【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL — 用户定义函数
本文翻译自官网:User-defined Functions https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/table/udfs.html
用户定义函数是一项重要功能,因为它们显着扩展了查询的表达能力。
注册用户定义的函数
在大多数情况下,必须先注册用户定义的函数,然后才能在查询中使用该函数。无需注册Scala Table API的函数。
通过调用registerFunction()方法在TableEnvironment中注册函数。 注册用户定义的函数后,会将其插入TableEnvironment的函数目录中,以便Table API或SQL解析器可以识别并正确转换它。
请在以下子会话中找到有关如何注册以及如何调用每种类型的用户定义函数(ScalarFunction,TableFunction和AggregateFunction)的详细示例。
标量函数
如果内置函数中未包含所需的标量函数,则可以为Table API和SQL定义自定义的,用户定义的标量函数。 用户定义的标量函数将零个,一个或多个标量值映射到新的标量值。
为了定义标量函数,必须扩展org.apache.flink.table.functions中的基类ScalarFunction并实现(一个或多个)评估方法。 标量函数的行为由评估方法确定。 评估方法必须公开声明并命名为eval。 评估方法的参数类型和返回类型也确定标量函数的参数和返回类型。 评估方法也可以通过实现多种名为eval的方法来重载。 评估方法还可以支持可变参数,例如eval(String ... strs)。
下面的示例演示如何定义自己的哈希码函数,如何在TableEnvironment中注册并在查询中调用它。 请注意,您可以在构造函数之前注册它的标量函数:
// must be defined in static/object context
class HashCode(factor: Int) extends ScalarFunction {
def eval(s: String): Int = {
s.hashCode() * factor
}
} val tableEnv = BatchTableEnvironment.create(env) // use the function in Scala Table API
val hashCode = new HashCode(10)
myTable.select('string, hashCode('string)) // register and use the function in SQL
tableEnv.registerFunction("hashCode", new HashCode(10))
tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT string, hashCode(string) FROM MyTable")
默认情况下,评估方法的结果类型由Flink的类型提取工具确定。 这对于基本类型或简单的POJO就足够了,但对于更复杂,自定义或复合类型可能是错误的。 在这些情况下,可以通过覆盖ScalarFunction#getResultType()来手动定义结果类型的TypeInformation。
下面的示例显示一个高级示例,该示例采用内部时间戳表示,并且还以长值形式返回内部时间戳表示。 通过重写ScalarFunction#getResultType(),我们定义了代码生成应将返回的long值解释为Types.TIMESTAMP。
object TimestampModifier extends ScalarFunction {
def eval(t: Long): Long = {
t % 1000
}
override def getResultType(signature: Array[Class[_]]): TypeInformation[_] = {
Types.TIMESTAMP
}
}
Table Function
与用户定义的标量函数相似,用户定义的表函数将零,一个或多个标量值作为输入参数。 但是,与标量函数相比,它可以返回任意数量的行作为输出,而不是单个值。 返回的行可能包含一列或多列。
为了定义表函数,必须扩展org.apache.flink.table.functions中的基类TableFunction并实现(一个或多个)评估方法。 表函数的行为由其评估方法确定。 必须将评估方法声明为公开并命名为eval。 通过实现多个名为eval的方法,可以重载TableFunction。 评估方法的参数类型确定表函数的所有有效参数。 评估方法还可以支持可变参数,例如eval(String ... strs)。 返回表的类型由TableFunction的通用类型确定。 评估方法使用受保护的collect(T)方法发出输出行。
在Table API中,表函数与.joinLateral或.leftOuterJoinLateral一起使用。 joinLateral运算符(叉号)将外部表(运算符左侧的表)中的每一行与表值函数(位于运算符的右侧)产生的所有行进行连接。 leftOuterJoinLateral运算符将外部表(运算符左侧的表)中的每一行与表值函数(位于运算符的右侧)产生的所有行连接起来,并保留表函数返回的外部行 一个空桌子。 在SQL中,使用带有CROSS JOIN和LEFT JOIN且带有ON TRUE连接条件的LATERAL TABLE(<TableFunction>)(请参见下面的示例)。
下面的示例演示如何定义表值函数,如何在TableEnvironment中注册表值函数以及如何在查询中调用它。 请注意,可以在注册表函数之前通过构造函数对其进行配置:
// The generic type "(String, Int)" determines the schema of the returned table as (String, Integer).
class Split(separator: String) extends TableFunction[(String, Int)] {
def eval(str: String): Unit = {
// use collect(...) to emit a row.
str.split(separator).foreach(x => collect((x, x.length)))
}
} val tableEnv = BatchTableEnvironment.create(env)
val myTable = ... // table schema: [a: String] // Use the table function in the Scala Table API (Note: No registration required in Scala Table API).
val split = new Split("#")
// "as" specifies the field names of the generated table.
myTable.joinLateral(split('a) as ('word, 'length)).select('a, 'word, 'length)
myTable.leftOuterJoinLateral(split('a) as ('word, 'length)).select('a, 'word, 'length) // Register the table function to use it in SQL queries.
tableEnv.registerFunction("split", new Split("#")) // Use the table function in SQL with LATERAL and TABLE keywords.
// CROSS JOIN a table function (equivalent to "join" in Table API)
tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT a, word, length FROM MyTable, LATERAL TABLE(split(a)) as T(word, length)")
// LEFT JOIN a table function (equivalent to "leftOuterJoin" in Table API)
tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT a, word, length FROM MyTable LEFT JOIN LATERAL TABLE(split(a)) as T(word, length) ON TRUE")
重要说明:不要将TableFunction实现为Scala对象。Scala对象是单例对象,将导致并发问题。
请注意,POJO类型没有确定的字段顺序。因此,您不能使用 AS 来重命名表函数返回的POJO字段。
默认情况下,TableFunction的结果类型由Flink的自动类型提取工具确定。 这对于基本类型和简单的POJO非常有效,但是对于更复杂,自定义或复合类型可能是错误的。 在这种情况下,可以通过重写TableFunction#getResultType()并返回其TypeInformation来手动指定结果的类型。
下面的示例显示一个TableFunction的示例,该函数返回需要显式类型信息的Row类型。 我们通过重写TableFunction#getResultType()来定义返回的表类型应为RowTypeInfo(String,Integer)。
class CustomTypeSplit extends TableFunction[Row] {
def eval(str: String): Unit = {
str.split(" ").foreach({ s =>
val row = new Row(2)
row.setField(0, s)
row.setField(1, s.length)
collect(row)
})
}
override def getResultType: TypeInformation[Row] = {
Types.ROW(Types.STRING, Types.INT)
}
}
聚合函数
用户定义的聚合函数(UDAGG)将表(具有一个或多个属性的一个或多个行)聚合到一个标量值。
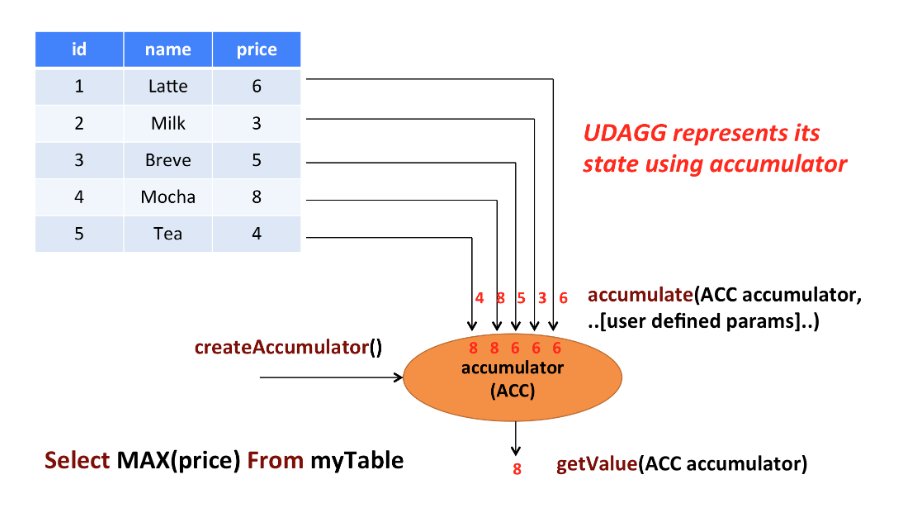
上图显示了聚合的示例。 假设您有一个包含饮料数据的表。 该表由三列组成,即ID,name和price 以及5行。 假设您需要在表格中找到所有饮料中最高的price ,即执行max()汇总。 您将需要检查5行中的每行,结果将是单个数字值。
用户定义的聚合函数通过扩展AggregateFunction类来实现。 AggregateFunction的工作原理如下。 首先,它需要一个累加器,它是保存聚合中间结果的数据结构。 通过调用AggregateFunction的createAccumulator()方法来创建一个空的累加器。 随后,为每个输入行调用该函数的accumulate()方法以更新累加器。 处理完所有行后,将调用该函数的getValue()方法以计算并返回最终结果。
每种方法都必须使用以下方法AggregateFunction:
createAccumulator()accumulate()getValue()
Flink的类型提取工具可能无法识别复杂的数据类型,例如,如果它们不是基本类型或简单的POJO。 因此,类似于ScalarFunction和TableFunction,AggregateFunction提供了一些方法来指定结果类型的TypeInformation(通过AggregateFunction#getResultType())和累加器的类型(通过AggregateFunction#getAccumulatorType())。
除上述方法外,还有一些可选择性实现的约定方法。 尽管这些方法中的某些方法使系统可以更有效地执行查询,但对于某些用例,其他方法是必需的。 例如,如果聚合功能应在会话组窗口的上下文中应用,则必须使用merge()方法(观察到“连接”它们的行时,两个会话窗口的累加器必须合并)。
AggregateFunction根据使用情况,需要以下方法:
retract()在有界OVER窗口上进行聚合是必需的。merge()许多批处理聚合和会话窗口聚合是必需的。resetAccumulator()许多批处理聚合是必需的。
必须将AggregateFunction的所有方法声明为public,而不是静态的,并且必须完全按上述名称命名。 方法createAccumulator,getValue,getResultType和getAccumulatorType在AggregateFunction抽象类中定义,而其他方法则是协定方法。 为了定义聚合函数,必须扩展基类org.apache.flink.table.functions.AggregateFunction并实现一个(或多个)累积方法。 累加的方法可以重载不同的参数类型,并支持可变参数。
下面给出了AggregateFunction的所有方法的详细文档。
/**
* Base class for user-defined aggregates and table aggregates.
*
* @tparam T the type of the aggregation result.
* @tparam ACC the type of the aggregation accumulator. The accumulator is used to keep the
* aggregated values which are needed to compute an aggregation result.
*/
abstract class UserDefinedAggregateFunction[T, ACC] extends UserDefinedFunction { /**
* Creates and init the Accumulator for this (table)aggregate function.
*
* @return the accumulator with the initial value
*/
def createAccumulator(): ACC // MANDATORY /**
* Returns the TypeInformation of the (table)aggregate function's result.
*
* @return The TypeInformation of the (table)aggregate function's result or null if the result
* type should be automatically inferred.
*/
def getResultType: TypeInformation[T] = null // PRE-DEFINED /**
* Returns the TypeInformation of the (table)aggregate function's accumulator.
*
* @return The TypeInformation of the (table)aggregate function's accumulator or null if the
* accumulator type should be automatically inferred.
*/
def getAccumulatorType: TypeInformation[ACC] = null // PRE-DEFINED
} /**
* Base class for aggregation functions.
*
* @tparam T the type of the aggregation result
* @tparam ACC the type of the aggregation accumulator. The accumulator is used to keep the
* aggregated values which are needed to compute an aggregation result.
* AggregateFunction represents its state using accumulator, thereby the state of the
* AggregateFunction must be put into the accumulator.
*/
abstract class AggregateFunction[T, ACC] extends UserDefinedAggregateFunction[T, ACC] { /**
* Processes the input values and update the provided accumulator instance. The method
* accumulate can be overloaded with different custom types and arguments. An AggregateFunction
* requires at least one accumulate() method.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which contains the current aggregated results
* @param [user defined inputs] the input value (usually obtained from a new arrived data).
*/
def accumulate(accumulator: ACC, [user defined inputs]): Unit // MANDATORY /**
* Retracts the input values from the accumulator instance. The current design assumes the
* inputs are the values that have been previously accumulated. The method retract can be
* overloaded with different custom types and arguments. This function must be implemented for
* datastream bounded over aggregate.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which contains the current aggregated results
* @param [user defined inputs] the input value (usually obtained from a new arrived data).
*/
def retract(accumulator: ACC, [user defined inputs]): Unit // OPTIONAL /**
* Merges a group of accumulator instances into one accumulator instance. This function must be
* implemented for datastream session window grouping aggregate and dataset grouping aggregate.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which will keep the merged aggregate results. It should
* be noted that the accumulator may contain the previous aggregated
* results. Therefore user should not replace or clean this instance in the
* custom merge method.
* @param its an [[java.lang.Iterable]] pointed to a group of accumulators that will be
* merged.
*/
def merge(accumulator: ACC, its: java.lang.Iterable[ACC]): Unit // OPTIONAL /**
* Called every time when an aggregation result should be materialized.
* The returned value could be either an early and incomplete result
* (periodically emitted as data arrive) or the final result of the
* aggregation.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which contains the current
* aggregated results
* @return the aggregation result
*/
def getValue(accumulator: ACC): T // MANDATORY /**
* Resets the accumulator for this [[AggregateFunction]]. This function must be implemented for
* dataset grouping aggregate.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which needs to be reset
*/
def resetAccumulator(accumulator: ACC): Unit // OPTIONAL /**
* Returns true if this AggregateFunction can only be applied in an OVER window.
*
* @return true if the AggregateFunction requires an OVER window, false otherwise.
*/
def requiresOver: Boolean = false // PRE-DEFINED
}
以下示例显示了怎么使用
- 定义一个
AggregateFunction计算给定列上的加权平均值 - 在
TableEnvironment中注册函数 - 在查询中使用该函数。
为了计算加权平均值,累加器需要存储所有累加数据的加权和和计数。 在我们的示例中,我们将一个WeightedAvgAccum类定义为累加器。 累加器由Flink的检查点机制自动备份,并在无法确保一次准确语义的情况下恢复。
我们的WeightedAvg AggregateFunction的accumulate()方法具有三个输入。 第一个是WeightedAvgAccum累加器,其他两个是用户定义的输入:输入值ivalue和输入iweight的权重。 尽管大多数聚合类型都不强制使用retract(),merge()和resetAccumulator()方法,但我们在下面提供了它们作为示例。 请注意,我们在Scala示例中使用了Java基本类型并定义了getResultType()和getAccumulatorType()方法,因为Flink类型提取不适用于Scala类型。
import java.lang.{Long => JLong, Integer => JInteger}
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.{Tuple1 => JTuple1}
import org.apache.flink.api.java.typeutils.TupleTypeInfo
import org.apache.flink.table.api.Types
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.AggregateFunction
/**
* Accumulator for WeightedAvg.
*/
class WeightedAvgAccum extends JTuple1[JLong, JInteger] {
sum = 0L
count = 0
}
/**
* Weighted Average user-defined aggregate function.
*/
class WeightedAvg extends AggregateFunction[JLong, CountAccumulator] {
override def createAccumulator(): WeightedAvgAccum = {
new WeightedAvgAccum
}
override def getValue(acc: WeightedAvgAccum): JLong = {
if (acc.count == 0) {
null
} else {
acc.sum / acc.count
}
}
def accumulate(acc: WeightedAvgAccum, iValue: JLong, iWeight: JInteger): Unit = {
acc.sum += iValue * iWeight
acc.count += iWeight
}
def retract(acc: WeightedAvgAccum, iValue: JLong, iWeight: JInteger): Unit = {
acc.sum -= iValue * iWeight
acc.count -= iWeight
}
def merge(acc: WeightedAvgAccum, it: java.lang.Iterable[WeightedAvgAccum]): Unit = {
val iter = it.iterator()
while (iter.hasNext) {
val a = iter.next()
acc.count += a.count
acc.sum += a.sum
}
}
def resetAccumulator(acc: WeightedAvgAccum): Unit = {
acc.count = 0
acc.sum = 0L
}
override def getAccumulatorType: TypeInformation[WeightedAvgAccum] = {
new TupleTypeInfo(classOf[WeightedAvgAccum], Types.LONG, Types.INT)
}
override def getResultType: TypeInformation[JLong] = Types.LONG
}
// register function
val tEnv: StreamTableEnvironment = ???
tEnv.registerFunction("wAvg", new WeightedAvg())
// use function
tEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT user, wAvg(points, level) AS avgPoints FROM userScores GROUP BY user")
表聚合函数
用户定义的表聚合函数(UDTAGG)将一个表(具有一个或多个属性的一个或多个行)聚合到具有多行和多列的结果表中。

上图显示了表聚合的示例。 假设您有一个包含饮料数据的表。 该表由三列组成,即ID,name 和 price 以及5行。 假设您需要在表格中找到所有饮料中 price 最高的前2个,即执行top2()表汇总。 您将需要检查5行中的每行,结果将是带有前2个值的表。
用户定义的表聚合功能通过扩展TableAggregateFunction类来实现。 TableAggregateFunction的工作原理如下。 首先,它需要一个累加器,它是保存聚合中间结果的数据结构。 通过调用TableAggregateFunction的createAccumulator()方法来创建一个空的累加器。 随后,为每个输入行调用该函数的accumulate()方法以更新累加器。 处理完所有行后,将调用该函数的emitValue()方法来计算并返回最终结果。
每种方法都必须使用以下方法TableAggregateFunction:
createAccumulator()accumulate()
Flink的类型提取工具可能无法识别复杂的数据类型,例如,如果它们不是基本类型或简单的POJO。 因此,类似于ScalarFunction和TableFunction,TableAggregateFunction提供了一些方法来指定结果类型的TypeInformation(通过TableAggregateFunction#getResultType())和累加器的类型(通过TableAggregateFunction#getAccumulatorType())。
除上述方法外,还有一些可选择性实现的约定方法。 尽管这些方法中的某些方法使系统可以更有效地执行查询,但对于某些用例,其他方法是必需的。 例如,如果聚合功能应在会话组窗口的上下文中应用,则必须使用merge()方法(观察到“连接”它们的行时,两个会话窗口的累加器必须合并)。
TableAggregateFunction根据使用情况,需要以下方法:
retract()在有界OVER窗口上进行聚合是必需的。merge()许多批处理聚合和会话窗口聚合是必需的。resetAccumulator()许多批处理聚合是必需的。emitValue()是批处理和窗口聚合所必需的。
TableAggregateFunction的以下方法用于提高流作业的性能:
emitUpdateWithRetract()用于发出在撤回模式下已更新的值。
对于emitValue方法,它根据累加器发出完整的数据。 以TopN为例,emitValue每次都会发出所有前n个值。 这可能会给流作业带来性能问题。 为了提高性能,用户还可以实现emmitUpdateWithRetract方法来提高性能。 该方法以缩回模式增量输出数据,即,一旦有更新,我们必须先缩回旧记录,然后再发送新的更新记录。 如果所有方法都在表聚合函数中定义,则该方法将优先于emitValue方法使用,因为emitUpdateWithRetract被认为比emitValue更有效,因为它可以增量输出值。
必须将TableAggregateFunction的所有方法声明为public,而不是静态的,并且其命名必须与上述名称完全相同。 方法createAccumulator,getResultType和getAccumulatorType在TableAggregateFunction的父抽象类中定义,而其他方法则是契约方法。 为了定义表聚合函数,必须扩展基类org.apache.flink.table.functions.TableAggregateFunction并实现一个(或多个)累积方法。 累加的方法可以重载不同的参数类型,并支持可变参数。
下面给出了TableAggregateFunction的所有方法的详细文档。
/**
* Base class for user-defined aggregates and table aggregates.
*
* @tparam T the type of the aggregation result.
* @tparam ACC the type of the aggregation accumulator. The accumulator is used to keep the
* aggregated values which are needed to compute an aggregation result.
*/
abstract class UserDefinedAggregateFunction[T, ACC] extends UserDefinedFunction { /**
* Creates and init the Accumulator for this (table)aggregate function.
*
* @return the accumulator with the initial value
*/
def createAccumulator(): ACC // MANDATORY /**
* Returns the TypeInformation of the (table)aggregate function's result.
*
* @return The TypeInformation of the (table)aggregate function's result or null if the result
* type should be automatically inferred.
*/
def getResultType: TypeInformation[T] = null // PRE-DEFINED /**
* Returns the TypeInformation of the (table)aggregate function's accumulator.
*
* @return The TypeInformation of the (table)aggregate function's accumulator or null if the
* accumulator type should be automatically inferred.
*/
def getAccumulatorType: TypeInformation[ACC] = null // PRE-DEFINED
} /**
* Base class for table aggregation functions.
*
* @tparam T the type of the aggregation result
* @tparam ACC the type of the aggregation accumulator. The accumulator is used to keep the
* aggregated values which are needed to compute an aggregation result.
* TableAggregateFunction represents its state using accumulator, thereby the state of
* the TableAggregateFunction must be put into the accumulator.
*/
abstract class TableAggregateFunction[T, ACC] extends UserDefinedAggregateFunction[T, ACC] { /**
* Processes the input values and update the provided accumulator instance. The method
* accumulate can be overloaded with different custom types and arguments. A TableAggregateFunction
* requires at least one accumulate() method.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which contains the current aggregated results
* @param [user defined inputs] the input value (usually obtained from a new arrived data).
*/
def accumulate(accumulator: ACC, [user defined inputs]): Unit // MANDATORY /**
* Retracts the input values from the accumulator instance. The current design assumes the
* inputs are the values that have been previously accumulated. The method retract can be
* overloaded with different custom types and arguments. This function must be implemented for
* datastream bounded over aggregate.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which contains the current aggregated results
* @param [user defined inputs] the input value (usually obtained from a new arrived data).
*/
def retract(accumulator: ACC, [user defined inputs]): Unit // OPTIONAL /**
* Merges a group of accumulator instances into one accumulator instance. This function must be
* implemented for datastream session window grouping aggregate and dataset grouping aggregate.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which will keep the merged aggregate results. It should
* be noted that the accumulator may contain the previous aggregated
* results. Therefore user should not replace or clean this instance in the
* custom merge method.
* @param its an [[java.lang.Iterable]] pointed to a group of accumulators that will be
* merged.
*/
def merge(accumulator: ACC, its: java.lang.Iterable[ACC]): Unit // OPTIONAL /**
* Called every time when an aggregation result should be materialized. The returned value
* could be either an early and incomplete result (periodically emitted as data arrive) or
* the final result of the aggregation.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which contains the current
* aggregated results
* @param out the collector used to output data
*/
def emitValue(accumulator: ACC, out: Collector[T]): Unit // OPTIONAL /**
* Called every time when an aggregation result should be materialized. The returned value
* could be either an early and incomplete result (periodically emitted as data arrive) or
* the final result of the aggregation.
*
* Different from emitValue, emitUpdateWithRetract is used to emit values that have been updated.
* This method outputs data incrementally in retract mode, i.e., once there is an update, we
* have to retract old records before sending new updated ones. The emitUpdateWithRetract
* method will be used in preference to the emitValue method if both methods are defined in the
* table aggregate function, because the method is treated to be more efficient than emitValue
* as it can outputvalues incrementally.
*
* @param accumulator the accumulator which contains the current
* aggregated results
* @param out the retractable collector used to output data. Use collect method
* to output(add) records and use retract method to retract(delete)
* records.
*/
def emitUpdateWithRetract(accumulator: ACC, out: RetractableCollector[T]): Unit // OPTIONAL /**
* Collects a record and forwards it. The collector can output retract messages with the retract
* method. Note: only use it in `emitRetractValueIncrementally`.
*/
trait RetractableCollector[T] extends Collector[T] { /**
* Retract a record.
*
* @param record The record to retract.
*/
def retract(record: T): Unit
}
}
以下示例显示了怎么使用
- 定义一个
TableAggregateFunction用于计算给定列的前2个值 - 在
TableEnvironment中注册函数 - 在Table API查询中使用该函数(Table API仅支持TableAggregateFunction)。
要计算前2个值,累加器需要存储所有已累加数据中的最大2个值。 在我们的示例中,我们定义了一个Top2Accum类作为累加器。 累加器由Flink的检查点机制自动备份,并在无法确保一次准确语义的情况下恢复。
我们的Top2 TableAggregateFunction的accumulate()方法有两个输入。 第一个是Top2Accum累加器,另一个是用户定义的输入:输入值v。尽管merge()方法对于大多数表聚合类型不是强制性的,但我们在下面提供了示例。 请注意,我们在Scala示例中使用了Java基本类型并定义了getResultType()和getAccumulatorType()方法,因为Flink类型提取不适用于Scala类型。
import java.lang.{Integer => JInteger}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.Types
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.TableAggregateFunction
/**
* Accumulator for top2.
*/
class Top2Accum {
var first: JInteger = _
var second: JInteger = _
}
/**
* The top2 user-defined table aggregate function.
*/
class Top2 extends TableAggregateFunction[JTuple2[JInteger, JInteger], Top2Accum] {
override def createAccumulator(): Top2Accum = {
val acc = new Top2Accum
acc.first = Int.MinValue
acc.second = Int.MinValue
acc
}
def accumulate(acc: Top2Accum, v: Int) {
if (v > acc.first) {
acc.second = acc.first
acc.first = v
} else if (v > acc.second) {
acc.second = v
}
}
def merge(acc: Top2Accum, its: JIterable[Top2Accum]): Unit = {
val iter = its.iterator()
while (iter.hasNext) {
val top2 = iter.next()
accumulate(acc, top2.first)
accumulate(acc, top2.second)
}
}
def emitValue(acc: Top2Accum, out: Collector[JTuple2[JInteger, JInteger]]): Unit = {
// emit the value and rank
if (acc.first != Int.MinValue) {
out.collect(JTuple2.of(acc.first, 1))
}
if (acc.second != Int.MinValue) {
out.collect(JTuple2.of(acc.second, 2))
}
}
}
// init table
val tab = ...
// use function
tab
.groupBy('key)
.flatAggregate(top2('a) as ('v, 'rank))
.select('key, 'v, 'rank)
以下示例显示如何使用emitUpdateWithRetract方法仅发出更新。 为了仅发出更新,在我们的示例中,累加器同时保留了旧的和新的前2个值。 注意:如果topN的N大,则保留旧值和新值都可能无效。 解决这种情况的一种方法是将输入记录以累加方法存储到累加器中,然后在emitUpdateWithRetract中执行计算。
import java.lang.{Integer => JInteger}
import org.apache.flink.table.api.Types
import org.apache.flink.table.functions.TableAggregateFunction
/**
* Accumulator for top2.
*/
class Top2Accum {
var first: JInteger = _
var second: JInteger = _
var oldFirst: JInteger = _
var oldSecond: JInteger = _
}
/**
* The top2 user-defined table aggregate function.
*/
class Top2 extends TableAggregateFunction[JTuple2[JInteger, JInteger], Top2Accum] {
override def createAccumulator(): Top2Accum = {
val acc = new Top2Accum
acc.first = Int.MinValue
acc.second = Int.MinValue
acc.oldFirst = Int.MinValue
acc.oldSecond = Int.MinValue
acc
}
def accumulate(acc: Top2Accum, v: Int) {
if (v > acc.first) {
acc.second = acc.first
acc.first = v
} else if (v > acc.second) {
acc.second = v
}
}
def emitUpdateWithRetract(
acc: Top2Accum,
out: RetractableCollector[JTuple2[JInteger, JInteger]])
: Unit = {
if (acc.first != acc.oldFirst) {
// if there is an update, retract old value then emit new value.
if (acc.oldFirst != Int.MinValue) {
out.retract(JTuple2.of(acc.oldFirst, 1))
}
out.collect(JTuple2.of(acc.first, 1))
acc.oldFirst = acc.first
}
if (acc.second != acc.oldSecond) {
// if there is an update, retract old value then emit new value.
if (acc.oldSecond != Int.MinValue) {
out.retract(JTuple2.of(acc.oldSecond, 2))
}
out.collect(JTuple2.of(acc.second, 2))
acc.oldSecond = acc.second
}
}
}
// init table
val tab = ...
// use function
tab
.groupBy('key)
.flatAggregate(top2('a) as ('v, 'rank))
.select('key, 'v, 'rank)
实施UDF的最佳做法
Table API和SQL代码生成在内部尝试尽可能多地使用原始值。 用户定义的函数可能会通过对象创建,转换和装箱带来很多开销。 因此,强烈建议将参数和结果类型声明为基本类型,而不是其框内的类。 Types.DATE和Types.TIME也可以表示为int。 Types.TIMESTAMP可以表示为long。
我们建议用户定义的函数应使用Java而不是Scala编写,因为Scala类型对Flink的类型提取器构成了挑战。
将UDF与 Runtime 集成
有时,用户定义的函数可能有必要在实际工作之前获取全局运行时信息或进行一些设置/清理工作。 用户定义的函数提供可被覆盖的open()和close()方法,并提供与DataSet或DataStream API的RichFunction中的方法相似的功能。
open()方法在评估方法之前被调用一次。 最后一次调用评估方法之后调用close()方法。
open()方法提供一个FunctionContext,其中包含有关在其中执行用户定义的函数的上下文的信息,例如度量标准组,分布式缓存文件或全局作业参数。
通过调用FunctionContext的相应方法可以获得以下信息:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
getMetricGroup() |
此并行子任务的度量标准组。 |
getCachedFile(name) |
分布式缓存文件的本地临时文件副本。 |
getJobParameter(name, defaultValue) |
与给定键关联的全局作业参数值。 |
以下示例片段显示了如何FunctionContext在标量函数中使用它来访问全局job参数:
object hashCode extends ScalarFunction {
var hashcode_factor = 12
override def open(context: FunctionContext): Unit = {
// access "hashcode_factor" parameter
// "12" would be the default value if parameter does not exist
hashcode_factor = context.getJobParameter("hashcode_factor", "12").toInt
}
def eval(s: String): Int = {
s.hashCode() * hashcode_factor
}
}
val tableEnv = BatchTableEnvironment.create(env)
// use the function in Scala Table API
myTable.select('string, hashCode('string))
// register and use the function in SQL
tableEnv.registerFunction("hashCode", hashCode)
tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT string, HASHCODE(string) FROM MyTable")
欢迎关注Flink菜鸟公众号,会不定期更新Flink(开发技术)相关的推文

【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL — 用户定义函数的更多相关文章
- 【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL — Hive —— Hive 函数
本文翻译自官网:Hive Functions https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/table/hive/h ...
- 【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL — 内置函数
本文翻译自官网:Built-In Functions https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/table/fu ...
- Flink Table Api & SQL 翻译目录
Flink 官网 Table Api & SQL 相关文档的翻译终于完成,这里整理一个安装官网目录顺序一样的目录 [翻译]Flink Table Api & SQL —— Overv ...
- 【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL — 性能调优 — 流式聚合
本文翻译自官网:Streaming Aggregation https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/table ...
- 【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL — SQL客户端Beta 版
本文翻译自官网:SQL Client Beta https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/table/sqlCl ...
- 【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL —— Overview
本文翻译自官网:https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/table/ Flink Table Api & ...
- 【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL —— 概念与通用API
本文翻译自官网:https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/table/common.html Flink Tabl ...
- 【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL —— 数据类型
本文翻译自官网:https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/table/types.html Flink Table ...
- 【翻译】Flink Table Api & SQL —Streaming 概念 ——在持续查询中 Join
本文翻译自官网 : Joins in Continuous Queries https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9 ...
随机推荐
- openssl获取ssl证书,配置https
- node基础学习——操作文件系统fs
操作文件系统fs 1.在Node.js中,使用fs模块来实现所有有关文件及目录的创建.写入及删除.在fs模块中,所有对文件及目录的操作都可以使用同步与异步两种方法,具有Sync后缀的方法均为同步方法. ...
- 【7-9 有重复的数据I (20 分)】【此题卡输入,需要自己写个输入挂】
参考一个博客的输入挂,先挂在此处,以备以后使用. import java.io.*; import java.util.*; import java.math.*; public class Main ...
- CentOS7怎样安装Redis4.0.12
一.安装 yum -y install tcl安装相关依赖 mkdir /usr/local/redis创建redis安装目录 cd /usr/local/redis 进入redis目录 wget h ...
- Codeforces B. Mouse Hunt(强连通分解缩点)
题目描述: Mouse Hunt time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
- poj3974 Palindrome(Manacher最长回文)
之前用字符串hash+二分过了,今天刚看了manacher拿来试一试. 这manacher也快太多了%%% #include <iostream> #include <cstring ...
- JQuery系列(2) - 事件处理
JQuery事件绑定 (1)on方法 on方法是jQuery事件绑定的统一接口.后面介绍的事件绑定的那些简便方法,其实都是on方法的简写形式. $('li').on('click', function ...
- Oracle两表关联,只取B表的第一条记录
背景: A表.B表两表关联,关联出来的结果里B表有不止一条,需求是只要B表结果中的某一条(按某字段排序) 首先想到了直接写个带排序的子查询去匹配外围的值,从这个结果集中只要第一条,但是经过验证发现, ...
- intellij高亮字体背景颜色
https://blog.csdn.net/aosica321/article/details/52956419 https://blog.csdn.net/lxzpp/article/details ...
- 关于AndroidStudio的apk打包遇到的问题记录
12月份末尾,想来个总结,主要是得记一些重要的. 首先就得是AndroidStudi内的apk打包,就是弄当前项目app的安装包出来. 下面就说下具体步骤和注意问题. 首先 : 看到AndroidSt ...
