HDU 6305.RMQ Similar Sequence-笛卡尔树+数学期望 (2018 Multi-University Training Contest 1 1008)
6305.RMQ Similar Sequence
这个题的意思就是对于A,B两个序列,任意的l,r,如果RMQ(A,l,r)=RMQ(B,l,r),B序列里的数为[0,1]的实数,B的重量为B的所有元素的和,否则为0。问你B的期望重量是多少。
dls讲题说是笛卡尔树,笛卡尔树是一种特定的二叉树数据结构,具体的看这篇博客吧:【pushing my way】笛卡尔树
这个题就是笛卡尔树同构的问题,假设A的笛卡尔树的子树大小为sz[u],那么序列B与A同构的概率为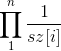 ,因为B中的数满足均匀分布(因为B中的元素为[0,1]中的任意实数),所以每个位置的期望值为(0+1)/2,那么B的重量总和为n/2,所以B的重量的期望值为
,因为B中的数满足均匀分布(因为B中的元素为[0,1]中的任意实数),所以每个位置的期望值为(0+1)/2,那么B的重量总和为n/2,所以B的重量的期望值为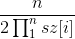 。
。
贴一下官方题解:
RMQ-Similar实际上就是A和B的笛卡尔树一样,这样我们就有了一个二叉树,然后可以在树上分析了。 考虑到B中有元素相同的概率是0,于是可以假设B里面元素互不相同,也就是说可以假定是一个排列。 显然,符合笛卡尔树的排列就是这个树的拓扑序列个数,就是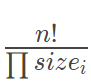 。然后显然每个排列期望的和是
。然后显然每个排列期望的和是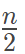 ,于是答案就是
,于是答案就是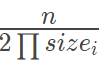 。
。
代码(参考别人的模板):
//1008-6305-RMQ的概念、笛卡尔树模板题,同构求bi的拓扑序个数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cassert>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=1e6+;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod=1e9+; stack<int>st;
ll inv[maxn];
int n; struct node{
int val,sz;
int l,r,par;
}t[maxn]; void init()
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
t[i].l=,t[i].r=,t[i].par=,t[i].sz=;//初始化
t[].val=inf;
while(!st.empty())
st.pop();
st.push();
} void build()
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
while(!st.empty()&&t[st.top()].val<t[i].val)//从栈顶往栈底遍历,
st.pop();
int par=st.top();
t[i].par=par;//i.par为st.pop()
t[i].l=t[par].r;
t[t[par].r].par=i;
t[par].r=i;//右子树
st.push(i);
}
} void dfs(int u)
{
if(u==) return ;
t[u].sz=;
dfs(t[u].l);
dfs(t[u].r);
t[u].sz+=t[t[u].l].sz+t[t[u].r].sz;
} void Inv(){//扩展gcd求逆元
inv[]=;
for(int i=;i<maxn;i++)
inv[i]=inv[mod%i]*(mod-mod/i)%mod;
} int main()
{
int T;
Inv();
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d",&n);
init();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&t[i].val);
build();
dfs(t[].r); ll ans=n*inv[]%mod;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
ans=ans*inv[t[i].sz]%mod;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}
代码(标程):
#include <cstdio>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue> using int64 = long long; const int mod = 1e9 + ; int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for (int cas = ; cas <= T; ++cas) {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
std::vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
} std::vector<int> left(n, -), right(n, -), stk(n), parent(n, -);
for (int i = , top = ; i < n; ++i) {
int last = -;
while (top && a[i] > a[stk[top - ]]) {
last = stk[--top];
}
if (top) {
right[stk[top - ]] = i;
parent[i] = stk[top - ];
}
left[i] = last;
if (last != -) parent[last] = i;
stk[top++] = i;
} std::vector<int> inv(n + , );
for (int i = ; i < n + ; ++i) {
inv[i] = int64(mod - mod / i) * inv[mod % i] % mod;
} using pii = std::pair<int, int>;
{
std::vector<pii> a(n), b(n);
std::queue<int> queue;
std::vector<int> cnt(n);
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
a[i] = b[i] = {inv[], };
if (left[i] == - && right[i] == -) {
queue.push(i);
}
cnt[i] = (left[i] != -) + (right[i] != -);
}
while (!queue.empty()) {
int u = queue.front(); queue.pop();
pii res = {(int64)a[u].first * inv[a[u].second] % mod * b[u].first % mod * inv[b[u].second] * % mod, a[u].second + b[u].second + };
int p = parent[u];
if (p == -) {
printf("%d\n", res.first);
break;
}
if (cnt[p] == ) a[p] = res;
else if (cnt[p] == ) b[p] = res;
--cnt[p];
if (cnt[p] == ) queue.push(p);
}
}
}
return ;
}
讲道理,还是有点不太清楚,还不熟练,多学习一下。
溜了。。。
HDU 6305.RMQ Similar Sequence-笛卡尔树+数学期望 (2018 Multi-University Training Contest 1 1008)的更多相关文章
- HDU - 6305 RMQ Similar Sequence(笛卡尔树)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6305 题目 对于A,B两个序列,任意的l,r,如果RMQ(A,l,r)=RMQ(B,l,r),B序列里的数为[0 ...
- hdu 6305 RMQ Similar Sequence——概率方面的思路+笛卡尔树
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6305 看题解,得知: 0~1内随机取实数,取到两个相同的数的概率是0,所以认为 b 序列是一个排列. 两个 ...
- [乱搞]hdu 6406 Taotao picks apples 笛卡尔树+倍增
题目链接 Problem Description There is an apple tree in front of Taotao's house. When autumn comes, n app ...
- 2018 Multi-University Training Contest 1 H - RMQ Similar Sequence(HDU - 6305 笛卡尔树)
题意: 对于一个序列a,构造一个序列b,使得两个序列,对于任意的区间 [l, r] 的区间最靠近左端点的那个最大值的位置,并且序列 b 满足 0 < bi < 1. 给定一个序列 a ,求 ...
- [模板] 笛卡尔树 && RMQ
话说我noip之前为什么要学这种东西... 简介 笛卡尔树(Cartesian Tree) 是一种二叉树, 且同时具有以下两种性质: 父亲节点的值大于/小于子节点的值; 中序遍历的结果为原序列. 笛卡 ...
- hdu 1506 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram——笛卡尔树
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1506 关于笛卡尔树的构建:https://www.cnblogs.com/reverymoon/p/952 ...
- HDU - 1506 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram (单调栈/笛卡尔树)
题意:求一个直方图中最大矩形的面积. 很经典的一道问题了吧,可以用单调栈分别求出每个柱子左右两边第一个比它低的柱子(也就相当于求出了和它相连的最后一个比它高的柱子),确定每个柱子的左右边界,每个柱子的 ...
- HDU 1506 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram(单调栈、笛卡尔树)
题意:给定n个连续排列的矩形的高,矩形的宽都为1.问最大矩形覆盖. 例如:n = 7,h[i] = (2 1 4 5 1 3 3),最大覆盖为8. Sample Input 7 2 1 4 5 1 3 ...
- 笛卡尔树--牛客第四场(sequence)
思路: O(n)建一颗笛卡尔树,再O(n)dfs向上合并答案就行了. #define IOS ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); #include &l ...
随机推荐
- Java算法求最大最小值,倒序,冒泡排序,斐波纳契数列,日历一些经典算法
一,求最大,最小值 int[] a={21,31,4,2,766,345,2,34}; //这里防止数组中有负数,所以初始化的时候给的数组中的第一个数. int max=a[0]; int min=a ...
- ScrollView中ViewPager无法正常滑动问题
本文主要介绍如何解决ViewPager在ScrollView中滑动经常失效.无法正常滑动问题. 解决方法只需要在接近水平滚动时ScrollView不处理事件而交由其子View(即这里的ViewPage ...
- 剑指Offer - 九度1360 - 乐透之猜数游戏
剑指Offer - 九度1360 - 乐透之猜数游戏2014-02-05 19:54 题目描述: 六一儿童节到了,YZ买了很多丰厚的礼品,准备奖励给JOBDU里辛劳的员工.为了增添一点趣味性,他还准备 ...
- 《Cracking the Coding Interview》——第4章:树和图——题目7
2014-03-19 04:48 题目:最近公共父节点问题. 解法1:Naive算法,先对其高度,然后一层一层往上直到找到结果. 代码: // 4.7 Least Common Ancestor // ...
- 就算WORD高手也无法解释的Word的一些疑惑.,一些已经解决,一些没有解决
如下功能如何用? 1.选项->保存->显示其他保存位置(即使可能需要登录)? 解答:您能告诉我吗? 2.字体->为字体调整字间距? 解答:自动调整某些字符之前的距离,使得更加美观.例 ...
- 关于windows10设置环境变量的问题
在设置环境变量的时候往往在网上能找到这样的文章: 1:新建环境变量 2:将新增的环境变量 加到path 变量中: 3.由于有的小伙伴的 系统是 windows10 在点击 编辑path 环境变量的时候 ...
- tomcat启动后服务访问404
. 解决办法: 在tomcat文件中有个work文件夹.其中,tomcat属于admin用户,work属于 admin用户 ,启动服务由admin用户启动. 但是发现work文件下的目录权限属于 ...
- centos下vsftpd登录后无法看见文件,无法创建文件及文件夹
centos下vsftpd不能显示文件,不能创建文件及文件夹 这是由于selinux的机制 运行如下命令查看: [root@SZCLC6X-AMP-4393 www]# getsebool -a|gr ...
- linux kernal oom killer 学习
背景 我有2个定时任务,一个任务A是00:00开跑,另一个B是04:00开跑.正常情况下A会在2点多时候跑完,但是某一天因为某一步骤用的时间过久,导致4点还没跑完,这时候A内存占用大约在12g左右.4 ...
- 【现代程序设计】homework-02
迟交了这么久,一定是0分了.可是我再怎么挣扎,还是不会.交了一维和二维的,这里说说思路吧.. 对于二维的情况,主要的思路就是将二维数组求矩形最大子数组的情况转化为一维的情况.因为所求的是矩形,我们就可 ...
