数据结构5_java---二叉树,树的建立,树的先序、中序、后序遍历(递归和非递归算法),层次遍历(广度优先遍历),深度优先遍历,树的深度(递归算法)
1、二叉树的建立
首先,定义数组存储树的data,然后使用list集合将所有的二叉树结点都包含进去,最后给每个父亲结点赋予左右孩子。
需要注意的是:最后一个父亲结点需要单独处理
public static TreeNode root;
//建立二叉树内部类
class TreeNode{
public Object data; //携带变量
public TreeNode lchild,rchild; //左右孩子
public TreeNode() {
data = null;
lchild = null;
rchild = null;
}
public TreeNode(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void setLeft(TreeNode left)
{
this.lchild = left;
}
public void setRight(TreeNode right)
{
this.rchild = right;
}
}
//建立二叉树,通过List作为中间过渡量
public void CreatBinTree(int []datas,List<TreeNode> nodelist) {
for(int i=0;i<datas.length;i++)
{
TreeNode aNode = new TreeNode(datas[i]);
nodelist.add(aNode);
}
//给所有父亲结点设定子节点
for(int index = 0;index<nodelist.size()/2-1;index++)
{
//在起始结点为0时,为N的父亲结点他的左孩子为2*N+1,右孩子为2*N+2
nodelist.get(index).lchild = nodelist.get(2*index+1);
nodelist.get(index).rchild = nodelist.get(2*index+2);
}
//单独处理最后一个父亲结点
int index = nodelist.size()/2-1;
nodelist.get(index).lchild = nodelist.get(2*index+1);
if(nodelist.size()%2==1)
nodelist.get(index).rchild = nodelist.get(2*index+2);
}
2、先序遍历
2.1 递归方法
//先序遍历,递归操作
public void PreOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if(root == null)
return ;
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
PreOrder(root.lchild);
PreOrder(root.rchild);
}
2.2 非递归操作,使用栈(两种方法)
本人认为第一种方法相对容易理解,较为简单
方法一:
思想:
(1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
(2)若结点非空,读取该节点,并将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,移到最左孩子
(3)若栈非空,取出栈顶元素,此时父节点已读,所以移向右孩子
****************核心为:边读取左结点变将其压入栈中,左孩子对下一级来说上也代表父亲结点,所以之后可以直接读取右孩子。*******************
/*
* 方法一:先序遍历,使用栈操作,相对较简单
* 思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,读取该节点,并将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,移到最左孩子
* (3)若栈非空,取出栈顶元素,此时父节点已读,所以移向右孩子
* 核心为:边读取左结点变将其压入栈中,左孩子对下一级来说上也代表父亲结点,所以之后可以直接读取右孩子。
*/
public void preOrder1()
{
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty()||node!=null)
{
while(node!=null)
{
System.out.print(node.data+" "); //访问该节点
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
if(!stack.isEmpty())
{
node = stack.pop();
node = node.rchild;
}
}
}
方法二:
思想:
(1)首先将根节点入栈
(2)判断非空,将结点从栈中取出并访问
(3)依次访问栈中的左孩子,并将右孩子放入栈中,结点不断往左孩子移动
(4)重复步骤(2)(3),直到栈为空
/*
* 方法二:先序遍历,使用栈操作,相对较麻烦
* 思想:
* (1)首先将根节点入栈
* (2)判断非空,将结点从栈中取出并访问
* (3)依次访问栈中的左孩子,并将右孩子放入栈中,结点不断往左孩子移动
* (4)重复步骤(2)(3),直到栈为空
*/
public void preOrder2() throws Exception
{
TreeNode pNode = root;
if(pNode!=null) //首先判断根结点是否为空
{
Stack<TreeNode> astack = new Stack<>(); //构造栈操作
astack.push(pNode); //将根节点压入栈中
while(!astack.isEmpty()) //循环操作直到栈中没有结点存在,即最右结点访问完毕
{
pNode = astack.pop(); //首先将结点从栈中取出
System.out.print(pNode.data+" "); //访问该节点
while(pNode!=null) //若该结点不为空
{
if(pNode.lchild!=null) //访问左子树
System.out.print(pNode.lchild.data+" ");
if(pNode.rchild!=null) //将右子树压入栈中
astack.push(pNode.rchild);
pNode = pNode.lchild; //进入到下一个左子树中
}
} }
}
3、中序遍历
3.1 递归操作
//中序遍历,递归操作
public void inOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if(root==null)
return ;
inOrder(root.lchild);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
inOrder(root.rchild);
}
3.2 非递归操作,栈
思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边
* (3)若栈非空,则取出栈顶元素,并读取访问数据,而后结点向右孩子移动
/*
* 中序遍历,使用栈操作
* 思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边
* (3)若栈非空,则取出栈顶元素,并读取访问数据,而后结点向右孩子移动
*/
public void inOrder1() throws Exception
{
TreeNode node = root;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(node!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
{
while(node!=null)
{
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
if(stack!=null)
{
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
node = node.rchild;
}
}
}
4、后序遍历
4.1 递归操作
//后序遍历,递归操作
public void postOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if(root==null)
return ;
postOrder(root.lchild);
postOrder(root.rchild);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
}
4.2 非递归操作
前提:设置标志结点pre,指示是否访问过某结点
思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边
* (3)若栈非空,首先取出栈顶元素的右孩子赋给tmp
1、若栈顶元素的右孩子为空或者等于pre(即已访问过),则弹出元素并访问,将该结点赋值给pre,并将当前结点赋值为null
2、否则的话将右孩子赋值给当前结点
/*
* 后序遍历,栈操作
* 前提:设置标志结点pre,指示是否访问过某结点
* 思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边
* (3)若栈非空,首先取出栈顶元素的右孩子赋给tmp
* 1、若栈顶元素的右孩子为空或者等于pre(即已访问过),则弹出元素并访问,将该结点赋值给pre,并将当前结点赋值为null
* 2、否则的话将右孩子赋值给当前结点
*/
public void postOrder1()
{
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root,pre = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty()||node!=null)
{
while(node!=null)
{
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
if(!stack.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode tmp = stack.peek().rchild;
if(tmp==null||tmp==pre)
{
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
pre = node;
node = null;
}else {
node = tmp;
} }
} }
5、层次遍历(广度优先遍历)使用队列
思想:
* (1)读取根节点,并将其压入队列中
* (2)以队列的长度作为循环的判断条件,取出队收元素并访问,访问后将其弹出
* (3)判断是否有左右孩子,若有则加入队列中。
public void bfs()
{
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
if(root==null)
return ;
queue.offer(root);
while(queue.size()>0) {
TreeNode node = queue.peek();
queue.poll();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
if(node.lchild!=null)
{
queue.offer(node.lchild);
}
if(node.rchild!=null)
{
queue.offer(node.rchild);
}
} }
6、深度优先遍历
此部分相对较难理解,自行琢磨
public void dfs(TreeNode node,List<List<Integer>> nList,List<Integer> list)
{
if(node==null)
return ;
if(node.lchild==null&node.rchild==null)
{
list.add((Integer) node.data);
nList.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
list.add((Integer) node.data);
dfs(node.lchild, nList, list);
dfs(node.rchild, nList, list);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
7、求树的深度
(1)若二叉树为空,则返回0
(2)若二叉树非空,求左子树的深度,求右子树的深度
(3)比较左右子树的深度,求最大值加1,即为二叉树的深度
//求二叉树的深度
public int Depth(TreeNode node)
{
if(node==null)
return 0;
else {
int ldepth = Depth(node.lchild);
System.out.println("node'data:"+node.data+"ldepth: "+ldepth);
int rdepth = Depth(node.rchild);
System.out.println("node'data:"+node.data+"rdepth: "+rdepth+" ");
if(ldepth<rdepth)
return rdepth+1;
else
return ldepth+1;
}
}
7、应用及全部代码展示
package Main; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack; import javax.naming.directory.SearchControls;
public class Main{
public static TreeNode root;
//建立二叉树内部类
class TreeNode{
public Object data; //携带变量
public TreeNode lchild,rchild; //左右孩子
public TreeNode() {
data = null;
lchild = null;
rchild = null;
}
public TreeNode(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void setLeft(TreeNode left)
{
this.lchild = left;
}
public void setRight(TreeNode right)
{
this.rchild = right;
}
}
//建立二叉树,通过List作为中间过渡量
public void CreatBinTree(int []datas,List<TreeNode> nodelist) {
for(int i=0;i<datas.length;i++)
{
TreeNode aNode = new TreeNode(datas[i]);
nodelist.add(aNode);
}
//给所有父亲结点设定子节点
for(int index = 0;index<nodelist.size()/2-1;index++)
{
//在起始结点为0时,为N的父亲结点他的左孩子为2*N+1,右孩子为2*N+2
nodelist.get(index).lchild = nodelist.get(2*index+1);
nodelist.get(index).rchild = nodelist.get(2*index+2);
}
//单独处理最后一个父亲结点
int index = nodelist.size()/2-1;
nodelist.get(index).lchild = nodelist.get(2*index+1);
if(nodelist.size()%2==1)
nodelist.get(index).rchild = nodelist.get(2*index+2);
}
//先序遍历,递归操作
public void PreOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if(root == null)
return ;
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
PreOrder(root.lchild);
PreOrder(root.rchild);
}
/*
* 方法一:先序遍历,使用栈操作,相对较简单
* 思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,读取该节点,并将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,移到最左孩子
* (3)若栈非空,取出栈顶元素,此时父节点已读,所以移向右孩子
* 核心为:边读取左结点变将其压入栈中,左孩子对下一级来说上也代表父亲结点,所以之后可以直接读取右孩子。
*/
public void preOrder1()
{
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty()||node!=null)
{
while(node!=null)
{
System.out.print(node.data+" "); //访问该节点
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
if(!stack.isEmpty())
{
node = stack.pop();
node = node.rchild;
}
}
}
/*
* 方法二:先序遍历,使用栈操作,相对较麻烦
* 思想:
* (1)首先将根节点入栈
* (2)判断非空,将结点从栈中取出并访问
* (3)依次访问栈中的左孩子,并将右孩子放入栈中,结点不断往左孩子移动
* (4)重复步骤(2)(3),直到栈为空
*/
public void preOrder2() throws Exception
{
TreeNode pNode = root;
if(pNode!=null) //首先判断根结点是否为空
{
Stack<TreeNode> astack = new Stack<>(); //构造栈操作
astack.push(pNode); //将根节点压入栈中
while(!astack.isEmpty()) //循环操作直到栈中没有结点存在,即最右结点访问完毕
{
pNode = astack.pop(); //首先将结点从栈中取出
System.out.print(pNode.data+" "); //访问该节点
while(pNode!=null) //若该结点不为空
{
if(pNode.lchild!=null) //访问左子树
System.out.print(pNode.lchild.data+" ");
if(pNode.rchild!=null) //将右子树压入栈中
astack.push(pNode.rchild);
pNode = pNode.lchild; //进入到下一个左子树中
}
} }
}
//中序遍历,递归操作
public void inOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if(root==null)
return ;
inOrder(root.lchild);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
inOrder(root.rchild);
}
/*
* 中序遍历,使用栈操作
* 思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边
* (3)若栈非空,则取出栈顶元素,并读取访问数据,而后结点向右孩子移动
*/
public void inOrder1() throws Exception
{
TreeNode node = root;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(node!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
{
while(node!=null)
{
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
if(stack!=null)
{
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
node = node.rchild;
}
}
}
//后序遍历,递归操作
public void postOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if(root==null)
return ;
postOrder(root.lchild);
postOrder(root.rchild);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
}
/*
* 后序遍历,栈操作
* 前提:设置标志结点pre,指示是否访问过某结点
* 思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边
* (3)若栈非空,首先取出栈顶元素的右孩子赋给tmp
* 1、若栈顶元素的右孩子为空或者等于pre(即已访问过),则弹出元素并访问,将该结点赋值给pre,并将当前结点赋值为null
* 2、否则的话将右孩子赋值给当前结点
*/
public void postOrder1()
{
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode node = root,pre = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty()||node!=null)
{
while(node!=null)
{
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
if(!stack.isEmpty())
{
TreeNode tmp = stack.peek().rchild;
if(tmp==null||tmp==pre)
{
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
pre = node;
node = null;
}else {
node = tmp;
} }
} }
/*层次遍历,即广度优先遍历,从上到下遍历二叉树
* 思想:
* (1)读取根节点,并将其压入队列中
* (2)以队列的长度作为循环的判断条件,取出队收元素并访问,访问后将其弹出
* (3)判断是否有左右孩子,若有则加入队列中。
* */
public void bfs()
{
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
if(root==null)
return ;
queue.offer(root);
while(queue.size()>0) {
TreeNode node = queue.peek();
queue.poll();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
if(node.lchild!=null)
{
queue.offer(node.lchild);
}
if(node.rchild!=null)
{
queue.offer(node.rchild);
}
} }
/*
* 深度优先遍历,从左到右遍历二叉树
* */
public void dfs(TreeNode node,List<List<Integer>> nList,List<Integer> list)
{
if(node==null)
return ;
if(node.lchild==null&node.rchild==null)
{
list.add((Integer) node.data);
nList.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
list.add((Integer) node.data);
dfs(node.lchild, nList, list);
dfs(node.rchild, nList, list);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
//查找算法
public static TreeNode Searchparameter(TreeNode root,int x)
{
TreeNode node = root;
if(root==null)
return null;
else {
if(node.data.equals(x))
return node;
else {
TreeNode aNode = Searchparameter(node.lchild, x);
if(aNode==null)
return Searchparameter(node.rchild, x);
else
return aNode;
}
}
}
//求二叉树的深度
public int Depth(TreeNode node)
{
if(node==null)
return 0;
else {
int ldepth = Depth(node.lchild);
int rdepth = Depth(node.rchild);
if(ldepth<rdepth)
return rdepth+1;
else
return ldepth+1;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int datas[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
List<TreeNode> nodelist = new LinkedList<>();
Main aMain = new Main();
aMain.CreatBinTree(datas,nodelist);
root = nodelist.get(0); System.out.println("First order traversal(recursive):");
aMain.PreOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("First order traversal(stack--1):");
aMain.preOrder1();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("First order traversal(stack--2):");
aMain.preOrder2();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Inorder traversal(recursive):");
aMain.inOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Inorder traversal(stack--1):");
aMain.inOrder1();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Postorder traversal(recursive):");
aMain.postOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Postorder traversal(stack--1):");
aMain.postOrder1();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Level traversal(queue--1):");
aMain.bfs(); List<List<Integer>> rst = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Depth first traversal(queue--1):");
aMain.dfs(root,rst,list);
System.out.println(rst);
int x = 6;
TreeNode aNode = Searchparameter(root,x);
System.out.println(aNode.data); int depth = aMain.Depth(root);
System.out.println("the depth of the tree is :"+depth);
} }
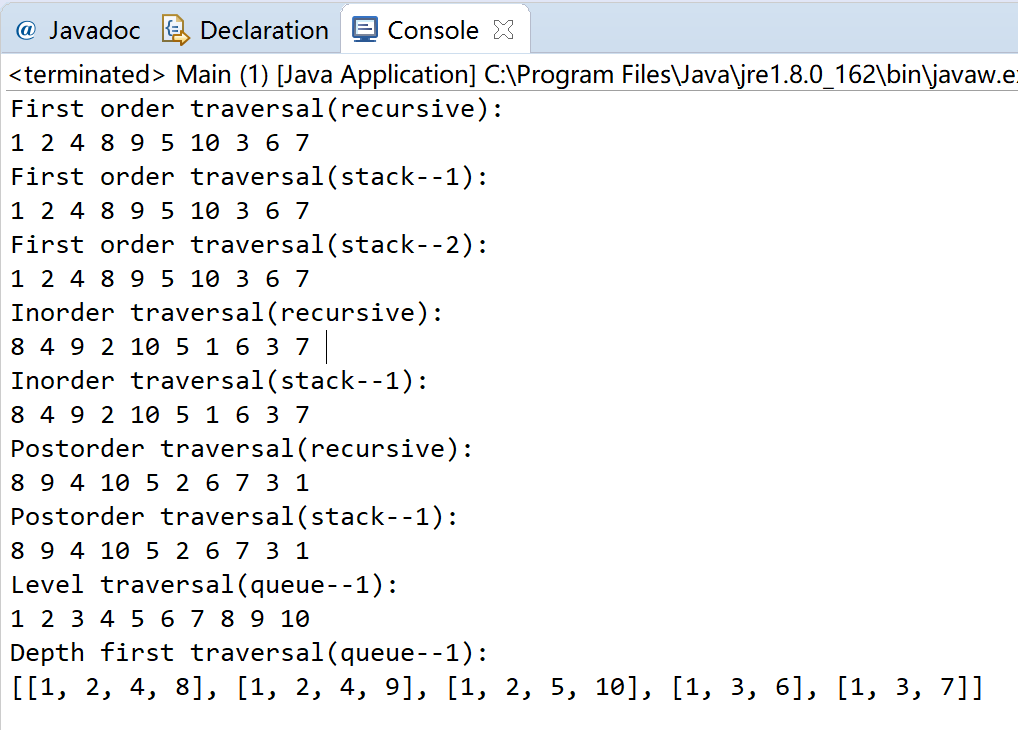
结果展示:
数据结构5_java---二叉树,树的建立,树的先序、中序、后序遍历(递归和非递归算法),层次遍历(广度优先遍历),深度优先遍历,树的深度(递归算法)的更多相关文章
- 【图数据结构的遍历】java实现广度优先和深度优先遍历
[图数据结构的遍历]java实现广度优先和深度优先遍历 宽度优先搜索(BFS)遍历图需要使用队列queue数据结构: 深度优先搜索(DFS, Depth First Search)的实现 需要使用到栈 ...
- 【数据结构】二叉树的遍历(前、中、后序及层次遍历)及leetcode107题python实现
文章目录 二叉树及遍历 二叉树概念 二叉树的遍历及python实现 二叉树的遍历 python实现 leetcode107题python实现 题目描述 python实现 二叉树及遍历 二叉树概念 二叉 ...
- 二叉树的创建、遍历(递归和非递归实现)、交换左右子数、求高度(c++实现)
要求:以左右孩子表示法实现链式方式存储的二叉树(lson—rson),以菜单方式设计并完成功能任务:建立并存储树.输出前序遍历结果.输出中序遍历结果.输出后序遍历结果.交换左右子树.统计高度,其中对于 ...
- 前、中、后序遍历随意两种是否能确定一个二叉树?理由? && 栈和队列的特点和区别
前序和后序不能确定二叉树理由:前序和后序在本质上都是将父节点与子结点进行分离,但并没有指明左子树和右子树的能力,因此得到这两个序列只能明确父子关系,而不能确定一个二叉树. 由二叉树的中序和前序遍历序列 ...
- 如何求先序排列和后序排列——hihocoder1049+洛谷1030+HDU1710+POJ2255+UVA548【二叉树递归搜索】
[已知先序.中序求后序排列]--字符串类型 #1049 : 后序遍历 时间限制:10000ms 单点时限:1000ms 内存限制:256MB 描述 小Ho在这一周遇到的问题便是:给出一棵二叉树的前序和 ...
- 分别求二叉树前、中、后序的第k个节点
一.求二叉树的前序遍历中的第k个节点 //求先序遍历中的第k个节点的值 ; elemType preNode(BTNode *root,int k){ if(root==NULL) return ' ...
- HDU 1710 (二叉树的前序和中序,求后序)
题目链接 题目大意: 输入二叉树的前序.中序遍历,请输出它的后序遍历 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> ; // 长度为n s1 前 ...
- hdu1710-Binary Tree Traversals (由二叉树的先序序列和中序序列求后序序列)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java ...
- LeetCode:二叉树的前、中、后序遍历
描述: ------------------------------------------------------- 前序遍历: Given a binary tree, return the pr ...
随机推荐
- mysql数据库事务隔离原理
今天在学习JDBC的时候看到了关于MySQL的事务的隔离级别的问题,感觉内容挺高级的,所以记录一篇文章,以备后面使用. 数据库隔离级别有四种,应用<高性能mysql>一书中的说明: 然后说 ...
- 002:CSS基础
注意:蓝色 重要:红色 目录: 1. 学会使用CSS选择器: 9大选择器.交集选择器.并集选择器.后代选择器.子代选择器.伪类选择器. 2.font.color.横向竖向居中.文本修饰.首行缩进. f ...
- Java线程池Executor&ThreadPool
java自1.5版本之后,提供线程池,供开发人员快捷方便的创建自己的多线程任务.下面简单的线程池的方法及说明. 1.Executor 线程池的顶级接口.定义了方法execute(Runnable),该 ...
- 【linux】【mysql】mysql主从数据库
系统环境:Centos7 主:192.168.8.162 从:192.168.8.127 前提条件 a.关闭防火墙 systemctl stop firewalld 关闭防火墙开机自启 system ...
- Kubernetes的Deployment对象使用
一.什么是Deployment对象 明明ReplicaSet已经可以控制pod的数量了,为什么还需要Deployment? Deploymen实际上一个两层控制器,遵循一种滚动更新的方式来实升级现有的 ...
- connection pool exhausted
1.发现问题 生产环境发现有一些redis报错日志 connection pool exhausted.如果redis中没有数据 就直接回源 查DB.暂时不会有什么大问题.中文意思是连接池耗尽. 2. ...
- 从零开始入门 K8s | 应用配置管理
一.需求来源 背景问题 首先一起来看一下需求来源.大家应该都有过这样的经验,就是用一个容器镜像来启动一个 container.要启动这个容器,其实有很多需要配套的问题待解决: 第一,比如说一些可变的配 ...
- Spring 梳理-MVC-配置DispatcherServet和ContextLoaderListener
在使用JavaConfig时,AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer会自动注册 DispatcherServlet 和 Context ...
- 【爬虫小程序:爬取斗鱼所有房间信息】Xpath(多线程版)
# 本程序亲测有效,用于理解爬虫相关的基础知识,不足之处希望大家批评指正 from queue import Queue import requests from lxml import etree ...
- PHP将base64数据流转换成图片并保存
Base64是网络上最常见的用于传输8Bit字节码的编码方式之一,Base64就是一种基于64个可打印字符来表示二进制数据的方法.可查看RFC2045-RFC2049,上面有MIME的详细规范. Ba ...
