22 }
23 }
24 }
25 });
26 writeThread.setDaemon(true);
27 writeThread.setName("DubboMonitorAsyncWriteLogThread");
28 writeThread.start();
29 chartFuture = scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
30 public void run() {
31 try {
32 draw(); // draw chart
33 } catch (Throwable t) {
34 logger.error("Unexpected error occur at draw stat chart, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
35 }
36 }
37 }, 1, 300, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
38 statisticsDirectory = ConfigUtils.getProperty("dubbo.statistics.directory");
39 chartsDirectory = ConfigUtils.getProperty("dubbo.charts.directory");
40 }

write()将统计数据写入文件,draw()将统计数据画成图片。这两种方式在实际使用中都不会用到。
最后来看一下获取Monitor实例的过程(帮助我们开发自定义的Monitor):
1 Monitor monitor = monitorFactory.getMonitor(url);
MonitorFilter中的monitorFactory实例是:MonitorFactory$Adaptive。

1 package com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor;
2
3 import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;
4
5 public class MonitorFactory$Adaptive implements com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.MonitorFactory {
6 public com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.Monitor getMonitor(com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg0) {
7 if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
8 com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0;
9 String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol());
10 if (extName == null)
11 throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.MonitorFactory) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
12 com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.MonitorFactory extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.MonitorFactory) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.MonitorFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
13 return extension.getMonitor(arg0);
14 }
15 }

首先,根据输入的url中的protocol来获取相关的MonitorFactory(这里protocol默认是dubbo,所以获取的是DubboMonitorFactory,可以通过指定dubbo:monitor标签中的protocol属性来自定义获取XxxMonitorFactory),之后调用DubboMonitorFactory.getMonitor(arg0)。该方法在其父类AbstractMonitorFactory中:

1 /**
2 * AbstractMonitorFactory. (SPI, Singleton, ThreadSafe)
3 */
4 public abstract class AbstractMonitorFactory implements MonitorFactory {
5 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractMonitorFactory.class);
6
7 // lock for getting monitor center
8 private static final ReentrantLock LOCK = new ReentrantLock();
9
10 // monitor centers Map<RegistryAddress, Registry>
11 private static final Map<String, Monitor> MONITORS = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Monitor>();
12
13 private static final Map<String, ListenableFuture<Monitor>> FUTURES = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ListenableFuture<Monitor>>();
14
15 private static final ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, 10, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), new NamedThreadFactory("DubboMonitorCreator", true));
16
17 public static Collection<Monitor> getMonitors() {
18 return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(MONITORS.values());
19 }
20
21 public Monitor getMonitor(URL url) {
22 url = url.setPath(MonitorService.class.getName()).addParameter(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, MonitorService.class.getName());
23 String key = url.toServiceStringWithoutResolving();// dubbo://10.211.55.5:9090/com.alibaba.dubbo.monitor.MonitorService
24 Monitor monitor = MONITORS.get(key);
25 Future<Monitor> future = FUTURES.get(key);
26 if (monitor != null || future != null) {
27 return monitor;
28 }
29
30 LOCK.lock();
31 try {
32 monitor = MONITORS.get(key);
33 future = FUTURES.get(key);
34 if (monitor != null || future != null) {
35 return monitor;
36 }
37
38 final URL monitorUrl = url;
39 // 使用另外的线程MonitorCreator来创建Monitor实例(原因是:即使Monitor创建失败,也不会影响主流程)
40 final ListenableFutureTask<Monitor> listenableFutureTask = ListenableFutureTask.create(new MonitorCreator(monitorUrl));
41 listenableFutureTask.addListener(new MonitorListener(key));
42 executor.execute(listenableFutureTask);
43 FUTURES.put(key, listenableFutureTask);
44
45 return null;
46 } finally {
47 // unlock
48 LOCK.unlock();
49 }
50 }
51
52 protected abstract Monitor createMonitor(URL url);
53
54 // Callable和Runnable一样,也是创建一个线程去执行,只是Callable有返回值(T call()),而Runnable无返回值(void run())
55 class MonitorCreator implements Callable<Monitor> {
56
57 private URL url;
58
59 public MonitorCreator(URL url) {
60 this.url = url;
61 }
62
63 @Override
64 public Monitor call() throws Exception {
65 Monitor monitor = AbstractMonitorFactory.this.createMonitor(url);//调用子类的createMonitor方法创建Monitor
66 return monitor;
67 }
68 }
69
70 class MonitorListener implements Runnable {
71
72 private String key;
73
74 public MonitorListener(String key) {
75 this.key = key;
76 }
77 // listenableFutureTask一旦isDone()完成(正常完成、抛出异常、被中断等),就会立即执行该方法
78 @Override
79 public void run() {
80 try {
81 ListenableFuture<Monitor> listenableFuture = AbstractMonitorFactory.FUTURES.get(key);
82 AbstractMonitorFactory.MONITORS.put(key, listenableFuture.get());
83 AbstractMonitorFactory.FUTURES.remove(key);
84 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
85 logger.warn("Thread was interrupted unexpectedly, monitor will never be got.");
86 AbstractMonitorFactory.FUTURES.remove(key);
87 } catch (ExecutionException e) {
88 logger.warn("Create monitor failed, monitor data will not be collected until you fix this problem. ", e);
89 }
90 }
91 }
92 }

来看DubboMonitorFactory.createMonitor(url):

1 /**
2 * DefaultMonitorFactory
3 */
4 public class DubboMonitorFactory extends AbstractMonitorFactory {
5
6 private Protocol protocol;
7
8 private ProxyFactory proxyFactory;
9
10 public void setProtocol(Protocol protocol) {
11 this.protocol = protocol;
12 }
13
14 public void setProxyFactory(ProxyFactory proxyFactory) {
15 this.proxyFactory = proxyFactory;
16 }
17
18 @Override
19 protected Monitor createMonitor(URL url) {
20 url = url.setProtocol(url.getParameter(Constants.PROTOCOL_KEY, "dubbo"));
21 if (url.getPath() == null || url.getPath().length() == 0) {
22 url = url.setPath(MonitorService.class.getName());
23 }
24 String filter = url.getParameter(Constants.REFERENCE_FILTER_KEY);
25 if (filter == null || filter.length() == 0) {
26 filter = "";
27 } else {
28 filter = filter + ",";
29 }
30 url = url.addParameters(Constants.CLUSTER_KEY, "failsafe", Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false),
31 Constants.REFERENCE_FILTER_KEY, filter + "-monitor");
32 // 创建Invoker<MonitorService>,内部会构造与MonitorService实现类SimpleMonitorService所在的检测中心dubbo-simple-monitor的长连接
33 Invoker<MonitorService> monitorInvoker = protocol.refer(MonitorService.class, url);
34 // 获取MonitorService的代理
35 MonitorService monitorService = proxyFactory.getProxy(monitorInvoker);
36 return new DubboMonitor(monitorInvoker, monitorService);
37 }
38
39 }

注意:这里的SimpleMonitorService其实会部署在dubbo-simple-monitor中,被provider和consumer中的DubboMonitor调用。
第六章 dubbo源码解析目录的更多相关文章
- 第零章 dubbo源码解析目录
第一章 第一个dubbo项目 第二章 dubbo内核之spi源码解析 2.1 jdk-spi的实现原理 2.2 dubbo-spi源码解析 第三章 dubbo内核之ioc源码解析 第四章 dubb ...
- 第六章 ReentrantLock源码解析2--释放锁unlock()
最常用的方式: int a = 12; //注意:通常情况下,这个会设置成一个类变量,比如说Segement中的段锁与copyOnWriteArrayList中的全局锁 final Reentrant ...
- 第六章 HashSet源码解析
6.1.对于HashSet需要掌握以下几点 HashSet的创建:HashSet() 往HashSet中添加单个对象:即add(E)方法 删除HashSet中的对象:即remove(Object ke ...
- dubbo源码解析五 --- 集群容错架构设计与原理分析
欢迎来我的 Star Followers 后期后继续更新Dubbo别的文章 Dubbo 源码分析系列之一环境搭建 博客园 Dubbo 入门之二 --- 项目结构解析 博客园 Dubbo 源码分析系列之 ...
- dubbo源码解析-spi(一)
前言 虽然标题是dubbo源码解析,但是本篇并不会出现dubbo的源码,本篇和之前的dubbo源码解析-简单原理.与spring融合一样,为dubbo源码解析专题的知识预热篇. 插播面试题 你是否了解 ...
- Dubbo 源码解析四 —— 负载均衡LoadBalance
欢迎来我的 Star Followers 后期后继续更新Dubbo别的文章 Dubbo 源码分析系列之一环境搭建 Dubbo 入门之二 --- 项目结构解析 Dubbo 源码分析系列之三 -- 架构原 ...
- dubbo源码解析-spi(4)
前言 本篇是spi的第四篇,本篇讲解的是spi中增加的AOP,还是和上一篇一样,我们先从大家熟悉的spring引出AOP. AOP是老生常谈的话题了,思想都不会是一蹴而就的.比如架构设计从All in ...
- dubbo源码解析-spi(3)
前言 在上一篇的末尾,我们提到了dubbo的spi中增加了IoC和AOP的功能.那么本篇就讲一下这个增加的IoC,spi部分预计会有四篇,因为这东西实在是太重要了.温故而知新,我们先来回顾一下,我们之 ...
- 第十四章 Executors源码解析
前边两章介绍了基础线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的使用方式.工作机理.参数详细介绍以及核心源码解析. 具体的介绍请参照: 第十二章 ThreadPoolExecutor使用与工作机理 第十 ...
- 第九章 LinkedBlockingQueue源码解析
1.对于LinkedBlockingQueue需要掌握以下几点 创建 入队(添加元素) 出队(删除元素) 2.创建 Node节点内部类与LinkedBlockingQueue的一些属性 static ...
随机推荐
- 2024御网线上Pwn方向题解
ASM Checksec检查保护 基本上保护都关闭了 64位ida逆向 程序只有一段,并且返回地址就是输入的数据,看起来就是srop了,找一下可以用的gadget 通过异或清空rax值,然后通过异或e ...
- 2022/1/25-2022牛客寒假算法基础集训营1B-炸鸡块君与FIFA22(线段树)
题目描述 热爱足球(仅限游戏)的炸鸡块君最近购买了FIFA22,并且沉迷于FIFA22的Rivals排位上分. 在该排位系统中,每局游戏可能有胜利(用W表示).失败(用L表示).平局(用D表示)三种结 ...
- PostgreSQL中将对象oid和对象名相互转换
PostgreSQL中将对象oid转为对象名 使用pg的内部数据类型将对象oid转为对象名,可以简化一些系统视图的关联查询. 数据库类型转换对应类型的oid 可以用以下数据库类型转换对应类型的oid( ...
- 《刚刚问世》系列初窥篇-Java+Playwright自动化测试-4-启动浏览器-基于Maven(详细教程)
1.简介 上一篇文章,宏哥已经在搭建的java项目环境中添加jar包实践了如何启动浏览器,今天就在基于maven项目的环境中给小伙伴们或者童鞋们演示一下如何启动浏览器. 2.eclipse中新建mav ...
- json编码格式化美化
有时候你想存储一个json到文件中,然后让别人调用或者读取或者作为临时存储,诸如此类. 但是php json_encode后数据是压缩的没有格式化,导致读起来有点费劲. 所以你可以这样(php 5.4 ...
- AI那么厉害,那测试开发和自动化测试这些职位是不是就多余了?
在当今科技飞速发展的时代,AI大模型如ChatGPT等如同璀璨星辰般闪耀登场,它们的强大功能引发了各个领域的诸多思考.在软件测试领域,不少人心里直犯嘀咕:这AI大模型都这么厉害了,那测试开发和自动化测 ...
- java内存区域——daicy
Java虚拟机 运行时数据区 主要分为五部分:方法区,堆(这两块是所有线程共享的区域),程序计数器,本地方法栈,虚拟机栈(vm stack)(这三块为线程隔离区域) 程序计数器(Program Cou ...
- 这些 JavaScript 编码习惯,让你最大程度提高你的项目可维护性!
前言: 因为 JavaScript 语言是一门极其松散.极其自由的语言,这意味着我们可以随心所欲的操作它,这是他的优点,但同时也是它的缺点.在编码过程中,我们需要一种良好的规范或者习惯来保持应用程序的 ...
- Python版本与Jupyter记录
最近使用Python的时候,遇到一个版本问题.我本地安装的Python版本是3.8.0,在使用match...case...语法时,提示如下报错: 查询之后,才知晓3.8.0还没有match语法,ma ...
- E. Photoshoot for Gorillas
题意 给定一个整数 \(T\),代表共有\(T\)组测试用例,对于每组测试用例: 给定四个整数 \(n,m,k和w(1 \leq n,m \leq 2 * 10^5, 1 \leq w \leq n ...
