五 shell 变量与字符串操作
特点:1 shell变量没有数据类型的区分
2 Shell 把任何存储在变量中的值,皆视为以字符组成的“字符串”。
3 设定的变量值只在当前shell环境中有作用
4 不能以数字开头
5 =号两边不能存在空格
6 若变量值中存在空格,必须用括号将变量值括起来 I = “Jack Black”
在编写shell时,如果变量未赋值,后续使用时不会出现任何错误。如果要显示错误提示,则需要命令 shopt -s -o nounset
shopt -s -o nounset解析如下

.范例如下
[root@localhost ~]# vim test1.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo $Infomix
[root@localhost ~]# sh test1.sh
# 未提示任何错误
[root@localhost ~]# vim test1.sh
[root@localhost ~]# vim test1.sh
#!/bin/bash
shopt -s -o nounset #添加错误提示 echo $Infomix
[root@localhost ~]# sh test1.sh
test1.sh:行4: Infomix: 为绑定变量 #提示错误
二 取得变量值
$变量名称=${变量名称}
如果变量作为字符的一部分输出时,则必须用${}将变量括起来,否则shell将无法识别变量。$会将后面的所有字符当做变量的一部分,肯定是找不到变量的
[root@localhost ~]# myname='lsq'
[root@localhost ~]# echo $myname
lsq
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${myname}
lsq
[root@localhost ~]# echo hello${myname}boy
hellolsqboy
[root@localhost ~]# echo hello$mynameboy
hello
如果后面接的不是字符,也不是_下划线,则不需要{}来括起来。变量后接中文也是可以的。呵呵。
[root@localhost ~]# dir2=sbin
[root@localhost ~]# echo /usr/local/$dir2/config
/usr/local/sbin/config
$是去变量值的特殊字符,如果要显示$怎么操作,转义字符 \ 或者用单引号括起来 '$i'
Bash除了echo之外,还提供了一个c类似的printf的语法。感觉这个东西有字符串格式化的意思。体会一下
%s 以字符串的形式显示变量值
[root@localhost ~]# printf "%s" "$dir2"
sbin[root@localhost ~]# printf "%s\n" "$dir2"
sbin #\n和c语言一样,都是换行的意思。
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# SP='ABC 123 XYZ'
[root@localhost ~]# printf "%q\n" "$SP"
ABC\ \ XYZ #%q会将变量值中的特殊字符,用\字符转义,实例中就是在空格前加\
三 取消与清空变量
unset 变量名
unset -v 变量名 -v 表示取消的是变量
unset -f 函数名 -f 表示取消的是函数
清空变量值
变量名= 跟unset的区别是,清空变量值,该变量还存在,只不过值变成空而已。unset则会将变量销毁
四 变量和引号
双引号和单引号的区别
前边说过,变量赋值可以用单引号或者双引号,但是二者是有区别的
双引号相对于单引号可以有如下操作
1 替换变量 例
[root@localhost shellscript]# vim test2.sh
#! /bin/bash shopt -s -o nounset
myname="Bash shell"
#echo $myname
hello="hello ,i am $myname"
echo $hello
[root@localhost shellscript]# sh test2.sh
hello ,i am Bash shell #将变量名myname用Bash shell 进行了替换
#但是如果我们用单引号
[root@localhost shellscript]# vim test2.sh
#! /bin/bash
shopt -s -o nounset
myname="Bash shell"
#echo $myname
#hello="hello ,i am $myname"
hello='hello ,i am ,$myname'
echo $hello
[root@localhost shellscript]# sh test2.sh
hello ,i am ,$myname #看到了么?他不会替换,他会将变量名整体输出
如果要在双引号中输出变量名而非替换,则需要用到\转义字符转义
2 替换命令执行结果
3 替换算数运算结果
四 变量的有效范围
变量的有效范围就是当前所处的shell环境
如果要让变量在所有的shell都执行,那就需要将该变量设置成环境变量
通过 export 命令就可以将变量设置成环境变量。
export testVar="hello world"
或
testVar="hello world"
export testVar
取消环境变量
testVar=
或者
unset testVar
五 Bash 的内置变量














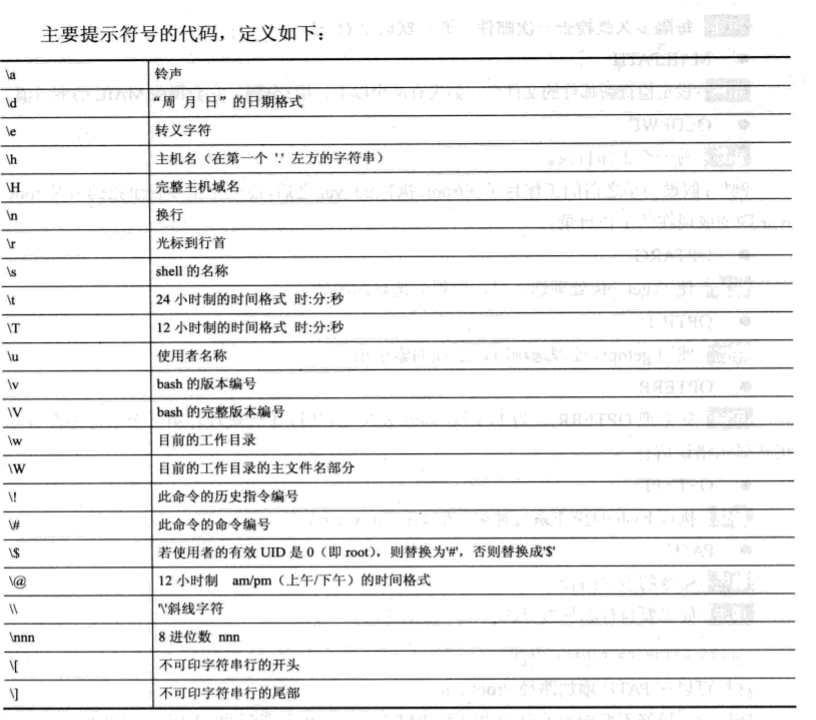

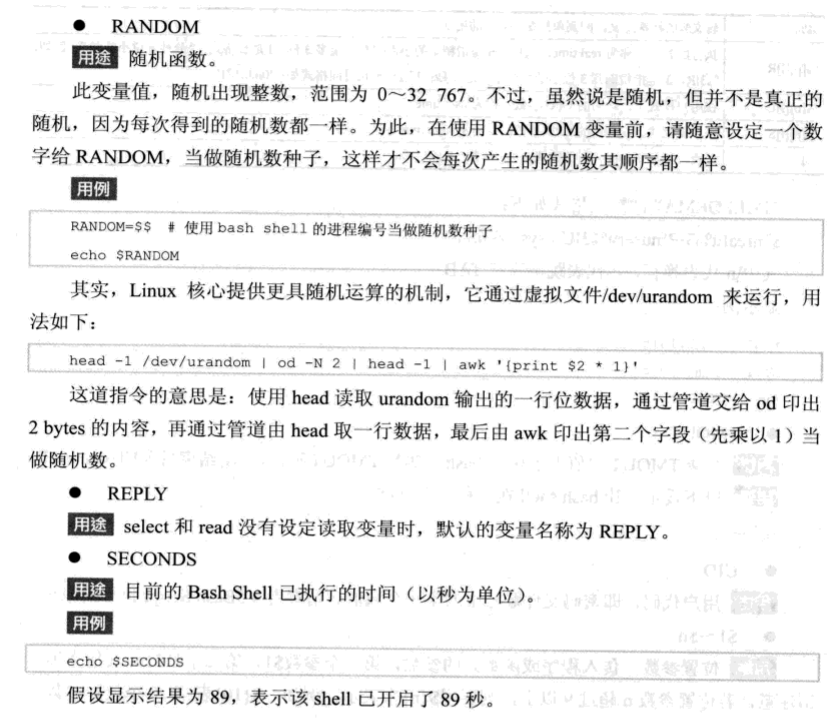

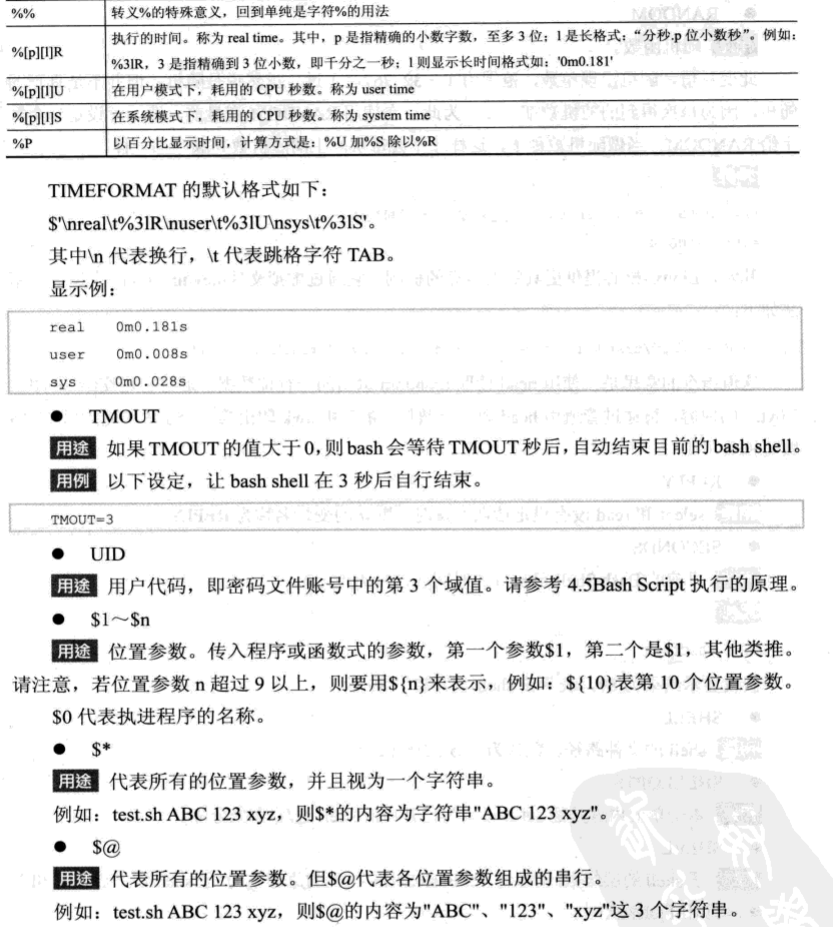
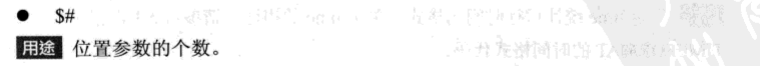

六 设置只读变量
readonly 命令和declare -r 命令
readonly 或 readonly -p 列出只读属性的变量列表
readonly -f 函数名 设置该函数不可修改
readonly -a 数组变量 设置后该数组为只读数组
例
s[]=
s[]=
s[]= readonly -a s #设置该数组为只读数组 s[]= 该行 会报错
调整变量的其他属性
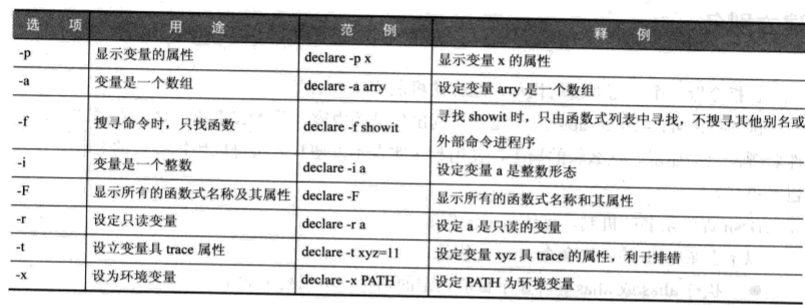
[root@localhost ~]# declare -i I= #设定该变量为整数变量
[root@localhost ~]# echo $I [root@localhost ~]# I="test" #如果传入字符串,则会将该变量变为0
[root@localhost ~]# echo $I [root@localhost ~]#
七 取别名
alias 变量名
[root@localhost ~]# alias -p #列出别名列表
alias cp='cp -i'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias l.='ls -d .* --color=auto'
alias ll='ls -l --color=auto'
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias perlll='eval `perl -Mlocal::lib`'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias which='alias | /usr/bin/which --tty-only --read-alias --show-dot --show-tilde'
alias 别名=指令 注意:=号两边不允许有空格。 如需要有空格,必须用括号括起来。如上例中alias l.='ls -d .*'
unalias 取消别名
八 自定义工作环境
以一般账号的角色工作时,默认的工作环境配置文件为
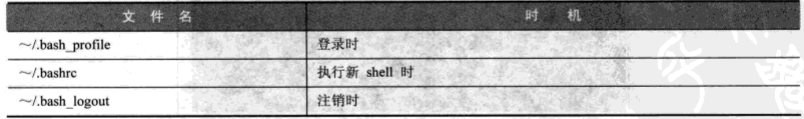
这里的~目录,一般指的是家目录
自定义工作环境的意义:让用户登录主机时,能拥有安全及易于执行命令的环境。包括 建立文件的权限 命令搜寻路径 环境变量 命令提示符 别名 喜好比较器 显示文件使用的颜色等
[root@localhost ~]# cd /root
[root@localhost ~]# cat .bash_profile #这个是root的默认配置文件
# .bash_profile # Get the aliases and functions
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
fi # User specific environment and startup programs PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin export PATH
[root@localhost /]# cd home #这个是普通用户的配置文件,普通用户在家目录 /home目录中
[root@localhost home]# ls
ftptest lsq
[root@localhost home]# cd lsq
[root@localhost lsq]# cat .bash_profile
# .bash_profile # Get the aliases and functions
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
fi # User specific environment and startup programs PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin export PATH
管理员维护的环境配置文件一般有三个 /etc/profile /etc/bashrc /etc/skel目录下的文件
其中 /etc/profile和/etc/bashrc中的设定,会影响所有账号的使用环境。
在/etc/profile中,通常会设定 umask,PATH,多国语言环境,提示符号,别名等
这是我本机的profile
[root@localhost etc]# cat profile
# /etc/profile # System wide environment and startup programs, for login setup
# Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc # It's NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you
# are doing. It's much better to create a custom.sh shell script in
# /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this
# will prevent the need for merging in future updates. pathmunge () {
case ":${PATH}:" in
*:"$1":*)
;;
*)
if [ "$2" = "after" ] ; then
PATH=$PATH:$
else
PATH=$:$PATH
fi
esac
} if [ -x /usr/bin/id ]; then
if [ -z "$EUID" ]; then
# ksh workaround
EUID=`/usr/bin/id -u`
UID=`/usr/bin/id -ru`
fi
USER="`/usr/bin/id -un`"
LOGNAME=$USER
MAIL="/var/spool/mail/$USER"
fi # Path manipulation
if [ "$EUID" = "" ]; then
pathmunge /usr/sbin
pathmunge /usr/local/sbin
else
pathmunge /usr/local/sbin after
pathmunge /usr/sbin after
fi HOSTNAME=`/usr/bin/hostname >/dev/null`
HISTSIZE=
if [ "$HISTCONTROL" = "ignorespace" ] ; then
export HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
else
export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
fi export PATH USER LOGNAME MAIL HOSTNAME HISTSIZE HISTCONTROL # By default, we want umask to get set. This sets it for login shell
# Current threshold for system reserved uid/gids is
# You could check uidgid reservation validity in
# /usr/share/doc/setup-*/uidgid file
if [ $UID -gt ] && [ "`/usr/bin/id -gn`" = "`/usr/bin/id -un`" ]; then
umask
else
umask
fi for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh /etc/profile.d/sh.local ; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null
fi
fi
done unset i
unset -f pathmunge
一下是本机普通用户的配置环境,在/etc/skel目录中
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/skel
[root@localhost skel]# ls
[root@localhost skel]# ls -la
总用量
drwxr-xr-x. root root 4月 .
drwxr-xr-x. root root 10月 : ..
-rw-r--r--. root root 10月 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r--. root root 10月 .bash_profile
-rw-r--r--. root root 10月 .bashrc
drwxr-xr-x. root root 8月 : .mozilla
[root@localhost skel]# cat .bash_profile
# .bash_profile # Get the aliases and functions
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
fi # User specific environment and startup programs PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin export PATH
[root@localhost skel]# cat .bashrc
# .bashrc # Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi # Uncomment the following line if you don't like systemctl's auto-paging feature:
# export SYSTEMD_PAGER= # User specific aliases and functions
[root@localhost skel]# cat .bash_logout
# ~/.bash_logout
九 数组
bash数组的特点: 1 没有个数限制 2 可以跳跃赋值 3 所以可以表达式表示,如1+2 4 bash只支持一维数组
[root@localhost ~]# A[]=
[root@localhost ~]# A[]=
[root@localhost ~]# A[]=
[root@localhost ~]# A[]="bash shell"
[root@localhost ~]# echo $A
5
[root@localhost ~]# echo $A[] 看出跟上一句的区别了么?他走的是C语言的路子,读取$A直接取得是数组首地址的值,如果要取数组剩余标的值,就需要下面的操作.也就是将整个数组包含小标用大括号括起来,表示一个整体变量,用$读出
[]
[root@localhost ~]# echo $(A[])
bash: A[]: 未找到命令... [root@localhost ~]# echo ${A[]} #这里要注意一下,取数组值的时候,用到的是{}大括号 [root@localhost ~]# echo ${A[+]} [root@localhost ~]# B={ }
bash: : 未找到命令...
[root@localhost ~]# B=( ) #数组群体赋值的时候,用到的是()小括号。这点要注意
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${B[]}
正因为,shell数组没有个数的限制,也就是说,不需要在使用数组的时候,首先要固定一下数组的长度,所以,他的自由度很大,可以给某一下标无限,跳跃似的赋值
取出所有数组元素
用@符号来代替数组下标
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${A[@]}
bash shell
取得数组个数
${#A[@]}的格式来取得数组的小标
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${#A[@]}
如果数组某个下标表示的值为字符串,还可以取得该字符串的长度
${#A[索引]}
如上例中,A【3】的值是bash shell。我们要想知道他的长度可以采用如下
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${#A[]}
删除数组和删除变量函数都用的同一个命令。unset
如果要删除整个数组可以用 unset A
如果要删除数组中的某个赋值 unset A[3] 就会将bash shell 删除。我们来试一下
[root@localhost ~]# unset A[] #将第三个数组值删除
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${#A[]}
0 #数组长度变为0
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${A[]}
#值变为空
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${A[@]}
28 #打印所有变量的时候,也可以证明A[3]确实没有了
[root@localhost ~]# unset A #取消掉整个数组A
[root@localhost ~]# echo ${A[@]} #整个数组A确实取消掉了。没有数组元素了 [root@localhost ~]#
十 Here Document
bash 有一种特殊的程序区域。就是 Here Document,也可以用来设定变量。
语法为 命令 <<标记
[root@localhost ~]# wc -l << countline
> line1
> line2
> line3
> countline
Here Document也支持变量替换。在输入的内容中,如果有变量,bash会在转向前,将变量值进行替换
[root@localhost ~]# From="From: me@example.edu.cn" #四个变量
[root@localhost ~]# To="To: you@example.edu.cn"
[root@localhost ~]# Subject="Subject: Hello world"
[root@localhost ~]# Msg="happy new year"
[root@localhost ~]# EM="20090310.txt"
[root@localhost ~]# cat > $EM <<here #进行转向
> $From
> $To
> $Subject
>
> $Msg
> here
[root@localhost ~]# cat .txt
From: me@example.edu.cn
To: you@example.edu.cn
Subject: Hello world happy new year
利用Here Document做多行批注
bash中,只支持单行注释,#来开头
利用Here Document来做多行批注,可以用:来操作 : <<DO-NOTHING
第一行,第二行,第三行 DO-NOTHING
利用Here Document夹带私货
书中就有一个夹带私货的例子。他是用Here Document写了一个C程序,然后在编译执行他,以便达到不可告人的目的,看看他是咋写的
[root@localhost ShellScript]# vim create_prg.sh
#! /bin/bash echo "正在产生hello.c。。。。"
echo
cat <<'EOF' >hello.c
#include <stdio.h> int main()
{
printf("Hello world!\n");
return ;
}
EOF echo "编译hello.c........"
echo
#编译Hello.c,并产生执行文件
gcc -o hello hello.c #若编译成功,则运行
if [ $? -eq ]; then
echo "执行 hello....."
echo
./hello
else
echo '执行失败'
fi
"create_prg.sh" [新] 27L, 374C 已写入
[root@localhost ShellScript]# sh create_prg.sh
正在产生hello.c。。。。 编译hello.c........ 执行 hello..... Hello world!
[root@localhost ShellScript]# ls
.txt create_prg.sh hello hello.c 这样就可以动态编写c程序,动态执行。神不知鬼不觉。。。
五 shell 变量与字符串操作的更多相关文章
- shell变量(字符串)间的连接
shell变量(字符串)间的连接 对于变量或者字符串的连接,shell提供了相当简单的做法,比string的连接还要直接. 直接放到一起或用双引号即可. 例如$a, $b,有 c=$a$b c=$a& ...
- shell中的字符串操作和数学运算
字符串操作 变量赋值: 说明:变量值可以用单引号.双引号.或者不加任何引号来赋值给变量 变量名="变量值" 变量名='变量值' 变量名=变量值 例如:str="hel ...
- linux shell学习(字符串操作)--01
http://blog.csdn.net/shuanghujushi/article/details/51298672 在bash shell的使用过程中,经常会遇到一些字符串string的操作,下面 ...
- shell编程之字符串操作
shell中字符串操作主要有以下几种,其中:pattern ,old中可以使用通配符: ${#var} :返回字符串变量var的长度 ${var:m} :返回${var}中从第m+1个字符到最后的部分 ...
- shell中的字符串操作
SHELL字符串操作 bash Shell提供了多种字符串处理的命令: awk命令 expr命令 字符串长度 ${#..} expr length awk的length(s) 实例: string=& ...
- shell变量,字符串,数组
一.shell变量定义: 命名只能使用英文字母,数字和下划线,首个字符不能以数字开头: 中间不能有空格,可以使用下划线: 不能使用标点符号: 不能使用bash里的关键字. 变量使用: 使用一个定义过的 ...
- shell中的字符串操作——字符串的切割
default.yaml {default_baseurl: 'http://10.113.10.68:8082'} test.sh a=`cat default.yaml` t=":&qu ...
- awk字符串操作(字符串链接、传入传出shell变量)
1.awk基础 awk的环境变量及其意义 https://blog.csdn.net/snowpay/article/details/52451718 linux awk命令详解 https:// ...
- shell 编程 && bash 简介(shell 变量、shell操作环境、数据流重导向、管线命令、shell script)
如何学习一门编程语言 数据类型 运算符 关键字 1 认识BASH 这个shell linux是操作系统核心,用户通过shell与核心进行沟通,达到我们想要的目的.硬件.核心.用户之间的关系: 原理:所 ...
随机推荐
- Task6.神经网络基础
BP: 正向计算loss,反向传播梯度. 计算梯度时,从输出端开始,前一层的梯度等于activation' *(与之相连的后一层的神经元梯度乘上权重的和). import torch from tor ...
- Angular:实现组件间双向数据绑定
学过Angular的同学都知道,输入框通过[(ngModel)]实现双向数据绑定,那么父子组件间能不能实现双向数据绑定呢?答案是肯定的. Angular中,我们常常需要通过方括号[]和圆括号()实现组 ...
- Mac终端的Cocoapods创建自己的私有库和公有库
一,前言 为什么要用Cocopods 通常在开发的过程中,大多时候,我们会处理一类相同的操作,比如对于字符串String的邮箱验证,是否为空,手机号验证,或者一些UIView的动画操作,我们为了避免写 ...
- python cv2在验证码识别中的使用
使用函数cv2.imread(filepath,flags)读入一副图片 filepath:要读入图片的完整路径 flags:读入图片的标志 cv2.IMREAD_COLOR:默认参数,读入一副彩色图 ...
- What is httpcontext
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.web.httpcontext?view=netframework-4.8 Encapsulate ...
- POJ 1066 Treasure Hunt [想法题]
题目链接: http://poj.org/problem?id=1066 --------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- leetcode 190. 颠倒二进制位(c++)
颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位. 示例 1: 输入: 00000010100101000001111010011100输出: 00111001011110000010100101000000 ...
- Java常用工具——java包装类
一.包装类和基本数据类型 装箱:基本数据类型——包装类 拆箱:包装类——基本数据类型 package com.imooc.wrap; public class WrapTestOne { public ...
- 为什么从pycharm中打开的html文件会显示404?
问题如图: 解决办法: 某次发现运行导入的html文件的时候,打开浏览器会报404错误:而运行自己写的html文件则正常显示:最后发现这是pycharm缓存问题,只需重启pycharm清除缓存就ok啦 ...
- Drone 的插件 - Docker 插件
Drone 插件市场 Drone 插件文档 原文地址 - Docker 插件的手册 Docker 插件可以用于构建镜像及发布镜像到 Docker registry.下面的 pipeline 配置,就使 ...
