Callable、Future、RunnableFuture、FutureTask的原理及应用
1. Callable、Future、RunnableFuture、FutureTask的继承关系
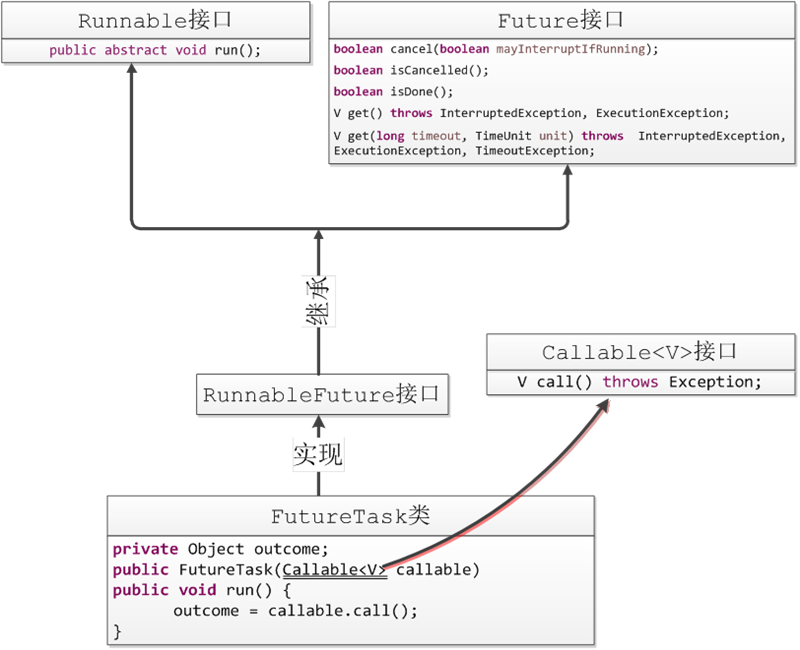
在多线程编程中,我们一般通过一个实现了Runnable接口的对象来创建一个线程,这个线程在内部会执行Runnable对象的run方法。如果说我们创建一个线程来完成某项工作,希望在完成以后该线程能够返回一个结果,但run方法的返回值是void类型,直接实现run方法并不可行,这时我们就要通过FutureTask类来间接实现。
FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture接口实际上仅仅是Runnable接口和Future接口的合体。Future接口提供取消任务、检测任务是否执行完成、等待任务执行完成获得结果等方法。从图中可以看出,FutureTask类中的run方法已经实现好了(图中的代码仅仅是核心代码),这个run方法实际上就是调用了由构造函数传递进来的call方法,并将返回值存储在FutureTask的私有数据成员outcome中。这样一来我们将FutureTask传递给一个Thread时,表面上我们仍然执行的是run,但在run方法的内部实际上执行的是带有返回值的call方法,这样即使得java多线程的执行框架保持不变,又实现了线程完成后返回结果的功能。同时FutureTask又将结果存储在outcome中,我们可以通过调用FutureTask对象的get方法获取outcome(也就是call方法的返回结果)。
|
Future接口功能介绍 |
|
|
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning); |
功能:设置线程的中断标志位 参数:mayInterruptIfRunning为ture,如果线程可以取消则设置线程的中断标志位 返回值:若线程已经完成,返回false;否则返回true 注意:要实现取消线程执行的功能,call函数需要在循环条件中检查中断标志位,以跳出循环 |
|
boolean isCancelled(); |
判断线程是否取消 |
|
boolean isDone(); |
线程执行完成,返回true;如果cancel方法返回true,则该方法也返回true |
|
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; |
获取call方法的返回结果,如果call方法没有执行完成,则会阻塞当前线程,直到call方法执行完毕,才被唤醒 |
|
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) |
设置时限的get方法。 |
2. Future及FutureTask的使用
Future以及FutureTask是线程池实现的基础元素,但不是说Future及FutureTask只能在线程池中才能使用,下面的例子就说明了FutureTask独立使用的情况。在这个例子中,我们首先随机产生了2000个整数存于数组中,然后创建了两个线程,一个线程寻找前1000个数的最大值,另个一线程寻找后1000个数的最大值。主线程比较这两个线程的返回结果来确定这2000个数的最大值值。
package javaleanning; import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class FutureDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException{
int[] a = new int[2000];
Random rd = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++){
a[i] = rd.nextInt(20000);
} class FindMax implements Callable<Integer>{
private int begin,end,int a[];
public FindMax(int a[],int begin, int end){
this.a = a;this.begin = begin;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int maxInPart = a[begin];
for(int i = begin; i <= end; i++){
if(a[i] > maxInPart){
maxInPart = a[i];
}
}
return new Integer(maxInPart);
}
} FutureTask<Integer> findMaxInFirstPart =new FutureTask<Integer>(new FindMax(a,0,999));
FutureTask<Integer> findMaxInSecondPart =new FutureTask<Integer>(new FindMax(a,1000,1999)); new Thread(findMaxInFirstPart).start();
new Thread(findMaxInSecondPart).start(); int maxInFirst = (int) findMaxInFirstPart.get();
int maxInSecond = (int) findMaxInSecondPart.get();
System.out.println("Max is " +(maxInFirst > maxInSecond ? maxInFirst:maxInSecond));
//验证结果是否正确
int max = a[0];
for(int i = 0; i < 2000; i++){
if(a[i] > max){
max = a[i];
}
}
System.out.println(max);
}
}
3. FutureTask的实现原理
构造函数
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}FutureTask有两个构造函数,通常来说我们使用第一个构造函数。这里要强调一下第二个构造函数,它有两个类型参数,分别是Runnable类型和泛型V,然后由这两个构造一个Callable对象。当线程运行结束以后会返回由构造函数传递进来的这个泛型result对象,也就是说返回的值并不是通过运行得到的,而是由构造函数获取的一个指定的对象。
重要数据成员
private volatile int state;
private Object outcome;
private volatile Thread runner;
private volatile WaitNode waiters;
state表明了线程运行call方法的状态,初始状态为0,完成后由run方法将其设置为1。通过get方法获取结果时就必须检查state的值,如果该值为0,表明需要等待该结果,get方法就会将当前线程阻塞。
outcome表示了call方法的返回结果
runner表示运行FutureTask方法的线程,其值会在run方法中进行初始化
waiters指向了因获取结果而等待的线程组成的队列
重要方法
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}从代码中可以看出run方法中调用了从构造函数传递来的call方法。
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}当call方法执行完毕后,run方法调用又调用了set方法,它主要实现两个功能,一个是将结果赋值给outcome,另一个是通过finishCompletion唤醒由调用此FutureTask对象的get方法而阻塞的线程
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}在get方法中首先判断了state的值,如果call方法还未完成,就会通过awaitDone来阻塞自己。
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
} int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!(state == NEW &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW,
mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED)))
return false;
try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
} finally { // final state
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED);
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion();
}
return true;
}在cannel方法中,如果允许对线程中断,则设置该线程的中断标志位,并通过finishCompletion方法唤醒因等待结果而阻塞的线程。
参考文章
[1] http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3949310.html
[2] http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1384351141649.html
Callable、Future、RunnableFuture、FutureTask的原理及应用的更多相关文章
- Java并发编程:ThreadPoolExecutor + Callable + Future(FutureTask) 探知线程的执行状况
如题 (总结要点) 使用ThreadPoolExecutor来创建线程,使用Callable + Future 来执行并探知线程执行情况: V get (long timeout, TimeUnit ...
- Callable Future接口的设计原理
我们都知道Callable接口作为任务给线程池来执行,可以通过Future对象来获取返回值,他们背后的实现原理是什么?通过总结背后的实现原理有助于我们深入的理解相关技术,做到触类旁通和举一反三. 文章 ...
- Future、FutureTask实现原理浅析(源码解读)
前言 最近一直在看JUC下面的一些东西,发现很多东西都是以前用过,但是真是到原理层面自己还是很欠缺. 刚好趁这段时间不太忙,回来了便一点点学习总结. 前言 最近一直在看JUC下面的一些东西,发现很多东 ...
- java多线程系列(七)---Callable、Future和FutureTask
Callable.Future和FutureTask 前言:如有不正确的地方,还望指正. 目录 认识cpu.核心与线程 java多线程系列(一)之java多线程技能 java多线程系列(二)之对象变量 ...
- Java 并发编程——Callable+Future+FutureTask
Java 并发编程系列文章 Java 并发基础——线程安全性 Java 并发编程——Callable+Future+FutureTask java 并发编程——Thread 源码重新学习 java并发 ...
- Java并发编程:Callable、Future和FutureTask
作者:海子 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/ 本博客中未标明转载的文章归作者海子和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置 ...
- Callable、Future和FutureTask
创建线程的2种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Runnable接口.这2种方式都有一个缺陷就是:在执行完任务之后无法获取执行结果. 如果需要获取执行结果,就必须通过共享变量或者使用线 ...
- Callable与Future、FutureTask的学习 & ExecutorServer 与 CompletionService 学习 & Java异常处理-重要
Callable是Java里面与Runnable经常放在一起说的接口. Callable是类似于Runnable的接口,实现Callable接口的类和实现Runnable的类都是可被其他线程执行的任务 ...
- Java并发:Callable、Future和FutureTask
Java并发编程:Callable.Future和FutureTask 在前面的文章中我们讲述了创建线程的2种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Runnable接口. 这2种方式都有一 ...
随机推荐
- Centos配置查看
Reference: [1] http://www.centoscn.com/CentOS/help/2013/0928/1743.html [2] http://www.cnblogs.com/hi ...
- 黑马程序员——File笔记读,写,复制
#region ReadAllBytes byte[] buffer = File.ReadAllBytes(@"C:\Users\dell\Desktop\新建文件夹.txt") ...
- Xamarin跨平台移动开发解决方案
Xamarin始创于2011年,旨在使移动开发变得难以置信地迅捷和简单.Xamarin的产品简化了针对多种平台的应用开发,包括iOS.Android.Windows Phone和Mac App.Xam ...
- Groonga 3.0.8 发布,全文搜索引擎
Groonga 3.0.8 改进了管理界面的可用性,支持 groonga_query_log_path 指令(groonga-httpd) 提供基于 nginx 的 HTTP 服务功能,改进了 del ...
- 基于资源的权限系统-API设计
概述 权限系统需要和别的系统集成,因此,良好的API是易用性的保证. 这里只设计一些权限相关的核心 API,关于用户,组织,导入导出之类的后续再逐步补充 API 设计 围绕权限有以下 4 类 API: ...
- React学习笔记---项目构建
简介 ReactJs由于有FB的支持,得到了社区的极大关注,同时由于ReactJs只希望专一的做好View层次上的工作,所以本身并没有涉及很多周边工具. 今天要介绍一款工具,同时包含一个构建项目模板的 ...
- 消息中间件与JMS标准
初识消息中间件 维基百科上对于消息中间件的定义是"Message-oriented middleware(MOM) is software infrastructure focused on ...
- 【C语言学习】《C Primer Plus》第11章 字符串和字符串函数
学习总结 1.字符串(character String)是以空字符串(\o)结尾的char数组. 2.gets()方法代表get String,它从系统的标准输入设备(通常是键盘)获取一个字符串,当字 ...
- 作业三:PSP记录耗时情况
PSP2.1 Personal Software Process Stage Time planning 计划 15min Estimate 估计这个任务多久完成 130min Developing ...
- Programming Entity Framework CodeFirst--表关系约定
表之间的关系分为一对多,多对多,一对一三种,实质就是对外键进行配置. 一.一对多 1. Required Destination包含Lodging>的集合. public class Desti ...
