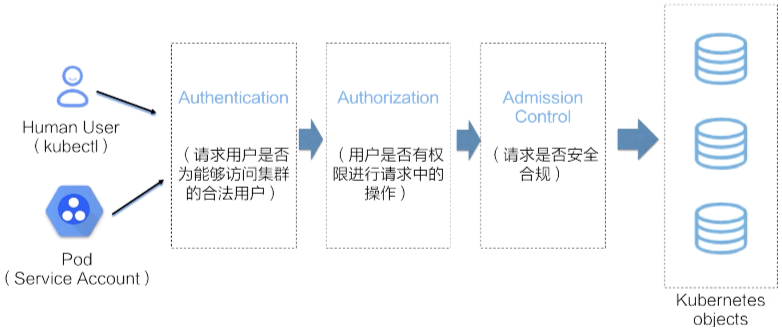
深入理解k8s中的访问控制(认证、鉴权、审计)流程
password,user,uid,"group1,group2,group3"
Authorization: Basic BASE64ENCODED(USER:PASSWORD)
cat << EOF | tee ca-config.json
{
"signing": {
"default": {
"expiry": "87600h"
},
"profiles": {
"kubernetes": {
"expiry": "87600h",
"usages": [
"signing",
"key encipherment",
"server auth",
"client auth"
]
}
}
}
}
EOF
其中:
- profiles:指定不同的过期时间、使用场景等参数。文件中可以定义多个,分别后续在签名证书时使用某一个
- signing:表示该证书可用于签名其它证书,生成的ca.pem证书中CA=TRUE
- key encipherment:表示密钥用法为密钥加密
- server auth:表示client可以用该CA 对server提供的证书进行验证
- client auth:表示server可以用该CA对client提供的证书进行验证
cat << EOF | tee ca-csr.json
{
"CN": "kubernetes",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size":
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "Shenzhen",
"ST": "Shenzhen",
"O": "k8s",
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
EOF
其中:
- CN:Common Name,用于从中提取该字段作为请求的用户名
- C:Country, 国家
- ST: State,州,省
- L: Locality,地区,城市
- O: Organization Name, 用于从中提前该字段作为请求用户所属的组
- OU: Organization Unit Name,组织单位名称,公司部门
cfssl gencert -initca ca-csr.json | cfssljson -bare ca

cat << EOF | tee kube-proxy-csr.json
{
"CN": "system:kube-proxy",
"hosts": [],
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size":
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"L": "Shenzhen",
"ST": "Shenzhen",
"O": "k8s",
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
EOF
使用根CA签署证书:
cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -config=ca-config.json -profile=kubernetes kube-proxy-csr.json | cfssljson -bare kube-proxy
kind: KubeletConfiguration
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
address: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
port: 10250
readOnlyPort: 10255
cgroupDriver: cgroupfs
clusterDNS: ["10.0.0.2"]
clusterDomain: cluster.local.
failSwapOn: false
authentication:
anonymous:
enabled: true
kubelet组件在工作时,采用主动的查询机制,即定期请求apiserver 获取自己所应当处理的任务,如哪些pod分配到了自己身上,从而去处理这些任务;同时kubelet自己还会暴露出两个本身api的端口,用于将自己本身的私有api暴露出去,这两个端口分别是该配置文件中指定的10250与10255。
openssl genrsa -out test.key
openssl req -new -key test.key -out test.csr -subj "/CN=xxxx/O=xxxx"
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: certificates.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CertificateSigningRequest
metadata:
name: xxxx
spec:
groups:
- system:authenticated
request: $(cat test.csr | base64 | tr -d "\n")
usages:
- client auth
EOF
PS:request中是base64编码的csr文件
NAME AGE REQUESTOR CONDITION
xxxx 10s admin Pending
# kubectl certificate approve john
certificatesigningrequest.certificates.k8s.io/xxxx approved
# openssl x509 -req -in test.csr -CA CA_LOCATION/ca.crt -Cakey CA_LOCATION/ca.key -Cacreateserial -out test.crt -days
# kubectl config view
kubectl默认会从$HOME/.kube目录下查找文件名为config 的文件,也可以通过设置环境变量KUBECONFIG或者通过设置--kubeconfig去指定其它kubeconfig文件。
文件格式为:
{
"apiVersion": "v1",
"kind": "Config",
"preferences": {},
"clusters": [
{
"cluster": {
"certificate-authority":
"server": "https://ip:6443"
},
"name": {cluster-name}
}
],
"contexts": [
{
"context": {
"cluster": {cluster-name},
"user": {user-name}
},
"name": {context-name}
}
],
"users": [
{
"name": {user-name},
"user": {
"client-certificate":
"client-key":
}
}
]
"current-context": {context-name},
}
若想要用base64编码数据代替认证文件,需要添加后缀-data,将 certificate-authority、client-certificate、client-key改为certificate-authority-data、client-certificate-data、client-key-data
# grep 'client-key-data' /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf | head -n | awk '{print $2}' | base64 -d
# grep 'client-certificate-data' /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf | head -n | awk '{print $2}' | base64 -d
# kubectl config set-cluster xxx --certificate-authority=ca.pem --embed-certs=true --server=https://ip:6443
# kubectl config set-credentials {user-name} --client-certificate=test.crt --client-key=test.key --embed-certs=true
# kubectl config set-context {context-name} --cluster={cluster-name} --user={user-name}
# export KUBECONFIG=file1:file2:file3
# kubectl config view --merge --flatten > ~/.kube/all-config
# export KUBECONFIG = ~/.kube/all-config
# kubectl config get-contests
# kubectl config use-context {your-contexts}
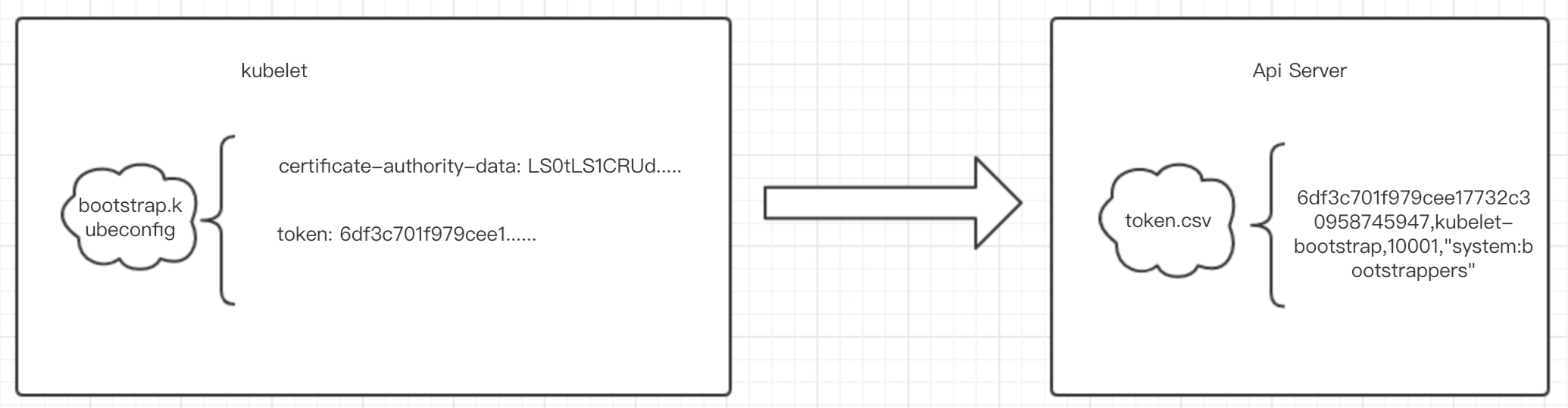
token,user,uid,"group1,group2,group3"
Authorization: Bearer 31ada4fd-adec-460c-809a-9e56ceb75269
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2019-11-19T03:07:32Z"
name: default
namespace: default
resourceVersion: "191"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/default/serviceaccounts/default
uid: b2322727-08d5-4095-acbe-1afee4fb5e6c
secrets:
- name: default-token-nfdr4
apiVersion: v1
data:
ca.crt: LS0tLS1...
namespace: ZGVmYXVsdA==
token: ZXlKaG...
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: default
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: b2322727-08d5-4095-acbe-1afee4fb5e6c
creationTimestamp: "2019-11-19T03:07:32Z"
name: default-token-nfdr4
namespace: default
resourceVersion: "190"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/default/secrets/default-token-nfdr4
uid: cbb919a4-6309-43c0-ac0b-566e30e9b116
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
name: default-token-jbcp7
readOnly: true
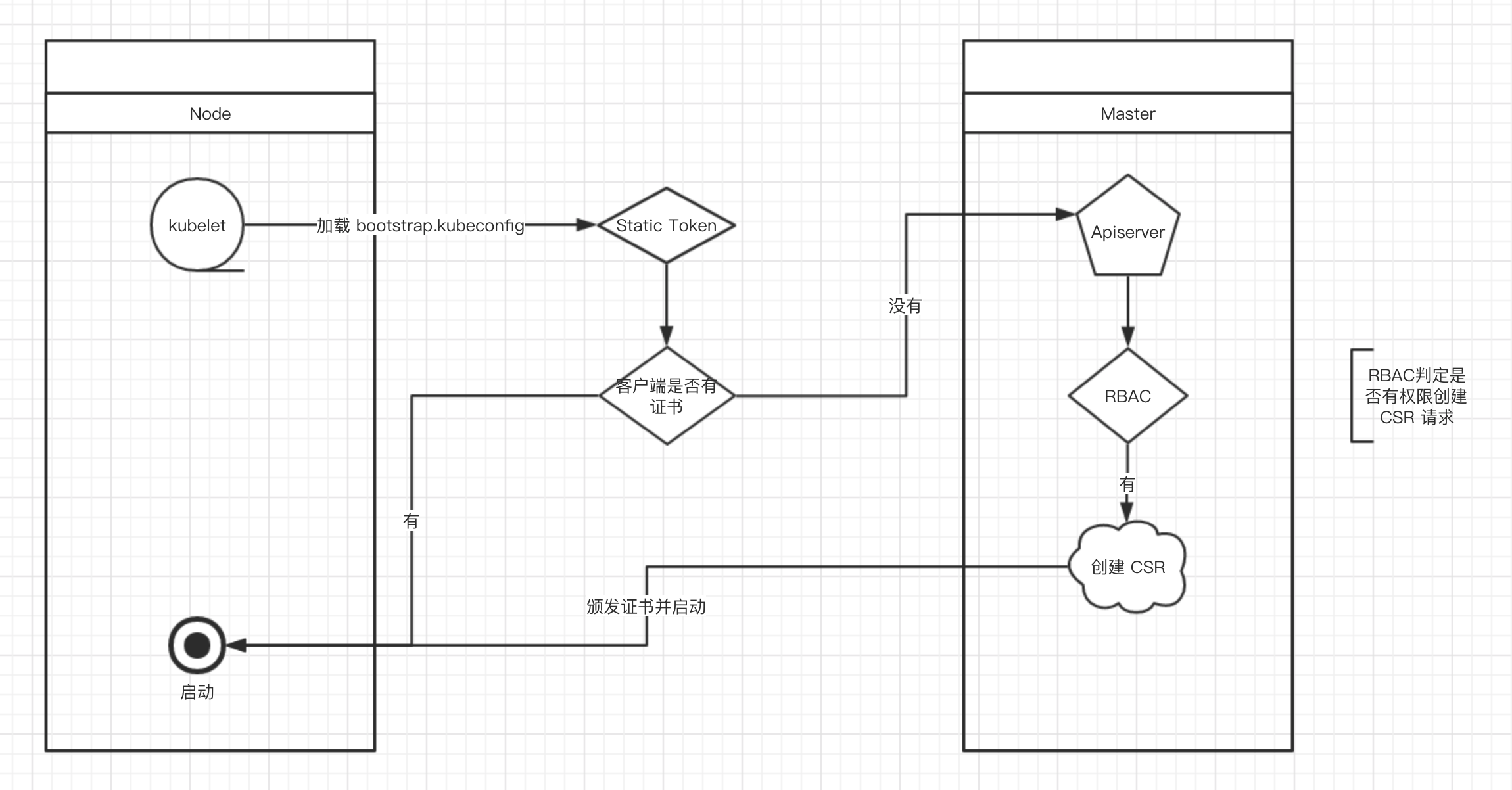
# head -c /dev/urandom | od -An -t x | tr -d ' '
8f01b7072246e0f3409d54e379c8699f
8f01b7072246e0f3409d54e379c8699f,kubelet-bootstrap,10001,"system:kubelet-bootstrap"
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding kubelet-bootstrap \
--clusterrole=system:node-bootstrapper \
--user=kubelet-bootstrap
BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN=01f6717d648e3e7e71282a9632dd99ab
KUBE_APISERVER="https://132.224.197.35:6443"
执行命令:
# kubectl config set-cluster kubernetes \
--certificate-authority=./ca.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--server=${KUBE_APISERVER} \
--kubeconfig=bootstrap.kubeconfig # kubectl config set-credentials kubelet-bootstrap \
--token=${BOOTSTRAP_TOKEN} \
--kubeconfig=bootstrap.kubeconfig # kubectl config set-context default \
--cluster=kubernetes \
--user=kubelet-bootstrap \
--kubeconfig=bootstrap.kubeconfig # kubectl config use-context default --kubeconfig=bootstrap.kubeconfig
# A ClusterRole which instructs the CSR approver to approve a user requesting node client credentials.
kind:ClusterRole
apiVersion:rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name:approve-node-client-csr
rules:
-apiGroups:["certificates.k8s.io"]
resources:["certificatesigningrequests/nodeclient"]
verbs:["create"] --- # A ClusterRole which instructs the CSR approver to approve a node renewing its own client credentials.
kind:ClusterRole
apiVersion:rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name:approve-node-client-renewal-csr
rules:
-apiGroups:["certificates.k8s.io"]
resources:["certificatesigningrequests/selfnodeclient"]
verbs:["create"] --- # A ClusterRole which instructs the CSR approver to approve a node requesting a serving cert matching its client cert.
kind:ClusterRole
apiVersion:rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name:approve-node-server-renewal-csr
rules:
-apiGroups:["certificates.k8s.io"]
resources:["certificatesigningrequests/selfnodeserver"]
verbs:["create"]
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding node-client-auto-approve-csr --clusterrole=approve-node-client-csr --group=system:bootstrappers
自动批准 kubelet 后续 renew 用于与 apiserver 通讯证书的 CSR 请求:
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding node-client-auto-renew-crt --clusterrole=approve-node-client-renewal-csr --group=system:nodes
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding node-server-auto-renew-crt --clusterrole=approve-node-server-renewal-csr --group=system:nodes
echo "$(head -c 6 /dev/urandom | md5sum | head -c 6)"."$(head -c 16 /dev/urandom | md5sum | head -c 16)”
47f392.d22d04e89a65eb22
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: bootstrap-token-07401b
namespace: kube-system
type: bootstrap.kubernetes.io/token
stringData:
description: "The default bootstrap token generated by 'kubeadm init'."
token-id: 47f392
token-secret: d22d04e89a65eb22
expiration: 2018-09-10T00:00:11Z
usage-bootstrap-authentication: "true"
usage-bootstrap-signing: "true"
auth-extra-groups: system:bootstrappers:worker,system:bootstrappers:ingress
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding kubelet-bootstrap \
--clusterrole=system:node-bootstrapper \
--group=system:bootstrappers
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding node-client-auto-approve-csr \
--clusterrole=system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:nodeclient \
--group=system:bootstrappers
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding node-client-auto-renew-crt \
--clusterrole=system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient \
--group=system:nodes
自动批准 system:nodes 组用户更新 kubelet 10250 api 端口证书的 CSR 请求:
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding node-server-auto-renew-crt \
--clusterrole=system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeserver \
--group=system:nodes
# kubectl config set-cluster kubernetes \
--certificate-authority=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/k8s-root-ca.pem \
--embed-certs=true \
--server=https://127.0.0.1:6443 \
--kubeconfig=bootstrap.kubeconfig # kubectl config set-credentials system:bootstrap:47f392 \
--token=47f392.d22d04e89a65eb22 \
--kubeconfig=bootstrap.kubeconfig # kubectl config set-context default \
--cluster=kubernetes \
--user=system:bootstrap:47f392 \
--kubeconfig=bootstrap.kubeconfig # kubectl config use-context default --kubeconfig=bootstrap.kubeconfig

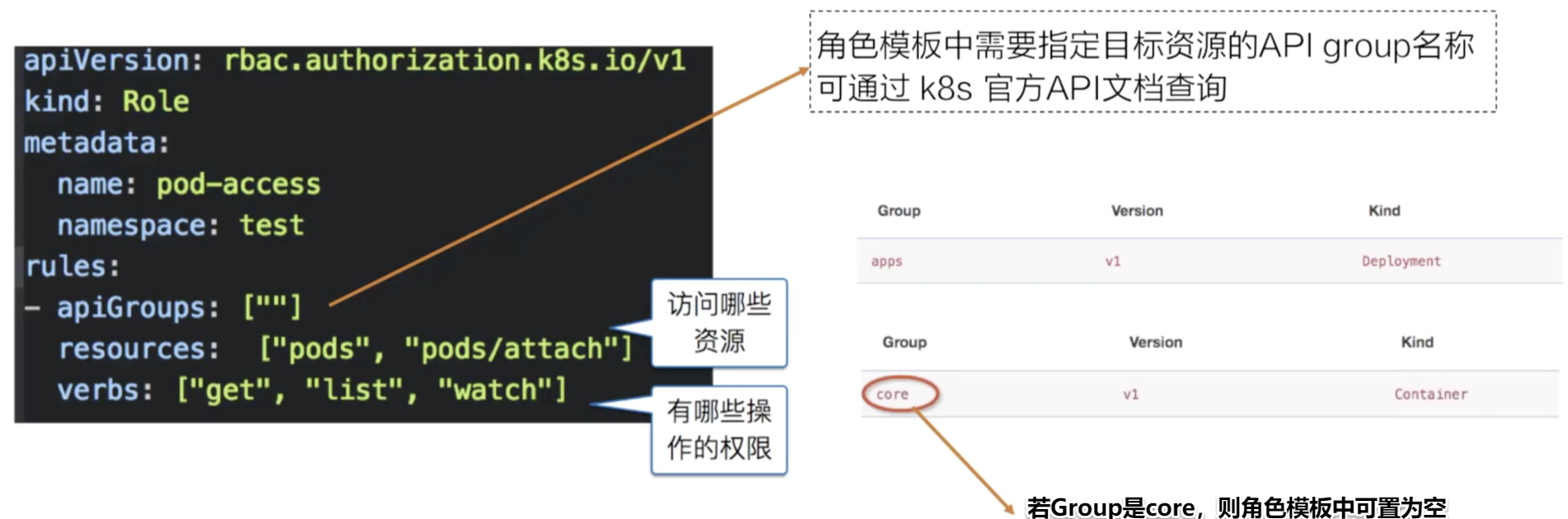
- Subjects:可以是开发人员、集群管理员这样的自然人,也可以是系统组件进程、Pod中的业务进程;
- API Resource:也就是请求对应的访问目标,在Kubernetes集群中指各类资源对象;
- Verbs:对应为请求对象资源可以进行哪些操作,如list、get、watch等。


# kube-apiserver -h | grep enable-admission-plugins
--admission-control strings Admission is divided into two phases. In the first phase, only mutating admission plugins run. In the second phase, only validating admission plugins run. The names in the below list may represent a validating plugin, a mutating plugin, or both. The order of plugins in which they are passed to this flag does not matter. Comma-delimited list of: AlwaysAdmit, AlwaysDeny, AlwaysPullImages, DefaultStorageClass, DefaultTolerationSeconds, DenyEscalatingExec, DenyExecOnPrivileged, EventRateLimit, ExtendedResourceToleration, ImagePolicyWebhook, LimitPodHardAntiAffinityTopology, LimitRanger, MutatingAdmissionWebhook, NamespaceAutoProvision, NamespaceExists, NamespaceLifecycle, NodeRestriction, OwnerReferencesPermissionEnforcement, PersistentVolumeClaimResize, PersistentVolumeLabel, PodNodeSelector, PodPreset, PodSecurityPolicy, PodTolerationRestriction, Priority, ResourceQuota, SecurityContextDeny, ServiceAccount, StorageObjectInUseProtection, TaintNodesByCondition, ValidatingAdmissionWebhook. (DEPRECATED: Use --enable-admission-plugins or --disable-admission-plugins instead. Will be removed in a future version.)
--enable-admission-plugins strings admission plugins that should be enabled in addition to default enabled ones (NamespaceLifecycle, LimitRanger, ServiceAccount, TaintNodesByCondition, Priority, DefaultTolerationSeconds, DefaultStorageClass, StorageObjectInUseProtection, PersistentVolumeClaimResize, MutatingAdmissionWebhook, ValidatingAdmissionWebhook, ResourceQuota). Comma-delimited list of admission plugins: AlwaysAdmit, AlwaysDeny, AlwaysPullImages, DefaultStorageClass, DefaultTolerationSeconds, DenyEscalatingExec, DenyExecOnPrivileged, EventRateLimit, ExtendedResourceToleration, ImagePolicyWebhook, LimitPodHardAntiAffinityTopology, LimitRanger, MutatingAdmissionWebhook, NamespaceAutoProvision, NamespaceExists, NamespaceLifecycle, NodeRestriction, OwnerReferencesPermissionEnforcement, PersistentVolumeClaimResize, PersistentVolumeLabel, PodNodeSelector, PodPreset, PodSecurityPolicy, PodTolerationRestriction, Priority, ResourceQuota, SecurityContextDeny, ServiceAccount, StorageObjectInUseProtection, TaintNodesByCondition, ValidatingAdmissionWebhook. The order of plugins in this flag does not matter.
可见,AC一共有几十种,下面介绍一些常用的:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: ns-quota-cns-test
namespace: cns-test
spec:
hard:
pods: "4"
requests.cpu: "1"
requests.memory: 1Gi
limits.cpu: "26"
limits.memory: 2Gi
scopeSelector:
matchExpressions:
- operator: Exists
scopeName: NotBestEffort
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: mem-limit-range
spec:
limits:
- default:
memory: 512Mi
defaultRequest:
memory: 256Mi
type: Container
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: security-context-demo
spec:
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
runAsGroup: 3000
fsGroup: 2000
volumes:
- name: sec-ctx-vol
emptyDir: {}
containers:
- name: sec-ctx-demo
image: busybox
command: [ "sh", "-c", "sleep 1h" ]
volumeMounts:
- name: sec-ctx-vol
mountPath: /data/demo
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
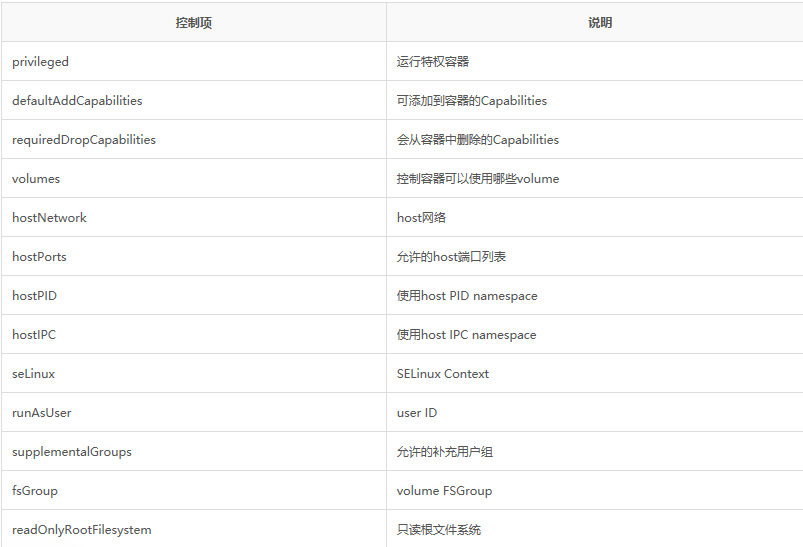
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
name: validation-kube-webhook-cfg
namespace: paas
labels:
app: paas-webhook
webhooks:
- name: nodeport.kube-webhook.cn
clientConfig:
service:
name: paas-webhook-svc
namespace: paas
path: "/validating"
caBundle: LS0tLS1...
rules:
- operations: [ "CREATE" ]
apiGroups: ["apps", "extensions", ""]
apiVersions: ["v1", "v1beta1"]
resources: ["services"]
namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
paas-webhook: enabled
type IWebHookServer interface {
mutating(ar *v1beta1.AdmissionReview) *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse
validating(ar *v1beta1.AdmissionReview) *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse
Start()
Stop()
}
type webHookServer struct {
server *http.Server
}
func (ws *webHookServer) Start() {
ws.server.ListenAndServeTLS("", "")
}
func (ws *webHookServer) Stop() {
glog.Infof("Got OS shutdown signal, shutting down wenhook server gracefully...")
ws.server.Shutdown(context.Background())
}
signalChan := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(signalChan, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
<-signalChan ws.Stop()
var service corev1.Service
json.Unmarshal(req.Object.Raw, &service)
resourceName, resourceNamespace, objectMeta = service.Name, service.Namespace, &service.ObjectMeta
type AdmissionResponse struct {
UID types.UID `json:"uid" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=uid"`
Allowed bool `json:"allowed" protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=allowed"`
Result *metav1.Status `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=status"`
Patch []byte `json:"patch,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=patch"`
PatchType *PatchType `json:"patchType,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=patchType"`
AuditAnnotations map[string]string `json:"auditAnnotations,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,6,opt,name=auditAnnotations"`
}
allowed := true
result = &metav1.Status{
Reason: "Unauthorized nodeport",
}
return &v1beta1.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: allowed,
Result: result,
}
webhook可以做到很多事情,例如限制每个namespace使用的端口号、为每个Pod插入sidecar容器等。
参考资料:
[1] https://kubernetes.io/docs/home/
[2] https://edu.aliyun.com/roadmap/cloudnative
[3] https://mritd.me/2018/08/28/kubernetes-tls-bootstrapping-with-bootstrap-token/
[4] https://mritd.me/2018/01/07/kubernetes-tls-bootstrapping-note/
[5] 郑东旭《Kubernetes源码剖析》
深入理解k8s中的访问控制(认证、鉴权、审计)流程的更多相关文章
- 认证鉴权与API权限控制在微服务架构中的设计与实现(四)
引言: 本文系<认证鉴权与API权限控制在微服务架构中的设计与实现>系列的完结篇,前面三篇已经将认证鉴权与API权限控制的流程和主要细节讲解完.本文比较长,对这个系列进行收尾,主要内容包括 ...
- Spring Security 接口认证鉴权入门实践指南
目录 前言 SpringBoot 示例 SpringBoot pom.xml SpringBoot application.yml SpringBoot IndexController SpringB ...
- 基于Springboot集成security、oauth2实现认证鉴权、资源管理
1.Oauth2简介 OAuth(开放授权)是一个开放标准,允许用户授权第三方移动应用访问他们存储在另外的服务提供者上的信息,而不需要将用户名和密码提供给第三方移动应用或分享他们数据的所有内容,OAu ...
- Mongodb 认证鉴权那点事
[TOC] 一.Mongodb 的权限管理 认识权限管理,说明主要概念及关系 与大多数数据库一样,Mongodb同样提供了一套权限管理机制. 为了体验Mongodb 的权限管理,我们找一台已经安装好的 ...
- nginx 请求文件 进行用户认证/鉴权: internal(限制为内部调用)
在进行WEB开发时, 必然会遇到向用户返回文件的场景(如图片, 文档等等), 当返回的文件较小时, 我们可以直接通过接口以数据流的形式向前台返回, 因为文件较小, 因此也不会太过于影响响应速度及服务器 ...
- web系统认证与鉴权中的一些问题
认证鉴权系统的初心: 空间管理: 1.他是谁? 他登陆了没有? 2.他要做什么? 2.1 他要使用什么功能? 他是否有这个功能的权限. 2.2 他要使用这个功能做什么操作? 他是否有这个功能的这个操作 ...
- 【Spring Cloud & Alibaba 实战 | 总结篇】Spring Cloud Gateway + Spring Security OAuth2 + JWT 实现微服务统一认证授权和鉴权
一. 前言 hi,大家好~ 好久没更文了,期间主要致力于项目的功能升级和问题修复中,经过一年时间的打磨,[有来]终于迎来v2.0版本,相较于v1.x版本主要完善了OAuth2认证授权.鉴权的逻辑,结合 ...
- K8S 中的容器编排和应用编排
众所周知,Kubernetes 是一个容器编排平台,它有非常丰富的原始的 API 来支持容器编排,但是对于用户来说更加关心的是一个应用的编排,包含多容器和服务的组合,管理它们之间的依赖关系,以及如何管 ...
- iOS进阶之UDP代理鉴权过程
上一篇介绍的是TCP代理的鉴权过程,这篇将介绍UDP代理的大致鉴权过程. 在UDP鉴权过程中,有几点是需要注意的.首先,UDP是一种无连接协议,不需要连接,使用广播的方式:其次,为了通过鉴权,所以需要 ...
随机推荐
- MyBatis--动态插入多条数据
MySQL支持的一种插入多行数据的INSERT语句写法是 INSERT INTO 表名 (字段名1,字段名2,字段名3) VALUES (值1,值2,值3,...),(值1,值2,值3,...)... ...
- ES6标准入门 2/26
第一章 ECMAScript6 简介 1.首先经典开头,ECMAScript跟JavaScript的关系,前者是后者的规格,后者是前者的一种实现.在日常场合中,这两个词是可以互换的. 2.ES6可以泛 ...
- PHP array_diff() 函数
实例 比较两个数组的值,并返回差集: <?php $a1=array("a"=>"red","b"=>"gree ...
- PHP is_string() 函数
is_string() 函数用于检测变量是否是字符串. PHP 版本要求: PHP 4, PHP 5, PHP 7高佣联盟 www.cgewang.com 语法 bool is_string ( mi ...
- P3565 由简单的树形dp 引入 长链刨分
这道题感觉不太行 因为自己没想出来. 先说一下暴力吧,取三个点 让两两之间的距离相等怎么做呢,看起来是很复杂的样子的,但是仔细观察发现 答案出自一个点的儿子之间 或者儿子和父亲之间. 暴力枚举三个点然 ...
- 问题记录,php webserver端跨子域setcookie后浏览器不存
如题. path已设置成/,domain也已指定成父级域名,数据包response中可见Set-Cookie header为期望的cookie数据,但浏览器就是不接收.存储该cookie, 浏览器端也 ...
- 022_go语言中的协程
代码演示 package main import "fmt" func f(from string) { for i := 0; i < 3; i++ { fmt.Print ...
- Python中匿名函数与内置高阶函数详解
大家好,从今天起早起Python将持续更新由小甜同学从 初学者的角度 学习Python的笔记,其特点就是全文大多由 新手易理解 的 代码与注释及动态演示 .刚入门的读者千万不要错过! 很多人学习pyt ...
- Nginx实现静态服务器+https+负载均衡
#user nobody; # 进程数=CPU总核数 worker_processes 2; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log ...
- JS 图片跟随鼠标移动案例
css代码 img { position: absolute; /* top: 2px; */ width: 50px; height: 50px; } HTML代码 <img src=&quo ...
