Kubernetes监控手册04-监控Kube-Proxy
简介
首先,请阅读文章《Kubernetes监控手册01-体系介绍》,回顾一下 Kubernetes 架构,Kube-Proxy 是在所有工作负载节点上的。
Kube-Proxy 默认暴露两个端口,10249用于暴露监控指标,在 /metrics 接口吐出 Prometheus 协议的监控数据:
[root@tt-fc-dev01.nj lib]# curl -s http://localhost:10249/metrics | head -n 10
# HELP apiserver_audit_event_total [ALPHA] Counter of audit events generated and sent to the audit backend.
# TYPE apiserver_audit_event_total counter
apiserver_audit_event_total 0
# HELP apiserver_audit_requests_rejected_total [ALPHA] Counter of apiserver requests rejected due to an error in audit logging backend.
# TYPE apiserver_audit_requests_rejected_total counter
apiserver_audit_requests_rejected_total 0
# HELP go_gc_duration_seconds A summary of the pause duration of garbage collection cycles.
# TYPE go_gc_duration_seconds summary
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0"} 2.5307e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.25"} 2.8884e-05
10256 端口作为健康检查的端口,使用 /healthz 接口做健康检查,请求之后返回两个时间信息:
[root@tt-fc-dev01.nj lib]# curl -s http://localhost:10256/healthz | jq .
{
"lastUpdated": "2022-11-09 13:14:35.621317865 +0800 CST m=+4802354.950616250",
"currentTime": "2022-11-09 13:14:35.621317865 +0800 CST m=+4802354.950616250"
}
所以,我们只要从 http://localhost:10249/metrics 采集监控数据即可。既然是 Prometheus 协议的数据,使用 Categraf 的 input.prometheus 来搞定即可。
Categraf prometheus 插件
配置文件在 conf/input.prometheus/prometheus.toml,把 Kube-Proxy 的地址配置进来即可:
interval = 15
[[instances]]
urls = [
"http://localhost:10249/metrics"
]
labels = { job="kube-proxy" }
urls 字段配置 endpoint 列表,即所有提供 metrics 数据的接口,我们使用下面的命令做个测试:
[work@tt-fc-dev01.nj categraf]$ ./categraf --test --inputs prometheus | grep kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules
2022/11/09 13:30:17 main.go:110: I! runner.binarydir: /home/work/go/src/categraf
2022/11/09 13:30:17 main.go:111: I! runner.hostname: tt-fc-dev01.nj
2022/11/09 13:30:17 main.go:112: I! runner.fd_limits: (soft=655360, hard=655360)
2022/11/09 13:30:17 main.go:113: I! runner.vm_limits: (soft=unlimited, hard=unlimited)
2022/11/09 13:30:17 config.go:33: I! tracing disabled
2022/11/09 13:30:17 provider.go:63: I! use input provider: [local]
2022/11/09 13:30:17 agent.go:87: I! agent starting
2022/11/09 13:30:17 metrics_agent.go:93: I! input: local.prometheus started
2022/11/09 13:30:17 prometheus_scrape.go:14: I! prometheus scraping disabled!
2022/11/09 13:30:17 agent.go:98: I! agent started
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_endpoint_changes_pending agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_count agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 319786
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_sum agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 17652.749911909214
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=+Inf 319786
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.001 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.002 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.004 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.008 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.016 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.032 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.064 274815
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.128 316616
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.256 319525
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=0.512 319776
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=1.024 319784
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=2.048 319784
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=4.096 319784
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=8.192 319784
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds_bucket agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics le=16.384 319786
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_service_changes_pending agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_last_queued_timestamp_seconds agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 1.6668536394083393e+09
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_iptables_restore_failures_total agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 0
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_endpoint_changes_total agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 219139
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_last_timestamp_seconds agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 1.6679718066295934e+09
13:30:17 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_service_changes_total agent_hostname=tt-fc-dev01.nj instance=http://localhost:10249/metrics 512372
Kube-Proxy 在 Kubernetes 架构中,负责从 APIServer 同步规则,然后修改 iptables 或 ipvs 配置,同步规则相关的指标就非常关键了,这里我就 grep 了这些指标作为样例。
通过 --test 看到输出了,就说明正常采集到数据了,你有几个工作负载节点,就分别去修改 Categraf 的配置即可。当然,这样做非常直观,只是略麻烦,如果未来扩容新的 Node 节点,也要去修改 Categraf 的采集配置,把 Kube-Proxy 这个 /metrics 地址给加上,如果你是用脚本批量跑的,倒是还可以,如果是手工部署就略麻烦。我们可以把 Categraf 采集器做成 Daemonset,这样就不用担心扩容的问题了,Daemonset 会被自动调度到所有 Node 节点。
Categraf 作为 Daemonset 部署
Categraf 作为 Daemonset 运行,首先要创建一个 namespace,然后相关的 ConfigMap、Daemonset 等都归属这个 namespace。只是监控 Kube-Proxy 的话,Categraf 的配置就只需要主配置 config.toml 和 prometheus.toml,下面我们就实操演示一下。
创建 namespace
[work@tt-fc-dev01.nj categraf]$ kubectl create namespace flashcat
namespace/flashcat created
[work@tt-fc-dev01.nj categraf]$ kubectl get ns | grep flashcat
flashcat Active 29s
创建 ConfigMap
ConfigMap 是用于放置 config.toml 和 prometheus.toml 的内容,我把 yaml 文件也给你准备好了,请保存为 categraf-configmap-v1.yaml
---
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: categraf-config
apiVersion: v1
data:
config.toml: |
[global]
hostname = "$HOSTNAME"
interval = 15
providers = ["local"]
[writer_opt]
batch = 2000
chan_size = 10000
[[writers]]
url = "http://10.206.0.16:19000/prometheus/v1/write"
timeout = 5000
dial_timeout = 2500
max_idle_conns_per_host = 100
---
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: categraf-input-prometheus
apiVersion: v1
data:
prometheus.toml: |
[[instances]]
urls = ["http://127.0.0.1:10249/metrics"]
labels = { job="kube-proxy" }
上面的 10.206.0.16:19000 只是举个例子,请改成你自己的 n9e-server 的地址。当然,如果不想把监控数据推给 Nightingale 也OK,写成其他的时序库(支持 remote write 协议的接口)也可以。hostname = "$HOSTNAME" 这个配置用了 $ 符号,后面创建 Daemonset 的时候会把 HOSTNAME 这个环境变量注入,让 Categraf 自动拿到。
下面我们把 ConfigMap 创建出来:
[work@tt-fc-dev01.nj yamls]$ kubectl apply -f categraf-configmap-v1.yaml -n flashcat
configmap/categraf-config created
configmap/categraf-input-prometheus created
[work@tt-fc-dev01.nj yamls]$ kubectl get configmap -n flashcat
NAME DATA AGE
categraf-config 1 19s
categraf-input-prometheus 1 19s
kube-root-ca.crt 1 22m
创建 Daemonset
配置文件准备好了,开始创建 Daemonset,注意把 HOSTNAME 环境变量注入进去,yaml 文件如下,你可以保存为 categraf-daemonset-v1.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
labels:
app: categraf-daemonset
name: categraf-daemonset
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: categraf-daemonset
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: categraf-daemonset
spec:
containers:
- env:
- name: TZ
value: Asia/Shanghai
- name: HOSTNAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: HOSTIP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.hostIP
image: flashcatcloud/categraf:v0.2.18
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: categraf
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/categraf/conf
name: categraf-config
- mountPath: /etc/categraf/conf/input.prometheus
name: categraf-input-prometheus
hostNetwork: true
restartPolicy: Always
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
volumes:
- configMap:
name: categraf-config
name: categraf-config
- configMap:
name: categraf-input-prometheus
name: categraf-input-prometheus
apply 一下这个 Daemonset 文件:
[work@tt-fc-dev01.nj yamls]$ kubectl apply -f categraf-daemonset-v1.yaml -n flashcat
daemonset.apps/categraf-daemonset created
[work@tt-fc-dev01.nj yamls]$ kubectl get ds -o wide -n flashcat
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
categraf-daemonset 6 6 6 6 6 <none> 2m20s categraf flashcatcloud/categraf:v0.2.17 app=categraf-daemonset
[work@tt-fc-dev01.nj yamls]$ kubectl get pods -o wide -n flashcat
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
categraf-daemonset-4qlt9 1/1 Running 0 2m10s 10.206.0.7 10.206.0.7 <none> <none>
categraf-daemonset-s9bk2 1/1 Running 0 2m10s 10.206.0.11 10.206.0.11 <none> <none>
categraf-daemonset-w77lt 1/1 Running 0 2m10s 10.206.16.3 10.206.16.3 <none> <none>
categraf-daemonset-xgwf5 1/1 Running 0 2m10s 10.206.0.16 10.206.0.16 <none> <none>
categraf-daemonset-z9rk5 1/1 Running 0 2m10s 10.206.16.8 10.206.16.8 <none> <none>
categraf-daemonset-zdp8v 1/1 Running 0 2m10s 10.206.0.17 10.206.0.17 <none> <none>
看起来一切正常,我们去 Nightingale 查一下相关监控指标,看看有了没有:
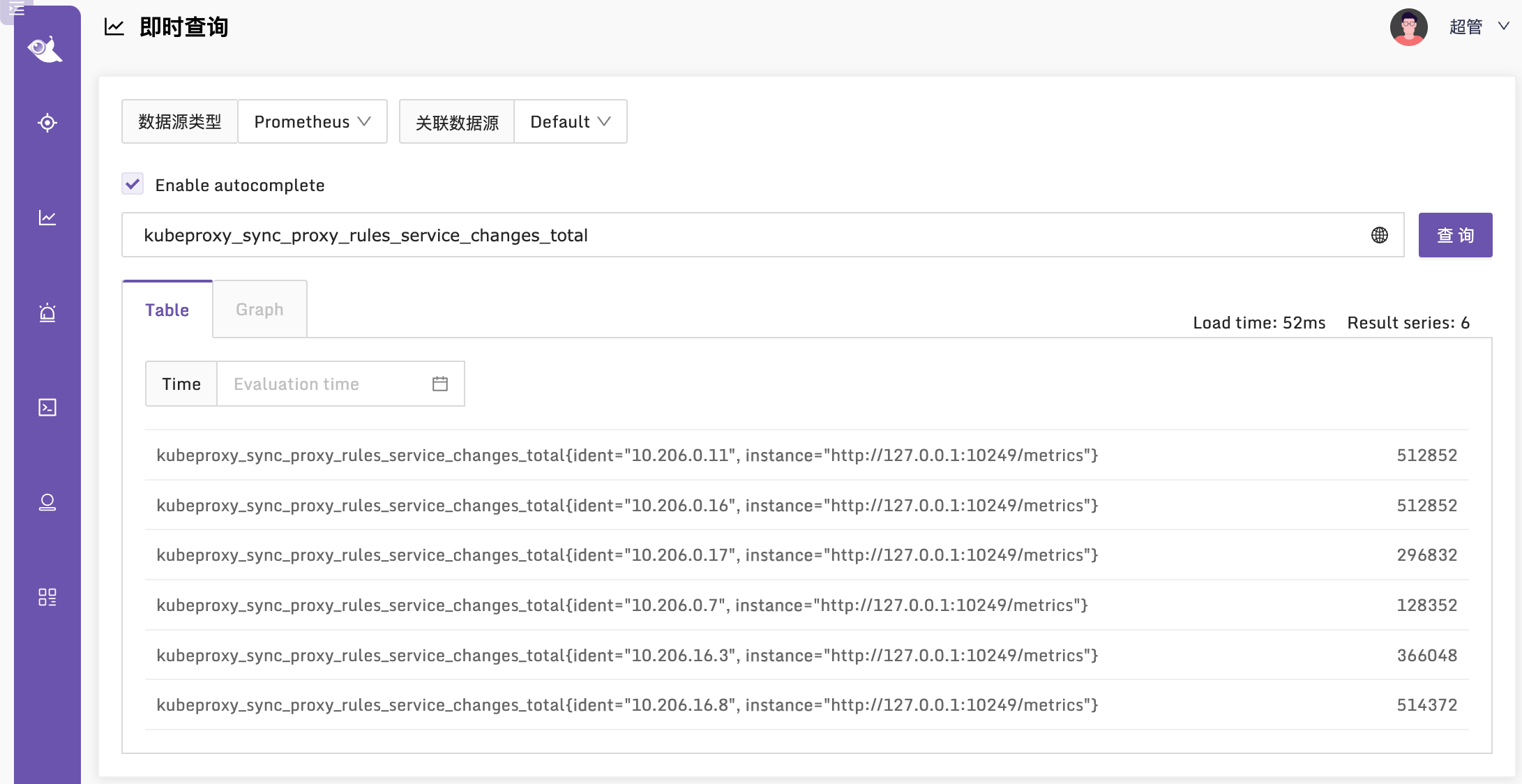
监控指标说明
Kube-Proxy 的指标,孔飞老师之前整理过,我也给挪到这个章节,供大家参考:
# HELP go_gc_duration_seconds A summary of the pause duration of garbage collection cycles.
# TYPE go_gc_duration_seconds summary
gc时间
# HELP go_goroutines Number of goroutines that currently exist.
# TYPE go_goroutines gauge
goroutine数量
# HELP go_threads Number of OS threads created.
# TYPE go_threads gauge
线程数量
# HELP kubeproxy_network_programming_duration_seconds [ALPHA] In Cluster Network Programming Latency in seconds
# TYPE kubeproxy_network_programming_duration_seconds histogram
service或者pod发生变化到kube-proxy规则同步完成时间指标含义较复杂,参照https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/sig-scalability/slos/network_programming_latency.md
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds [ALPHA] SyncProxyRules latency in seconds
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_duration_seconds histogram
规则同步耗时
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_endpoint_changes_pending [ALPHA] Pending proxy rules Endpoint changes
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_endpoint_changes_pending gauge
endpoint 发生变化后规则同步pending的次数
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_endpoint_changes_total [ALPHA] Cumulative proxy rules Endpoint changes
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_endpoint_changes_total counter
endpoint 发生变化后规则同步的总次数
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_iptables_restore_failures_total [ALPHA] Cumulative proxy iptables restore failures
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_iptables_restore_failures_total counter
本机上 iptables restore 失败的总次数
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_last_queued_timestamp_seconds [ALPHA] The last time a sync of proxy rules was queued
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_last_queued_timestamp_seconds gauge
最近一次规则同步的请求时间戳,如果比下一个指标 kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_last_timestamp_seconds 大很多,那说明同步 hung 住了
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_last_timestamp_seconds [ALPHA] The last time proxy rules were successfully synced
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_last_timestamp_seconds gauge
最近一次规则同步的完成时间戳
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_service_changes_pending [ALPHA] Pending proxy rules Service changes
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_service_changes_pending gauge
service变化引起的规则同步pending数量
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_service_changes_total [ALPHA] Cumulative proxy rules Service changes
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_service_changes_total counter
service变化引起的规则同步总数
# HELP process_cpu_seconds_total Total user and system CPU time spent in seconds.
# TYPE process_cpu_seconds_total counter
利用这个指标统计cpu使用率
# HELP process_max_fds Maximum number of open file descriptors.
# TYPE process_max_fds gauge
进程可以打开的最大fd数
# HELP process_open_fds Number of open file descriptors.
# TYPE process_open_fds gauge
进程当前打开的fd数
# HELP process_resident_memory_bytes Resident memory size in bytes.
# TYPE process_resident_memory_bytes gauge
统计内存使用大小
# HELP process_start_time_seconds Start time of the process since unix epoch in seconds.
# TYPE process_start_time_seconds gauge
进程启动时间戳
# HELP rest_client_request_duration_seconds [ALPHA] Request latency in seconds. Broken down by verb and URL.
# TYPE rest_client_request_duration_seconds histogram
请求 apiserver 的耗时(按照url和verb统计)
# HELP rest_client_requests_total [ALPHA] Number of HTTP requests, partitioned by status code, method, and host.
# TYPE rest_client_requests_total counter
请求 apiserver 的总数(按照code method host统计)
导入监控大盘
由于上面给出的监控方案是通过 Daemonset,所以各个 Kube-Proxy 的监控数据,是通过 ident 标签来区分的,并非是通过 instance 标签来区分,从 Grafana 官网找到一个分享,地址在 这里,改造之后的大盘在 这里 导入夜莺即可使用。
相关文章
关于作者
本文作者秦晓辉,快猫星云合伙人,文章内容是快猫技术团队共同沉淀的结晶,作者做了编辑整理,我们会持续输出监控、稳定性保障相关的技术文章,文章可转载,转载请注明出处,尊重技术人员的成果。
Kubernetes监控手册04-监控Kube-Proxy的更多相关文章
- Kubernetes监控手册-01体系概述
Kubernetes 监控体系驳杂,涉及到的内容非常多,总是感觉摸不到头绪,网上虽然有很多资料,都略显凌乱,没有一个体系化的讲解,今天开始,我们准备撰写一系列文章,把 Kubernetes 监控说透, ...
- 高可用Kubernetes集群-14. 部署Kubernetes集群性能监控平台
参考文档: Github介绍:https://github.com/kubernetes/heapster Github yaml文件: https://github.com/kubernetes/h ...
- (转)实验文档4:kubernetes集群的监控和日志分析
改造dubbo-demo-web项目为Tomcat启动项目 Tomcat官网 准备Tomcat的镜像底包 准备tomcat二进制包 运维主机HDSS7-200.host.com上:Tomcat8下载链 ...
- Kubernetes集群的监控报警策略最佳实践
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/M2l0ZgSsVc7r69eFdTj/article/details/79652064 本文为Kub ...
- Prometheus 监控K8S Node监控
Prometheus 监控K8S Node监控 Prometheus社区提供的NodeExporter项目可以对主机的关键度量指标进行监控,通过Kubernetes的DeamonSet可以在各个主机节 ...
- 【干货】解密监控宝Docker监控实现原理
分享人高驰涛(Neeke),云智慧高级架构师,PHP 开发组成员,同时也是 PECL/SeasLog 的作者.8 年研发管理经验,早期从事大规模企业信息化研发架构,09 年涉足互联网数字营销领域并深入 ...
- nagios监控linux主机监控内存脚本
说明 工作包括两部分监控端(一二三)和被监控端(四) 一.nrpe.cfg中添加脚本 nrpe.cfg中添加命令索引 command[check_used_mem]=/usr/local/nagios ...
- 探索Windows Azure 监控和自动伸缩系列2 - 获取虚拟机的监控定义和监控数据
上一篇博文介绍了如何连接Windows Azure: http://www.cnblogs.com/teld/p/5113063.html 本篇我们继续上次的示例代码,获取虚拟机的监控定义和监控数据. ...
- 指导手册04:运行MapReduce
指导手册04:运行MapReduce Part 1:运行单个MapReduce任务 情景描述: 本次任务要求对HDFS目录中的数据文件/user/root/email_log.txt进行计算处理, ...
- [博客迁移]探索Windows Azure 监控和自动伸缩系列2 - 获取虚拟机的监控定义和监控数据
上一篇博文介绍了如何连接Windows Azure: http://www.cnblogs.com/teld/p/5113063.html 本篇我们继续上次的示例代码,获取虚拟机的监控定义和监控数据. ...
随机推荐
- 力扣319(java)-灯泡开关(中等)
题目: 初始时有 n 个灯泡处于关闭状态.第一轮,你将会打开所有灯泡.接下来的第二轮,你将会每两个灯泡关闭第二个. 第三轮,你每三个灯泡就切换第三个灯泡的开关(即,打开变关闭,关闭变打开).第 i 轮 ...
- 如何将传统 Web 框架迁移部署到 Serverless 架构?
简介: 与其说 Serverless 架构是一个新的概念,不如说它是一种全新的思路,一种新的编程范式. 与其说 Serverless 架构是一个新的概念,不如说它是一种全新的思路,一种新的编程范式. ...
- 宜搭小技巧|维护Excel太麻烦?Excel一键转应用,为你的工作减负!
简介:只需6步,轻松学会「Excel一键创建应用」! 在钉钉的聊天窗口中,每天都会流转数量巨大的Excel表格,用于信息收集和数据统计,但有时这些表格并不能很好地帮助到我们的工作,相反还会带来许多不 ...
- Scheduled SQL: SLS 大规模日志上的全局分析与调度
简介: 本文总结了大规模日志全局分析的需求,讨论SLS上现有的典型分析方案,并延伸到 SLS 原生数据处理方案,介绍 Schedueld SQL 功能与最佳实践. 大规模日志全局分析的需求 数据大规模 ...
- 浅谈 Linux 高负载的系统化分析
简介: 浅谈 Linux 高负载的系统化分析,阿里云系统组工程师杨勇通过对线上各种问题的系统化分析. 讲解 Linux Load 高如何排查的话题属于老生常谈了,但多数文章只是聚焦了几个点,缺少整体 ...
- [Go] gorm 返回指定模型数据的处理方式
重新 var 声明一个变量,类型为包含指定字段的结构体. 查询的时候,还是使用原始模型类型的变量. example: // For return data var retMember struct { ...
- dotnet 6 命令行 cmd 设置输出英文解决中文乱码
我遇到在部署 CI 服务器,执行 cmd 命令构建,输出的中文是乱码.我期望让 dotnet 命令行输出使用英文解决乱码问题.通过设置 dotnet 命令行的语言文化,即可解决此问题 给 dotnet ...
- Git——分支管理(2)
Git--分支管理(2) 提示:图床在国外且动图比较多的情况下,需要时间加载. 目录: 目录 Git--分支管理(2) 提示:图床在国外且动图比较多的情况下,需要时间加载. 目录: Git基础 Git ...
- docker 权限问题 Got permission denied while trying to connect to the Docker daemon socket at 。。。
非root用户运行docker命令报如下错误 说明没有权限 haima@haima-PC:/usr/local/docker/docker_compose_efk$ docker ps -a Got ...
- gin+grom 求当天的数据列表 0点到24点
框架go-admin gin+gorm mysql表 CREATE TABLE `sq_user_ticket` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT C ...
