Scrapy持久化存储
基于终端指令的持久化存储
保证爬虫文件的parse方法中有可迭代类型对象(通常为列表or字典)的返回,该返回值可以通过终端指令的形式写入指定格式的文件中进行持久化操作;
执行输出指定格式进行存储:将爬取到的数据写入不同格式的文件中进行存储
scrapy crawl 爬虫名称 -o xxx.json
scrapy crawl 爬虫名称 -o xxx.xml
scrapy crawl 爬虫名称 -o xxx.csv
基于管道的持久化存储
scrapy框架中已经为我们专门集成好了高效、便捷的持久化操作功能,我们直接使用即可:
items.py : 数据结构模板文件,定义数据属性;
pipelines.py : 管道文件,接受item类型的数据,进行持久化操作;
持久化流程:
- 在爬虫文件中获取到数据后,将数据封装到 items对象中;
- 通过 yield 关键字将items对象提交给pipelines管道进行持久化操作;
- 在管道文件中的process_item方法中接收爬虫文件提交过来的item对象,然后编写持久化存储的代码将item对象存储的数据进行持久化存储;
settings.py文件中开启管道:
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'qiubaiPro.pipelines.QiubaiproPipelineByRedis': 300,
}
终端持久化存储示例:
将糗事百科首页中的段子和作者数据爬取下来,然后进行持久化存储
爬虫程序
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy class QiubaiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'qiubai'
# allowed_domains = ['www.qiushibaike.com']
start_urls = ['https://www.qiushibaike.com/text/'] def parse(self, response):
div_list = response.xpath('//div[@id="content-left"]/div')
all_data = []
# xpath返回的列表元素类型为Selector类型
for div in div_list:
# title = div.xpath('./div[1]/a[2]/h2/text() | ./div[1]/span[2]/h2/text()')[0].extract()
author = div.xpath('./div[1]/a[2]/h2/text() | ./div[1]/span[2]/h2/text()').extract_first()
content = div.xpath('./a[1]/div/span/text()').extract_first() dic = {
'author': author,
'content': content
} all_data.append(dic)
# 基于终端指令的持久化存储:可以通过终端指令的形式将parse方法的返回值中存储的数据进行本地磁盘的持久化存储
return all_data
settings
BOT_NAME = 'qiubaiPro'
USER_AGENT = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/68.0.3440.106 Safari/537.36'
SPIDER_MODULES = ['qiubaiPro.spiders']
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'qiubaiPro.spiders'
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False
执行:
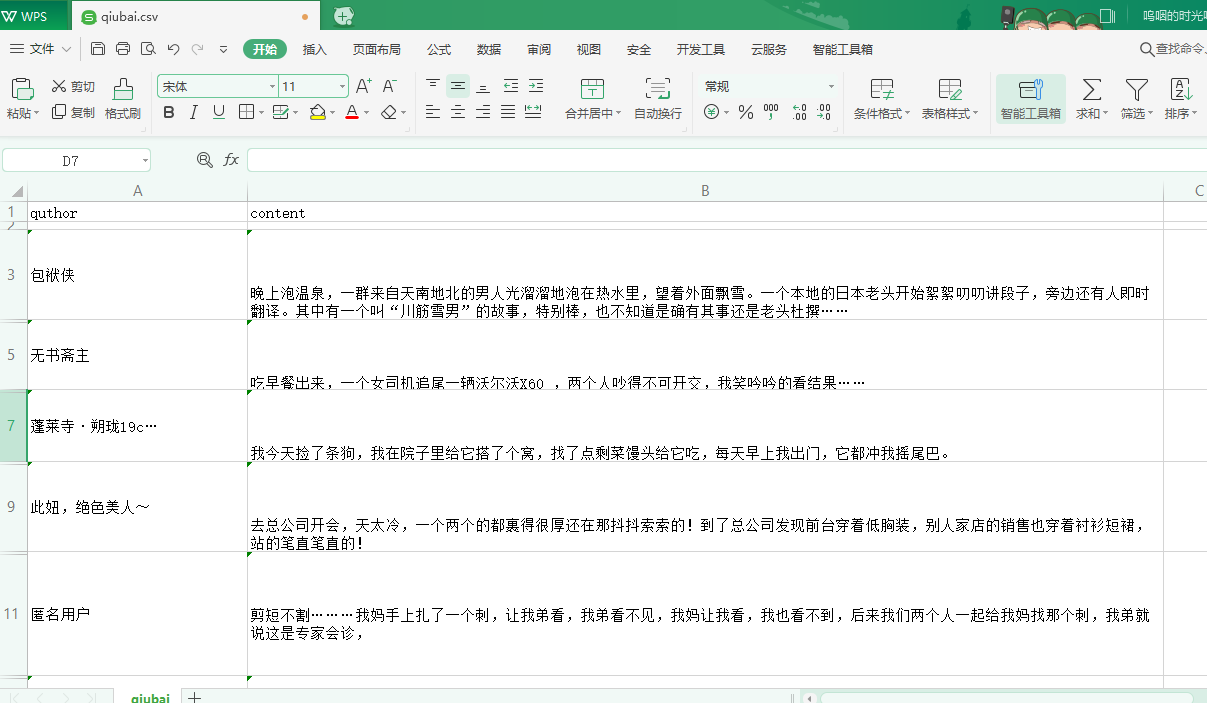
scrapy crawl qiubai -o qiubai.csv

执行完之后的结果:
管道持久化存储示例:
爬取Boss直聘网中Python爬虫岗位的职位名称,薪资,公司名称
爬虫程序
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
from bossPro.items import BossproItem class BossSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'boss'
allowed_domains = ['www.xxx.com']
start_urls = ['https://www.zhipin.com/job_detail/?query=Python爬虫&scity=101010100&industry=&position='] def parse(self, response):
li_list = response.xpath('//div[@class="job-list"]/ul/li')
for li in li_list:
title = li.xpath('.//div[@class="info-primary"]/h3[@class="name"]/a/div/text()').extract_first()
salary = li.xpath('.//div[@class="info-primary"]/h3[@class="name"]/a/span/text()').extract_first()
company = li.xpath('.//div[@class="company-text"]/h3/a/text()').extract_first() # 实例化一个item类型的对象
item = BossproItem()
# 将解析到的数据存储到item对象中
item["title"] = title
item["salary"] = salary
item["company"] = company # 将item对象提交给管道进行持久化存储
yield item
items
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html import scrapy class BossproItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
title = scrapy.Field()
salary = scrapy.Field()
company = scrapy.Field()
pipelines
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html # 管道文件:需要接收爬虫文件提交过来的数据,并对数据进行持久化存储.(IO操作)
class BossproPipeline(object):
fp = None
# 只会被执行一次(开始爬虫的时候执行一次)
def open_spider(self,spider):
print("开始爬虫")
self.fp = open('./job.txt','w',encoding='utf-8')
# 爬虫文件每提交一次,该方法就会被调用一次
def process_item(self, item, spider): #300表示为优先级,值越小优先级越高
self.fp.write(item['title'] + "\t" + item['salary'] + '\t' + item['company'] + '\n')
return item
# 结束爬虫时执行
def close_spider(self,spider):
self.fp.close()
print("爬虫结束") # 注意:默认情况下,管道机制并没有开启,需要手动在配置文件中进行开启 # 使用管道进行持久化的流程:
# 1.获取解析到的数据
# 2.将解析的数据存储到item对象(item类中进行相关属性的声明)
# 3.通过yield关键字将item提交到管道
# 4.管道文件中进行持久化存储代码的编写(process_item)
# 5.在配置文件中开启管道
settings
#开启管道
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'secondblood.pipelines.SecondbloodPipeline': 300, #300表示为优先级,值越小优先级越高
}
执行:
scrapy crawl boss --nolog

基于MySQL的持久化存储
pipelines
import pymysql
class mysqlPipeline(object):
conn = None
cursor = None
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.conn = pymysql.Connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='spider')
print(self.conn)
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor()
sql = 'insert into boss values("%s","%s","%s")'%(item['title'],item['salary'],item['company'])
try:
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
print (e)
self.conn.rollback() def close_spider(self,spider):
self.cursor.close()
self.conn.close()
settings
# 开启管道,自定义管道向不用的数据库存储数据
# 300是优先级,数字越小,优先级越高 ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'boss.pipelines.BossPipeline': 300,
'boss.pipelines.mysqlPipeLine': 301,
}
执行爬虫程序,并去数据库中查看数据

基于redis管道存储
pipelines
from redis import Redis
class RedisPipeline(object):
conn = None
def process_item(self,item,spider):
dic = {
"title":item["title"],
"salary":item["salary"],
"company":item["company"]
}
self.conn.lpush("jobInfo",json.dumps(dic))
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.conn = Redis(host='127.0.0.1',port=6379)
print (self.conn)
settings
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
#'bossPro.pipelines.BossproPipeline': 300,
#'bossPro.pipelines.mysqlPipeline': 301,
'bossPro.pipelines.RedisPipeline': 302,
}
执行代码并且查看redis中的数据

redis已经存在数据了,因为编码问题所以不显示中文.
Scrapy持久化存储的更多相关文章
- Scrapy持久化存储-爬取数据转义
Scrapy持久化存储 爬虫爬取数据转义问题 使用这种格式,会自动帮我们转义 'insert into wen values(%s,%s)',(item['title'],item['content' ...
- scrapy之持久化存储
scrapy之持久化存储 scrapy持久化存储一般有三种,分别是基于终端指令保存到磁盘本地,存储到MySQL,以及存储到Redis. 基于终端指令的持久化存储 scrapy crawl xxoo - ...
- scrapy 爬虫框架之持久化存储
scrapy 持久化存储 一.主要过程: 以爬取校花网为例 : http://www.xiaohuar.com/hua/ 1. spider 回调函数 返回item 时 要用y ...
- 11.scrapy框架持久化存储
今日概要 基于终端指令的持久化存储 基于管道的持久化存储 今日详情 1.基于终端指令的持久化存储 保证爬虫文件的parse方法中有可迭代类型对象(通常为列表or字典)的返回,该返回值可以通过终端指令的 ...
- scrapy框架持久化存储
基于终端指令的持久化存储 基于管道的持久化存储 1.基于终端指令的持久化存储 保证爬虫文件的parse方法中有可迭代类型对象(通常为列表or字典)的返回,该返回值可以通过终端指令的形式写入指定格式的文 ...
- scrapy框架的持久化存储
一 . 基于终端指令的持久化存储 保证爬虫文件的parse方法中有可迭代类型对象(通常为列表or字典)的返回,该返回值可以通过终端指令的形式写入指定格式的文件中进行持久化操作. 执行输出指定格式进行存 ...
- 爬虫--使用scrapy爬取糗事百科并在txt文件中持久化存储
工程目录结构 spiders下的first源码 # -*- coding: utf- -*- import scrapy from firstBlood.items import Firstblood ...
- 11,scrapy框架持久化存储
今日总结 基于终端指令的持久化存储 基于管道的持久化存储 今日详情 1.基于终端指令的持久化存储 保证爬虫文件的parse方法中有可迭代类型对象(通常为列表or字典)的返回,该返回值可以通过终端指令的 ...
- scrapy 框架持久化存储
1.基于终端的持久化存储 保证爬虫文件的parse方法中有可迭代类型对象(通常为列表或字典)的返回,该返回值可以通过终端指令的形式写入指定格式的文件中进行持久化操作. # 执行输出指定格式进行存储:将 ...
随机推荐
- orcl 中upper()和lower()和initcap()的用法
upper(字符串 | 列):输入的字符串变为大写返回: 将 bqh4表里的zym字段信息中含有字母的全部转成大写的方法: select * from bqh4 select upper(zym) f ...
- 事务的ACID性质
最近在读黄健宏的<Redis设计与实现>,现在看到了事务这章,由于之前(上学)没有好好整理过数据库事务的四大性质,导致现在(工作)看到了就和第一次知道一样((lll¬ω¬)).还是要把基础 ...
- 【转】Java学习---集合框架那些事
[原文]https://www.toutiao.com/i6593220692525711885/ Arraylist 与 LinkedList 异同 1. 是否保证线程安全: ArrayList 和 ...
- 【转】Java十大常用框架介绍(spring系+dubbo+RabbitMQ+Ehcache+redis)
一.SpringMVC Spring Web MVC是一种基于Java的实现了Web MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,即使用了MVC架构模式的思想,将web层进行职责解耦,基于请求驱动 ...
- Jenkins 基于 Docker git JAVA CI/CD
准备两台机器 192.168.31.200 centos7 docker harbor git 192.168.31.201 centos7 docker jenkins maven git Ha ...
- October 26th, 2017 Week 43rd Thursday
For success, attitude is equally as important as ability. 为取得成功,态度与能力一样重要. Today I read a news about ...
- 团队作业8-测试与发布(beta阶段)
小组成员 [组长]金盛昌(201421122043).刘文钊(20142112255).陈笑林(201421122042) 张俊逸(201421122044).陈志建(201421122040).陈金 ...
- 【2017下集美大学软工1412班_助教博客】团队作业4——Alpha冲刺日志公示
作业要求 团队作业4--第一次项目冲刺(Alpha版本) 团队评分结果和评分标准 检查项 总分 会议内容 代码签入 心得体会或其他记录 燃尽图 会议照片 评论区反馈 组别 分值 10 2 2 2 1 ...
- C借函数指针构造映射
这是候老师的<深入浅出 MFC>中C借函数指针构造映射截图,可以看到MFC们的映射思想:
- 学习Kali Linux必须知道的几点
Kali Linux 在渗透测试和白帽子方面是业界领先的 Linux 发行版.默认情况下,该发行版附带了大量入侵和渗透的工具和软件,并且在全世界都得到了广泛认可.即使在那些甚至可能不知道 Linux ...
