深入解析ES6中的promise

作者 | Jeskson来源 | 达达前端小酒馆
什么是Promise
Promise对象是用于表示一个异步操作的最终状态(完成或失败)以及其返回的值。
什么是同步,异步
同步任务会阻塞程序的执行,如alert,for
异步任务不会阻塞程序的执行,如setTimeou
使用Promise,then,catch,finally
Promise.all 和 Promise.race
Promise.resolve 和 Promise.reject
回调与Promise
回调函数,用于请求数据
function backFunction(fn) {
setTimeout(function() {
fn && fn();
}, 1000);
}
// 调用
backFunction(function() {
console.log(1); // 1
backFunction(function() {
console.log(2); // 2
backFunction(function() {
console.log(3); // 3
});
});
});Promise
function d() {
return new Promise(resolve = {
setTimeout(function() {
resolve(); // resolve成功的时候要做的事情
},1000);
// 1秒后调用resolve(),它是一个函数
})
}
d()
.then(function() {
console.log(1);
return d(); // Promise实例
})
.then(function() {
console.log(2);
return d(); // Promise实例
}).then(function() {
console.log(3);
});对比回调
// 动画
function moveTo(el, x, y, fn) {
el.style.transform = `translate(${x}px, ${y}px)`;
setTimeout(function() {
fn && fn();
},1000);
}
let el = document.querySelector('div');
document.querySelector('button').addeventListener('click', e
moveTo(el, 100, 100, function() {
console.log(1);
moveTo(el, 200, 200, function() {
console.log(2);
});
})
});// promise
function moveTo(el,x,y) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
el.style.transform = `translate(${x}px, ${y}px)`;
setTimeout(function() {
resolve();
},1000);
});
}
document.querySelector('button').addEventListener('click', e=>{
moveTo(el,100,100)
.then(function() {
console.log('da');
return moveTo(el, 200, 200);
})
.then(function() {
console.log('da2');
}).then(function() {
console.log('da2');
});
});信任问题
// 使用第三方库 回调
function method(fn) {
// 回调
setTimeout(function() {
// 回调
fn && fn();
// 有可以有bug,被多调用一次
fn && fn();
},1000);
}
// promise一旦被调用,成功或者是失败后,就不能再被修改
function method() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(function() {
//成功
resolve();
// 再调用就不会执行
resolve();
},1000);
});
}// 控制反转
function method(fn) {
setTimeout(function() {
// 执行回调
fn && fn.call({a:1, b:2)};
// 改变指向
},1000);
}
function method(fn) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
},1000);
});
}错误处理
then(resolve, reject)then方法中的第二个回调,是失败的时候要做的事情
catch使用实例的then方法,可以捕获错误
finally不论成功与否,finally中的内容一定会执行
function fn(val) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(val) {
resolve(); // 成功的时候
} else {
reject(); // 失败的时候
}
});
}fn(false)
.then( () => {
console.log("成功");
}, () => {
console.log("失败");
})
function fn(val) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(val) {
resolve(); // 成功的时候
} else {
reject('404'); // 失败的时候
}
});
}
fn(false)
.then( () => {
console.log("成功");
}, e => {
console.log(e);
})
promise 中resolve只能传递一个参数,如下:
function fn(val) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(val) {
resolve({name: 'da'}); // 成功的时候
} else {
reject('404'); // 失败的时候
}
});
}
fn(true)
.then( dada => {
console.log(data);
}, e => {
console.log(e);
})catch会捕获错误,如果在回调中没有对错误进行处理
fn(true)
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
return fn(false);
})
.then( () => {
console.log('da'); // 不会执行,没处理错误
})
.then( () => {
})
.catch(e => {
console.log(e);
return fn(false);
}); // 直接输出到这
不能保证catch被执行如果没有对失败做出处理,会报错
fn(true)
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
return fn(false);
})
.catch(e=> {
// 捕获错误
console.log(e);
return fn(false);
})
.finally( () => {
console.log(100);
});Promise的三种状态
pending为进行中的状态,fulfilled为成功的状态,rejected为失败的状态。状态的改变时不可返的,一旦决议就不能修改(决议,状态的改变为决议),状态只能从pending到fulfilled,或者,从pending到rejected。
Promise.all方法可以把多个promise的实例包装成一个新的promise实例
Promise.all( [promise1, promise2] ) : Promise
数组中,如果promise都为true,则返回为true,决议为成功
如果数组中有一个为promise,那么返回的是false,决议为失败
如果是一个空数组,那么返回为true,决议为成功模式多个请求的数据
function getData1() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log('第一条数据加载成功');
resolve('data1');
},1000);
});
}
function getData2() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log('第二条数据加载成功');
resolve('data2');
},1000);
});
}
function getData3() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log('第三条数据加载成功');
resolve('data3'); // 改为 reject('err')
},1000);
});
}let p = Promise.all( [getData1(), getData2(), getData3()] );
p.then(arr => {
console.log(arr);
});
// 失败
p.then(arr => {
console.log(arr);
}, e => {
console.log(e);
});
let p = Promise.all([]); // 决议为成功
p.then( () => {
console.log(`da`);
}, e => {
console.log(e);
});第一条数据加载成功
第二条数据加载成功
第三条数据加载成功不用Promise.all
let count = 0;
function getData1() {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log('第一条数据加载成功');
count ;
func();
},1000);
}
function getData2() {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log('第二条数据加载成功');
count ;
func();
},1000);
}
function getData3() {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log('第三条数据加载成功');
count ;
func();
},1000);
}
function getData4() {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log('第四条数据加载成功');
count ;
func();
},1000);
}
// 写一个方法:
function func() {
if(count < 4)return;
console.log('全部拿到了');
}调用
getData2();
getData3();
getData4();
let err = false;
function getData1() {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log('第一条数据加载成功');
if(status) err = true;
count ;
func();
},1000);
}
function func() {
if(count < 4)return;
console.log('全部拿到了');
if(err) {
// ...
}
}Promise.race()
Promise.race([promise1, promise2]) : Promiselet p = Promise.race([getData1(), getData2(),getData3()]);
p.then (data=>{
console.log(data);
})let flag = false;
function func(data) {
if(flag) return
flag = true;
console.log(data);
}
function getData1() {
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("第一条数据加载成功");
func({name: 'da'});
},500);
}
function getData2() {
setTimeout( () => {
console.log("第二条数据加载成功");
func({name: 'dada'});
}, 1000);
}
getData1();
getData2();
第一条数据加载成功
{name: 'da'}
第二条数据加载成功Promise.resolve与Promise.reject
Promise.resolve() 与 Promise.reject()
// Promise.resolve
传递一个普通的值
let p1 = new Promise(resolve => {
resolve('成功!');
});
let p2 = Promise.resolve('成功!');
// 传递一个promise实例
let pro = new Promise(resolve => {
resolve('da');
});
let p = Promise.resolve(pro);
p.then(data => void console.log(data));let obj = {
then (cb) {
console.log('da');
da('dada');
},
method() {
console.log('coding');
}
}
// 立即执行
Promise.resolve(obj).then(data => {
console.log(data);
});Promise异步:
console.log(1);
let p = new Promise(resolve => {
console.log(2);
resolve();
console.log(3);
});
console.log(4);
p.then(()=>{
console.log(5);
});
console.log(6);
// 123465
Promise改善了传统回调造成的代码难维护,控制反转等问题,promise是异步的,如果all接收的是空数组,马上会被决议为成功,如果race接受的是空数组,那么会被永远挂起,无限捕获错误问题。
resove和reject方法:
如果接收的是普通的值,那么就会立即决议为成功,并填充这个值,如果接收的是一个promise实例,那么返回这个promise实例,如果接收的是个thenable对象,则会把它包装成promise对象,并立即执行这个对象的then方法,reject会产生一个决议失败的promise并直接传递值。
JavaScript/ES6 Promise
JavaScript的Promise代表一个操作的结果还没有结果,就是如网络请求操作,当我们从某个数据源获取数据的时候,没有办法确定它什么时候能够返回,接受到响应。
Promise提供标准
doSomething()
.then(doSomethingElse)
.catch(handleError)
.then(doMore)
.then(doFinally)
.catch(handleAnotherError)创建Promise
一个Promise使用Promise构造器创建,接受两个参数resolve,reject
var promise = new Promise( function(resolve, reject) {
// new Promise resolve() reject()
}
XMLHttpRequest的promise版本:
function get(url) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
var req = new XMLHttpRequest();
req.open('GET', url);
req.onload = function() {
if(req.status == 200) {
resolve(req.response);
}else{
reject(Error(req.statusText));
}
};
req.onerror = function() {
reject(Error("Network Error"));
};
req.send();
});
}使用Promise
get(url)
.then(function(response) {
},function(err) {
})处理错误:
get(url)
.then(function(response){
}, undefined)
.then(undefined, function(err){
})get(url)
.then(function(response){
})
.catch(function(err){
})链式
get(url)
.then(function(response){
response = JSON.parse(response);
var secondURL = response.data.url
return get(secondURL);
})
.then(function(response){
response = JSON.parse(response);
var thirdURL = response.data.url
return get(thirdURL);
})
.catch(function(err){
handleError(err);
});并行执行Promise
Promise.all()方法每个promise数组成为则决议为成功,如果数组中有任意一个promise为失败则决议为失败。
任务一,任务二,任务三,.then() -> success 任务成功
ES6
Promise对象用于表示一个异步操作的最终状态,以及其返回的值。
语法:
new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
});几种状态:
pending初始状态,既不是成功,也不是失败状态;fulfilled意味着操作成功完成;rejected意味着操作失败。
pending状态的Promise对象可能会触发filfilled状态,并传递一个值给响应的状态处理方法,也可能触发失败状态rejected并传递失败信息。
Promise.all(iterable)
这个方法返回一个新的promise对象,该promise对象在itearable参数中,当里面所有的的promise对象决议成功的时候才触发成功,否则里面如何一个promise对象决议失败的时候,立即触发promise对象的失败。
Promise.all方法常用于处理多个promise对象的状态集合。
Promise.race(iterable)
当iterable参数里的任意一个子promise被决议成功或者是决议失败后,父promise会用子promise的成功返回值,或是失败返回。
Promise.reject(reason)
返回一个状态为失败的promise对象,将给定的失败信息传递给对应的处理方法。
Promise.resolve(value)
返回一个状态为失败的promise对象,将给定的失败信息传递给对应的处理方法。
const myPromise = new Promise( (resolve, reject) => {
resolve('resolve'); // filfilled
reject('reject'); // rejected
});function myFunction(url) {
return new Promise( (resolve, reject) => {
xhr.open ("GET", url);
xhr.onload = () => resolve(xhr.responseText);
xhr.onerror = () => reject(xhr.statusText);
xhr.send();
});
};当异步代码执行成功的时候,会调用resolve(),当异步代码执行失败的时候,会调用reject()。
模拟异步代码:
setTimeout(function(){
resolve('成功');
},250);
});
myPromise.then(function(successMsg){
});ES6 Promise对象
Promise对象是异步编程的一种解决方案,语法上,Promise是一个对象,从它那可以获取异步操作的信息。
Promise的状态,promise异步操作有三种状态,pending(进行中),fulfilled(已成功),reject(已失败)。除了异步操作的结果,任何其他操作都是无法改变这个状态。
const p1 = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
resolve('success1');
resolve('success2');
});
const p2 = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
resolve('success3');
reject('reject');
});
p1.then(function(value){
console.log(value); // success1
});
p2.then(function(value){
console.log(value); // success3
});缺点,一旦建立Promise就会立即执行,无法中途取消,如果不设置回调函数,Promise内部会抛出错误,不会反应到外部。
then方法,接收两个函数作为参数。
第一个参数是 Promise 执行成功时的回调,第二个参数是 Promise 执行失败时的回调,两个函数只会有一个被调用。
const p = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
resolve('success');
});
p.then(function(value){
console.log(value);
});
console.log('first');
// first
// successconst p = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
resolve(1);
}).then(function(value){ // 第一个then // 1
console.log(value);
return value * 2;
}).then(function(value){ // 第二个then // 2
console.log(value);
}).then(function(value){ // 第三个then // undefined
console.log(value);
return Promise.resolve('resolve');
}).then(function(value){ // 第四个then // resolve
console.log(value);
return Promise.reject('reject');
}).then(function(value){ // 第五个then //reject:reject
console.log('resolve:' value);
}, function(err) {
console.log('reject:' err);
});
then方法将返回一个resolved或是rejected状态的Promise对象用于链式调用。
热Promise
在JavaScript中,所有代码都是单线程的,也就是同步执行的,promise就是为了提供一个解决方案的异步编程。
promise的特点:只有异步操作可以决定当前处于的状态,并且任何其他操作无法改变这个状态;一旦状态改变,就不会在变。
状态改变的过程:从pending变为fulfilled和从pending变为rejected,状态改变后,就不会在改变了,这就叫已定型resolved
用法:
Promise对象是由关键字new及其构造函数来创建的。
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// do something here ...
if (success) {
resolve(value); // fulfilled
} else {
reject(error); // rejected
}
}); 函数接收两个函数作为参数,分别是resolve和reject,当异步操作执行成功后,会将异步操作的结果作为参数传入resolve函数并执行,此时的状态由Promise状态从pending变为fulfilled;而失败会将异步操作的错误作为参数传入reject函数并执行,此时Promise对象状态从pending变为rejected。
通过then方法,将指定resolved状态和rejected状态的回调函数。
promise.then(function(value) {
// success
}, function(error) {
// failure
});Promise.all(iterable),iterable必须是一个可以迭代的对象,如Array
返回值为一个新的Promise实例。
var p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 1000, 'one');
});
var p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 2000, 'two');
});
var p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 3000, 'three');
});
var p4 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject('p4 reject!');
});
var p5 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject('p5 reject!');
});
Promise.all([p1, p2, p3, p4, p5]).then(values => {
console.log(values);
}, reason => {
console.log(reason)
});
// p4 reject!Promise.race(iterable),同理,返回值为一个新的Promise实例。
返回的新实例状态,会是最先改变状态的那个实例,如果不是Promise实例,先用Promise.resolve方法,如果传入的迭代为空,则返回的Promise永久等待。
一个Promise实例原封不动的返回该实例;
var original = Promise.resolve('第二行');
var da = Promise.resolve(original);
da.then(function(value) {
console.log('value: ' value);
});
console.log('original === da ? ' (original === da));
// "original === da ? true"
// "value: 第二行"跟随这个thenable对象的,采用它的最终状态;
let thenable = {
then: function(resolve, reject) {
resolve(41);
}
}
let p = Promise.resolve(thenable);
p.then(function(value) {
console.log(value);
})
// 41直接将传入参数当最终结果,并返回一个新的Promise;
let p = Promsie.resolve(12);
p.then(function(number) {
console.log(number);
})
// 12直接返回一个resolved状态的Promise对象
let p = Promsie.resovle();
p.then(function() {
// do something
})Promise.prototype.then()
p.then(onResolve, onReject);
p.then(function(value) {
}, function(reason) {
});Promise.prototype. catch()
p.catch(onReject)
p.catch(function(reason) {
});
// bad
promise
.then(function(data) {
// success
}, function(err) {
// error
});
// good
promise
.then(function(data) {
// success
})
.catch(function(err) {
// error
});Promise.prototype. finally()
p.finally(onFinally);
p.finally(function() {
})该回调函数的不接受任何参数
promise是一个对象,代表一个异步操作,有三种状态,进行中,成功,失败。只有异步操作的结果的可以决定当前是哪种状态,promise一旦新建执行,就没有办法中途停止。
Promise.all方法用于将多个Promise实例,包装成一个新的Promise实例。只有当作为参数所有的promise函数运行完毕,才会执行.then回调。



//以往回调方式
函数1(function(){
//代码执行...(ajax1)
函数2(function(){
//代码执行...(ajax2)
函数3(function(data3){
//代码执行...(ajax3)
});
...
});
});
//Promise回调方式:链式调用,可构建多个回调函数。
promise().then().then()...catch()
//创建Promise实例
let promise = new Promise( (resolve, reject) => {
//执行相应代码 根据情况调用resolve或reject
...
})
//promise的then方法中执行回调
promise.then(function(){
//第一个参数是返回resolve时
},function(){
//第二个是回调返回reject时
}
}定时器调用
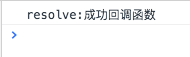
const promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
setTimeout(resolve,1000);
})
promise.then(function(){
console.log('resolve:成功回调函数')
},function(){
console.log('reject:失败回调函数')
})
传递参数:
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(reject,1000,'我是value值');
})
promise.then((value) => {
console.log('resolve:' value)
}).catch((value) => {
console.log('reject:' value)
})
//第一种,单个传值是无效的
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve,1000,'参数1','参数2');
})
promise.then((value1,value2) => {
console.log('value1:' value1) //value1:参数1
console.log('value2:' value2) //value2:undefined
}).catch((value) => {
console.log(value)
})
//第二种:数组传值
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve,1000,['参数1','参数2']);
})
promise.then((value1) => {
console.log('value1:' value1) //value1:参数1,参数2
}).catch((value) => {
console.log(value)
})
Promise.prototype.then方法:链式操作
getJSON("/posts.json").then(function(json) {
return json.post;
}).then(function(post) {
// proceed
});Promise.prototype.catch方法:捕捉错误
getJSON("/posts.json").then(function(posts) {
}).catch(function(error) {
console.log('发生错误!', error);
});Promise.all方法,Promise.race方法
var p = Promise.all([p1,p2,p3]);
var p = Promise.race([p1,p2,p3]);❤️ 不要忘记留下你学习的脚印 [点赞 收藏 评论]
作者Info:
【作者】:Jeskson
【原创公众号】:达达前端小酒馆。
【转载说明】:转载请说明出处,谢谢合作!~
关于目前文章内容即涉及前端,PHP知识点,如果有兴趣即可关注,很荣幸,能被您发现,真是慧眼识英!也感谢您的关注,在未来的日子里,希望能够一直默默的支持我,我也会努力写出更多优秀的作品。我们一起成长,从零基础学编程,将 Web前端领域、数据结构与算法、网络原理等通俗易懂的呈现给小伙伴。分享 Web 前端相关的技术文章、工具资源、精选课程、热点资讯。
若本号内容有做得不到位的地方(比如:涉及版权或其他问题),请及时联系我们进行整改即可,会在第一时间进行处理。
请点赞!因为你们的赞同/鼓励是我写作的最大动力!
欢迎关注达达的CSDN!
这是一个有质量,有态度的博客

深入解析ES6中的promise的更多相关文章
- ES6中的Promise用法
Node的产生,大大推动了Javascript这门语言在服务端的发展,使得前端人员可以以很低的门槛转向后端开发. 当然,这并不代表迸发成了全栈.全栈的技能很集中,绝不仅仅是前端会写一些HTML和一些交 ...
- es6中的promise对象
Promise是异步里面的一种解决方案,解决了回调嵌套的问题,es6将其进行了语言标准,同意了用法,提供了`promise`对象, promise对象有三种状态:pending(进行中) .Resol ...
- 深入理解 JavaScript 异步系列(3)—— ES6 中的 Promise
第一部分,Promise 加入 ES6 标准 原文地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/wangfupeng1988/p/6515855.html 未经作者允许不得转载! 从 jquer ...
- es6中的Promise学习
关于Promise Promise实例一旦被创建就会被执行 Promise过程分为两个分支:pending=>resolved和pending=>rejected Promise状态改变后 ...
- ES6中的Promise使用方法与总结
在javascript中,代码是单线程执行的,对于一些比较耗时的IO操作,都是通过异步回调函数来实现的. 但是这样会存在一个问题,当下一个的操作需要上一个操作的结果时,我们只能把代码嵌到上一个操作的回 ...
- [转]JS - Promise使用详解2(ES6中的Promise)
原文地址:https://www.hangge.com/blog/cache/detail_1638.html 2015年6月, ES2015(即 ECMAScript 6.ES6) 正式发布.其中 ...
- ES6中的Promise和Generator详解
目录 简介 Promise 什么是Promise Promise的特点 Promise的优点 Promise的缺点 Promise的用法 Promise的执行顺序 Promise.prototype. ...
- 理解ES6中的Promise
一.Promise的作用 在ajax请求数据的过程中,我们可以异步拿到我们想要的数据,然后在回调中做相应的数据处理. 这样做看上去并没有什么麻烦,但是如果这个时候,我们还需要做另外一个ajax请求,这 ...
- ES6中的promise
Promise 对象用于一个异步操作的最终完成(或失败)及其结果值的表示.简单点说,它就是用于处理异步操作的,异步处理成功了就执行成功的操作,异步处理失败了就捕获错误或者停止后续操作. 它的一般表示形 ...
随机推荐
- 对于 FFmpeg.NET 开源项目,我的更改
项目地址:https://github.com/cmxl/FFmpeg.NET 官方介绍 .NET wrapper for common ffmpeg tasks FFmpeg.NET provide ...
- Prometheus PromSQL 常用资源
Prometheus PromSQL 常用资源 PromSQL 使用 运算乘:*除:/加:+减:- 函数 sum() 函数:求出找到所有value的值 irate() 函数:统计平均速率 by (标签 ...
- CSS之flex布局和边框阴影
flex布局 main axis:主轴:cross axis:交叉轴 容器的子元素自动成为容器成员,成为flex 项目(item) flex容器属性 flex-direction 该属性决定主轴的 ...
- python 函数式编程 闭包,返回一个函数
参考链接:https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1016959663602400/1017434209254976 作业 #使用生成器 def createCounter( ...
- Django2.0版本以上与pymsql 不匹配问题以及解决方法
Django2.0版本以上与pymsql 不匹配问题以及解决方法 Django 2.0 以上 如果使用pymysql0.93,需要一下两步操作: # 1 第一次报错信息: File "D:\ ...
- Servlet处理(jQuery)Ajax请求
1. jQuery jQuery是一个JavaScript函数库,极大的简化了JavaScript编程,很容易学习.jQuery是目前最流行的开源js框架,并且提供了大量的扩展. 2. Aja ...
- JS--插件: 树Tree 开发与实现
日常在Web项目开发时,经常会碰到树形架构数据的显示,从数据库中获取数据,并且显示成树形.为了方便,我们可以写一个javascript的一个跨浏览器树控件,后续可以重复使用.本节分享一个自己开发的JS ...
- Vue – 基础学习(4):事件修饰符
Vue – 基础学习(3):事件修饰符
- Burp Suite渗透实战操作指南-上篇
Burp必备知识 在介绍功能之前有必要让大家了解一些burp的常用功能,以便在使用中更好的发挥麒麟臂的优势. 1.1 快捷键 很多人可能都没用过burp的快捷键吧,位置如下,不说话,如果不顺手可以自 ...
- App过大
最近开发中遇到一个报错信息 如下 Error:Cannot fit requested classes in a single dex file.Try supplying a main-dex li ...
