USACO-Greedy Gift Givers(贪婪的送礼者)-Section1.2<2>
【英文原题】
Greedy Gift Givers
A group of NP (2 ≤ NP ≤ 10) uniquely named friends has decided to exchange gifts of money. Each of these friends might or might not give some money to some or all of the other friends (although some might be cheap and give to no one). Likewise, each friend might or might not receive money from any or all of the other friends. Your goal is to deduce how much more money each person receives than they give.
The rules for gift-giving are potentially different than you might expect. Each person goes to the bank (or any other source of money) to get a certain amount of money to give and divides this money evenly among all those to whom he or she is giving a gift. No fractional money is available, so dividing 7 among 2 friends would be 3 each for the friends with 1 left over – that 1 left over goes into the giver's "account". All the participants' gift accounts start at 0 and are decreased by money given and increased by money received.
In any group of friends, some people are more giving than others (or at least may have more acquaintances) and some people have more money than others.
Given:
- a group of friends, no one of whom has a name longer than 14 characters,
- the money each person in the group spends on gifts, and
- a (sub)list of friends to whom each person gives gifts,
determine how much money each person ends up with.
IMPORTANT NOTE
The grader machine is a Linux machine that uses standard Unix conventions: end of line is a single character often known as '\n'. This differs from Windows, which ends lines with two characters, '\n' and '\r'. Do not let your program get trapped by this!
PROGRAM NAME: gift1
INPUT FORMAT
| Line # | Contents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A single integer, NP | |||
| 2..NP+1 | Line i+1 contains the name of group member i | |||
| NP+2..end | NP groups of lines organized like this:
|
SAMPLE INPUT (file gift1.in)
5
dave
laura
owen
vick
amr
dave
200 3
laura
owen
vick
owen
500 1
dave
amr
150 2
vick
owen
laura
0 2
amr
vick
vick
0 0
OUTPUT FORMAT
The output is NP lines, each with the name of a person followed by a single blank followed by the net gain or loss (final_money_value - initial_money_value) for that person. The names should be printed in the same order they appear starting on line 2 of the input.
All gifts are integers. Each person gives the same integer amount of money to each friend to whom any money is given, and gives as much as possible that meets this constraint. Any money not given is kept by the giver.
SAMPLE OUTPUT (file gift1.out)
dave 302
laura 66
owen -359
vick 141
amr -150
OUTPUT EXPLANATION
Five names: dave, laura, owen, vick, amr. Let's keep a table of the gives (money) each person 'has':
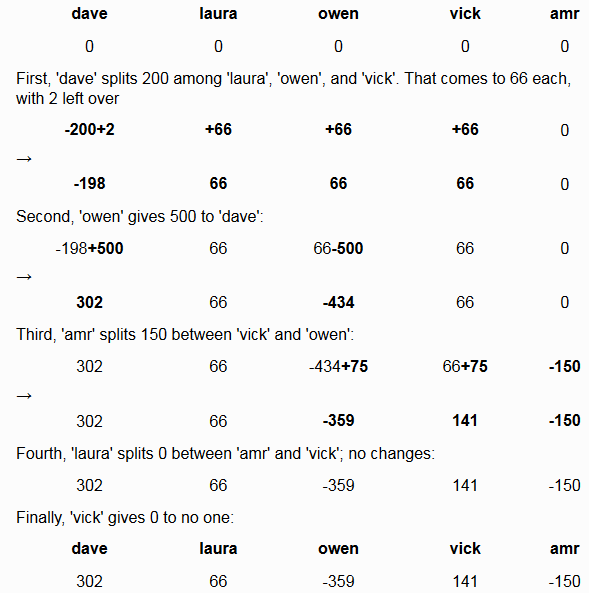
【中文翻译】
题目描述
对于一群(NP个)要互送礼物的朋友,GY要确定每个人送出的钱比收到的多多少。在这一个问题中,每个人都准备了一些钱来送礼物,而这些钱将会被平均分给那些将收到他的礼物的人。然而,在任何一群朋友中,有些人将送出较多的礼物(可能是因为有较多的朋友),有些人有准备了较多的钱。给出一群朋友,没有人的名字会长于 14 字符,给出每个人将花在送礼上的钱,和将收到他的礼物的人的列表,请确定每个人收到的比送出的钱多的数目。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第 1 行: 人数NP,2<= NP<=10
第 2 行 到 第NP+1 行:这NP个在组里人的名字一个名字一行
第NP+2到最后:
这里的I段内容是这样组织的:
第一行是将会送出礼物人的名字。
第二行包含二个数字:第一个是原有的钱的数目(在0到2000的范围里),第二个 NGi 是将收到这个人礼物的人的个数 如果 NGi 是非零的, 在下面 NGi 行列出礼物的接受者的名字,一个名字一行。
输出格式:
输出NP行
每行是人的名字和每个人收到的比送出的钱多的数目
输入输出样例
5
dave
laura
owen
vick
amr
dave
200 3
laura
owen
vick
owen
500 1
dave
amr
150 2
vick
owen
laura
0 2
amr
vick
vick
0 0 思路:这道题目是纯粹的模拟题,按照题目的要求来走。
这题可以用结构体来实现(网上有许多用map来解决的,但我学的是C所以没用,不过用map确实方便不少~)。
首先定义结构体变量people,将每个的名字进行存储,然后开始循环:
定位到当前要送礼的这个人(字符串查找),然后将这个人的钱平均分配给那些他要送给的人(即受赠人所拥有的钱增加)
一直这样循环完每一个人……
最后扫描一遍整个结构体,输出每个人的名字和他收到的比送出的钱多的数目(负数表示他“亏了”,正数表示他“赚了”) 代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct people//定义结构体people
{
char name[];//姓名
int money;//某人所拥有的钱数
int list;//要送礼物的列表人数
int give;//送给每个人的钱数
};
struct people p[];
int n,money,list,b; //人数n、某人所拥有的钱数(暂存)、要送礼物的列表人数(暂存)、送给每个人的钱数(暂存)
char man[];//姓名暂存变量
int moneys(int mo,int friends)//计算送给每个人的钱数
{
if(friends==)
{
return ;/*注意判断要送的人数(list)是否为0,否则会出现除数为0而运行错误的情况*/
}
return mo/friends;//若非0则返回结果(向下取整)
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int i,j,k;
for(i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",p[i].name);//输入每个人的明名字
}
for(i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s%d %d",man,&money,&list);//先将输入内容暂时存入变量中
for(j=;j<n;j++)
{
if(strcmp(man,p[j].name)==)//搜索姓名相符的变量
{
p[j].list=list;
p[j].give=moneys(money,p[j].list);//将信息存入此结构体变量内
b=j;//保存此变量的下标,留着送礼时用(因为j的值会变动)
}
}
for(j=;j<p[b].list;j++)//往下循环他将送礼的人
{
scanf("%s",man);//输入收礼人姓名
for(k=;k<n;k++)
{
if(strcmp(p[k].name,man)==)//搜索与姓名相符的变量
{
p[k].money+=p[b].give;//收礼人拥有钱数增加
p[b].money-=p[b].give;//送礼人钱数对应减少
}
}
}
}
for(i=;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%s %d\n",p[i].name,p[i].money);//按要求依次输出信息 。
}
return ;
}
USACO-Greedy Gift Givers(贪婪的送礼者)-Section1.2<2>的更多相关文章
- USACO . Greedy Gift Givers
Greedy Gift Givers A group of NP (2 ≤ NP ≤ 10) uniquely named friends has decided to exchange gifts ...
- Greedy Gift Givers 贪婪的送礼者 USACO 模拟
1002: 1.1.2 Greedy Gift Givers 贪婪的送礼者 时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB提交: 9 解决: 9[提交] [状态] [讨论版] [命题人:外部导入 ...
- USACO Training Section 1.1 贪婪的送礼者Greedy Gift Givers
P1201 [USACO1.1]贪婪的送礼者Greedy Gift Givers 题目描述 对于一群(NP个)要互送礼物的朋友,GY要确定每个人送出的钱比收到的多多少.在这一个问题中,每个人都准备了一 ...
- Java实现【USACO】1.1.2 贪婪的礼物送礼者 Greedy Gift Givers
[USACO]1.1.2 贪婪的礼物送礼者 Greedy Gift Givers 题目描述 对于一群要互送礼物的朋友,你要确定每个人送出的礼物比收到的多多少(and vice versa for th ...
- 洛谷 P1201 [USACO1.1]贪婪的送礼者Greedy Gift Givers
贪婪的送礼者Greedy Gift Givers 难度:☆ Code: #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <c ...
- USACO Section 1.1-2 Greedy Gift Givers
Greedy Gift Givers 贪婪的送礼者 对于一群(NP个)要互送礼物的朋友,GY要确定每个人送出的钱比收到的多多少. 在这一个问题中,每个人都准备了一些钱来送礼物,而这些钱将会被平均分给那 ...
- usaco training <1.2 Greedy Gift Givers>
题面 Task 'gift1': Greedy Gift Givers A group of NP (2 ≤ NP ≤ 10) uniquely named friends has decided t ...
- 119 - Greedy Gift Givers
Greedy Gift Givers The Problem This problem involves determining, for a group of gift-giving frien ...
- Section 1.1 Greedy Gift Givers
Greedy Gift Givers A group of NP (2 ≤ NP ≤ 10) uniquely named friends hasdecided to exchange gifts o ...
- 1.1.4 PROB Greedy Gift Givers
Greedy Gift Givers A group of NP (2 ≤ NP ≤ 10) uniquely named friends has decided to exchange gifts ...
随机推荐
- python 统计单词出现次数
#use python3.6 import re from collections import Counter FILESOURCE = './abc.txt' def getMostCommonW ...
- (转载)C #开源框架
Json.NET http://json.codeplex.com/ Json.Net 是一个读写Json效率比较高的.Net框架.Json.Net 使得在.Net环境下使用Json更加简单.通过Li ...
- LeetCode:汇总区间【228】
LeetCode:汇总区间[228] 题目描述 给定一个无重复元素的有序整数数组,返回数组区间范围的汇总. 示例 1: 输入: [0,1,2,4,5,7] 输出: ["0->2&quo ...
- C# 自定义异常类 throw语句抛出异常
Exception概述: 异常(Exception)一般分为两大类SystemException.ApplicationException,前者是预定义的异常类,后者是用户自定义异常类时需要继承的类 ...
- 基于socket实现上传文件
基于socket实现文件上传 客户端代码: #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- """ 这个是实现上传文件 首先让客 ...
- java深入探究05
通讯录小程序 需求说明: 功能: 添加联系人 修改联系人 删除联系人 查询所有联系人 要求: console控制 数据保存在xml 1.创建联系人类 /** * 联系人实体对象 * @author A ...
- html5新特性contenteditable 属性更容易实现动态表单
介绍html5新特性的一个属性:contenteditable 作用域全局.所有的块标签都可以,例如:span.p.div.td等标签.但是,不可以作用域<br/>类型的标签. conte ...
- name lookup of 'res' changed for new ISO 'res' scoping
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int pow ( int val, int exp ); int main() { int val = 2 ...
- 【BZOJ 4709】柠檬 斜率优化dp+单调栈
题意 给$n$个贝壳,可以将贝壳分成若干段,每段选取一个贝壳$s_i$,这一段$s_i$的数目为$num$,可以得到$num^2\times s_i$个柠檬,求最多能得到几个柠檬 可以发现只有在一段中 ...
- 一文读懂所有的编码方式(UTF-8、GBK、Unicode、宽字节...)
编码方式就分两类:ANSI编码.Unicode编码.这两类编码都兼容ASC码. ------------------------------------------------------------ ...
