IO知识点整理(序列化,管道流,数据流,字节数组流,与编码)
一:序列化的问题
1.序列号的使用问题
关于在序列化中的序列号的使用问题,一般要是使用。
因为,每次要序列化的类产生都会产生一个一个新的序列号,如果将这个类的程序修改后,就会产生新的序列号,以前序列化后的文件将不会被读取。
所以,为了程序修改后,以前序列化后的程序仍然可以被读取,使用静态的序列号十分有必要。
2.将数据进行序列化
中在ObjectOutputStream类。
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable; public class Test114 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
writeObj();
}
public static void writeObj() throws Exception{
ObjectOutputStream objo=new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("op.txt"));
objo.writeObject(new People0("lisi",10));
objo.close();
}
} class People0 implements Serializable{
//序列号
public static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;
//属性
private String name;
private int age;
public People0(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String toString() {
return name+":"+age;
}
}
3.运行结果
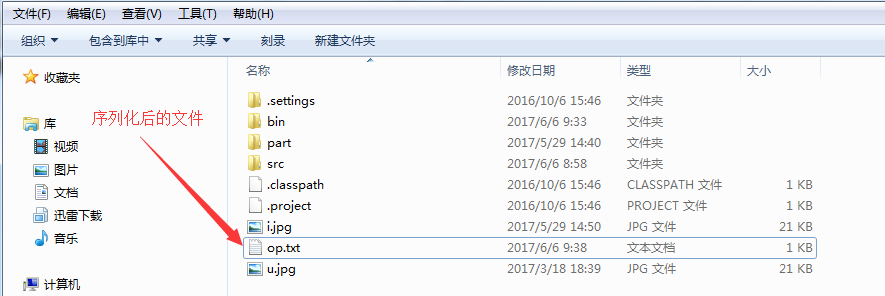
4.读序列化后的文件
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable; public class Test114 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//writeObj();
readObj();
}
public static void readObj() throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream readObj=new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("op.txt"));
People0 p=(People0)readObj.readObject();
//因为有toString方法,所以可以直接打印
System.out.println(p);
//
readObj.close();
}
public static void writeObj() throws Exception{
ObjectOutputStream objo=new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("op.txt"));
objo.writeObject(new People0("lisi",10));
objo.close();
}
} class People0 implements Serializable{
//序列号
public static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;
//属性
private String name;
private int age;
public People0(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String toString() {
return name+":"+age;
}
}
5.运行结果
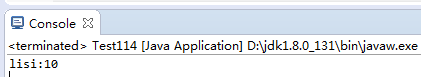
6.不能序列化的情况
类中的static不能够序列化,因为static的属性在方法区,而序列化主要是序列化的是栈里的文件数据。
同时transient修饰的属性不能够序列化。
7.不能序列化的程序演示
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable; public class Test114 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//writeObj();
readObj();
}
public static void readObj() throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream readObj=new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("op.txt"));
People0 p=(People0)readObj.readObject();
//因为有toString方法,所以可以直接打印
System.out.println(p);
//
readObj.close();
}
public static void writeObj() throws Exception{
ObjectOutputStream objo=new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("op.txt"));
objo.writeObject(new People0("lisi",10,"usa"));
objo.close();
}
} class People0 implements Serializable{
//序列号
public static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;
//属性
private String name;
//添加transient的修饰
private transient int age;
//新加static
private static String contry="cn";
public People0(String name,int age,String contry){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.contry=contry;
}
public String toString() {
return name+":"+age+":"+contry;
}
}
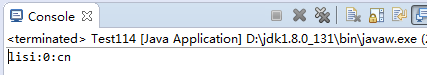
8.运行结果
运行的顺序是,先序列化,序列化后生成新的文件后,再进行反序列化。
这时,才会发现static与transient都没有被序列化。
二:管道流与RandomAccessFile
1.管道流
可以将读写进行相连。
管道输入流应该连接到管道输出流;管道输入流提供要写入管道输出流的所有数据字节。
通常,数据由某个线程从 PipedInputStream 对象读取,并由其他线程将其写入到相应的 PipedOutputStream。
不建议对这两个对象尝试使用单个线程,因为这样可能死锁线程。
2.管道流程序(多线程)
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream; public class Test115 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
PipedInputStream in=new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream out=new PipedOutputStream();
in.connect(out); //链接connect Writer w=new Writer(out);
Reader r=new Reader(in);
new Thread(w).start();
new Thread(r).start();
} }
class Writer implements Runnable{
private PipedOutputStream out;
public Writer(PipedOutputStream out){
this.out=out;
}
public void run(){
try{
Thread.sleep(5000);
out.write("sjhdbs".getBytes());
out.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.toString();
}
}
}
class Reader implements Runnable{
private PipedInputStream in;
public Reader(PipedInputStream in){
this.in=in;
}
public void run(){
try{
byte[] buf=new byte[1024];
int len=in.read(buf);
String str=new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println("str="+str);
in.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.toString();
}
}
}
3.运行结果

4.RandomAccessFile
该类不是算是IO体系中子类。
而是直接继承自Object。
但是它是IO包中成员。因为它具备读和写功能。
内部封装了一个数组,而且通过指针对数组的元素进行操作。
可以通过getFilePointer获取指针位置,
同时可以通过seek改变指针的位置。
通过构造函数可以看出,该类只能操作文件。
而且操作文件还有模式:只读r,,读写rw等。
5.写入程序
在程序中使用writeInt,这个方法是每次写入4个字节,如果使用write则是每次写入1个字节。
考虑到数字的越界,这里使用writeInt方法。
这个方法的写方式在下面的程序中没有什么特殊的地方。
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile; public class Test116 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
randomWrite();
}
/**
* 简单的写入
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void randomWrite() throws Exception{
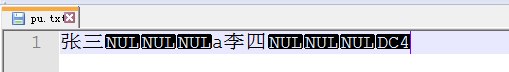
RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("pu.txt","rw");
raf.write("张三".getBytes());
raf.writeInt(97);
raf.write("李四".getBytes());
raf.writeInt(20);
raf.close();
}
}
6.结果
7.分别使用seek与skipBytes的读方式(待探求为啥读取有问题)
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile; public class Test117 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
System.out.println("seek function");
randomReadSeek();
System.out.println("skipBytes function");
randomReadSkipbytes();
}
/**
* seek function
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void randomReadSeek() throws Exception{
RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("pu.txt", "r");
raf.seek(0);
byte[] buf = new byte[8]; raf.read(buf); String name = new String(buf); int age = raf.readInt(); System.out.println("name="+name);
System.out.println("age="+age); raf.close();
}
public static void randomReadSkipbytes()throws Exception{
RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("pu.txt", "r");
raf.skipBytes(2);
byte[] buf = new byte[8]; raf.read(buf); String name = new String(buf); int age = raf.readInt(); System.out.println("name="+name);
System.out.println("age="+age); raf.close();
} }
三:数据流对象的操作
1.关于DataInputStream与DataOutputStream的介绍
其主要是将数据与流进行结合。
2.写数据程序
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream; public class Test118 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
dataWrite(); }
public static void dataWrite()throws Exception{
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.txt"));
dos.writeInt(78);
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeDouble(89.90907);
dos.close();
}
}
3.读的程序
注意点是,读取数据的时候,必须与写的数据类型相对应,保持读写的一致性。
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream; public class Test118 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//dataWrite();
dataRead();
}
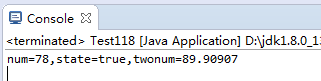
public static void dataRead() throws Exception{
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.txt"));
int num=dis.readInt();
boolean state=dis.readBoolean();
double twonum=dis.readDouble();
System.out.println("num="+num+",state="+state+",twonum="+twonum);
}
public static void dataWrite()throws Exception{
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.txt"));
dos.writeInt(78);
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeDouble(89.90907);
dos.close();
}
}
4.运行结果
5.关于DataInputStream中的writeUIF的特殊性(包含readUIF)

所以在下面,通过程序进行验证。
6.带编码的可以读写字串的程序
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream; public class Test119 { public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
writeUtf();
readUtf();
}
public static void writeUtf()throws Exception{
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("string.txt"));
dos.writeUTF("shdfcsdcnklbsnkl");
dos.close();
}
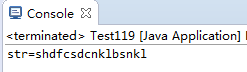
public static void readUtf()throws Exception{
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("String.txt"));
String str=dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("str="+str);
} }
7.运行结果
8.使用FileOutputStream的编码方式对字符串的读写
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; public class Test120 {
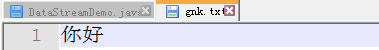
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
OutputStreamWriter fos=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("gnk.txt"),"gbk");
fos.write("你好");
fos.close();
}
}
9.结果
四:字节数组流的操作
1.程序
/*
用于操作字节数组的流对象。 ByteArrayInputStream :在构造的时候,需要接收数据源,。而且数据源是一个字节数组。 ByteArrayOutputStream: 在构造的时候,不用定义数据目的,因为该对象中已经内部封装了可变长度的字节数组。
这就是数据目的地。
因为这两个流对象都操作的数组,并没有使用系统资源。
所以,不用进行close关闭。
在流操作规律讲解时:
源设备,
键盘 System.in,硬盘 FileStream,内存 ArrayStream。
目的设备:
控制台 System.out,硬盘FileStream,内存 ArrayStream。
用流的读写思想来操作数据。
*/
import java.io.*;
class ByteArrayStream
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//数据源。
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream("ABCDEFD".getBytes());
//数据目的
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); int by = 0; while((by=bis.read())!=-1)
{
bos.write(by);
}
System.out.println(bos.size());
System.out.println(bos.toString());
}
}
五:编码
1.介绍
编码:将字符串变成字节数组
解码:将字节数组变成字符串
String-->byte[]; str.getBytes(charsetName);
byte[] -->String: new String(byte[],charsetName);
2.程序
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test121 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
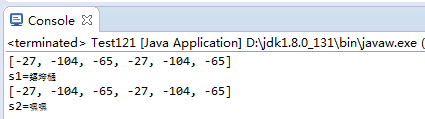
String str="嘿嘿";
byte[] buf1=str.getBytes("utf-8");
//打印字节码
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buf1));
//utf-8解码
String s1=new String(buf1,"gbk");
System.out.println("s1="+s1);
//再使用utf-8编码
byte[] buf2=s1.getBytes("gbk");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buf2));
//打印
String s2=new String(buf2,"utf-8");
System.out.println("s2="+s2);
}
}
3.结果
IO知识点整理(序列化,管道流,数据流,字节数组流,与编码)的更多相关文章
- 6.5(java学习笔记)其他流(字节数组流,数据流,对象流,打印流)
一.字节数组流 之前使用输入输出流的操作的对象是文件,而这里字节数组流操作的对象是内存,内存可以看做是一个字节数组. 使用字节数组流读写就可以看做是从内存A到内存B的读写,对象时内存即字节数组. 1. ...
- JAVA IO分析二:字节数组流、基本数据&对象类型的数据流、打印流
上一节,我们分析了常见的节点流(FileInputStream/FileOutputStream FileReader/FileWrite)和常见的处理流(BufferedInputStream/B ...
- Java:IO流其他类(字节数组流、字符数组流、数据流、打印流、Properities、对象流、管道流、随机访问、序列流、字符串读写流)
一.字节数组流: 类 ByteArrayInputStream:在构造函数的时候,需要接受数据源,而且数据源是一个字节数组. 包含一个内部缓冲区,该缓冲区包含从流中读取的字节.内部计数器跟踪 read ...
- Java IO学习笔记(三)转换流、数据流、字节数组流
转换流 1.转换流:将字节流转换成字符流,转换之后就可以一个字符一个字符的往程序写内容了,并且可以调用字符节点流的write(String s)方法,还可以在外面套用BufferedReader()和 ...
- Java文件与io——字节数组流数据流字符串流
字节数组流 ByteArrayInputStream:包含一个内部缓冲区,该缓冲区包含从流中读取的字节.内部计数器跟踪read方法要提供的下一个字节.关闭ByteArrayInputStream无效. ...
- IO知识点整理(文件File类的使用)
一: 1.API 2.构造函数的程序 注意这集中构造函数的特点. 同时,字段separator的使用. import java.io.File; public class Test101 { publ ...
- Java基础IO类之字节数组流
package IODemo; //字节数组流 :内部维护这着一个字节数组,我们可以利用流的读取机制来处理字符串 无需关闭,不会报IO异常 // ByteArrayInputstream ByteAr ...
- Java IO 流-- 字节数组流ByteArrayInPutStream ByteArrayOutPutStream
字节数组流输于缓冲流,放在jvm内存中,java可以直接操作.我们使用时可以不用关闭,交给GC垃圾回收机制处理. 当然我们为了保持良好习惯和代码一致性也可以加上关闭语句. 当其实我么打开ByteArr ...
- Java字节数组流学习
字节数组流 基于内存操作,内部维护着一个字节数组,我们可以利用流的读取机制来处理字符串.无需关闭,不会报IOException. ByteArrayInputStream 包含一个内部缓冲区,该缓冲区 ...
随机推荐
- 大数据高性能数据库Redis在Windows上的使用教程
Redis学习笔记----Redis在windows上的安装配置和使用 Redis简介 redis是一个key-value存储系统.和Memcached类似,它支持存储的value类型相对更多,包括s ...
- 洛谷P3862 8月月赛B
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P3862#sub P3862 8月月赛B 推公式:f(n)->f(n+1) 奇葩的预处理 https://www.l ...
- Go_21: Golang 中 time 包的使用二
常量声明: const TimeLayout = "2006-01-02 15:04:05" 这是个奇葩,必须是这个时间点,据说是 go 诞生之日, 记忆方法:6-1-2-3-4- ...
- Java基础-SSM之mybatis的树形控件(自关联)
Java基础-SSM之mybatis的树形控件(自关联) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.准备测试环境(创建数据库表) 1>.创建areas表: use y ...
- npm install --save
1. npm install:本地安装 2. npm install -g:全局安装 我们在使用 npm install 安装模块或插件时,有两种命令把它们写入到 package.json 文件中去, ...
- 安装mongodb以及设置为windows服务 详细步骤
我的win7 32的,注意版本要正确! 一.下载mongodb压缩包:mongodb-win32-i386-2.6.9.zip() 二.在D盘新建文件夹mongodb,将压缩我的解压文件放进去(有一个 ...
- [转载]Brackets - 强大免费的开源跨平台Web前端开发工具IDE (HTML/CSS/Javascript代码编辑器)
http://brackets.io/ Brackets 是一个免费.开源且跨平台的 HTML/CSS/JavaScript 前端 WEB 集成开发环境 (IDE工具).该项目由 Adobe 创建和维 ...
- AngularJS入门基础——过滤器
在HTML中的模板绑定符号{{ }}内通过 | 符号来调用过滤器 {{ name | uppercase }} 以HTML的形式使用过滤器时,如果需要传递参数给过滤器,只要在过滤器名字后面加冒号即 ...
- JavaScript编写风格指南 (二)
七:注释 // 频繁的使用注释有助于他人理解你的代码// 1.代码晦涩难懂// 2.可能被误认为是错误的代码// 3.必要但不明显的针对特定浏览器的代码// 4.对于对象,方法或者属性,生成文档是有必 ...
- P4549 【模板】裴蜀定理
题目描述 给出n个数(A1...An)现求一组整数序列(X1...Xn)使得S=A1X1+...AnXn>0,且S的值最小 输入输出格式 输入格式: 第一行给出数字N,代表有N个数 下面一行给出 ...
