CAN协议学习(二)MCAN控制器介绍
更多细节请参看MCAN2文档mcan2_ps.pdf。
一、MCAN2简介
MCAN2是Mentor公司开发的一个CAN2.0网络控制器的软核,初版2001年末版2006年。MCAN 2控制器实现了BOSCAN消息传输协议2.0a和2.0b。规范2.0a(相当于can 1.2)涵盖标准消息格式(11位标识符);规范2.0b涵盖标准和扩展消息格式(11位和29位标识符)。
二、总体架构
下图显示了MCAN2设计的主要功能块。
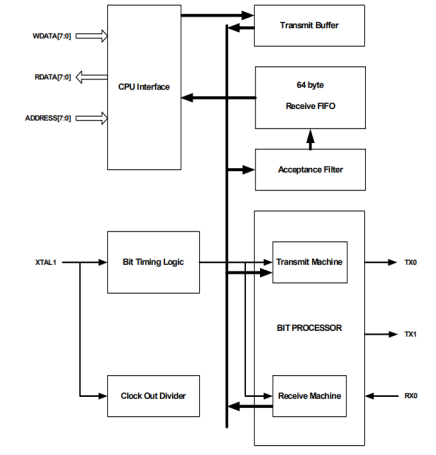
CPU对mcan 2的访问是通过独立的地址、输入数据和输出数据总线进行的。由主机设备将用于传输的消息放置到发送缓冲器中,以便由位处理器进行传输。设备接收到的消息首先由接收过滤器过滤,然后放入接收FIFO中。
CPU通过称为接收缓冲区的13字节窗口访问接收FIFO.结合接收FIFO使用接收缓冲区允许CPU在接收其他消息时处理一条消息。接收FIFO的总长度为64个字节,并以循环方式使用,使其能够同时容纳最多5个扩展的帧格式消息。
位定时逻辑块负责设备的波特率,并且是可编程的。所支持的波特率范围取决于主系统时钟XTAL1的频率,并且可以容易地跨越比BOSCH规范所选择的125kbud-1MBaud更宽的波特率范围。
CAN总线的接口由发送信号tx0、tx1和接收的rx 0提供。TX1通常与tx0相反,也可以编程为输出发送时钟,这对于测试非常有用。
三、发送、接收过程
要传输的数据以标准帧格式(SFF)或扩展帧格式(EFF)写入mcan 2的发送缓冲器(如下)。发送缓冲器包括CAN地址10h和1ch之间的13个字节,一个帧最多可以发送8个字节的数据。注意:在将数据写入缓冲区之前,需要检查传输缓冲区状态(状态寄存器,位2),以确保缓冲区“释放”(SR.2=‘1’)。当缓冲区被锁定时写入缓冲区的任何数据(SR.2=‘0’)都会丢失而没有任何指示。

发送缓冲器描述符字段的位布局如下所示.
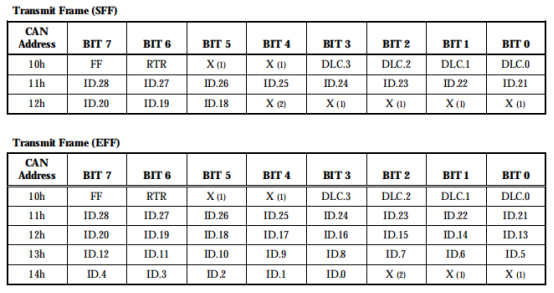
FF代表frame format:0为标准帧,1为拓展帧。
RTR代表REMOTE TRANSMISSION REQUEST:1表示为远程帧。
DLC代表DATA LENGTH CODE:范围0-8,大于8的数被自动解释为8。
ID代表IDENTIFIER:标识符充当消息的名称,用于接收过滤,并确定总线访问优先级。标识符的二进制值越低,优先级就越高。在标准帧格式(SFF)中,标识符由11位(id.28至id.18)组成。在扩展帧格式(Eff)消息中,标识符由29位(id.28到id.0)组成。id.28是最高位,首先在总线上传输。
mcan 2接收的数据首先由接收滤波器过滤,然后传递给接收FIFO。接受过滤器只传递那些具有与接收过滤器寄存器中记录的消息相匹配的标识位的消息。
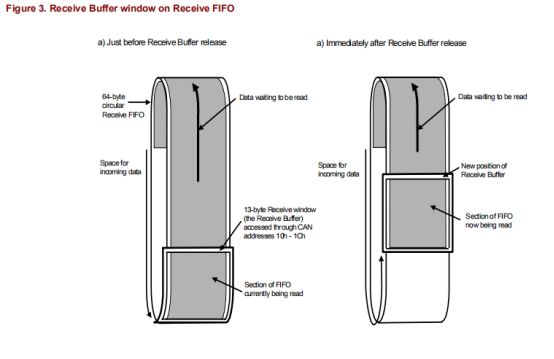
接收FIFO有64个字节深,允许最多5个完整扩展帧格式(EFF)消息的空间,并以循环方式使用。
放置在接收FIFO中的数据通过一个称为接收缓冲区的13字节窗口读取。该窗口位于can地址10h-1ch,即它占用与发送缓冲器相同的地址空间。与传输缓冲区一样,它足够宽,可以容纳一条包含最多8个字节数据的消息。
四、信号&寄存器描述
信号描述:
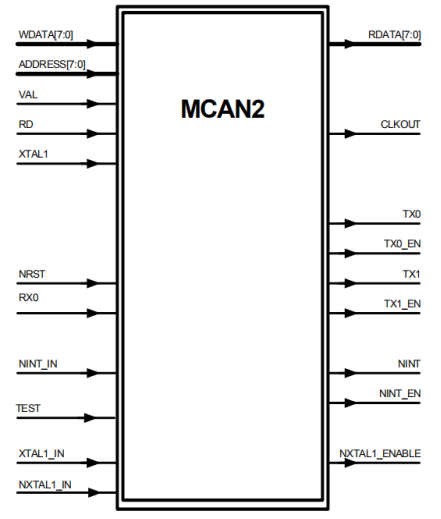

寄存器描述:

五、接收过滤
与过滤相关的寄存器:
10h-13h ACR0–3 Acceptance Code Registers 0-3
14h-17h AMR0–3 Acceptance Mask Registers 0-3
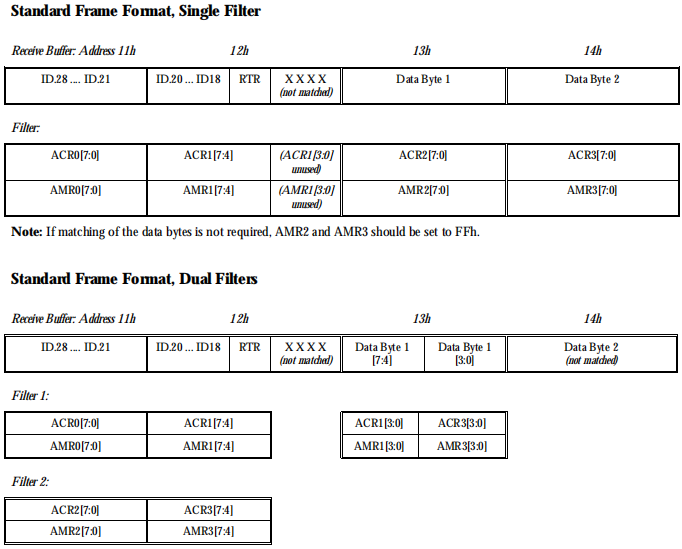
MCAN2的接收过滤模块首先将接收到的数据帧的ID部分与ACR即接收码寄存器比较,如果一致则接收,如果不一致则丢弃;AMR是接收掩码寄存器,如果某位设为‘1’,则将ACR对应的位设为‘不关心’。根据MOD.3为0或1来设置单过滤或双过滤模式,具体如下图。
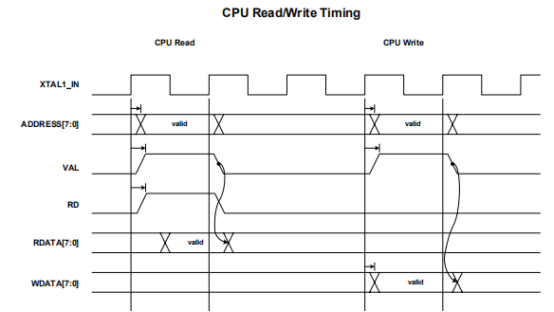
六、时序图
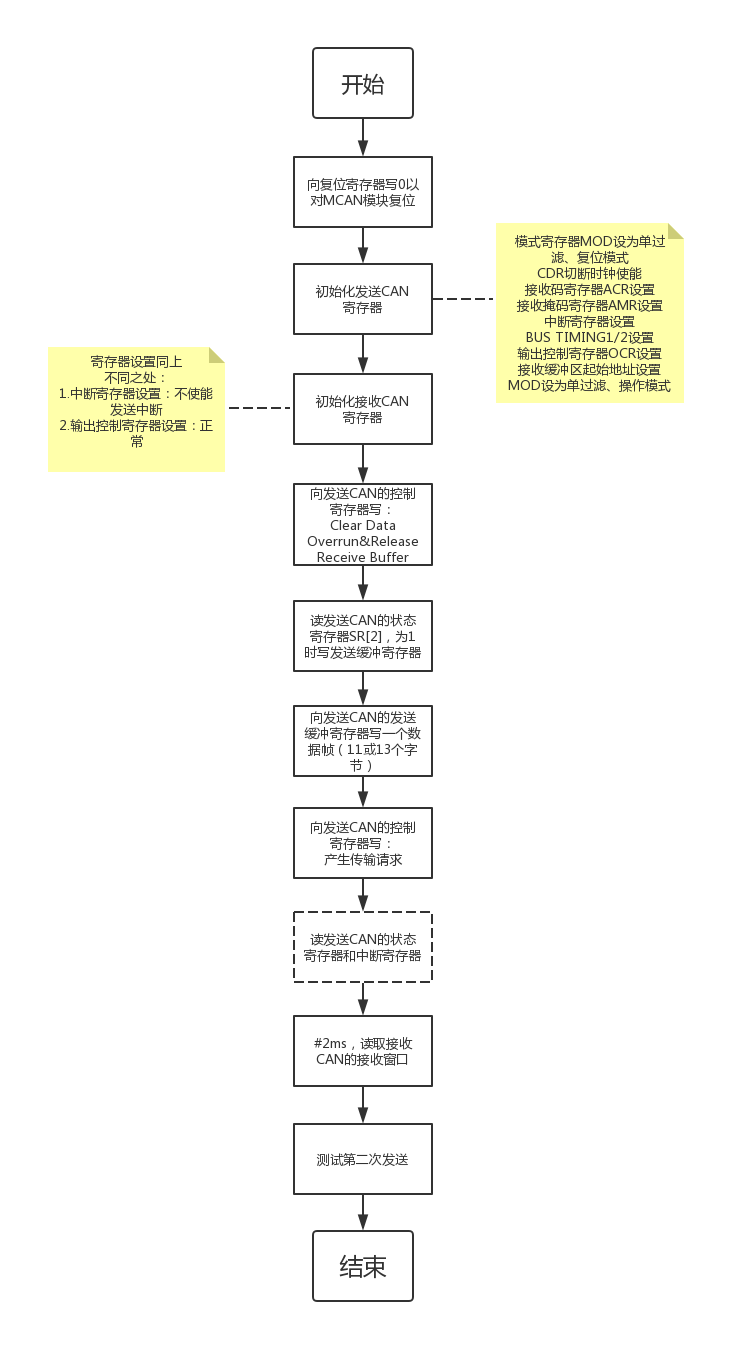
七、测试程序(流程图&代码)

//test CAN 2019.03.22 by zhou
assign F_can_rx[]=(F_can_tx[]=='b1)?F_can_tx[0]:((F_can_tx[0]==1'b1)?F_can_tx[]:'bZ); //star
assign F_can_rx[]=(F_can_tx[]=='b1)?F_can_tx[3]:((F_can_tx[3]==1'b1)?F_can_tx[]:'bZ); //earth
assign F_can_rx[]=(F_can_tx[]=='b1)?F_can_tx[1]:((F_can_tx[1]==1'b1)?F_can_tx[]:'bZ); //star
assign F_can_rx[]=(F_can_tx[]=='b1)?F_can_tx[2]:((F_can_tx[2]==1'b1)?F_can_tx[]:'bZ); //earth
task CPU_READ_NPT; //just read data, no display
input [:] addr;
output [:] rddata;
begin
#120ns
@(posedge S_cpu_clk)
F_nrd = 'b1;
F_nwr = 'b1;
F_ncs = 'b1;
F_addr =addr;
@(posedge S_cpu_clk)
F_nrd = 'b0;
F_nwr = 'b1;
F_ncs = 'b0;
F_addr =addr;
@(posedge S_cpu_clk)
wait (F_nrdy==);
rddata = F_data_o;
//$display("the addr %h read result is %h",addr, rddata);
@(posedge S_cpu_clk)
F_nrd = 'b1;
F_nwr = 'b1;
F_ncs = 'b1;
F_addr =;
end
endtask
task CAN_TEST_ALL;
begin
CAN_TEST('h0700,16'h1201,'h0500,16'h1100,'h03);
//CAN_TEST(16'h0701,16'h1200,16'h0600,16'h1000,8'h12);
end
endtask
task CAN_TEST;
input [:] reset_reg_star;
input [:] reset_reg_earth;
input [:] base_reg_star;
input [:] base_reg_earth;
input [:] connect;
int i_cnt;
logic [:] can_rdata;
begin
$display("=============CAN %h TEST START=============",connect);
CPU_WRITE(reset_reg_star,'h0000);//CAN1A RST begin
#170ns;
CPU_WRITE(reset_reg_star,'h0001);//CAN1A RST end
CPU_WRITE(reset_reg_earth,'h0000);//CAN2B RST begin
#170ns;
CPU_WRITE(reset_reg_earth,'h0001);//CAN2B RST end
//////////////////can init 1A&2B begin////////////////
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star,'h09); //CAN1A INIT [star]
CPU_READ_NPT(base_reg_star,can_rdata);
if(can_rdata != 'h09)
begin
$display("the addr base_reg_star read result is %h,wrong!(should be 8'h09)",can_rdata);
$stop;
end
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h1F,8'h08);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h10,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h11,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h12,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h13,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h14,8'hFF); // ////CARE ID:MUST 00
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h15,8'hFF);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h16,8'hFF);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h17,8'hFF);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h04,8'h03);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h06,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h07,8'h16);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h08,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h1E,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h00,8'h08);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h00,8'h09); //CAN2B INIT [earth]
CPU_READ_NPT(base_reg_earth+'h00,can_rdata);
if(can_rdata != 'h09)
begin
$display("the addr base_reg_earth+8'h00 read result is %h,wrong!(should be 8'h09)",can_rdata);
$stop;
end
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h1F,8'h08);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h10,8'h12); // //// ID:MUST 122X
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h11,8'h24);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h12,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h13,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h14,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h15,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h16,8'hFF);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h17,8'hFF);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h04,8'h01);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h06,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h07,8'h16);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h08,8'h02);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h1E,8'h00);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h00,8'h08);
//////////////////can init end///////////////////////////
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h01,8'h0C); //CLR RX FIFO
CPU_READ(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata); //SR[2]=?0
while(can_rdata[] == )
begin
#1us;
CPU_READ_NPT(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata);
end
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h10,8'h08); //Transmit Frame Information:standard,8 data
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h11,8'h56); //identifier:ff0
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h12,8'h60);
for(i_cnt=;i_cnt<;i_cnt++)
begin
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h10+i_cnt,i_cnt);//write data to transmit buffer,发送一帧标准帧数据
end
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h01,8'h01); //trans enable
CPU_READ(base_reg_star+'h03,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata);
while(can_rdata[] == )
begin
#1us;
CPU_READ_NPT(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata);
end
CPU_READ(base_reg_star+'h03,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata);
#2ms;
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h10,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h11,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h12,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h13,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h14,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h15,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h16,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h17,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h18,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h19,can_rdata);
//CPU_READ(base_reg_star+8'h03,can_rdata);
//CPU_READ(base_reg_star+8'h02,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h1a,can_rdata);
///////////////////////////////////second sending///////////////////////////////
$display("####################################");
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h01,8'h0C);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_earth+'h01,8'h0C);
CPU_READ(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata); //SR[2]=?0
while(can_rdata[] == )
begin
#1us;
CPU_READ_NPT(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata);
end
CPU_READ(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata);
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h10,8'h08); //Transmit Frame Information:standard,8 data
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h11,8'h00); //identifier:00
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h12,8'h00);
for(i_cnt=;i_cnt<;i_cnt++)
begin
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h10+i_cnt,i_cnt);//write data to transmit buffer,发送一帧标准帧数据
end
CPU_WRITE(base_reg_star+'h01,8'h01); //trans enable
CPU_READ(base_reg_star+'h02,can_rdata); //SR[2]=?0
#2ms
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h10,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h11,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h12,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h13,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h14,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h15,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h16,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h17,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h18,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h19,can_rdata);
//CPU_READ(base_reg_star+8'h03,can_rdata);
//CPU_READ(base_reg_star+8'h02,can_rdata);
CPU_READ(base_reg_earth+'h1a,can_rdata);
$display("CAN %h TEST Success!\n",connect);
end
endtask
MCAN2测试代码
CAN协议学习(二)MCAN控制器介绍的更多相关文章
- WebService学习--(二)webservice相关介绍
一.WebService是什么? 1. 基于Web的服务:服务器端整出一些资源让客户端应用访问(获取数据) 2. 一个跨语言.跨平台的规范(抽象) 3. 多个跨平台.跨语言的应用间通信整合的方案(实际 ...
- TCP/IP协议学习(二) LWIP用户自定义配置文件解析
LWIP协议支持用户配置,可以通过用户裁剪实现最优化配置,LWIP默认包含opts.h作为系统默认配置,不过通过添加lwipopts.h文件并包含在opts.h头文件之前就可以对lwip进行用户裁剪, ...
- Asp.Net MVC学习总结(二)——控制器与动作(Controller And Action)
一.理解控制器 1.1.什么是控制器 控制器是包含必要的处理请求的.NET类,控制器的角色封装了应用程序逻辑,控制器主要是负责处理请求,实行对模型的操作,选择视图呈现给用户. 简单理解:实现了ICon ...
- HTTP协议学习笔记(二)
HTTP协议学习笔记(二) 1.HTTP报文 HTTP报文:用于HTTP协议交互的信息.请求报文:请求端(客户端)的HTTP报文叫做请求报文.响应报文:响应端(服务端)的HTTP报文叫做响应报文. H ...
- 8086汇编语言学习(二) 8086汇编开发环境搭建和Debug模式介绍
1. 8086汇编开发环境搭建 在上篇博客中简单的介绍了8086汇编语言.工欲善其事,必先利其器,在8086汇编语言正式开始学习之前,先介绍一下如何搭建8086汇编的开发环境. 汇编语言设计之初是用于 ...
- TCP/IP协议学习之实例ping命令学习笔记
TCP/IP协议学习之实例ping命令学习笔记(一) 一. 目的为了让网络协议学习更有效果,在真实网络上进行ping命令前相关知识的学习,暂时不管DNS,在内网中,进行2台主机间的ping命令的整个详 ...
- python学习第二讲,pythonIDE介绍以及配置使用
目录 python学习第二讲,pythonIDE介绍以及配置使用 一丶集成开发环境IDE简介,以及配置 1.简介 2.PyCharm 介绍 3.pycharm 的安装 二丶IDE 开发Python,以 ...
- SpringMVC入门学习(二)
SpringMVC入门学习(二) ssm框架 springMVC 在上一篇博客中,我简单介绍了一下SpringMVC的环境配置,和简单的使用,今天我们将进一步的学习下Springmvc的操作. mo ...
- 苹果ANCS协议学习【转】
苹果ANCS协议学习 转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/alexcai/p/4321514.html 综述 苹果通知中心(Apple Notification Center Serv ...
随机推荐
- 用SparkSQL构建用户画像
用SparkSQL构建用户画像 二. 前言 大数据时代已经到来,企业迫切希望从已经积累的数据中分析出有价值的东西,而用户行为的分析尤为重要. 利用大数据来分析用户的行为与消费习惯,可以预测商品的发展 ...
- #424 Div2 C
#424 Div2 C 题意 给出 k 个分数,初始分数未知,按顺序把这 k 个分数加到初始分数上,已知 n 个加入分数后的结果(无序),问初始分数有多少种可能. 分析 也就是说这 n 个结果,它们之 ...
- spoj 913 Query on a tree II (倍增lca)
Query on a tree II You are given a tree (an undirected acyclic connected graph) with N nodes, and ed ...
- python全栈开发- day14列表推导式、生成器表达式、模块基础
一.列表推导式 #1.示例 数据量小 egg_list=[] for i in range(10): egg_list.append('鸡蛋%s' %i) egg_list=['鸡蛋%s' %i fo ...
- DQL数据查询语言——连接查询
--内连接 两种写法 等值连接select r.*,b.bummc from t_hq_ryxx r, t_hq_bm b where r.bumbm = b.bumbm select r.*,b.b ...
- 博客 | 基于Travis CI实现Hexo在Github和Coding的同步自动化部署
文章目录 完成Hexo主题安装和配置 基于Travis CI实现同步部署 参考内容 相关链接 待补充 完成Hexo主题安装和配置 如果您还没有安装Hexo环境,请参考Hexo文档安装,也给出这样两篇博 ...
- 第九章 Android-UI组件(2)
一.图像视图(ImageView) 布局 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayo ...
- 使用 SVG 来实现波浪 (wave) 动画效果
如下图所示的波浪动画效果,实现方法有很多,比如CSS或者是js等方法都可以实现.不过,要是使用SVG来实现的,我觉得比其它两种方法都要简单.这篇文章就来讲讲使用SVG来实现类似这样的波浪动画效果是多么 ...
- 一个小时内学习SQLite数据库
一个小时内学习SQLite数据库 2012-05-11 10:24 红薯 OSCHINA 字号:T | T SQLite 是一个开源的嵌入式关系数据库,实现自包容.零配置.支持事务的SQL数据库引擎. ...
- securecrt中进入uboot命令行时,出现无法键入任何指令的问题解决方法
securecrt中进入uboot命令行时,出现无法键入任何指令的问题解决方法 可能出现以下几种情况 1.securecrt在创建连接时,忘记取消勾选流控: 2.usb转串口线坏了3.uboot有问题 ...
