Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) E. Anton and Permutation(树状数组套主席树 求出指定数的排名)
4 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Anton likes permutations, especially he likes to permute their elements. Note that a permutation of n elements is a sequence of numbers {a1, a2, ..., an}, in which every number from 1 to n appears exactly once.
One day Anton got a new permutation and started to play with it. He does the following operation q times: he takes two elements of the permutation and swaps these elements. After each operation he asks his friend Vanya, how many inversions there are in the new permutation. The number of inversions in a permutation is the number of distinct pairs (i, j) such that 1 ≤ i < j ≤ n and ai > aj.
Vanya is tired of answering Anton's silly questions. So he asked you to write a program that would answer these questions instead of him.
Initially Anton's permutation was {1, 2, ..., n}, that is ai = i for all i such that 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and q (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ q ≤ 50 000) — the length of the permutation and the number of operations that Anton does.
Each of the following q lines of the input contains two integers li and ri (1 ≤ li, ri ≤ n) — the indices of elements that Anton swaps during the i-th operation. Note that indices of elements that Anton swaps during the i-th operation can coincide. Elements in the permutation are numbered starting with one.
Output q lines. The i-th line of the output is the number of inversions in the Anton's permutation after the i-th operation.
5 4
4 5
2 4
2 5
2 2
1
4
3
3
2 1
2 1
1
6 7
1 4
3 5
2 3
3 3
3 6
2 1
5 1
5
6
7
7
10
11
8
Consider the first sample.
After the first Anton's operation the permutation will be {1, 2, 3, 5, 4}. There is only one inversion in it: (4, 5).
After the second Anton's operation the permutation will be {1, 5, 3, 2, 4}. There are four inversions: (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5) and (3, 4).
After the third Anton's operation the permutation will be {1, 4, 3, 2, 5}. There are three inversions: (2, 3), (2, 4) and (3, 4).
After the fourth Anton's operation the permutation doesn't change, so there are still three inversions.
【分析】题意很简单,就是动态的求区间逆序数。当时没做出来,赛后看了题解,学了发树状数组套主席树(内层主席树外层树状数组)学了一上午=_=借这个题好好说一下我对这个的理解吧,有啥不对的希望大佬能指出来OTZ.
主席树套树状数组就是梳妆数组的每一个节点都是一颗主席树,可以理解为线段树吧。主席树可以静态的求出排名,而动态的可以借助树状数组求,logn。而对于每一棵主席树,从i~n一棵一棵的建,可以这么理解,其实每一棵树都是一样的,包括所有的节点,只是有些节点隐藏起来了,只显现了一部分,显现了哪些部分呢?这就要考虑到树状数组了。树状数组的每一个节点,都与一个lowbit有关,刷过树状数组的应该知道,见下图
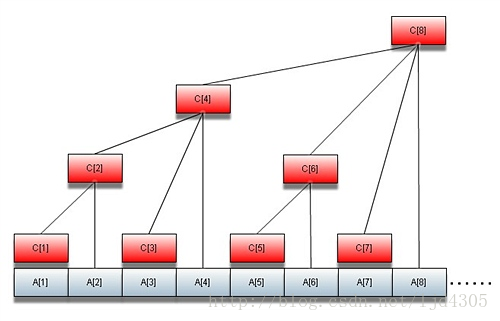
比如说对于4节点,(对于这个题目)初始就只显现了1~4区间的值。而对于6节点就之显现了5~6节点,注意,我这里说的是初始阶段。好嘞,现在来说修改。比如说我要把num[2]和num[6]换一下,那我们就把第二个节点的num[6]点亮(即显现),怎么点亮了?注意,我们一开始是按照从小到大的顺序存的,即每一刻主席树的叶子节点(包括未显现的)从左到右-->从小到大,那么就可以在lson,rson里找了,复杂度logn。找到之后就点亮,sz[]++.然后往上lowbit,将所有与之相关的节点的主席树相关位置都做同样的修改,复杂度logn。现在说查询,树状数组的查询会吧,就是lowbit求前缀和嘛,这个也一样,从上往下求lowbit前缀。对于每一刻主席树,先找到这个值,然后这个值(叶子节点)左边的叶子节点个数即是这棵书中比他小的,然后把所有相关的lowbit节点的线段树(不重合)的所有比他小的值得个数加起来,logn*logn。
嗯。。。这差不多就是我的理解了,要是有啥不对的,请大佬一定要指出来呀,嘻嘻。。。
听说还有一种叫 分块 的东西比这个简单,明天就学,学会了再写个做法,嘻嘻。。。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define met(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof a)
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 2e7+;
int sz[N],lson[N],rson[N],num[N],bit[N],n,total;
int addson() {return ++total;}
int lowbit(int x) {return x&(-x);}
void add(int &x,int l,int r,int y,int z){
if (!x)x=addson();
sz[x]+=z;
if (l==r) return;
int mid=(l+r)>>;
if (y<=mid) add(lson[x],l,mid,y,z);
else add(rson[x],mid+,r,y,z);
}
int ask(int x,int l,int r,int y){
if (!x) return ;
if (l==r) return sz[x];
int mid=(l+r)>>;
if (y<=mid) return ask(lson[x],l,mid,y);
else return sz[lson[x]]+ask(rson[x],mid+,r,y);
}
ll bigask(int x,int y){
ll now=;
while (x) {
now+=ask(bit[x],,n,y);
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return now;
}
void bigadd(int x,int y,int z){
while (x<=n) {
add(bit[x],,n,y,z);
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int main(){
int m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
ll sum=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)bigadd(i,num[i]=i,);
while (m--) {
int l,r;
scanf("%d %d",&l,&r);
if (l==r) {
printf("%lld\n",sum);
continue;
}
if (l>r)swap(l,r);
if (r-l>) {
sum-=*(bigask(r-,num[l])-bigask(l,num[l]));
sum+=*(bigask(r-,num[r])-bigask(l,num[r]));
}
if (num[l]<num[r]) ++sum;
else --sum;
printf("%lld\n",sum);
bigadd(l,num[l],-);
bigadd(l,num[r],);
bigadd(r,num[r],-);
bigadd(r,num[l],);
swap(num[l],num[r]);
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) E. Anton and Permutation(树状数组套主席树 求出指定数的排名)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) D. Anton and School - 2 数学
D. Anton and School - 2 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/785/problem/D Description As you probabl ...
- Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) C. Anton and Fairy Tale 二分
C. Anton and Fairy Tale 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/785/problem/C Description Anton likes to ...
- Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) B. Anton and Classes 水题
B. Anton and Classes 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/785/problem/B Description Anton likes to pl ...
- Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) A - Anton and Polyhedrons 水题
A - Anton and Polyhedrons 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/785/problem/A Description Anton's favo ...
- 【组合数】【乘法逆元】 Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) D. Anton and School - 2
http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/50996 官方题解讲得很明白,在这里我复述一下. 枚举每个左括号,考虑计算一定包含其的简单括号序列的个数,只考虑其及其左侧的左括号, ...
- Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) D. Anton and School - 2
题目链接 转自 给你一个字符串问你能构造多少RSBS. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long #define fi first #def ...
- 【二分】Codeforces Round #404 (Div. 2) C. Anton and Fairy Tale
当m>=n时,显然答案是n: 若m<n,在第m天之后,每天粮仓减少的量会形成等差数列,只需要二分到底在第几天,粮仓第一次下降到0即可. 若直接解不等式,可能会有误差,需要在答案旁边扫一下. ...
- Codeforces 605D - Board Game(树状数组套 set)
Codeforces 题目传送门 & 洛谷题目传送门 事实上是一道非常容易的题 很容易想到如果 \(c_i\geq a_j\) 且 \(d_i\geq b_j\) 就连一条 \(i\to j\ ...
- 贪心 Codeforces Round #288 (Div. 2) B. Anton and currency you all know
题目传送门 /* 题意:从前面找一个数字和末尾数字调换使得变成偶数且为最大 贪心:考虑两种情况:1. 有偶数且比末尾数字大(flag标记):2. 有偶数但都比末尾数字小(x位置标记) 仿照别人写的,再 ...
随机推荐
- [Leetcode] scramble string 乱串
Given a string s1, we may represent it as a binary tree by partitioning it to two non-empty substrin ...
- 【BZOJ 4514】[Sdoi2016]数字配对 费用流
利用spfa流的性质,我直接拆两半,正解分奇偶(妙),而且判断是否整除且质数我用的是暴力根号,整洁判断质数个数差一(其他非spfa流怎么做?) #include <cstdio> #inc ...
- ubuntu12.04 Qt WebKit编译
转载自:http://my.oschina.net/u/257674/blog/167050 官方文档: http://trac.webkit.org/wiki/BuildingQtOnLinux#D ...
- MySQL 8.0.11 中使用 grant ... identified by 时 error 1064 near 'identified by '密码'' at line 1
(1)问题: 当使用 grant 权限列表 on 数据库 to '用户名'@'访问主机' identified by '密码'; 时会出现"......near 'identifie ...
- threadlocal作用
理解:通过thread创建局部变量,每个线程可以获得该变量的副本,再每个线程中操作该副本相互之间不产生影响. 解决:数据库连接 常规一个线程连接一个数据库是没有问题的,但是在高并发的情况下,可能线程一 ...
- 【CF24D】Broken Robot (DP+高斯消元)
题目链接 题意:给定一个\(n\times m\)的矩阵,每次可以向→↓←移动一格,也可以原地不动,求从\((x,y)\)到最后一行的期望步数. 此题标签\(DP\) 看到上面这个肯定会想到 方法一: ...
- thinkphp 随机获取一条数据
$data=$AD->field("ID,Answer,State")->limit(1)->order('rand()')->select();
- 解决cursor未关闭造成的死锁
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zc474235918/article/details/72731363/ https://blog.csdn.net/zmx729618/artic ...
- HDU1385 (Floyd记录路径)
Minimum Transport Cost Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/O ...
- ReadOnly与Enabled
txtDlrCode.ReadOnly = true; 1.当设置为只读,文本框有点击事件,点击该文本框还是可以响应点击事件 2.设置为只读,C#后台无法取得文本框的值,txtDlrCode.Text ...
