ViewStub 的使用
一、内容概述
举例说明ViewStub标签的使用
二、ViewStub类的文档说明及应用场举例
文档描述:
A ViewStub is an invisible, zero-sized View that can be used to lazily inflate layout resources at runtime. When a ViewStub is made visible, or when inflate() is invoked, the layout resource is inflated. The ViewStub then replaces itself in its parent with the inflated View or Views. Therefore, the ViewStub exists in the view hierarchy until setVisibility(int) or inflate() is invoked. The inflated View is added to the ViewStub's parent with the ViewStub's layout parameters. Similarly, you can define/override the inflate View's id by using the ViewStub's inflatedId property. For instance:
<ViewStub android:id="@+id/stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/subTree"
android:layout="@layout/mySubTree"
android:layout_width="120dip"
android:layout_height="40dip" />
The ViewStub thus defined can be found using the id "stub." After inflation of the layout resource "mySubTree," the ViewStub is removed from its parent. The View created by inflating the layout resource "mySubTree" can be found using the id "subTree," specified by the inflatedId property. The inflated View is finally assigned a width of 120dip and a height of 40dip. The preferred way to perform the inflation of the layout resource is the following:
ViewStub stub = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub);
View inflated = stub.inflate();
When inflate() is invoked, the ViewStub is replaced by the inflated View and the inflated View is returned. This lets applications get a reference to the inflated View without executing an extra findViewById().
上面的问题大致意思是:
ViewStub 是一种不可见且不占屏幕大小的View,它可以用于运行时延迟加载一个布局文件,当它的visibility被设置为View.visiable或者它的inflate方法被调用时
它所引用的布局文件就会被加载,接着ViewStub会用它加载的那个布局文件的View来替代自己。
在上面的例子中,我们可以用id为stub来findViewById,而当我们调用ViewStub.inflate()或者ViewStub.setVisiable(View.VISIABLE)时,那么它的将变成一个由mySubTree布局文件指定的View,而我们可以使用id为subTree去索引这个View。
应用举例:
如下是应用的布局框架,中间的那个FrameLayout正式我们当前Activity的布局,而上面就有一个ViewStub,具体它是系统用来干嘛呢,可以进一步查找。
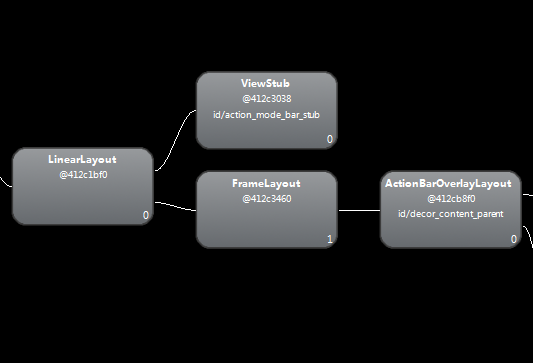
三、我的demo
1. 定义一个用ViewStub延迟加载的布局文件,这里简单定义如下(headbar.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button
android:id="@+id/back"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:text="back" >
</Button> <Button
android:id="@+id/go"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="go" >
</Button> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/go"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/back"
android:text="as you see" >
</TextView> </RelativeLayout>
2.mainActivity的布局文件(activity_main.xml)
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.stubview.MainActivity" > <ViewStub
android:id="@+id/hiddenHead"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inflatedId="@+id/headbar"
android:layout="@layout/headbar" >
</ViewStub> <Button
android:id="@+id/show"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="加载View" /> </RelativeLayout>
3.mainActivity中的使用ViewStub 代码
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
findViewById(R.id.show).setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
ViewStub stubView = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.hiddenHead);
View view = stubView.inflate();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"hiddenHead View 的id为" + view.getId(),
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
}
附代码参考https://github.com/LuLei2013/StubView.git
ViewStub 的使用的更多相关文章
- ViewStub的使用
ViewStub是一个不可见的.大小为0的控件,运行时ViewStub可以滞后加载.当ViewStub置为可见或者调用inflate()的时候,布局就会加载出来.用加载进来的布局取代ViewStub在 ...
- ViewStub源码分析
ViewStub是一种特殊的View,Android官方给出的解释是:一种不可见的(GONE).size是0的占位view,多用于运行时 延迟加载的,也就是说真正需要某个view的时候.在实际项目中, ...
- include、merge 、ViewStub
在布局优化中,Androi的官方提到了这三种布局<include />.<merge />.<ViewStub />,并介绍了这三种布局各有的优势,下面也是简单说一 ...
- Android实战技巧:ViewStub的应用
在开发应用程序的时候,经常会遇到这样的情况,会在运行时动态根据条件来决定显示哪个View或某个布局.那么最通常的想法就是把可能用到的View都写在上面,先把它们的可见性都设为View.GONE,然后在 ...
- ViewStub的简单用法和说明
最近无意间知道了ViewStub,所以特地的去了解了一下 都知道ViewStub是一个不可见的,大小为0的View,实际上跟include差不多,但是ViewStub要更加节约资源.被称为是" ...
- Android引导指示层的制作 (ViewStub + SharePreference)
引导指示界面是个什么鬼东西?一张图即明了:
- 【转】Android布局优化之ViewStub
ViewStub是Android布局优化中一个很不错的标签/控件,直接继承自View.虽然Android开发人员基本上都听说过,但是真正用的可能不多. ViewStub可以理解成一个非常轻量级的Vie ...
- Android性能优化之一:ViewStub
ViewStub是Android布局优化中一个很不错的标签/控件,直接继承自View.虽然Android开发人员基本上都听说过,但是真正用的可能不多. ViewStub可以理解成一个非常轻量级的Vie ...
- Android优化——UI优化(三)使用ViewStub延迟加载
使用ViewStub延迟加载 1.ViewStub延迟加载 ViewStub是一个不可见的,大小为0的View,最佳用途就是实现View的延迟加载,在需要的时候再加载View,可Java中常见的性能优 ...
- ViewStub的简单解析和使用场景
ViewStub是Android布局优化中一个很不错的标签/控件,直接继承自View.虽然Android开发人员基本上都听说过,但是真正用的可能不多. ViewStub可以理解成一个非常轻量级的Vie ...
随机推荐
- (18)python 打包发布
1.安装 pyinstaller pip install pyinstaller 2.创建文件 pyinstaller yourprogram.py 试了半天总是报 TypeError: expect ...
- 洛谷 P1068 分数线划定【结构体排序】
题目描述 世博会志愿者的选拔工作正在 A 市如火如荼的进行.为了选拔最合适的人才,A 市对 所有报名的选手进行了笔试,笔试分数达到面试分数线的选手方可进入面试.面试分数线根 据计划录取人数的150%划 ...
- HDU 1558 Segment set(并查集)
题意: 给你一些线段的起点和终点的坐标,最后问和某个线段相连的或者间接相连的线段有多少个(包括本身)? P X1 Y1X2 Y2 起点(X1,X2)终点(X2,Y2):按照出现次数依次编号为1,2, ...
- Express处理GET/POST请求(POST请求包含文件)
Express处理GET/POST请求(POST请求包含文件) GET 使用简洁的pug模板引擎,写一个表单,提交方法是GET 前端页面代码 enctype,默认是application/x-www- ...
- Spring中BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别
1. BeanFactory负责读取bean配置文档,管理bean的加载,实例化,维护bean之间的依赖关系,负责bean的生命周期. 2. ApplicationContext除了提供上述BeanF ...
- POJ 2482 Stars in Your Window(扫描线+线段树)
[题目链接] http://poj.org/problem?id=2482 [题目大意] 给出一些点的二维坐标和权值,求用一个长H,宽W的矩形能框住的最大权值之和, 在矩形边缘的点不计算在内 [题解] ...
- 【kruscal】【最小生成树】poj3522 Slim Span
求一个生成树,使得最大边权和最小边权之差最小.由于数据太小,暴力枚举下界,求出相应的上界.最后取min即可. #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm& ...
- Exercise02_03
import java.util.Scanner; public class Mi { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input = ...
- 【读书笔记】Elasticsearch集成Hadoop最佳实践
前言 本文记录[Elasticsearch集成Hadoop最佳实战]读书笔记 本书总计209页,共7章节,计划时间:20180712-20180717 (每天至少40页) 本文代码地址: https: ...
- spark DiskBlockManager
RDD本身presist可以是本地存储,本地存储级别的持久化实现方式如下: DiskBlockManager负责管理和维护block和磁盘存储的映射关系,通过blockId作为文件名称,然后如果是多个 ...
