gym923B
Even though he isn't a student of computer science, Por Costel the pig has started to study Graph Theory. Today he's learning about Bellman-Ford, an algorithm that calculates the minimum cost path from a source node (for instance, node 1) to all the other nodes in a directed graph with weighted edges. Por Costel, utilizing his scarce programming knowledge has managed to scramble the following code in C++, a variation of the Bellman-Ford algorithm:

You can notice a lot of deficiencies in the above code. In addition to its rudimentary documentation, we can see that Por Costel has stored this graph as an array of edges (the array  ). An edge is stored as the triplet
). An edge is stored as the triplet 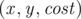 signifying an edge that spans from
signifying an edge that spans from  to
to 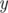 and has weight
and has weight 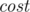 . But even worse is the fact that the algorithm is SLOW!
. But even worse is the fact that the algorithm is SLOW!
As we want our hooved friend to walk away with a good impression about computer science, we want his code to execute as FAST as possible. In order to do so, we can modify the order of edges in the array  so that the while loop executes a small number of times.
so that the while loop executes a small number of times.
Given a directed graph of 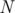 nodes and
nodes and  edges, you are asked to produce an ordering of the edges such that the Bellman-Ford algorithm written by Por Costel should finish after at most two iterations of the while loop(that is, the program should enter the while loop at most twice).
edges, you are asked to produce an ordering of the edges such that the Bellman-Ford algorithm written by Por Costel should finish after at most two iterations of the while loop(that is, the program should enter the while loop at most twice).
The first line of the file algoritm.in will contain an integer 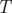
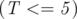 , the number of test cases.
, the number of test cases.
Each of the 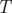 test cases has the following format: on the first line, there are two numbers
test cases has the following format: on the first line, there are two numbers 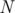 and
and  (
(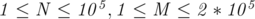 ), the number of nodes and the number of edges in the graph respectively.
), the number of nodes and the number of edges in the graph respectively.
The next  lines describe the edges, each containing three integers
lines describe the edges, each containing three integers 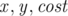 signifying there is an edge from node
signifying there is an edge from node  to node
to node 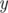 with weight
with weight 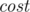 (
(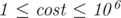 )
)
It is guaranteed that node 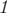 has at least one outgoing edge.
has at least one outgoing edge.
The graph may contain self loops and/or multiple edges.
The output file algoritm.out should contain 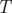 lines representing the answers to each test case.
lines representing the answers to each test case.
For each test case you should output a permutation of numbers from 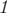 to
to  , representing the order of the edges you want in Por Costel's array of edges
, representing the order of the edges you want in Por Costel's array of edges  .
.
The edges are considered indexed by the order in which they are given in the input (the  -th edge read is the edge with index
-th edge read is the edge with index  ).
).
If there are multiple solutions, you are allowed to print any of them.
1
4 4
1 2 1
3 4 2
2 3 3
1 3 1
1 4 2 3
dijiestra存访问路径
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int inf=1<<29;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
struct edge
{
int v,val,i;
};
priority_queue<PII,vector<PII>,greater<PII> >q;
vector<edge>graph[100100];
vector<int>num;
int n,m,u,v,val,T;
int d[100100],used[200100],use[200100];
void dijiestra()
{
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
q.push(PII(0,1));
while(!q.empty())
{
PII x=q.top();q.pop();
int u=x.second;
if(used[u]) continue;
used[u]=1;
for(int i=0;i<graph[u].size();i++)
{
edge x=graph[u][i];
int v=x.v,val=x.val;
if(d[v]>d[u]+val){d[v]=d[u]+val;num.push_back(x.i);use[x.i]=1;q.push(PII(d[v],v));}
}
}
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<d[i]<<" ";
// cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<num.size();i++) printf("%d ",num[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) if(!use[i]) printf("%d ",i);
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
freopen("algoritm.in","r",stdin);
freopen("algoritm.out","w",stdout);
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) d[i]=inf;
memset(use,0,sizeof(use));
num.clear();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&val);
edge e;
e.v=v,e.val=val,e.i=i;
graph[u].push_back(e);
}
dijiestra();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
graph[i].clear();
}
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
gym923B的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- netty5和4.x,3.x的一些区别
http://item.congci.com/item/netty-5-0-4-0-xin-bianhua-he-zhuyi-dian
- git删除分支|查看分支动态
git不能在当前分支下删除你当前所在的分支,比如你要删除new分支,而现在正在处于new分支下,则执行git branch -d new的时候会报错 error: Cannot delete bran ...
- 关于高负载服务器Kernel的TCP参数优化
net.ipv4.tcp_mem 内核分配给TCP连接的内存,单位是Page,1 Page = 4096 Bytes,可用命令查看: #getconf PAGESIZE 4096 net.ipv4.t ...
- 执行sudo时报错:effective uid is not 0
http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/c45ad29cd83d4b051753e232.html 今天将 / 授权给了一个普通用户 导致一些问题. 启事: 操作前一 ...
- 安卓开发:效果图中标注的像素尺寸如何转换为安卓的dp尺寸?
我们的UI基于1920x1080分辨率给的尺寸标注,但是在安卓开发中大家一般都使用dp.sp来标注界面尺寸,所以需要一个dp与sp的转换公式. 一开始参考的的这篇文章:关于Android开发中px.d ...
- PhoneGap: Android平台入门例子(Hello World)
Hello World Demo: http://docs.phonegap.com/en/2.0.0/guide_getting-started_android_index.md.html#Gett ...
- servlet乱码问题总结
在学习时servlet乱码问题还是挺严重的,总结一下有三种情况 1.新建HTML页面后浏览出现乱码 2.以post形式请求时出现乱码 3.以get形式请求时出现乱码 让我们一个一个来解决吧 1.新建H ...
- lecture16-联合模型、分层坐标系、超参数优化及本课未来的探讨
这是HInton的第16课,也是最后一课. 一.学习一个图像和标题的联合模型 在这部分,会介绍一些最近的在学习标题和描述图片的特征向量的联合模型上面的工作.在之前的lecture中,介绍了如何从图像中 ...
- K-means算法和矢量量化
语音信号的数字处理课程作业——矢量量化.这里采用了K-means算法,即假设量化种类是已知的,当然也可以采用LBG算法等,不过K-means比较简单.矢量是二维的,可以在平面上清楚的表示出来. 1. ...
- 拦截PHP各种异常和错误,发生致命错误时进行报警,万事防患于未然
在日常开发中,大多数人的做法是在开发环境时开启调试模式,在产品环境关闭调试模式.在开发的时候可以查看各种错误.异常,但是在线上就把错误显示的关闭. 上面的情形看似很科学,有人解释为这样很安全,别人看不 ...
