android学习笔记56——Service
Service四大组件之一,需要在AndroidMainfest.xml中添加相关配置,运行于后台,不与用户进行交换,没有UI...
配置时可通过《intent-filter.../》元素指定它可被那些Intent启动。
Android系统本身提供了大量的Service组件,可通过这些系统Service来操作Android系统本身。
BroadcastReceiver组件就是一个全局的事件监听器,只不过其用于监听系统发出的BroadCast,通过使用BroadcastReceiver,即可在不同应用程序之间通信。
创建、配置Service操作步骤:
1.定义一个基础Service的子类;
2.在AndroidMainfest.xml中添加配置;
Service与Activity都继承自Context,都可调用Context里定义的如:getResources()、getContentResolver()等方法。
Service也定义了生命周期,方法如下:
| abstract IBinder onBind(Intent intent) | 该方法是Service子类必须实现的方法,该方法返回一个IBinder对象,应用程序可通过该对象与Service组件通信 |
| void oncreate() | 当Service第一次被创建后将立即回调该方法 |
| void onDestory(0 | 当该Service被关闭之前将会回调该方法 |
| void onStartCommand(Intent intent,int flags,int startId) | 该方法的早期版本是void onStart(Intent intent,int startId),每次客户端调用startService(Intent)方法启动该Service时都会回调该方法 |
| boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) | 当该Service上绑定的所有客户端都断开连接时将会回调该方法 |
实例如下:
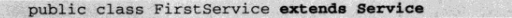

配置如下:

Android系统中运行Service有两种方式:
1.通过Context的startService():通过该方法启动服务,访问者与服务直接没有关联,即使访问者退出了,服务仍然运行——因此Service和访问者直接无法进行通信、数据交换。
2.通过Context的bindService():通过该方法启动服务,访问者与服务绑定在一起,访问者退出,服务也将跟随访问者状态被终止
——如果Service和访问者之间需要进行数据交换或方法调用,则应该使用bindService()和unbindService()方法启动、关闭服务。
启动和停止Service
如下图所示:

注意:
每当Service被创建时回调onCreate()方法,每次Service被启动时会回调onStart(),多次启动一个已有的Service组件将不会再回调onCreate(),但每次启动时都会回调onStart()。
绑定本地Service并与之通信
Context的bindService方法的完整方法签名为:bindService(Intent service,ServiceConnection conn,int flags):
service——该参数通过Intent指定要启动的服务;
ServiceConnection ——该参数是一个ServiceConnection对象,该对象用于监听访问者与Service之间的连接情况。
当访问者与Service之间连接成功时将回调该ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected(ComponetName name,IBinder binder)方法;
当访问者与Service之间断开连接时将回调该ServiceConnection对象的onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name)方法。
flags——指定绑定时是否自动创建Service(如果Service还未创建)。该参数可指定为0(不自动创建)或BIND_AUTO_CREATE(自动创建)。
1.注意到ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected方法中有一个IBinder对象,该对象即可实现与被绑定Service之间的通信。
2.当开发Service类时,该Service类必须提供一个IBinder binder(Intent intent)方法,在绑定本地Service的情况下,onBind(Intent intent)方法返回的IBinder对象将会传给ServiceConnection对象里的
onSeviceConnected(ComponentName name ,IBinder binder)方法的service参数,这样访问者就可通过该IBinder对象与Service进行通信。
注意:实际上开发时通常会采用继承Binder(IBinder的实现类)的方式实现自己的IBinder对象。
实例如下:
布局文件==》
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/photo12"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <Button
android:id="@+id/btnBinder"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="binder"
android:textSize="25dp" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/btnUnBinder"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="unbinder"
android:textSize="25dp" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/btnServiceStatus"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="service status"
android:textSize="25dp" /> </LinearLayout> AndroidMainfest.xml==>
添加
<service android:name="com.example.myservice1.BindService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.myservice1.MainActivity"/>
</intent-filter>
</service> 代码实现==》
package com.example.myservice1; import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log; public class BindService extends Service
{
private Integer count = 0;
private boolean quit;
// 定义onBinder方法所返回的对象
private MyBinder binder = new MyBinder(); // 通过继承Binder来实现IBinder类f
public class MyBinder extends Binder
{
public int getCount()
{
// 获取Service的运行状态:count
return count;
}
} @Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent)
{
System.out.println("Service is Binded");
Log.i("swg", "Service is Binded");
return binder;
} @Override
public void onCreate()
{
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("Service is onCreate");
Log.i("swg", "Service is onCreate");
// 启动一条线程、动态地修改count状态值
new Thread()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
while (!quit)
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
}
}
}.start();
} @Override
public void onDestroy()
{
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("Service is onDestroy");
Log.i("swg", "Service is onDestroyed");
this.quit = true;
} @Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent)
{
System.out.println("Service is onUnbind");
Log.i("swg", "Service is onUnbind");
// return super.onUnbind(intent);
return true;
} } package com.example.myservice1; import com.example.myservice1.BindService.MyBinder;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection; @SuppressLint("ShowToast")
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
BindService.MyBinder binder;
final String TAG = "com.example.myservice1.MainActivity"; private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection()
{
// 当Activity与服务连接成功时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service)
{
System.out.println("-------------Service is onServiceConnected-------------");
Log.i("swg", "-------------Service is onServiceConnected-------------");
// 获取Service的onBind方法所返回的MyBinder对象
binder = (MyBinder) service;
} // 当Activity与服务断开连接时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name)
{
System.out.println("-------------Service is onServiceDisconnected-------------");
Log.i("swg", "-------------Service is onServiceDisconnected-------------");
} }; @Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button btnBinder = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnBinder);
Button btnUnBinder = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnUnBinder);
Button btnServiceStatus = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnServiceStatus);
btnBinder.setOnClickListener(new MyButtonClick());
btnUnBinder.setOnClickListener(new MyButtonClick());
btnServiceStatus.setOnClickListener(new MyButtonClick());
} private class MyButtonClick implements OnClickListener
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(TAG);
try
{
switch (v.getId())
{
case R.id.btnBinder:
Log.i("swg", "-------------onClick is btnBinder-------------");
bindService(intent, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);// 绑定时自动创建服务
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Service btnBinder success", 3000)
.show();
break;
case R.id.btnUnBinder:
Log.i("swg", "-------------onClick is btnUnBinder-------------");
unbindService(conn);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Service btnUnBinder success", 3000)
.show();
break;
case R.id.btnServiceStatus:
Log.i("swg", "-------------onClick is btnServiceStatus-------------");
// 获取并显示Service的count值
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Service count==" + binder.getCount(), 5000)
.show();
break;
}
} catch (Exception e)
{
//Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Service error==" + e.getMessage(), 5000).show();
return;
}
}
} }
运行效果:
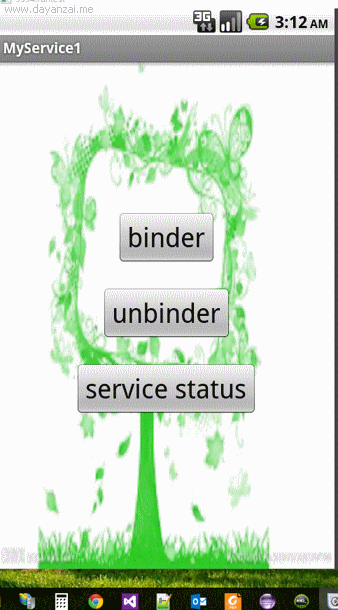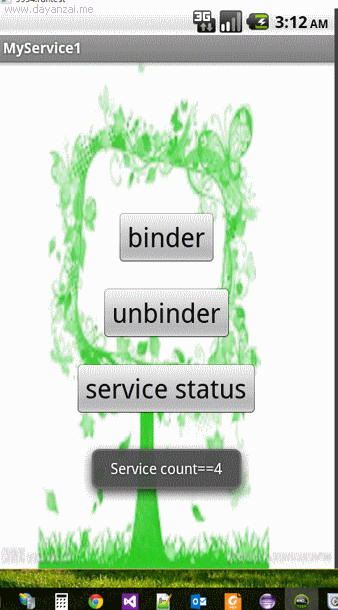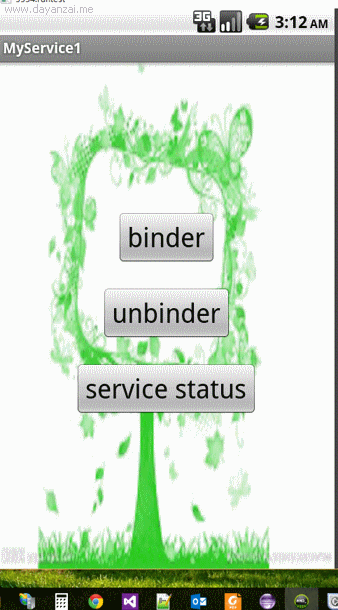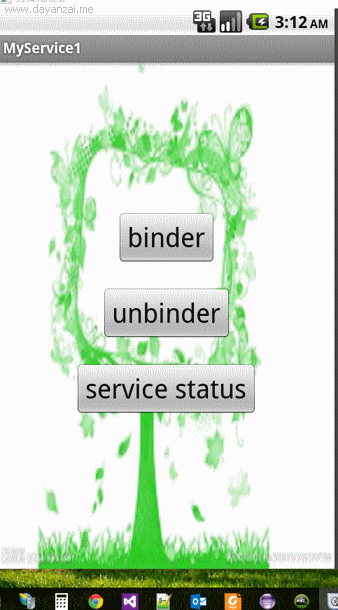
注意:对于Service的onBind()所返回的IBinder对象来说,其可被当成该Service组件所返回的回调对象,Service允许客户端通过该IBinder对象访问
Service内部的数据,这样即可实现客户端与Service之间的通信。
与多次调用startService()启动Service不同的是,多次调用bindService()并不会重复执行绑定;
前者,启动一次服务,系统就会调用一次服务的onStart(),后者,系统只会调用onBind()方法一次。
android学习笔记56——Service的更多相关文章
- Android学习笔记--服务(Service)
1.服务概述 1.服务是Android四大组件之一,在使用上可以分为本地服务和远程服务,本地服务是指在不影响用户操作的情况下在后台默默的执行一个耗时操作,例如下载,音频播放等.远程服务是指可以供其他应 ...
- Android学习笔记之Service
与服务通信 用bindservice 而startservice并无通信条件. service 为android为系统服务,所以程序员无法new出来,只能建立服务,共其他组件使用. package c ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(七七):服务(2):Local Service
目录(?)[-] Local service代码 调用Local ServiceLocal Service client代码 AndroidManifestxml定义Serviceacitivty的l ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(七八):服务(3):远程服务:AIDL文件
目录(?)[-] 在AIDL中定义服务接口 根据AIDL文件自动生成接口代码 文章转载只能用于非商业性质,且不能带有虚拟货币.积分.注册等附加条件.转载须注明出处:http://blog.csdn.n ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(七六):服务(1):local和remote
文章转载只能用于非商业性质,且不能带有虚拟货币.积分.注册等附加条件.转载须注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/flowingflying/ Android提供服务,服务是运行在后台的 ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(七四):HTTP服务(8):使用后台线程AsyncTask
目录(?)[-] 5秒超时异常 AsyncTask 实现AsyncTask抽象类 对AsyncTask的调用 在哪里运行 其他重要method 文章转载只能用于非商业性质,且不能带有虚拟货币.积分.注 ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(七五):HTTP服务(9):DownloadManager
目录(?)[-] 小例子 保存在哪里下载文件信息设置和读取 查看下载状态和取消下载 文章转载只能用于非商业性质,且不能带有虚拟货币.积分.注册等附加条件,转载须注明出处:http://blog.csd ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(七十):HTTP服务(4):SOAP/JSON/XML、异常
目录(?)[-] SOAP JSON和XMLPullParser Exception处理 文章转载只能用于非商业性质,且不能带有虚拟货币.积分.注册等附加条件,转载须注明出处:http://blog. ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(六八):HTTP服务(2):HTTP POST
目录(?)[-] 找一个测试网站 HTTP POST小例子 上次学习了HTTP GET请求,这次学习一下HTTP POST. 找一个测试网站 小例子好写,但要找个测试网站就有些麻烦,一下子无从入手,都 ...
随机推荐
- python 学习笔记-----编码问题
1.python 最早支持的是ASCII编码. 所以对于普通的字符串"ABC"为ASCII编码的形式.字母和数字之间的转换函数为ord('字母')和chr(‘数字’)函数. ord ...
- SQL SERVER CURSOR游标的使用(转载)
一:认识游标 游标(Cursor)它使用户可逐行访问由SQL Server返回的结果集. 使用游标(cursor)的一个主要的原因就是把集合操作转换成单个记录处理方式. 用SQL语言从数据库中检索数据 ...
- Svn常见问题及相关原因
1. svn: Server sent unexpected return value (500 Internal Server Error) in response to OPTIONS reque ...
- XListView理念
package com.example.testxml1; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.InputStream;import ...
- HTML5 的data-* 自定义属性
HTML5增加了一项新功能是自定义数据属性,也就是 data-*自定义属性. 在HTML5中我们可以使用以data-为前缀来设置我们需要的自定义属性,来进行一些数据的存放. 当然高级浏览器下可通过脚本 ...
- java eclipse环境搭建环境
开发环境搭建: JDK的安装 http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads 下载文件:jdk-8u101-windows-x64.ex ...
- Http协议(一)
Http是一种无状态,面向连接的协议.是客户端与服务端进行超文本传输协议(HTTP)的一种通信协议.目前我们使用的是Http/1.1版本. Cookie是解决http无状态,相当于一个只有一天记忆的人 ...
- HttpURLConnection发送和接受返回值
URL url = new URL(sb.toString());//请求的地址 HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.open ...
- CSS中相对定位与绝对定位
看了几个讲解定位的博客,觉得还不错,分享之: 博客一:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4bcf4a5e010008o0.html 文章中,主要需要参考的有两点: 1,相对 ...
- Jdk内置性能测试工具的介绍
(一) JConsole JConsole使用JVM的可扩展性Java管理扩展(JMX)工具来提供关于运行于Java平台的应用程序的性能和资源消耗的信息. 在J2SE 5.0软件中,你需要启动使用-D ...
