hashMap的源码实现
1、初步认识hashMap
public static void main(String[] args) {
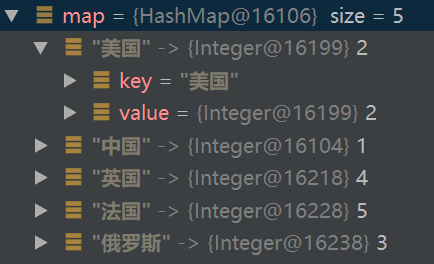
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(5);
map.put("中国", 1);
map.put("美国", 2);
map.put("俄罗斯", 3);
map.put("英国", 4);
map.put("法国", 5);
for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
}
debug模式,从数据结构上认知HashMap:
JDK8中HashMap的数据结构源码:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
2、HashMap的两个重要参数
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
* table的默认初始容量
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.(负载因子)
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
- capacity 就是初始化HashMap时的数组容量,load factor 指负载因子;
- 当我们对迭代性能要求比较高时,不能把capacity设置的太大;同时load factor不要超过0.75,否则会明显增加冲突几率,降低HashMap性能;
- hashMap中元素数量( put 的元素个数) > (负载因子 * 容量) 时,就需要扩容为原来的2倍。
3、HashMap的put(Key k,Value v)的原理
数据存储的步骤:
- 当在第一次put时,先对table初始化,通过hash计算得到存放位置table[i],存放。
- 当再次put时,同样经过hash计算得到位置,则采用链表法解决冲突,存放在相同位置的next区域。
- 在JDK8中设置了链表的默认阈值为8,如果超过这个值,则进行树化。
- 如果节点已经存在就替换old value(保证key的唯一性)。
- 如果bucket满了(超过load factor*current capacity),就要resize,变为原来2倍。
面试题:解释HashMap的原理,数据量增大时,数据结构是什么样的?
在数据量小的时候,HashMap是按照链表的模式存储的。当数据量变大之后,为了进行快速的查找,会将这个链表变成红黑树(均衡二叉树),用hash码作为数据的定位来进行保存。
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
} /**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
hashMap的源码实现的更多相关文章
- HashMap的源码分析
hashMap的底层实现是 数组+链表 的数据结构,数组是一个Entry<K,V>[] 的键值对对象数组,在数组的每个索引上存储的是包含Entry的节点对象,每个Entry对象是一个单链表 ...
- HashMap的源码学习以及性能分析
HashMap的源码学习以及性能分析 一).Map接口的实现类 HashTable.HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap 二).HashMap和HashTable的区别 1).H ...
- HashMap的源码分析与实现 伸缩性角度看hashmap的不足
本文介绍 1.hashmap的概念 2.hashmap的源码分析 3.hashmap的手写实现 4.伸缩性角度看hashmap的不足 一.HashMap的概念 HashMap可以将其拆分为Hash散列 ...
- Java——HashMap底层源码分析
1.简介 HashMap 根据键的 hashCode 值存储数据,大多数情况下可以直接定位到它的值,因而具有很快的访问速度,但遍历顺序却是不确定的. HashMap 最多只允许一条记录的key为 nu ...
- Java中HashMap的源码分析
先来回顾一下Map类中常用实现类的区别: HashMap:底层实现是哈希表+链表,在JDK8中,当链表长度大于8时转换为红黑树,线程不安全,效率高,允许key或value为null HashTable ...
- java基础,集合,HashMap,源码解析
最怕,你以为你懂咯,其实你还不懂: 见贤思齐,看看那些我们习以为常的集合,通过相关定义.源码,思考分析,加深对其的理解,提高编码能力,能做一个略懂的程序员: 做几个我们常用的集合类.开篇HashMap ...
- 【JDK8】HashMap集合 源码阅读
JDK8的HashMap数据结构上复杂了很多,因此读取效率得以大大提升,关于源码中红黑树的增删改查,博主没有细读,会在下一篇博文中使用Java实现红黑树的增删改查. 下面是类的结构图: 代码(摘抄自J ...
- HashMap框架源码深入解读,面试不用愁
在Java Collections Framework的体系中中,主要有两个重要的接口,一个是List.Set和Queue所属的Collection,还有一个就是Map接口了.在上一篇文章中介绍了Li ...
- java jdk 中HashMap的源码解读
HashMap是我们在日常写代码时最常用到的一个数据结构,它为我们提供key-value形式的数据存储.同时,它的查询,插入效率都非常高. 在之前的排序算法总结里面里,我大致学习了HashMap的实现 ...
随机推荐
- Markdown 设置字体大小颜色及背景色
一.更改字体.大小.颜色 <font face="黑体">我是黑体字</font><font face="微软雅黑">我是微 ...
- [CodeForces 663E] - Binary Table(FWT)
题目 Codeforces 题目链接 分析 大佬博客,写的很好 本蒟蒻就不赘述了,就是一个看不出来的异或卷积 精髓在于 mask对sta的影响,显然操作后的结果为mask ^ sta AC code ...
- 动手动脑---找出指定文件夹下所有包容指定字符串的txt文件
思路:先判断是否为文件,如果是文件,则需要判断改文件名是否包含字符串"txt",包含则输出.如果是文件夹的话,先需要判断文件名是否包含".txt"(因为文件名也 ...
- Mysql注入绕过安全狗
转载请加原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Yang34/p/12055052.html 微信公众号:信Yang安全.同步更新,欢迎关注.文末有二维码. 正好最近在搞注入,昨天现 ...
- Redis的移库操作
1.Redis默认有16个数据库,一般情况下使用0库: 2.移库操作: 将mysets移到一号库: 通过Redis查看器查看: 通过命令查看:
- 完美兼容IE10以下所有版本
IE一直是个恶心东西 各种不支持 现在发现了个好东西可以兼容ie10以下所有浏览器 <!--[if lte IE 9]><script>window.location.href ...
- VS2017 Asp.Net调式闪退处理
- [SNOI2019]纸牌
传送门 Description 有一副纸牌.牌一共有\(n\)种,分别标有 \(1,2,...,n\),每种有\(C\)张.故这副牌共有\(nC\)张. 三张连号的牌(\(i,i+1,i+2\))或三 ...
- css笔记 - column分栏
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- JavaScript中class类的介绍
class的概念 一.我们为什么要用到class类? 因为通过class类来创建对象,使得开发者不必写重复的代码,以达到代码复用的目的.它基于的逻辑是,两个或多个对象的结构功能类似,可以抽象出一个模板 ...
