实体之间的关系【Entity Relationships】(EF基础系列篇9)
Here, you will learn how entity framework manages the relationships between entities.
Entity framework supports three types of relationships, same as database: 1) One to One 2) One to Many, and 3) Many to Many.
We have created an Entity Data Model for the SchoolDB database in the Create Entity Data Model section. The following figure shows the visual designer for that EDM with all the entities and relationships among them.
EF实体之间的关系分为:
1.一对一;
2.一对多;
3.多对多;
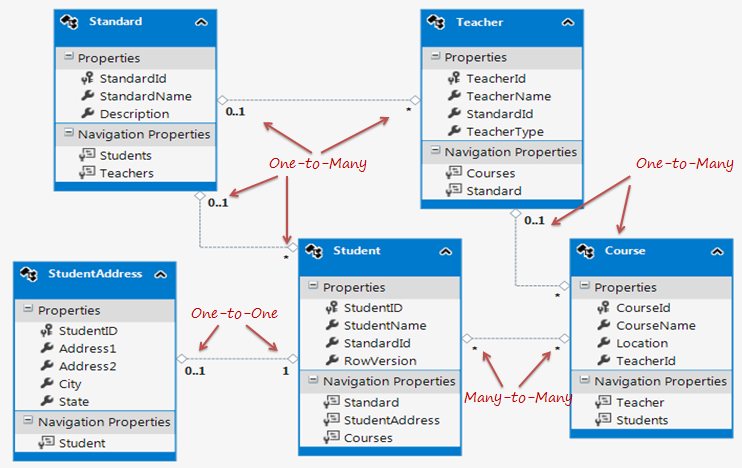
Let's see how each relation (association) is being managed by entity framework.
One-to-One Relationship:
As you can see in the above figure, Student and StudentAddress have a One-to-One relationship (zero or one). A student can have only one or zero address. Entity framework adds Student navigation property into StudentAddress entity and StudentAddress navigation entity into Student entity. Also, StudentAddress entity has StudentId property as PrimaryKey which makes it a One-to-One relationship.
The following code snippet shows Student and StudentAddress entity classes.
public partial class Student
{
public Student()
{
this.Courses = new HashSet<Course>();
}
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardId { get; set; }
public byte[] RowVersion { get; set; }
public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
public virtual StudentAddress StudentAddress { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Course> Courses { get; set; }
}
public partial class StudentAddress
{
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string Address1 { get; set; }
public string Address2 { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
public virtual Student Student { get; set; }
}
As you can see in the above code, Student entity class includes StudentAddress navigation property and StudentAddress includes Student navigation property with foreign key property StudentId. This way EF handles one-to-one relationship between entities.
One-to-Many Relationship:
The Standard and Teacher entities have a One-to-Many relationship marked by multiplicity where 1 is for One and * is for many. This means that Standard can have many Teachers whereas Teacher can associate with only one Standard.
To represent this, The Standard entity has the collection navigation property Teachers (please notice that it's plural), which indicates that one Standard can have a collection of Teachers (many teachers). And Teacher entity has a Standard navigation property (Not a Collection) which indicates that Teacher is associated with one Standard. Also, it contains StandardId foreign key (StandardId is a PK in Standard entity). This makes it One-to-Many relationship.
The following code snippet shows Standard and Teacher entity class created by EDM.
public partial class Standard
{
public Standard()
{
this.Students = new HashSet<Student>();
this.Teachers = new HashSet<Teacher>();
}
public int StandardId { get; set; }
public string StandardName { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Teacher> Teachers { get; set; }
}
public partial class Teacher
{
public Teacher()
{
this.Courses = new HashSet<Course>();
}
public int TeacherId { get; set; }
public string TeacherName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardId { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> TeacherType { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Course> Courses { get; set; }
public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
}
As you can see in the above code snippet, Standard entity class has Teachers property of type ICollection, so that it can contain multiple Teacher objects. (It initializes Teachers property with HashSet<Teacher> in the constructor, so that you can add Teacher objects into collection without worrying about initializing it.)
Also, Teacher entity class includes Standard property with StandardId for foreign key property. Entity framework includes this foreign key property because we checked Include foreign key columns in the model in the EDM wizard while creating EDM in the Create Entity Data Model section.
Many-to-Many Relationship:
Student and Course have Many-to-Many relationships marked by * multiplicity. It means one Student can enrol for many Courses and also, one Course can be be taught to many Students.
The database design includes StudentCourse joining table which includes the primary key of both the tables (Student and Course table). Entity Framework represents many-to-many relationships by not having entityset for the joining table in CSDL, instead it manages this through mapping.
As you can see in the above figure, Student entity includes Courses property and Course entity includes Students property to represent many-to-many relationship between them.
The following code snippet shows Student and Course entity classes.
public partial class Student
{
public Student()
{
this.Courses = new HashSet<Course>();
}
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardId { get; set; }
public byte[] RowVersion { get; set; }
public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
public virtual StudentAddress StudentAddress { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Course> Courses { get; set; }
}
public partial class Course
{
public Course()
{
this.Students = new HashSet<Student>();
}
public int CourseId { get; set; }
public string CourseName { get; set; }
public System.Data.Entity.Spatial.DbGeography Location { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> TeacherId { get; set; }
public virtual Teacher Teacher { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
Note: Entity framework supports many-to-many relationship only when the joining table (StudentCourse in this case) does NOT include any columns other than PKs of both the tables. If the join tables contain additional columns, such as DateCreated, then the EDM creates entity for middle table as well and you will have to manage CRUD operation for many-to-many entities manually.
Open EDM in XML view. You can see that SSDL has StudentCourse entityset, but CSDL doesn't have StudentCourse entityset. Instead, it's being mapped in the navigation property of the Student and Course entity. In MSL (C-S Mapping), it has mapping between Student and Course put into the StudentCourse table in <AssociationSetMapping/>
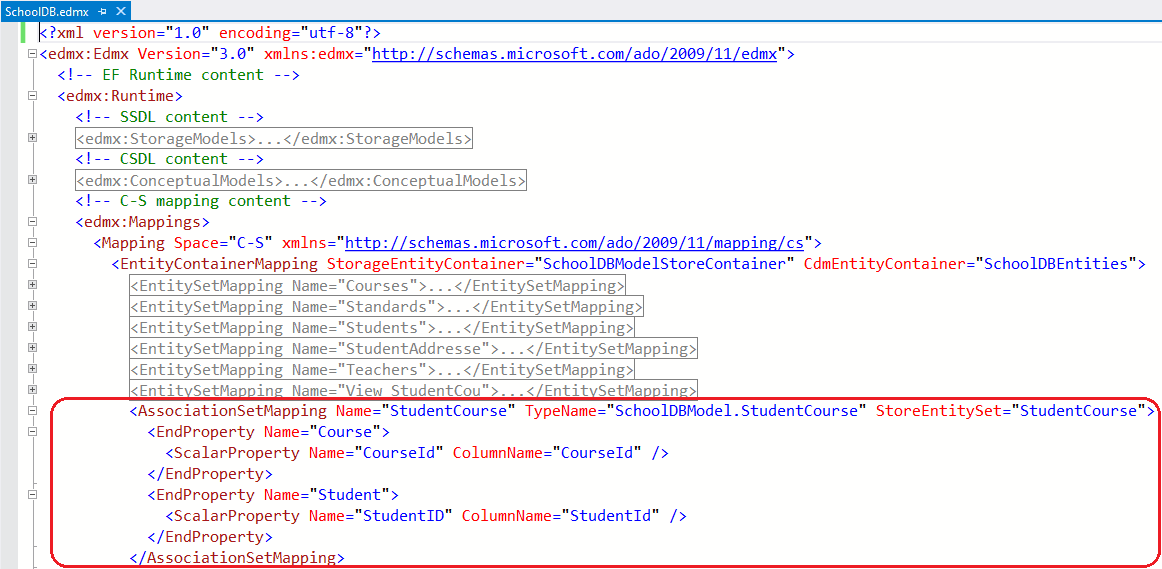
Thus, Many-to-Many relationship is being managed by C-S mapping in EDM. So when you add a Student in a Course or a Course in a Student entity and when you save it, it will then insert PK of the added student and course in StudentCourse table. So this mapping not only enables a convenient association directly between the two entities, but also manages querying, inserts, and updates across this joint.
Entity Graph:
When an entity has a relationship with other entities, then the full object hierarchy is called an 'entity graph'. For example the following is a Student entity graph, that includes hierarchy of Student entity with Standard, StudentAddress & Course entities.
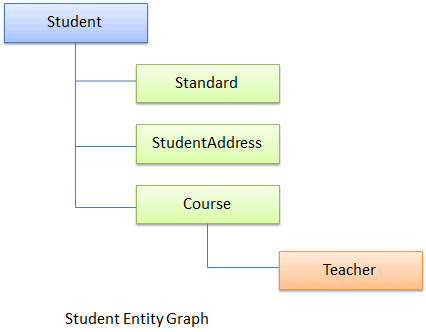
Learn about the lifecycle of these entities in the next section.
一对一关系:
Student和StudentAddress之间:
public partial class Student
{
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardID { get; set; }
public string RowVersion { get; set; }
public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
public virtual StudentAddress StudentAddress { get; set; }
}
public partial class StudentAddress
{
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string Address1 { get; set; }
public string Address2 { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string State { get; set; }
public virtual Student Student { get; set; }
}
一对多关系:
上面很多,就举出一例吧,Teacher和Standard
public partial class Standard
{
public Standard()
{
this.Students = new HashSet<Student>();
this.Teachers = new HashSet<Teacher>();
}
public int StandardID { get; set; }
public string StandardName { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Teacher> Teachers { get; set; }
}
public partial class Teacher
{
public Teacher()
{
this.Courses = new HashSet<Course>();
}
public int TeacherID { get; set; }
public string TeacherName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardID { get; set; }
public string TeacherType { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Course> Courses { get; set; }
public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
}
多对多关系:
Student和Course之间:
public partial class Student
{
public Student()
{
this.Course = new HashSet<Course>();
}
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> StandardID { get; set; }
public string RowVersion { get; set; }
public virtual Standard Standard { get; set; }
public virtual StudentAddress StudentAddress { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Course> Course { get; set; }
}
public partial class Course
{
public Course()
{
this.Student = new HashSet<Student>();
}
public int CourseID { get; set; }
public string CourseName { get; set; }
public string Location { get; set; }
public Nullable<int> TeacherID { get; set; }
public virtual Teacher Teacher { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Student> Student { get; set; }
}
注意:需要注意的是,EF支持多对多的关系,仅仅是关联表(这里是StudentCourse),不包含Student和Course主键之外,任何其他的列的表。如果关联表包含了其他的列,比如删除日期(Datedelete),然后你必须得手动去操作,来实现多对多的关系;
我们以XML视图,来打开实体数据模型,可以看到在SSDL中,可以看到StudentCourse EntitySet实体集, CSDL不包含StudentCourse实体集,代替是的,它被映射成在Student和Course的导航属性里面,在MSL(C-S Mapping)中可以看到它在<AssociationSetMapping>节点中
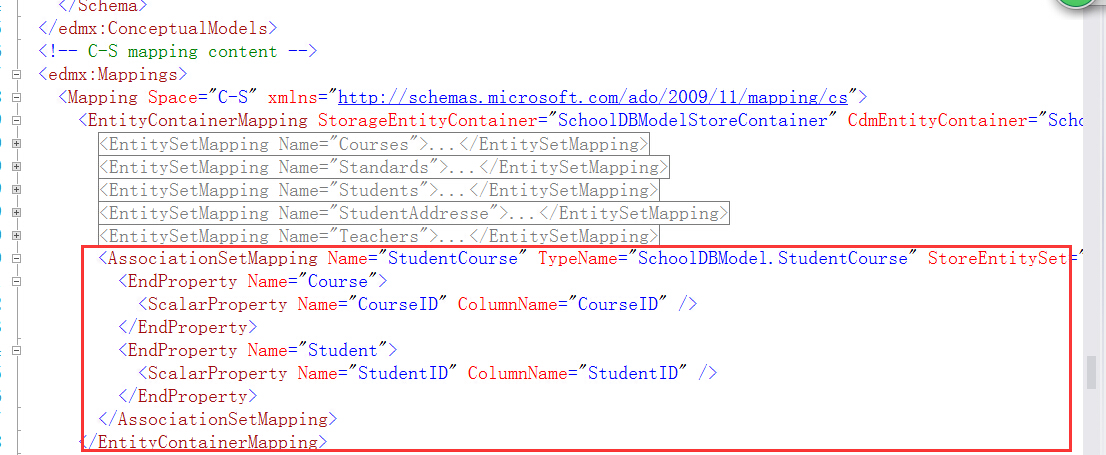
所以,多对多的关系在实体数据模型的C-S mapping部分中,所以当你向Student表中添加一个Course的时候,或者向Course表中添加一个Student的时候,然后你保存的时候,将会把你插入的学生的或者课程的主键添加到StudentCourse表中,所以这个映射不仅方便关联这两个实体,而且方面管理增删查改的操作;
实体之间的关系【Entity Relationships】(EF基础系列篇9)的更多相关文章
- 安装Entity Framework【Setup Entity Framework Environment】(EF基础系列篇4)
Entity Framework 5.0 API是分布在两个地方:NuGet和.NET Framework中,这个.NET framework 4.0/4.5包含EF核心的API,然而通过NuGet包 ...
- EF框架组件详述【Entity Framework Architecture】(EF基础系列篇3)
我们来看看EF的框架设计吧: The following figure shows the overall architecture of the Entity Framework. Let us n ...
- EF中的实体类型【Types of Entity in Entity】(EF基础系列篇8)
We created EDM for existing database in the previous section. As you have learned in the previous se ...
- 1.翻译:EF基础系列--什么是Entity Framework?
大家好,好久不见,EF系列之前落下了,还是打算重新整理一下. 先说说目前的打算:先简单了解一下EF基础系列-->然后就是EF 6 Code-First系列-->接着就是EF 6 DB-Fi ...
- 6.翻译:EF基础系列---什么是EF中的实体?
原文地址:http://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/basics/what-is-entity-in-entityframework.aspx EF中的实体就是继承 ...
- 【Basics of Entity Framework】【EF基础系列1】
EF自己包括看视频,看MSDN零零散散的学了一点皮毛,这次打算系统学习一下EF.我将会使用VS2012来学习这个EF基础系列. 现在看看EF的历史吧: EF版本 相关版本特性介绍 EF3.5 基于数据 ...
- 10.翻译:EF基础系列---EF中的持久性
原文链接:http://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/EntityFramework4.3/persistence-in-entity-framework.aspx ...
- 8.翻译:EF基础系列----EF中实体的状态
原文链接:http://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/basics/entity-states.aspx 在实体的生命周期中,EF API维护着每一个实体的状态,对于 ...
- 7.翻译:EF基础系列---EF中的实体类型
原文地址:http://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/Types-of-Entities.aspx 在Entity Framework中有两种实体类型:一种是POCO ...
随机推荐
- .NET开源OpenID和OAuth解决方案Thinktecture IdentityServer
现代的应用程序看起来像这样: 典型的交互操作包括: 浏览器与 web 应用程序进行通信 Web 应用程序与 web Api (有时是在他们自己的有时代表用户) 通信 基于浏览器的应用程序与 web A ...
- node(async原理)
node中的async是用来实现同步操作的,提供包括map.Series等方法,本文不做赘述. 由于项目需要在浏览器端用了async.js,因此仔细看了下它的代码.原来,一直以为node是在服务端调用 ...
- 谈谈对Spring IOC的理解
学习过Spring框架的人一定都会听过Spring的IoC(控制反转) .DI(依赖注入)这两个概念,对于初学Spring的人来说,总觉得IoC .DI这两个概念是模糊不清的,是很难理解的,今天和大家 ...
- Azure Blob Storage 基本用法 -- Azure Storage 之 Blob
Azure Storage 是微软 Azure 云提供的云端存储解决方案,当前支持的存储类型有 Blob.Queue.File 和 Table. 笔者在<Azure Table storage ...
- Module Zero概览
返回<Module Zero学习目录> 介绍 ABP框架的设计是独立于任何数据库模式的且尽可能地使用泛型.因此,它避开了一些要求数据存储的抽象和可选的概念(如审计日志,session管理和 ...
- 《Entity Framework 6 Recipes》中文翻译系列 (6) -----第二章 实体数据建模基础之使用Code First建模自引用关系
2-5 使用Code First建模自引用关系 问题 你的数据库中一张自引用的表,你想使用Code First 将其建模成一个包含自关联的实体. 解决方案 我们假设你有如图2-14所示的数据库关系图的 ...
- Html5 布局方式
在Html5之前,统一采用的是Div+css的方式进行布局,但是却和开发人员的命名方式,喜好有关.在新的Html5中,布局却显得更加人性化,更易理解了.如增加了Header,Footer,Sectio ...
- 构建hibernate
package hanqi.dao; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hib ...
- html5的audio在safari(windows)中无效
因为mac下的safari不会有这样的问题(OSX默认都装的有QuickTime),而windows下用safari的比例实在小不用考虑. apple算是偷了一个小懒.而所谓的需要quicktime并 ...
- Mesh Data Structure in OpenCascade
Mesh Data Structure in OpenCascade eryar@163.com 摘要Abstract:本文对网格数据结构作简要介绍,并结合使用OpenCascade中的数据结构,将网 ...
