java自定义注解实现前后台参数校验
2016.07.26
首先介绍些基本概念:
Annotations(also known as metadata)provide a formalized way to add information to your code so that you can easily use that data at some later point.
Annotations are partly motivated by a general trend toward combining metadata with source-code files,instead of keeping it in external documents. They are also a response to feature pressure from other languages like C#.
Annotations are one of the fundamental language changes introduced in Java SE5. They provide information that you need to fully describe your program, but that cannot be expressed in Java.Thus,annotations allow you to store extra information about your program in a format that is tested and verified by the compiler.Annotations can be used to generate descriptor files or even new class definitions and help ease the burden of writing "boilerplate" code.Using annotations,you can keep this metadata in the Java source code,and have the advantage of cleaner looking code,compile-time type checking and the annotation API to help build processing tools for your annotations.
---《Thinking in java》
1.java用@interface xx{}定义一个注解。
2.There are currently only three standard annotations(described earlier)(@Override @Deprecated @SuppressWarnings)and four meta-annotations defined in the Java language(@Target @Retention @Documented @Inherited):
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) // 注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) // 默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到
(RUNTIME的值得注意下,因为意味着可以反射来获取)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) // 接口、类、枚举、注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) // 字段、枚举的常量
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) // 方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) // 构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE) // 局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) // 注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) // 包
有一种做法就是在定义注解时加上@Taget(xx)和@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) ,但没有在注解中写方法,只是在运行时通过反射机制来获取注解,然后自己写相应逻辑(所谓注解解析器)
大概是类似的写法:
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Documented
@Inherited
@Target({ ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Validate
{
public int min() default 1; public int max() default 10; public boolean isNotNull() default true;
}
之后运行时,用反射获取注解,具体不谈。
之前在网上查找这方面技术文章找到的都是这种,给当时的我带来很大困惑。觉得不是我想要的。
关于Java 注解,在《java编程思想》一书里第十章有详细的介绍(包括@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)的方式,的注解处理器的例子),具体不多谈。
其实是可以通过@Constraint来限定自定义注解的方法。
@Constraint(validatedBy = xxxx.class)
下面是我做的 java自定义注解实现前后台参数校验 的代码示例:
package sonn.sonnannotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; import javax.validation.Constraint;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
import javax.validation.Payload; import sonn.util.StringUtill; /**
* @ClassName: IsValidString
* @Description: 自定义注解实现前后台参数校验,判断是否包含非法字符
* @author 无名
* @date 2016-7-25 下午8:22:58
* @version 1.0
*/
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = IsValidString.ValidStringChecker.class)
@Documented
public @interface IsValidString
{
String message() default "The string is invalid."; Class<?>[] groups() default {}; Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default{}; class ValidStringChecker implements ConstraintValidator<IsValidString,String>
{ @Override
public void initialize(IsValidString arg0)
{
} @Override
public boolean isValid(String strValue, ConstraintValidatorContext context)
{
if(StringUtill.isStringEmpty(strValue))
{
return true;
}
if(strValue.contains("<"))
{
return false;
}
return true;
} }
}
上述代码,通过@Constraint(validatedBy = IsValidString.ValidStringChecker.class)限定了注解的方法逻辑---该注解类的名为ValidStringChecker的内部类。
而该内部类实现了ConstraintValidator<IsValidString,String>接口
官方文档是这样描述的:
Interface ConstraintValidator<A extends Annotation,T>
public interface ConstraintValidator<A extends Annotation,T>
Defines the logic to validate a given constraintAfor a given object typeT.Implementations must comply to the following restriction:
Tmust resolve to a non parameterized type- or generic parameters of
Tmust be unbounded wildcard types
The annotation
SupportedValidationTargetcan be put on aConstraintValidatorimplementation to mark it as supporting cross-parameter constraints. Check outSupportedValidationTargetandConstraintfor more information.
实现的isValid方法便是,该接口的校验方法。
试验一下效果,在要校验的实体类字段加上注解:

写文章页面,文章标题内加入'<'然后提交:
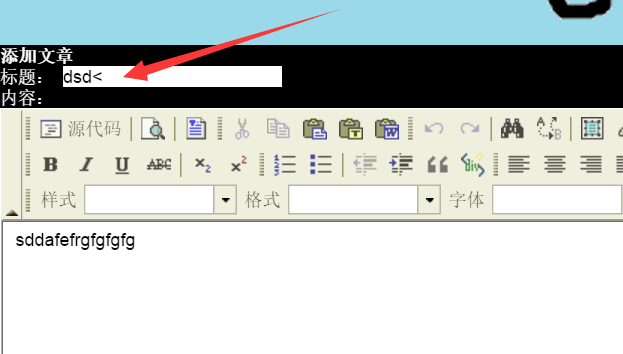
提交失败,报500错误,说明注解生效:

但这样还有问题,我的blog网站不能直接打印出报错信息。还是要搞一个error页面出来。
这个简单,web.xml下加入error页面路径,然后做一个页面即可:
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/error.jsp</location>
</error-page>
参考文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/liangweiping/p/3837332.html
java自定义注解实现前后台参数校验的更多相关文章
- Java自定义注解源码+原理解释(使用Java自定义注解校验bean传入参数合法性)
Java自定义注解源码+原理解释(使用Java自定义注解校验bean传入参数合法性) 前言:由于前段时间忙于写接口,在接口中需要做很多的参数校验,本着简洁.高效的原则,便写了这个小工具供自己使用(内容 ...
- java自定义注解类
一.前言 今天阅读帆哥代码的时候,看到了之前没有见过的新东西, 比如java自定义注解类,如何获取注解,如何反射内部类,this$0是什么意思? 于是乎,学习并整理了一下. 二.代码示例 import ...
- java自定义注解注解方法、类、属性等等【转】
http://anole1982.iteye.com/blog/1450421 http://www.open-open.com/doc/view/51fe76de67214563b20b385320 ...
- java自定义注解知识实例及SSH框架下,拦截器中无法获得java注解属性值的问题
一.java自定义注解相关知识 注解这东西是java语言本身就带有的功能特点,于struts,hibernate,spring这三个框架无关.使用得当特别方便.基于注解的xml文件配置方式也受到人们的 ...
- Java自定义注解和运行时靠反射获取注解
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/bao19901210/article/details/17201173/ java自定义注解 Java注解是附加在代码中的一些元信息,用于一些工具在编 ...
- Java自定义注解的实现
Java自定义注解的实现,总共三步(eg.@RandomlyThrowsException): 1.首先编写一个自定义注解@RandomlyThrowsException package com.gi ...
- JAVA自定义注解 ------ Annotation
日常开发工作中,合理的使用注解,可以简化代码编写以及使代码结构更加简单,下面记录下,JAVA自定义注解的开发过程. 定义注解声明类. 编写注解处理器(主要起作用部分). 使用注解. 相关知识点介绍, ...
- SpringBoot Validation参数校验 详解自定义注解规则和分组校验
前言 Hibernate Validator 是 Bean Validation 的参考实现 .Hibernate Validator 提供了 JSR 303 规范中所有内置 constraint 的 ...
- Java 自定义注解 校验指定字段对应数据库内容重复
一.前言 在项目中,某些情景下我们需要验证编码是否重复,账号是否重复,身份证号是否重复等... 而像验证这类代码如下: 那么有没有办法可以解决这类似的重复代码量呢? 我们可以通过自定义注解校验的方式去 ...
随机推荐
- 禁止VMware虚拟机与Host的时间同步
禁止VMware虚拟机与Host的时间同步 1. 查看虚拟机是否安装了 VMware Tools, 如果有安装,则将 VMware Tools 属性窗口的“选项”-->“其他选项”中“虚拟机与宿 ...
- ServiceStack.OrmLite中的一些"陷阱"(1)
使用过ServiceStack.Ormlite的人都应该知道,其作为一个轻量级的ORM,使用的便捷度非常高,用起来就一个字:爽!而支撑其便捷度的,是库内大量地使用了扩展方法及静态变量. 首先先从源头入 ...
- mvc+mysql+EF
网上有很多关于EF在联机情况下利用nuget管理器安装的案例,我就讲一下脱机状况吧! 一.建立一个文件夹,例如D:/Packages 放入安装EF和mysql需要的包:EntityFramework. ...
- app.js
//第一步,引入express模块 var exp = require('express'), http = require('http'),//引入http模块 path = req ...
- linux mysql
安装mysql 1.使用rpm 安装mysql 或者使用yum安装 使用rpm 安装 下载 Centos 7 所需要的mysql包 tar -xf 解压整合包 根据依赖 安装 common>li ...
- bochs上网及配置
下载并安装bochs2.6:(不能是更高版本) 创建bochs 时注意勾选Dlx linux Demo,但是其文件bochsrc.bxrc中无Ne2k网卡选项,这一段要自己添加,详情见后. 先确定我们 ...
- kafka及zookeeper安装
kafka_2.9.2-0.8.1.tgzzookeeper-3.4.8.tar.gz 安装 zookeeper1 export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/zookeeper/bin ...
- 转:如何调试PHP的Core之获取基本信息
其实一直想写这个系列, 但是一想到这个话题的宽泛性, 我就有点感觉无法组织. 今天我也不打算全部讲如何调试一个PHP的Core文件, 也不会介绍什么是Coredump, 选择一个相对比较简单的方向来介 ...
- PHP程序员如何突破技术瓶颈
身边有几个做PHP开发的朋友,也接触到不少的PHP工程师,他们常疑虑自己将来在技术上的成长与发展,我常给他们一些建议,希望他们能破突自己,有更好的发展. 先明确我所指的PHP工程题,是指毕业工作后,主 ...
- Android JIT实时编译器的设置
在Android JIT实时编译是在Android 2.2之后才引入的,JIT编译器可以显著的提高机器的性能,经过测试,android 2.2的性能较android 2.1提高了 2-5倍.JIT提 ...
