K8s中Pod健康检查源代码分析
了解k8s中的Liveness和Readiness
Liveness:
表明是否容器正在运行。如果liveness探测为fail,则kubelet会kill掉容器,并且会触发restart设置的策略。默认不设置的情况下,该状态为success.
Readiness:
表明容器是否可以接受服务请求。如果readiness探测失败,则endpoints控制器会从endpoints中摘除该Pod IP。在初始化延迟探测时间之前,默认是Failure。如果没有设置readiness探测,该状态为success。
代码分析
基于Kubernetes 1.11.0
1.启动探测
在kubelet启动是时候会启动健康检查的探测:
kubelet.go中Run方法
...
kl.probeManager.Start() //启动探测服务
...2.看一下probeManager都做了哪些事情
prober_manager.go中我们看一下这段代码:
// Manager manages pod probing. It creates a probe "worker" for every container that specifies a
// probe (AddPod). The worker periodically probes its assigned container and caches the results. The
// manager use the cached probe results to set the appropriate Ready state in the PodStatus when
// requested (UpdatePodStatus). Updating probe parameters is not currently supported.
// TODO: Move liveness probing out of the runtime, to here.
type Manager interface {
// AddPod creates new probe workers for every container probe. This should be called for every
// pod created.
AddPod(pod *v1.Pod)
// RemovePod handles cleaning up the removed pod state, including terminating probe workers and
// deleting cached results.
RemovePod(pod *v1.Pod)
// CleanupPods handles cleaning up pods which should no longer be running.
// It takes a list of "active pods" which should not be cleaned up.
CleanupPods(activePods []*v1.Pod)
// UpdatePodStatus modifies the given PodStatus with the appropriate Ready state for each
// container based on container running status, cached probe results and worker states.
UpdatePodStatus(types.UID, *v1.PodStatus)
// Start starts the Manager sync loops.
Start()
}这是一个Manager的接口声明,该Manager负载pod的探测。当执行AddPod时,会为Pod中每一个容器创建一个执行探测任务的worker, 该worker会对所分配的容器进行周期性的探测,并把探测结果缓存。当UpdatePodStatus方法执行时,该manager会使用探测的缓存结果设置PodStatus为近似Ready的状态: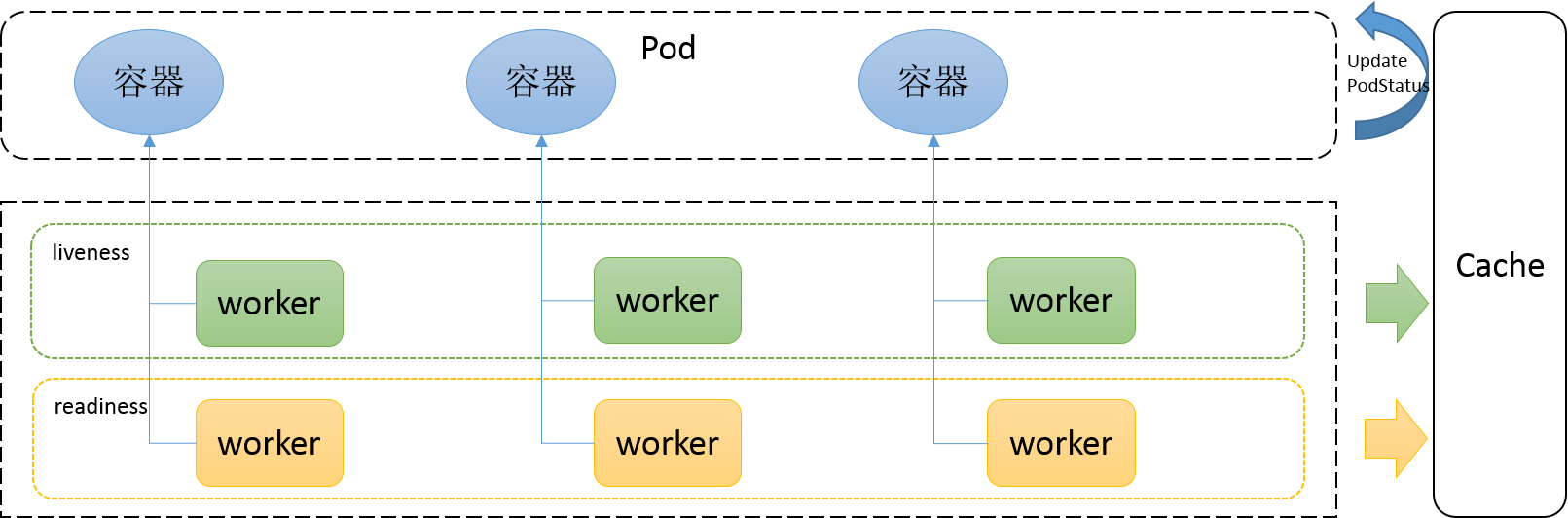
3.一“探”究竟
先看一下探测的struct
type Probe struct {
// The action taken to determine the health of a container
Handler `json:",inline" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=handler"`
// Number of seconds after the container has started before liveness probes are initiated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
// +optional
InitialDelaySeconds int32 `json:"initialDelaySeconds,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=initialDelaySeconds"`
// Number of seconds after which the probe times out.
// Defaults to 1 second. Minimum value is 1.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes
// +optional
TimeoutSeconds int32 `json:"timeoutSeconds,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=timeoutSeconds"`
// How often (in seconds) to perform the probe.
// Default to 10 seconds. Minimum value is 1.
// +optional
PeriodSeconds int32 `json:"periodSeconds,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,4,opt,name=periodSeconds"`
// Minimum consecutive successes for the probe to be considered successful after having failed.
// Defaults to 1. Must be 1 for liveness. Minimum value is 1.
// +optional
SuccessThreshold int32 `json:"successThreshold,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,5,opt,name=successThreshold"`
// Minimum consecutive failures for the probe to be considered failed after having succeeded.
// Defaults to 3. Minimum value is 1.
// +optional
FailureThreshold int32 `json:"failureThreshold,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,6,opt,name=failureThreshold"`
}initialDelaySeconds: 表示容器启动之后延迟多久进行liveness探测
timeoutSeconds:每次执行探测的超时时间
periodSeconds:探测的周期时间
successThreshold:最少连续几次探测成功的次数,满足该次数则认为success。
failureThreshold:最少连续几次探测失败的次数,满足该次数则认为fail
Handler:
不论是liveness还是readiness都支持3种类型的探测方式:执行命令、http方式以及tcp方式。
// Handler defines a specific action that should be taken
// TODO: pass structured data to these actions, and document that data here.
type Handler struct {
// One and only one of the following should be specified.
// Exec specifies the action to take.
// +optional
Exec *ExecAction `json:"exec,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=exec"`
// HTTPGet specifies the http request to perform.
// +optional
HTTPGet *HTTPGetAction `json:"httpGet,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=httpGet"`
// TCPSocket specifies an action involving a TCP port.
// TCP hooks not yet supported
// TODO: implement a realistic TCP lifecycle hook
// +optional
TCPSocket *TCPSocketAction `json:"tcpSocket,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=tcpSocket"`
}接下来看一下prober.go中的runProbe方法。
func (pb *prober) runProbe(probeType probeType, p *v1.Probe, pod *v1.Pod, status v1.PodStatus, container v1.Container, containerID kubecontainer.ContainerID) (probe.Result, string, error) {
timeout := time.Duration(p.TimeoutSeconds) * time.Second
if p.Exec != nil {
glog.V(4).Infof("Exec-Probe Pod: %v, Container: %v, Command: %v", pod, container, p.Exec.Command)
command := kubecontainer.ExpandContainerCommandOnlyStatic(p.Exec.Command, container.Env)
return pb.exec.Probe(pb.newExecInContainer(container, containerID, command, timeout))
}
if p.HTTPGet != nil {
scheme := strings.ToLower(string(p.HTTPGet.Scheme))
host := p.HTTPGet.Host
if host == "" {
host = status.PodIP
}
port, err := extractPort(p.HTTPGet.Port, container)
if err != nil {
return probe.Unknown, "", err
}
path := p.HTTPGet.Path
glog.V(4).Infof("HTTP-Probe Host: %v://%v, Port: %v, Path: %v", scheme, host, port, path)
url := formatURL(scheme, host, port, path)
headers := buildHeader(p.HTTPGet.HTTPHeaders)
glog.V(4).Infof("HTTP-Probe Headers: %v", headers)
if probeType == liveness {
return pb.livenessHttp.Probe(url, headers, timeout)
} else { // readiness
return pb.readinessHttp.Probe(url, headers, timeout)
}
}
if p.TCPSocket != nil {
port, err := extractPort(p.TCPSocket.Port, container)
if err != nil {
return probe.Unknown, "", err
}
host := p.TCPSocket.Host
if host == "" {
host = status.PodIP
}
glog.V(4).Infof("TCP-Probe Host: %v, Port: %v, Timeout: %v", host, port, timeout)
return pb.tcp.Probe(host, port, timeout)
}
glog.Warningf("Failed to find probe builder for container: %v", container)
return probe.Unknown, "", fmt.Errorf("Missing probe handler for %s:%s", format.Pod(pod), container.Name)
}1.执行命令方式
通过newExecInContainer方法调用CRI执行命令: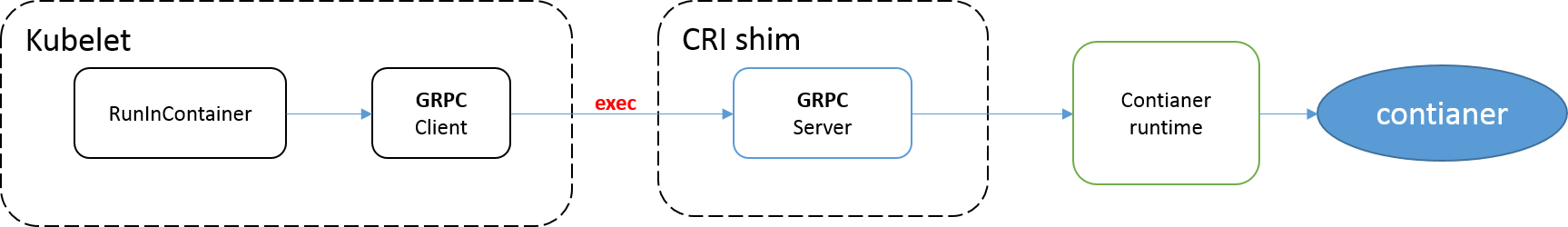
// ExecAction describes a "run in container" action.
type ExecAction struct {
// Command is the command line to execute inside the container, the working directory for the
// command is root ('/') in the container's filesystem. The command is simply exec'd, it is
// not run inside a shell, so traditional shell instructions ('|', etc) won't work. To use
// a shell, you need to explicitly call out to that shell.
// Exit status of 0 is treated as live/healthy and non-zero is unhealthy.
// +optional
Command []string `json:"command,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=command"`
}2.http GET方式
通过http GET方式进行探测。
Port:表示访问容器的端口
Host:表示访问的主机,默认是Pod IP
// HTTPGetAction describes an action based on HTTP Get requests.
type HTTPGetAction struct {
// Path to access on the HTTP server.
// +optional
Path string `json:"path,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=path"`
// Name or number of the port to access on the container.
// Number must be in the range 1 to 65535.
// Name must be an IANA_SVC_NAME.
Port intstr.IntOrString `json:"port" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=port"`
// Host name to connect to, defaults to the pod IP. You probably want to set
// "Host" in httpHeaders instead.
// +optional
Host string `json:"host,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=host"`
// Scheme to use for connecting to the host.
// Defaults to HTTP.
// +optional
Scheme URIScheme `json:"scheme,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=scheme,casttype=URIScheme"`
// Custom headers to set in the request. HTTP allows repeated headers.
// +optional
HTTPHeaders []HTTPHeader `json:"httpHeaders,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,5,rep,name=httpHeaders"`
}3.tcp方式
通过设置主机和端口即可进行tcp方式访问
// TCPSocketAction describes an action based on opening a socket
type TCPSocketAction struct {
// Number or name of the port to access on the container.
// Number must be in the range 1 to 65535.
// Name must be an IANA_SVC_NAME.
Port intstr.IntOrString `json:"port" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=port"`
// Optional: Host name to connect to, defaults to the pod IP.
// +optional
Host string `json:"host,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=host"`
}此处脑洞一下:如果三种探测方式都设置了,会如何执行处理?
思考
通过k8s部署生产环境应用时,建议设置上liveness和readiness, 这也是保障服务稳定性的最佳实践。
另外由于Pod Ready不能保证实际的业务应用Ready可用,在最新的 1.14 版本中新增了一个Pod Readiness Gates 特性 。通过这个特性,可以保证应用Ready后进而设置Pod Ready。
结尾
针对上面的脑洞:如果三种探测方式都设置了,会如何执行处理?
答:我们如果在Pod中设置多个探测方式,提交配置的时候会直接报错:
此处继续源代码:在validation.go中validateHandler中进行了限制(也为上面Handler struct提到的"One and only one of the following should be specified."提供了事实依据)
func validateHandler(handler *core.Handler, fldPath *field.Path) field.ErrorList {
numHandlers := 0
allErrors := field.ErrorList{}
if handler.Exec != nil {
if numHandlers > 0 {
allErrors = append(allErrors, field.Forbidden(fldPath.Child("exec"), "may not specify more than 1 handler type"))
} else {
numHandlers++
allErrors = append(allErrors, validateExecAction(handler.Exec, fldPath.Child("exec"))...)
}
}
if handler.HTTPGet != nil {
if numHandlers > 0 {
allErrors = append(allErrors, field.Forbidden(fldPath.Child("httpGet"), "may not specify more than 1 handler type"))
} else {
numHandlers++
allErrors = append(allErrors, validateHTTPGetAction(handler.HTTPGet, fldPath.Child("httpGet"))...)
}
}
if handler.TCPSocket != nil {
if numHandlers > 0 {
allErrors = append(allErrors, field.Forbidden(fldPath.Child("tcpSocket"), "may not specify more than 1 handler type"))
} else {
numHandlers++
allErrors = append(allErrors, validateTCPSocketAction(handler.TCPSocket, fldPath.Child("tcpSocket"))...)
}
}
if numHandlers == 0 {
allErrors = append(allErrors, field.Required(fldPath, "must specify a handler type"))
}
return allErrors
}本文作者:元毅
本文为云栖社区原创内容,未经允许不得转载。
K8s中Pod健康检查源代码分析的更多相关文章
- Kubernetes中Pod健康检查
目录 1.何为健康检查 2.探针分类 2.1.LivenessProbe探针(存活性探测) 2.2.ReadinessProbe探针(就绪型探测) 3.探针实现方法 3.1.Container Exe ...
- Knative Serving 健康检查机制分析
作者| 阿里云智能事业群技术专家牛秋霖(冬岛) 导读:从头开发一个Serverless引擎并不是一件容易的事情,今天咱们就从Knative的健康检查说起.通过健康检查这一个点来看看Serverles ...
- kubernetes之pod健康检查
目录 kubernetes之pod健康检查 1.概述和分类 2.LivenessProbe探针(存活性探测) 3.ReadinessProbe探针(就绪型探测) 4.探针的实现方式 4.1.ExecA ...
- 如何从Serilog请求日志记录中排除健康检查终结点
这是在ASP.NET Core 3.X中使用Serilog.AspNetCore系列文章的第四篇文章:. 第1部分-使用Serilog RequestLogging减少日志详细程度 第2部分-使用Se ...
- Java中arraylist和linkedlist源代码分析与性能比較
Java中arraylist和linkedlist源代码分析与性能比較 1,简单介绍 在java开发中比較经常使用的数据结构是arraylist和linkedlist,本文主要从源代码角度分析arra ...
- 在.NET Core 中实现健康检查
.NET Core中提供了开箱即用的运行状况检查,首先,我将在.NET Core API应用程序中执行运行状况检查,接下来,我们将使用DbContext集成SQL Server或数据库的运行状况检查, ...
- 如何在 ASP.Net Core 中实现 健康检查
健康检查 常用于判断一个应用程序能否对 request 请求进行响应,ASP.Net Core 2.2 中引入了 健康检查 中间件用于报告应用程序的健康状态. ASP.Net Core 中的 健康检查 ...
- k8s 中 Pod 的控制器
k8s 中 Pod 的控制器 前言 Replication Controller ReplicaSet Deployment 更新 Deployment 回滚 deployment StatefulS ...
- pod健康检查(liveness probe存活探针&&readiness probe 可读性探针)
在Kubernetes集群当中,我们可以通过配置liveness probe(存活探针)和readiness probe(可读性探针)来影响容器的生存周期.参考文档:https://kubernete ...
随机推荐
- 一站式WPF--依赖属性(DependencyProperty)一
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 提供了一组服务,这些服务可用于扩展公共语言运行时 (CLR) 属性的功能,这些服务通常统称为 WPF 属性系统.由 WPF ...
- 个人站长建议直接封掉的IP地址列表
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve" deny="164.100.196.21 ...
- springmvc java程序文件保存地址的路径问题
会保存为这种斜杠 不论之前填写的是什么样
- CentOS 6.8 Java 环境搭建
1.搜索 Java 1.7 64 2.下载 文件 3.Xshell 安装lrzsz 4.选择路径 5.使用 rz 命令选择上传 6.打开 /etc/profile vim /etc/profile ...
- IO 性能 $ iostat -kx 2$ vmstat 2 10$ mpstat 2 10$ dstat --top-io --top-bio
这些命令对于调试后端性能非常有用. 检查磁盘使用量:服务器硬盘是否已满? 是否开启了swap交换模式 (si/so)? CPU被谁占用:系统进程? 用户进程? 虚拟机? dstat 是我的最爱.用 ...
- The content of element type must match解决方法
当我在mybatis的核心配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中配置别名的时候,老是提示错误. 把鼠标移到上去就可以看到详细的内容 如下图所示: 问题原因: 通过错误的提示信息,原来这个xml文件 ...
- 分布式--ActiveMQ 消息中间件(一) https://www.jianshu.com/p/8b9bfe865e38
1. ActiveMQ 1). ActiveMQ ActiveMQ是Apache所提供的一个开源的消息系统,完全采用Java来实现,因此,它能很好地支持J2EE提出的JMS(Java Message ...
- Win32 Console Application、Win32 Application、MFC三者之间的联系和区别
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/c_base_jin/article/details/52304845 在windows编程中,我们或多或少都听说这三个名称,分别是Win32 Cons ...
- ubuntu 安装 lrzsz 上传下载
原文:ubuntu 安装 lrzsz 上传下载 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,随意转载. https://blog.csdn.net/Michel4Liu/article/details/808223 ...
- php is_null、empty、isset的区别
isset 判断变量是否已存在 empty 判断变量是否为空或为0 is_null 判断变量是否为NULL 变量 empty is_null isset $a=”” true false true $ ...
