POJ 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are! (半平面交)
题目链接:POJ 3130
Problem Description
After counting so many stars in the sky in his childhood, Isaac, now an astronomer and a mathematician uses a big astronomical telescope and lets his image processing program count stars. The hardest part of the program is to judge if shining object in the sky is really a star. As a mathematician, the only way he knows is to apply a mathematical definition of stars.
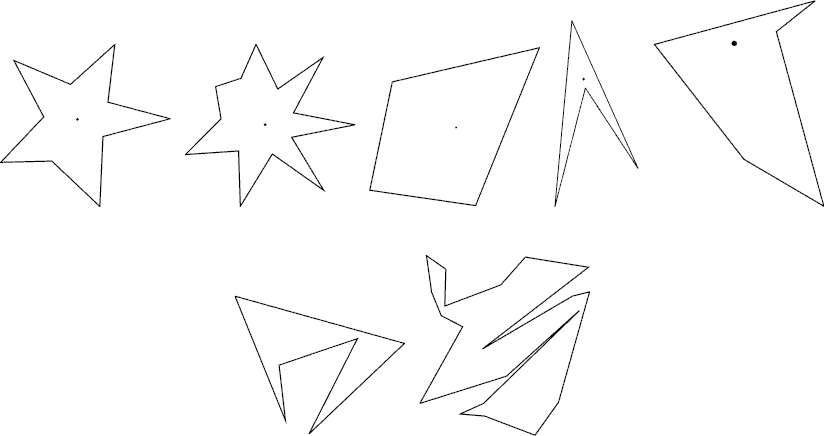
The mathematical definition of a star shape is as follows: A planar shape \(F\) is star-shaped if and only if there is a point \(C \in F\) such that, for any point \(P \in F\), the line segment \(CP\) is contained in \(F\). Such a point \(C\) is called a center of \(F\). To get accustomed to the definition let’s see some examples below.
The first two are what you would normally call stars. According to the above definition, however, all shapes in the first row are star-shaped. The two in the second row are not. For each star shape, a center is indicated with a dot. Note that a star shape in general has infinitely many centers. Fore Example, for the third quadrangular shape, all points in it are centers.
Your job is to write a program that tells whether a given polygonal shape is star-shaped or not.
Input
The input is a sequence of datasets followed by a line containing a single zero. Each dataset specifies a polygon, and is formatted as follows.
n
x1 y1
x2 y2 … xn yn
The first line is the number of vertices, \(n\), which satisfies \(4 \le n \le 50\). Subsequent \(n\) lines are the \(x\)- and \(y\)-coordinates of the \(n\) vertices. They are integers and satisfy \(0 \le x_i \le 10000\) and \(0 \le yi \le 10000 (i = 1, …, n)\). Line segments \((x_i, y_i)–(x_{i + 1}, y_{i + 1}) (i = 1, …, n − 1)\) and the line segment \((x_n, y_n)–(x_1, y_1)\) form the border of the polygon in the counterclockwise order. That is, these line segments see the inside of the polygon in the left of their directions.
You may assume that the polygon is simple, that is, its border never crosses or touches itself. You may assume assume that no three edges of the polygon meet at a single point even when they are infinitely extended.
Output
For each dataset, output “1” if the polygon is star-shaped and “0” otherwise. Each number must be in a separate line and the line should not contain any other characters.
Sample Input
6
66 13
96 61
76 98
13 94
4 0
45 68
8
27 21
55 14
93 12
56 95
15 48
38 46
51 65
64 31
0
Sample Output
1
0
Source
Solution
题意
给定 \(n\) 个点的多边形,求多边形是否有核。
题解
半平面交
半平面交求多边形的核的面积,如果面积为 0,就没有核。
Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const db eps = 1e-10;
const db pi = acos(-1.0);
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ll maxn = 1e3 + 10;
inline int dcmp(db x) {
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x > 0? 1: -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
inline void input() {
scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);
}
bool operator<(const Point &a) const {
return (!dcmp(x - a.x))? dcmp(y - a.y) < 0: x < a.x;
}
bool operator==(const Point &a) const {
return dcmp(x - a.x) == 0 && dcmp(y - a.y) == 0;
}
db dis2(const Point a) {
return pow(x - a.x, 2) + pow(y - a.y, 2);
}
db dis(const Point a) {
return sqrt(dis2(a));
}
db dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
db dis() {
return sqrt(dis2());
}
Point operator+(const Point a) {
return Point(x + a.x, y + a.y);
}
Point operator-(const Point a) {
return Point(x - a.x, y - a.y);
}
Point operator*(double p) {
return Point(x * p, y * p);
}
Point operator/(double p) {
return Point(x / p, y / p);
}
db dot(const Point a) {
return x * a.x + y * a.y;
}
db cross(const Point a) {
return x * a.y - y * a.x;
}
db ang(Point a) {
return acos((a.dis() * dis()) / dot(a));
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
Point p[maxn], ip[maxn];
class Line {
public:
Point s, e;
db angle;
Line() {}
Line(Point s, Point e) : s(s), e(e) {}
inline void input() {
s.input();e.input();
}
bool operator<(const Line &a) const {
Line l = a;
if(dcmp(angle - l.angle) == 0) {
return l.toLeftTest(s) == 1;
}
return angle < l.angle;
}
void get_angle() {
angle = atan2(e.y - s.y, e.x - s.x);
}
int toLeftTest(Point p) {
if((e - s).cross(p - s) > 0) return 1;
else if((e - s).cross(p - s) < 0) return -1;
return 0;
}
int linecrossline(Line l) {
if(dcmp((e - s).cross(l.e - l.s)) == 0) {
if(dcmp((l.s - e).cross(l.e - s)) == 0) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
return 2;
}
Point crosspoint(Line l) {
db a1 = (l.e - l.s).cross(s - l.s);
db a2 = (l.e - l.s).cross(e - l.s);
db x = (s.x * a2 - e.x * a1) / (a2 - a1);
db y = (s.y * a2 - e.y * a1) / (a2 - a1);
if(dcmp(x) == 0) x = 0;
if(dcmp(y) == 0) y = 0;
return Point(x, y);
}
};
Line l[maxn], q[maxn];
db half_plane(int cnt) {
sort(l + 1, l + 1 + cnt);
int tmp = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= cnt; ++i) {
if(dcmp(l[i].angle - l[tmp].angle) == 1) l[++tmp] = l[i];
}
cnt = tmp;
int head = 1, tail = 2;
q[1] = l[1], q[2] = l[2];
for(int i = 3; i <= cnt; ++i) {
while(head < tail && l[i].toLeftTest(q[tail].crosspoint(q[tail - 1])) == -1) {
--tail;
}
while(head < tail && l[i].toLeftTest(q[head].crosspoint(q[head + 1])) == -1) {
++head;
}
q[++tail] = l[i];
}
while(head < tail && q[head].toLeftTest(q[tail].crosspoint(q[tail - 1])) == -1) {
--tail;
}
while(head < tail && q[tail].toLeftTest(q[head].crosspoint(q[head + 1])) == -1) {
++head;
}
if(tail - head + 1 <= 2) {
return 0.0;
}
tmp = 0;
for(int i = head; i < tail; ++i) {
ip[++tmp] = q[i].crosspoint(q[i + 1]);
}
ip[++tmp] = q[head].crosspoint(q[tail]);
db ans = 0;
for(int i = 3; i <= tmp; ++i) {
ans += (ip[i - 1] - ip[1]).cross(ip[i] - ip[1]);
}
return ans * 0.5;
}
int main() {
int n;
while(~scanf("%d", &n) && n) {
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
p[i].input();
if(i > 1) {
l[++cnt].e = p[i];
l[cnt].s = p[i - 1];
l[cnt].get_angle();
}
}
l[++cnt].e = p[1];
l[cnt].s = p[n];
l[cnt].get_angle();
if(dcmp(half_plane(cnt)) == 0) {
printf("0\n");
} else {
printf("1\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
POJ 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are! (半平面交)的更多相关文章
- POJ 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are! (半平面相交)
Description After counting so many stars in the sky in his childhood, Isaac, now an astronomer and a ...
- poj 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are! - 求多边形有没有核 - 模版
/* poj 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are! - 求多边形有没有核 */ #include <stdio.h> #include ...
- POJ 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are! /POJ 3335 Rotating Scoreboard 初涉半平面交
题意:逆时针给出N个点,求这个多边形是否有核. 思路:半平面交求多边形是否有核.模板题. 定义: 多边形核:多边形的核可以只是一个点,一条直线,但大多数情况下是一个区域(如果是一个区域则必为 ).核内 ...
- poj 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are!
http://poj.org/problem?id=3130 #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorit ...
- POJ 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are!(半平面交求多边形的核)
题目链接 题意 : 给你一个多边形,问你该多边形中是否存在一个点使得该点与该多边形任意一点的连线都在多边形之内. 思路 : 与3335一样,不过要注意方向变化一下. #include <stdi ...
- poj 3130 How I Mathematician Wonder What You Are! 【半平面交】
求多边形的核,直接把所有边求半平面交判断有无即可 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> # ...
- POJ 3525 Most Distant Point from the Sea (半平面交向内推进+二分半径)
题目链接 题意 : 给你一个多边形,问你里边能够盛的下的最大的圆的半径是多少. 思路 :先二分半径r,半平面交向内推进r.模板题 #include <stdio.h> #include & ...
- 【POJ 3335】 Rotating Scoreboard (多边形的核- - 半平面交应用)
Rotating Scoreboard Description This year, ACM/ICPC World finals will be held in a hall in form of a ...
- POJ 3525 Most Distant Point from the Sea (半平面交+二分)
Most Distant Point from the Sea Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 3476 ...
随机推荐
- gradle 排除jar
排除fastjson的包,其他同理compile('com.qq.sdk:core:2.0.3') { exclude group: 'com.alibaba'}
- spring restTemplate使用方法
https://github.com/lenve/SimpleSpringCloud/tree/master/RestTemplate在Spring Cloud中服务的发现与消费一文中,当我们从服务消 ...
- 仿flask写的web框架
某大佬仿flask写的web框架 web_frame.py from werkzeug.local import LocalStack, LocalProxy def get_request_cont ...
- webservice 应用
一直以来,dashboard就会面临一个非常难堪的问题.就是刷新速度太慢了.它要连接query 来获取数据.而query每刷一次都需要时间.这是无可避免的结果.尽管它也是结果集,可还是比较慢.最近实践 ...
- 洛谷P2602 [ZJOI2010]数字计数(数位dp)
数字计数 题目传送门 解题思路 用\(dp[i][j][k]\)来表示长度为\(i\)且以\(j\)为开头的数里\(k\)出现的次数. 则转移方程式为:\(dp[i][j][k] += \sum_{t ...
- 浅析Draw Call
Draw Call是CPU对GPU的一种命令,仅仅指向一个需要被渲染的图元列表,在OpenGL和DirectX中分别体现为glDrawElements和DrawIndexedPrimitive图像编程 ...
- [已解决]报错: twisted 18.7.0 requires PyHamcrest>=1.9.0
1.下载对应的Twisted,下载地址:https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#twisted 2.通过Anaconda3的Anaconda Promp ...
- java final关键字详解
final是java中保留关键字,可以声明成员变量.类.方法与本地变量,一旦引用final关键字,将不能再改变这个引用,编译器会检查代码,要是想改变该引用,会报错. final变量? 凡是对成员变量或 ...
- Java面试宝典(1)Java基础部分
Java面试宝典 题目,日积月累,等到出去面试时,一切都水到渠成,面试时就自然会游刃有余了. 答题时,先答是什么,再答有什么作用和要注意什么(这部分最重要,展现自己的心得) 答案的段落分别,层次分明, ...
- Node.js中的fs文件系统
fs.stat 检测是文件还是目录 fs.mkdir 创建目录 fs.writeFile 创建写入文件 fs.appendFile 追加文件 fs.readFile 读取文件 fs.readdir 读 ...