Matplotlib绘图设置---文字和标签
文字和文字位置
通过plt.text()或ax.text()命令可在图形上添加文字。
Signature:
ax.text(x, y, s, fontdict=None, withdash=<deprecated parameter>, **kwargs)
Docstring:
Add text to the axes.
Add the text *s* to the axes at location *x*, *y* in data coordinates.
Parameters
----------
x, y : scalars
The position to place the text. By default, this is in data
coordinates. The coordinate system can be changed using the
*transform* parameter.
s : str
The text.
fontdict : dictionary, optional, default: None
A dictionary to override the default text properties. If fontdict
is None, the defaults are determined by your rc parameters.
withdash : boolean, optional, default: False
Creates a `~matplotlib.text.TextWithDash` instance instead of a
`~matplotlib.text.Text` instance.
Returns
-------
text : `.Text`
The created `.Text` instance.
Other Parameters
----------------
**kwargs : `~matplotlib.text.Text` properties.
Other miscellaneous text parameters.
Examples
--------
Individual keyword arguments can be used to override any given
parameter::
>>> text(x, y, s, fontsize=12)
The default transform specifies that text is in data coords,
alternatively, you can specify text in axis coords (0,0 is
lower-left and 1,1 is upper-right). The example below places
text in the center of the axes::
>>> text(0.5, 0.5, 'matplotlib', horizontalalignment='center',
... verticalalignment='center', transform=ax.transAxes)
You can put a rectangular box around the text instance (e.g., to
set a background color) by using the keyword `bbox`. `bbox` is
a dictionary of `~matplotlib.patches.Rectangle`
properties. For example::
>>> text(x, y, s, bbox=dict(facecolor='red', alpha=0.5))
text函数中transform参数用于设置坐标变换,Matplotlib一共有三种方式设置文字位置:
- ax.transData : 默认的,以数据为基准的坐标变换(x轴和y轴的标签作为数据坐标);
- ax.transAxes: 以坐标轴为基准的坐标变换(以坐标轴左下角原点,按坐标轴尺寸的比例呈现坐标);
- fig.transFigure:以图形为基准的坐标变换(以图纸左下角原点,按图形尺寸的比例呈现坐标)。
三个坐标系呈现的文字都是左对齐,当改变坐标轴上下限时,只有transData坐标会受影响,其它两个坐标系不变。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(facecolor='lightgray')
ax.axis([0, 10, 0, 10])
ax.text(1, 5, ".Data:(1, 5)", transform=ax.transData)
ax.text(0.5, 0.1, ".Axes:(0.5, 0.1)", transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(0.2, 0.2, ".Figure:(0.2, 0.2)", transform=fig.transFigure)
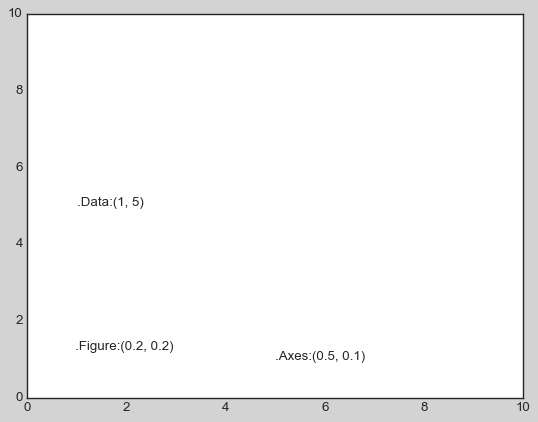
ax.set_xlim(0, 2)
ax.set_ylim(-6, 6)
fig

箭头和注释
Matplotlib中plt.annotate()/ax.annotate()函数可用于创建文字以及箭头等。
Signature:
ax.annotate(s, xy, *args, **kwargs)
Docstring:
Annotate the point *xy* with text *text*.
In the simplest form, the text is placed at *xy*.
Optionally, the text can be displayed in another position *xytext*.
An arrow pointing from the text to the annotated point *xy* can then
be added by defining *arrowprops*.
Parameters
----------
text : str
The text of the annotation. *s* is a deprecated synonym for this
parameter.
xy : (float, float)
The point *(x,y)* to annotate.
xytext : (float, float), optional
The position *(x,y)* to place the text at.
If *None*, defaults to *xy*.
xycoords : str, `.Artist`, `.Transform`, callable or tuple, optional
The coordinate system that *xy* is given in. The following types
of values are supported:
- One of the following strings:
================= =============================================
Value Description
================= =============================================
'figure points' Points from the lower left of the figure
'figure pixels' Pixels from the lower left of the figure
'figure fraction' Fraction of figure from lower left
'axes points' Points from lower left corner of axes
'axes pixels' Pixels from lower left corner of axes
'axes fraction' Fraction of axes from lower left
'data' Use the coordinate system of the object being
annotated (default)
'polar' *(theta,r)* if not native 'data' coordinates
================= =============================================
- An `.Artist`: *xy* is interpreted as a fraction of the artists
`~matplotlib.transforms.Bbox`. E.g. *(0, 0)* would be the lower
left corner of the bounding box and *(0.5, 1)* would be the
center top of the bounding box.
- A `.Transform` to transform *xy* to screen coordinates.
- A function with one of the following signatures::
def transform(renderer) -> Bbox
def transform(renderer) -> Transform
where *renderer* is a `.RendererBase` subclass.
The result of the function is interpreted like the `.Artist` and
`.Transform` cases above.
- A tuple *(xcoords, ycoords)* specifying separate coordinate
systems for *x* and *y*. *xcoords* and *ycoords* must each be
of one of the above described types.
See :ref:`plotting-guide-annotation` for more details.
Defaults to 'data'.
textcoords : str, `.Artist`, `.Transform`, callable or tuple, optional
The coordinate system that *xytext* is given in.
All *xycoords* values are valid as well as the following
strings:
================= =========================================
Value Description
================= =========================================
'offset points' Offset (in points) from the *xy* value
'offset pixels' Offset (in pixels) from the *xy* value
================= =========================================
Defaults to the value of *xycoords*, i.e. use the same coordinate
system for annotation point and text position.
arrowprops : dict, optional
The properties used to draw a
`~matplotlib.patches.FancyArrowPatch` arrow between the
positions *xy* and *xytext*.
If *arrowprops* does not contain the key 'arrowstyle' the
allowed keys are:
========== ======================================================
Key Description
========== ======================================================
width The width of the arrow in points
headwidth The width of the base of the arrow head in points
headlength The length of the arrow head in points
shrink Fraction of total length to shrink from both ends
? Any key to :class:`matplotlib.patches.FancyArrowPatch`
========== ======================================================
If *arrowprops* contains the key 'arrowstyle' the
above keys are forbidden. The allowed values of
``'arrowstyle'`` are:
============ =============================================
Name Attrs
============ =============================================
``'-'`` None
``'->'`` head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2
``'-['`` widthB=1.0,lengthB=0.2,angleB=None
``'|-|'`` widthA=1.0,widthB=1.0
``'-|>'`` head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2
``'<-'`` head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2
``'<->'`` head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2
``'<|-'`` head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2
``'<|-|>'`` head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2
``'fancy'`` head_length=0.4,head_width=0.4,tail_width=0.4
``'simple'`` head_length=0.5,head_width=0.5,tail_width=0.2
``'wedge'`` tail_width=0.3,shrink_factor=0.5
============ =============================================
Valid keys for `~matplotlib.patches.FancyArrowPatch` are:
=============== ==================================================
Key Description
=============== ==================================================
arrowstyle the arrow style
connectionstyle the connection style
relpos default is (0.5, 0.5)
patchA default is bounding box of the text
patchB default is None
shrinkA default is 2 points
shrinkB default is 2 points
mutation_scale default is text size (in points)
mutation_aspect default is 1.
? any key for :class:`matplotlib.patches.PathPatch`
=============== ==================================================
Defaults to None, i.e. no arrow is drawn.
annotation_clip : bool or None, optional
Whether to draw the annotation when the annotation point *xy* is
outside the axes area.
- If *True*, the annotation will only be drawn when *xy* is
within the axes.
- If *False*, the annotation will always be drawn.
- If *None*, the annotation will only be drawn when *xy* is
within the axes and *xycoords* is 'data'.
Defaults to *None*.
**kwargs
Additional kwargs are passed to `~matplotlib.text.Text`.
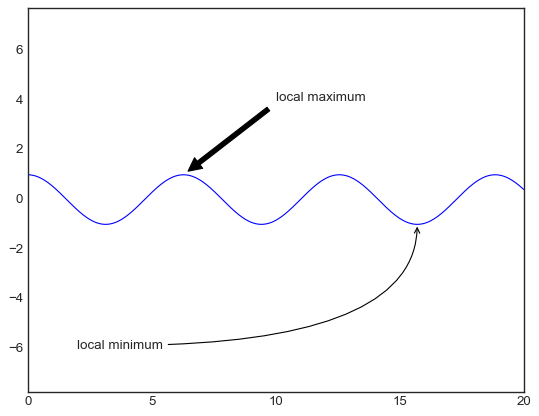
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 20, 1000)
ax.plot(x, np.cos(x))
ax.axis('equal')
#arrowprops用于设置箭头风格,xy设置箭头位置,xytext设置文字位置
ax.annotate('local maximum', xy=(6.28, 1), xytext=(10, 4),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))
ax.annotate('local minimum', xy=(5 * np.pi, -1), xytext=(2, -6),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->",connectionstyle="angle3,angleA=0,angleB=90"))
Matplotlib绘图设置---文字和标签的更多相关文章
- Python matplotlib绘图设置图例
一.语法简介 plt.legend(loc=2,edgecolor='red',facecolor='green',shadow='True',fontsize=10) #edgecolor 图例边框 ...
- 【划重点】Python matplotlib绘图设置坐标轴的刻度
一.语法简介 plt.xticks(ticks,labels,rotation=30,fontsize=10,color='red',fontweight='bold',backgroundcolor ...
- Python matplotlib绘图设置坐标轴的标题
一.语法简介 plt.xlabel("销售月份",fontsize=16,color='red',fontweight='bold',loc='center',background ...
- python绘图设置标题、标签,无法显示中文
先说解决办法:在程序开始之前,引入使用的模块之后,添加如下代码: plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unico ...
- matplotlib绘图教程,设置标签与图例
大家好,欢迎大家阅读周四数据处理专题,我们继续介绍matplotlib作图工具. 在上一篇文章当中我们介绍了matplotlib这个包当中颜色.标记和线条这三种画图的设置,今天我们同样也介绍三种新的设 ...
- Matplotlib绘图双纵坐标轴设置及控制设置时间格式
双y轴坐标轴图 今天利用matplotlib绘图,想要完成一个双坐标格式的图. fig=plt.figure(figsize=(20,15)) ax1=fig.add_subplot(111) ax1 ...
- matplotlib 绘图
http://blog.csdn.net/jkhere/article/details/9324823 都打一遍 5 matplotlib-绘制精美的图表 matplotlib 是python最著名的 ...
- matplotlib绘图的基本操作
转自:Laumians博客园 更简明易懂看Matplotlib Python 画图教程 (莫烦Python)_演讲•公开课_科技_bilibili_哔哩哔哩 https://www.bilibili. ...
- python中利用matplotlib绘图可视化知识归纳
python中利用matplotlib绘图可视化知识归纳: (1)matplotlib图标正常显示中文 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['fo ...
- matplotlib绘图基本用法-转自(http://blog.csdn.net/mao19931004/article/details/51915016)
本文转载自http://blog.csdn.net/mao19931004/article/details/51915016 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C ...
随机推荐
- 【Azure 微服务】面对Service Fabric中节点状态不正常(Disabling/Warning/RemoveNode)的几种尝试解决方案
问题描述 发现 Service Fabric 的节点状态异常,如出现 Disabling, Warning,或者 RemoveNode的情况,并且持续很长时间都没有变化(2小时以上).如何来缓解这种问 ...
- Vue3学习(二十一)- 文档管理页面布局修改
写在前面 按照国际惯例,要先聊下生活,吐槽一番,今天是2月14日,也是下午听老妈说,我才知道! 现在真的是对日期节日已经毫无概念可言,只知道星期几. 现在已经觉得写博客也好,学习文章也罢,和写日记一样 ...
- Java 关于继承小练习
1 package com.bytezero.inherit; 2 3 /* 4 * 面向对象的特征二:继承性 5 * 6 * 一.继承性的好处: 7 * ①减少了代码的冗余,提供了代码的复用性 8 ...
- Metasploitable3 渗透测试
1.信息手机阶段 信息收集经常使用的软件 功能也比较强大的Nmap Nmap nmap -p- -sS -sV -n -v --reason --open -oX demon.xml 192.168. ...
- vim技巧--提取文本与文本替换
前几天遇到一个使用情景,需要从一个包含各个读取代码文件路径及名字的文件中把文件路径提取出来,做一个filelist,这里用到了文本的提取和替换,这里做个小总结记录一下. 从网上找了一个作者写的代码用来 ...
- 关闭 nginx | taskkill /f /t /im nginx.exe
stop.bat taskkill /f /t /im nginx.exe pause
- A Representation Learning Framework for Property Graphs-KDD19
一.摘要 图上的表示学习,也称为图嵌入,已经证明了它对一系列机器学习应用程序的重大影响,如分类.预测和推荐. 然而,现有工作在很大程度上忽略了那些可以被表示为属性图的现代应用程序中的节点以及边的属性中 ...
- Linux int型转换为char*型几种方法总结
一 前记 这种转换,windows下最常用就是atoi()函数.可惜的是,在Linux中没有itoa()函数,只有atoi() 这点很有趣,居然不对称. 所以在Linux中实现从整型到char*的 ...
- 一次对requirements环境的配置
事情是这样的,我需要跑通一个代码,因此要配置环境,但是并不能利用requirements中给的指令直接配置,于是开始找一些其他的解决方法.作为一名小白,总是绕很多弯路. 记下一些蜿蜒. 首先,摘录re ...
- Android 设置任意View的背景为圆形或圆角
原文地址: Android 设置任意View的背景为圆形或圆角 - Stars-One的杂货小窝 我的需求主要还是在SurfaceView需要设置为圆形背景,在网上找了下,发现一个可行方法,做个记录 ...
