C语言强化——链表(1)
目录
- 链表的增删(不带头结点)
- 链表相关面试题
- 合并两个有序链表
- 单链表原地逆置
- 找出链表的倒数第四个节点
- 找出链表的中间节点
- 判断单链表是否有环
- 求链表交点
- 删除有序单链表中重复的元素
- 链表按奇数、偶数值拆分
链表的增删(不带头结点)
func.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node * next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode*, pNode*, int);
void listHeadInsert(pNode*, pNode*, int);
void listSortInsert(pNode*, pNode*, int);
void listDeleteNode(pNode*, pNode*, int);
void listPrint(pNode head);
func.c
#include "func.h"
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listHeadInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *head) {
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
}
void listSortInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
pNode pCur, pPre;
pCur = pPre = *head;
if (NULL == *head) {
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else if (pCur->val > val) { //头插
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
else {
while (pCur) { //中间插入
if (val < pCur->val) {
pPre->next = newNode;
newNode->next = pCur;
break;
}
pPre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
if (NULL == pCur) { //尾部插入
pPre->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
}
void listDeleteNode(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode pPre, pCur;
pPre = pCur = *head;
if (pCur == NULL) {
printf("list is empty!\n");
//printf("Delete failed , doesn't find the node!\n");
return;
}
else if (pCur->val == val) { //删除的是头部
*head = pCur->next;
}
else {
while (pCur) {
if (pCur->val == val) {
pPre->next = pCur->next;
break;
}
pPre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
if (pCur == *tail) {
*tail = pPre;
}
if (NULL == pCur) {
printf("Don't find the node!\n");
}
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
main.c
#include "func.h"
int main() {
printf("please input the key of node:\n");
pNode head = NULL, tail = NULL;
int val;
while (scanf("%d", &val) != EOF) {
//listTailInsert(&head, &tail, val);
//listHeadInsert(&head, &tail, val);
listSortInsert(&head, &tail, val);
}
while (printf("please input delete num:\n"), scanf("%d", &val) != EOF){
listDeleteNode(&head, &tail, val);
listPrint(head);
}
listPrint(head);
return 0;
}
链表相关面试题
- 合并两个有序链表
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1,sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
pNode head = NULL, tail = NULL;
void Union(pNode head1, pNode tail1, pNode head2, pNode tail2, int len1, int len2) {
int i = 0;
while (head1 && head2) {
if (head1->val >= head2->val) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, head2->val);
head2 = head2->next;
}
else {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, head1->val);
head1 = head1->next;
}
}
while (head1) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, head1->val);
head1 = head1->next;
}
while (head2) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, head2->val);
head2 = head2->next;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int a[5] = { 1,2,7,9,13 };
int b[8] = { 3,4,6,8,9,11,15,19 };
pNode head1, head2, tail1, tail2;
head1 = head2 = tail1 = tail2 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 5;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head1, &tail1, a[i]);
}
for (int i = 0;i < 8;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head2, &tail2, b[i]);
}
printf("两个有序链表:\n");
listPrint(head1);
listPrint(head2);
printf("合并后:\n");
Union(head1, tail1, head2, tail2, 5, 8);
listPrint(head);
return 0;
}

- 单链表原地逆置
(三指针法:用三个指针分别指向前三个节点,记为A、B、C,第一步让B的next指向A,A的next置为NULL,接着用循环,每次让B的next指向A,并且让三个指针同时往后移一个为止,直到c为NULL为止。)
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
pNode* reverse(pNode *head) {
pNode a = *head, b = (*head)->next, c = b->next;
b->next = a;
a->next = NULL;
while (c) {
a = b;
b = c;
c = c->next;
b->next = a;
}
return b;
}
int main() {
int a[5] = { 1,9,3,-2,7 };
pNode head, tail;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 5;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
pNode t = reverse(&head);
listPrint(t);
return 0;
}

- 找出链表的倒数第四个节点
(双指针法,让第一个结点先移动4次,第二个结点再出发)
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int a[10] = { 1,9,3,-2,7,99,6,-3,5,0 };
pNode head, tail, last;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
last = head;
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++) {
head = head->next;
}
while (head) {
head = head->next;
last = last->next;
}
printf("倒数第四个节点的值为%d\n", last->val);
return 0;
}

- 找出链表的中间节点
(双指针法:第一个指针每次移动2步,第二个指针每次移动1步)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void findMidNode(pNode head) {
pNode t1, t2;
t1 = t2 = head;
while (t2) {
t2 = t2->next;
t2 = t2->next;
t1 = t1->next;
}
printf("中间节点为%d\n", t1->val);
}
int main() {
int a[11] = { 1,9,3,-2,7,99,6,-3,5,0,-8 };
pNode head, tail, last;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
findMidNode(head);
return 0;
}

- 判断单链表是否有环
(双指针法,快指针每次移动2步,慢指针每次移动1步,若有环快指针必定会在一圈内与慢指针相遇)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int judge(pNode head) {
pNode slow, fast;
slow = fast = head;
while (fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
fast = fast->next;
if (slow == fast) {
printf("有环!\n");
return 0;
}
}
printf("无环!\n");
return 1;
}
int main() {
int a[11] = { 1,9,3,-2,7,99,6,-3,5,0,-8 };
int b[11] = { 1,9,3,-2,7,99,6,-3,5,0,-8 };
pNode head, tail;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
if (judge(head)) { //无环,输出链表
listPrint(head);
}
printf("------------------\n");
pNode head2, tail2;
head2 = tail2 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head2, &tail2, b[i]);
}
tail2->next = head2; //构造环
if (judge(head2)) { //有环不输出
listPrint(head2);
}
return 0;
}

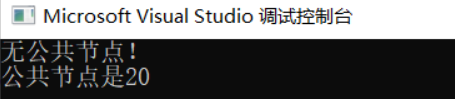
- 求两个链表的相交结点
(维护两个指针,先让长的链表的头指针往后移,直至和短链表的长度相同,再同时将两个链表的指针比较并后移)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) { //链表为空
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void findcommon(pNode head1, pNode head2, int len1, int len2) {
if (len1 > len2) {
while (len1 - len2) {
head1 = head1->next;
--len1;
}
}
else {
while (len2 - len1) {
head2 = head2->next;
--len2;
; }
}
while (head1&&head2) {
if (head1 == head2) {
printf("公共节点是%d\n", head1->val);
return;
}
head1 = head1->next;
head2 = head2->next;
}
printf("无公共节点!\n");
return;
}
int main() {
int a[5] = { 1,2,7,9,13 };
int b[10] = { 3,4,6,8,9,11,15,19,9,2 };
int c[5] = { 20,21,22,23,24 };
pNode head1, head2, tail1, tail2;
head1 = head2 = tail1 = tail2 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 5;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head1, &tail1, a[i]);
}
for (int i = 0;i < 10;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head2, &tail2, b[i]);
}
findcommon(head1, head2, 5, 10);
pNode head3, tail3;
head3 = tail3 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 5;++i) {
listTailInsert(&head3, &tail3, c[i]);
}
tail1->next = head3;
tail2->next = head3;
findcommon(head1, head2, 10, 15);
return 0;
}
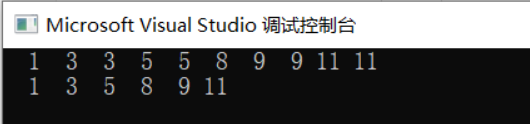
- 删除有序单链表中的重复元素
(双指针)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void listTailInsert(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val)
{
pNode newNode = (pNode)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) {
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head)
{
while (head) {
printf("%3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void DeleteCommon(pNode *head) {
pNode pCur, pPre, pFree;
pPre = *head;
pCur = (*head)->next;
while (pCur) {
if (pCur->val == pPre->val) {
pFree = pCur;
pPre->next = pCur->next;
pCur = pCur->next;
free(pFree);
}
else {
pPre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
}
}
int main() {
int a[10] = { 1,3,3,5,5,8,9,9,11,11 };
pNode head, tail;
head = tail = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
listTailInsert(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
DeleteCommon(&head);
listPrint(head);
return 0;
}
- 链表按奇数、偶数值拆分
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct node
{
int val;
struct node *next;
}Node, *pNode;
void InsertTail(pNode *head, pNode *tail, int val) {
pNode newNode = (char*)calloc(1, sizeof(Node));
newNode->val = val;
if (NULL == *tail) {
*head = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
else {
(*tail)->next = newNode;
*tail = newNode;
}
}
void partition(pNode head, pNode *head1, pNode *tail1, pNode *head2, pNode *tail2) {
while (head) {
int t = head->val;
if (t % 2 == 1) {
InsertTail(head1, tail1, t);
}
else {
InsertTail(head2, tail2, t);
}
head = head->next;
}
}
void listPrint(pNode head) {
while (head) {
printf("%-3d", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int a[9] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
pNode head, tail, head1, tail1, head2, tail2;
head = tail = head1 = tail1 = head2 = tail2 = NULL;
for (int i = 0;i < 9;++i) {
InsertTail(&head, &tail, a[i]);
}
listPrint(head);
partition(head, &head1, &tail1, &head2, &tail2);
listPrint(head1);
listPrint(head2);
return 0;
}

C语言强化——链表(1)的更多相关文章
- C语言强化——链表(2)
目录 链表的应用: 栈 循环队列 C语言实现动态数组 数组实现定长元素个数层次建树 队列实现不定元素个数层次建树 (*) 栈 栈(链表应用) "stack.h" #include ...
- C语言之链表
这两天在复习C语言的知识,为了给下个阶段学习OC做准备,以下的代码的编译运行环境是Xcode5.0版本,写篇博文把昨天复习的C语言有关链表的知识给大家分享一下,以下是小菜自己总结的内容,代码也是按照自 ...
- C语言习题 链表建立,插入,删除,输出
Problem B: C语言习题 链表建立,插入,删除,输出 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB Submit: 222 Solved: 92 [Subm ...
- YTU 2430: C语言习题 链表建立,插入,删除,输出
2430: C语言习题 链表建立,插入,删除,输出 时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB 提交: 576 解决: 280 题目描述 编写一个函数creatlink,用来建立一个动态链表 ...
- 关于c语言单项链表尾添加
犹豫了几天,看了很多大牛写的关于c语言链表,感触很多,终于下定决心,把自己对于链表的理解随之附上,可用与否,自行裁夺.由于作者水平有限也是第一次写,不足之处,竭诚希望得到各位大神的批评指正.制作不易, ...
- C语言之链表list
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include <string.h& ...
- C语言:链表实现的一个实例
问题:写一个程序输入你一年看过的所有电影以及每部电影的各种信息(简化问题:每部电影只要求输入片名和评价) 链表实现: #include<stdio.h> #include<stdli ...
- C语言单链表实现19个功能完全详解
谢谢Lee.Kevin分享了这篇文章 最近在复习数据结构,想把数据结构里面涉及的都自己实现一下,完全是用C语言实现的. 自己编写的不是很好,大家可以参考,有错误希望帮忙指正,现在正处于编写阶段,一共将 ...
- (转)c语言_链表实例讲解(两个经典例子)
建立一个学生成绩的线性链表,对其实现插入,删除,输出,最后销毁. #include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h> struct grade { ...
随机推荐
- [Educational Codeforces Round 55 (Rated for Div. 2)][C. Multi-Subject Competition]
https://codeforc.es/contest/1082/problem/C 题目大意:有m个类型,n个人,每个人有一个所属类型k和一个能力v,要求所选的类型的人个数相等并且使v总和最大(n, ...
- <jsp:include>动作元素,附:最易出错的一点
先定义一个date.jsp,再定义一个main.jsp.用<jsp:include plage = "相对url地址" flush = "true"> ...
- 【vue】vue使用Element组件时v-for循环里的表单项验证方法
转载至:https://www.jb51.net/article/142750.htm标题描述看起来有些复杂,有vue,Element,又有表单验证,还有v-for循环?是不是有点乱?不过我相信开发中 ...
- CH4912 Meteors
题意 4912 Meteors 0x49「数据结构进阶」练习 描述 Byteotian Interstellar Union有N个成员国.现在它发现了一颗新的星球,这颗星球的轨道被分为M份(第M份和第 ...
- hibernate(一)
hibernate介绍 jdbc缺点 1代码结构防繁琐,面向纯sql语句的编程,对于查询而言只要查询数据库的一张表,不需有如下编码 2有connection缓存,没有数据缓存 3.事务自动开启,有 ...
- Python 不可变对象练习
Python 不可变对象练习 str 是不可变对象,就是对这个对象进行操作不会改变这个对象的数据. 如下: >>> a = 'abc' >>> a.replace( ...
- 一个小工具 TcpTextListener
项目地址 : https://github.com/kelin-xycs/TcpTextListener 这是一个 可以 监听 Tcp (Http) 传输数据 的 小工具 . 不是 抓包 .不要 ...
- monkey如何获取app包名
别人学习网址:http://www.51testing.com/html/58/15092658-2984032.html 使用aapt aapt是sdk自带的一个工具,在sdk\builds- ...
- HTMLParser 笔记
# 关于html.parse.HTMLParser的使用 from html.parser import HTMLParser class MyHtmlParser(HTMLParser): # 使用 ...
- hadoop行业技术创新解决方案
如今有很多公司都在努力挖掘他们拥有的大量数据,包括结构化.非结构化.半结构化以及二进制数据等,来探索对数据的深入利用. 大多数公司估计他们只分析了已有数据的12%,剩余88%还没有被充分利用.大量的数 ...
